
Role Selective and Nonselective Media for Isolation of Burkholderia
Species from Patients with Suspected Melioidosis
R. Lia Kusumawati
1
, Mirzan Hasibuan
2
, Afrinayanti W. Siregar
2
and Tryna Tania
3
1
Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Universitas No.1 Kampus USU Medan
20155, Indonesia
2
University of Sumatera Utara Hospital, Jl. Dr. T Mansyur No. 66 Kampus USU Medan 20154, Indonesia
3
Resident in Departement of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Jl. Pegangsaan Timur 16 Cikini
Jakarta 10320, Indonesia
Keywords: Burkholderia Species, Ashdown’s Selective Agar, Melioidosis
Abstract: Melioidosis is an infectious disease caused by the Burkholderia bacteria species, especially Burkholderia
pseudomallei and Burkholderia cepacia, disease is endemic in Southeast Asia and Northern Australia. As a
tropical country like Indonesia, this is a very serious global threat. This study aims to compare selective and
non-selective media in diagnosing Melioidosis based on the results of culture of clinical specimens of
patients with suspected Melioidosis. The results showed that as many as 112 (100%) of suspected clinical
samples of bacterial melioidosis were grown on nonselective media, Mac-Conkey agar and 110 (98.2%)
bacteria growing on Columbia agar agar medium. While on Ashdown’s Selective Agar (ASA) there is
bacterial growth of 10 samples (8.9%.). Where 7 of 10 samples are is Burkholderia species (Burkhoderia
cepacia 5 and Burkholderia pseudomallei 2). The results of this study indicate that Ashdown's media plays
an important role in selecting Burkholderia species as the cause of Melioidosis.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Burkholderia genus is made up of a variety of
species, Gram-negative bacilli, saprophytes in soil
and water reservoirs, endemic to tropical and
subtropical regions such as Southeast Asia and
Northern Australia. Some species of the
Burkholderia genus are widely used in
biotechnology, bioremediation, biocontrol and
agricultural industries (Estrada-De et.al, 2001).
Three known species from this genus as an etiologic
agent and cause fatal diseases in humans and
animals are Burkholderia pseudomallei,
Burkholderia mallei, and Burkholderia cepacia
[2]
.
The disease that caused by these three species are
known as melioidosis. Melioidosis is an infectious
disease that has a complex spectrum such as local
skin lesions, sub acute pneumonia, abscess on
infected organ, musculoskeletal infections, and
fulminant pneumonia (Cheng et.al, 2005).
Burkholderia pseudomallei has been known for
causing severe sepsis that leading to mortality of the
patient (Currie et.al, 2010).
This situation is a serious global threat,
especially for a tropical country, such as Indonesia.
The clinical diagnosis of melioidosis remains
difficult since the disease has no pathognomonic
signs and symptoms (Wiersinga et.al, 2006). Current
standard diagnostics are routine culture on non-
selective media such as blood agar and selective
gram-negative Mac-Conkey. However, both media
are not selective for Burkholderia species, so
Burkholderia bacterial colonies are difficult to
distinguish from other bacterial colonies. Therefore,
selective media is needed to overcome difficulties of
the diagnosis. Selective media such as Ashdown's
Selective Agar (ASA) as a standard to establish
laboratory diagnosis of melioidosis. This study
focused on the role of selective and nonselective
media for culture clinical samples collected from
patients suspected with Melioidosis.
582
Kusumawati, R., Hasibuan, M., Siregar, A. and Tania, T.
Role Selective and Nonselective Media for Isolation of Burkholderia Species from Patients with Suspected Melioidosis.
DOI: 10.5220/0010079305820585
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
582-585
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 METHOD
A descriptive study, comparing the role of selective
and nonselective media in growing Burkholderia
species bacteria. Samples were collected by using
total sampling method between January and June
2018, based on inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Identification of bacterial colonies was
phenotypically tested by using Vitek 2 Compact.
2.1 Specimen Collection
samples were collected from all clinical specimens
that sent to Universitas Sumatera Utara Hospital
Microbiology Laboratory from patients suspected
with melioidosis based on the physician diagnosis on
the Clinical Microbiology laboratory request form.
Several types of specimens collected in the form
were throat swab, blood, urine, pus, sputum and
respiratory secretions.
2.2 Non-selective Media Columbia
Agar and Mac-Conkey Agar
Columbia agar media preparation are made by
dissolving 3.8 gram of Columbia into 100 mL of
sterile aquadest and sterilized by using autoclave at
121
o
C for 15 minutes. After sterilization, put
solution at room temperature until medium
temperature reaches 40-45
o
C, 5% blood sheep was
added and homogenized, then poured on sterile
petridish. For Mac-Conkey agar media, 5.15 gram
are dissolved into 100 mL of sterile aquadest and
autoclaved. After sterilization process, put the
solution at room temperature until medium
temperature reaches 50
o
C and finally poured on
sterile petridish.
2.3 Selective Media Ashdown's
Selective Agar (ASA)
Selective media preparation by weighing the
composition of media consisting of Tryptone soya
broth 10 gram, agar bacterial 15 gram, 40 ml
glycerol, 5 mL of 0.1% crystal violet, 5 mL of 1%
neutral red and 950 mL of distilled water, all of the
material were dissolved into an Erlenmeyer and
sterillized by using an autoclave at 121
o
C for 15
minutes. Put the solution at room temperature until
the temperature reaches 50
o
C, gentamycin was
added with concentration 4mg/liter and
homogenized, then the media is poured on sterile
petridish.
2.4 Bacterial Culture
Bacterial culture was done on by using selective
ASA medium, as well as on routine media,
Columbia Blood Agar and Mac-Conkey Agar.
Bacterial culture was incubated at 35°C for 24-48
hours. Microscopic and macroscopic identification
were done for every grown colonies.
2.5 Identification
The identification was started with macroscopic
observation of bacterial colonies by performing a
morphological selection of the suspected
Burkholderia species bacteria. Followed by
microscopic observation with Gram staining. The
suspected Burkholderia species underwent
identification stage by using the Vitek 2 Compact.
Phenotypically, this tool can identify Burkholderia
species bacteria using GN card and simultaneously
performing antibiotic susceptibility test by using
AST GN card.
2.6 Data Analysis
Data of the comparison between selective and non-
selective media in growing Burkholderia species
was analysed. All results were presented in the
tabulation and percentage.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Based on the results of culture of clinical specimens
from patients suspected with Melioidosis on routine
or non-selective media (Columbia Agar and Mac-
Conkey Agar) for 24 hours found the growing
bacteria Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia,
Pseudomonas putida, Pseudomonas aeruginosa,
Pseudomonas stutzeri, Pseudomonas fluorescens,
Serratia marcescens and Acinetobacter baumannii.
While Burkholderia colony species were not seen
yet, the incubation time on nonselective media
therefore was extended to 48 hours. Based on
observed colonies of Burkholderia species after 48
hours, it was seen in streaks thus continued to
subculture and identification stage. However, in both
media colonies of Burkhokderia species bacteria
were not typical, making it a little difficult to do the
selection.
Columbia or blood agar was used as a
nonselective medium to evaluate the vitality of the
Role Selective and Nonselective Media for Isolation of Burkholderia Species from Patients with Suspected Melioidosis
583
strain. Almost all bacteria can grow on this medium
so there will be a competition for growth between
species of bacteria (Edler, et.al, 2017). Whereas
Mac-Conkey was more selective towards Gram-
negative bacteria, but the growth of Burkholderia
species requires accuracy and a longer incubation
time (> 48 hours) to ensure the presence or absence
of Burkholderia species colonies.
In contrast to Ashdown's agar selective
media, at 24 hours the bacteria had grown and
shown a distinctive colony morphology such as
round, convex, absorbed little of the red pigment,
and wavy surfaces. Based on the identification
results using the GN identification card Vitek 2
Compact, colonies that grow on Ashdown's selective
media were Burkholderia pseudomallei and
Burkholderia cepacia. While other colonies that
grew on this selective media were Pseudomonas
putida and Pseudomonas stutzeri. The results of the
growth comparison on selective and nonselective
media can be seen in table 1.
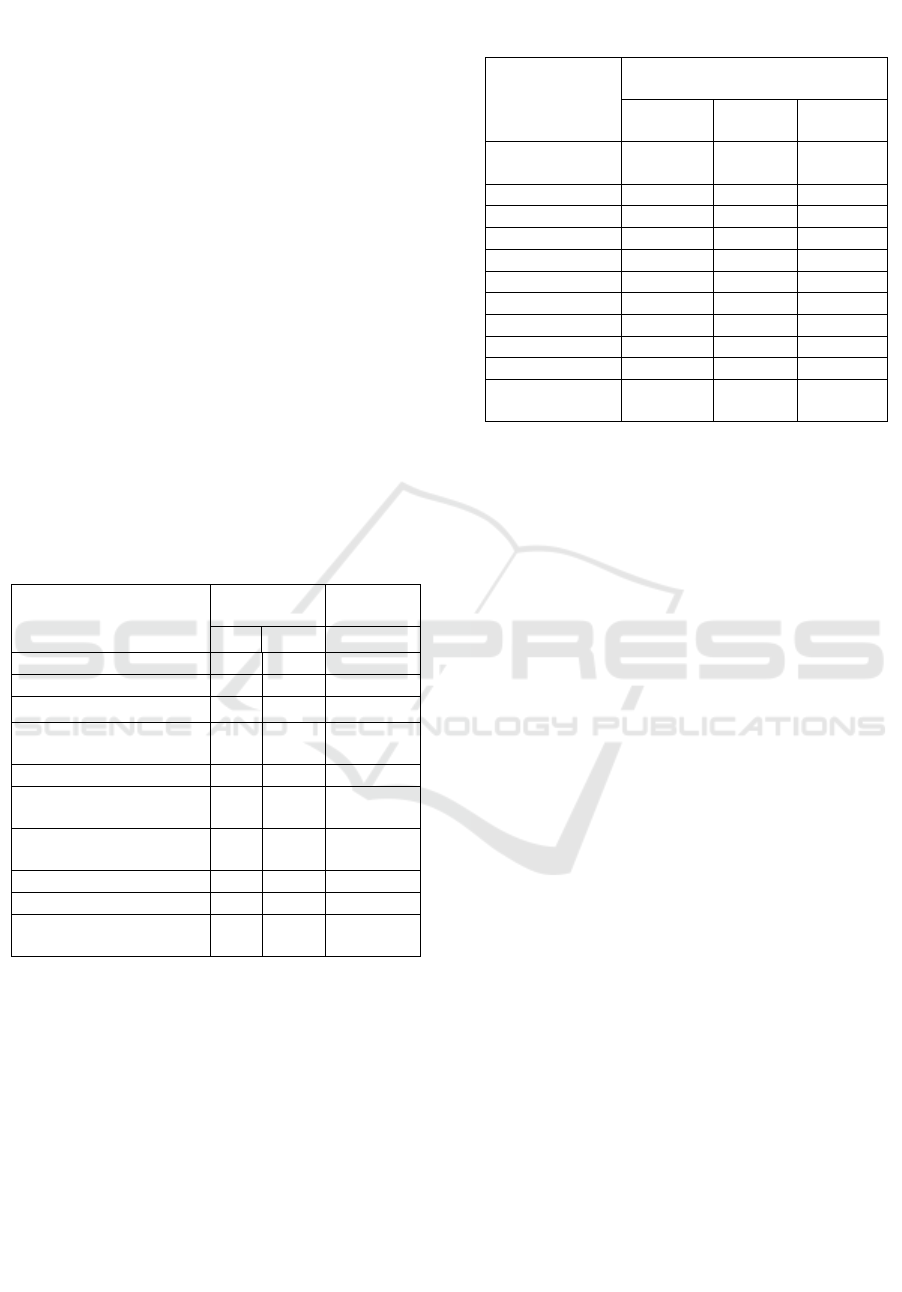
Table 1: Growth of clinical strains at 48 hours on selective
and nonselective media
Bacterial growth Nonselectiv
e
Selective
CA MCA ASA
Escherichia coli + + -
K
lebsiella pneumoniae + + -
Pseudomonas putida + + +
Pseudomonas
aeruginosa
+ + -
Pseudomonas stutzeri + + +
Pseudomonas
f
luorescens
+ + +
Burkholderia
pseudomallei
+ + +
B
urkholderia ce
p
acia + + +
Serratia marcescens + + -
Acinetobacter
baumannii
+ + -
The results of culture from 112 specimens of
patients suspected with Melioidosis showed bacterial
growth in Columbia Agar Blood medium which was
110 (9.8%) and in Mac-Conkey media. While on
Ashdown's selective media, bacterial growth was
seen in 10 samples, consisted of Burkholderia
pseudomallei 2 (1.8%), Burkholderia cepacia 5
(4.4%), Pseudomonas stutzeri 2 (1.8%) and
Pseudomonas putida 1 (0.9%). All bacterial growth
from all clinical samples of patients suspected with
Melioidosis were presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Other microorganisms growth seen on media
Bacterial
species
No. (%) growth of bacterial
isolates in each media
CA
(n=112)
MCA
(n=112)
ASA
(n=112)
Escherichia
coli
8(7.1) 8(7.1) 0(0)
K
.
p
neumoniae 28
(
25
)
28
(
25
)
0
(
0
)
P.
p
utida 1
(
0.9
)
1
(
0.9
)
1
(
0.9
)
P. aeruginosa 54(48) 54(48) 0(0)
P. stutzeri 2(1.8) 2(1.8) 2(1.8)
P.
f
luorescens 3
(
2.6
)
3
(
2.6
)
0
(
0
)
B
.
p
seudomallei 1
(
0.9
)
1
(
0.9
)
2
(
1.8
)
B
.cepacia 1(0.9) 3(2.6) 5(4.4)
S. marcescens 2
(
1.8
)
2
(
1.8
)
0
(
0
)
A
. baumannii 10
(
8.9
)
10
(
8.9
)
0
(
0
)
Total : 110(98.2
)
112(100
)
10(8.9)
Based on the results of selective and
nonselective media comparison, it can be seen that
Ashdown's selective media has a higher selection
rate for the growth of Burkholderia. This findings
indicated the use of media has of great significance
role in establishing diagnosis of Melioidosis.
Although the media is very selective, Pseudomonas
growth was also seen in this study. It is possible that
Pseudomonas-type bacteria were found to be
resistant to Gentamycin so that it grew in selective
Ashdown’s Media agar. So the composition of the
media needs to be modified to the ASA medium.
Modification of ASA media media was
needed as Burkholderia pseudomallei selective agar
(BPSA), this medium was designed to improve
recovery from strains that easier to be inhibited by
Burkholderia pseudomallei, Burkholderia cepacia,
and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, used to determine the
selectivity and sensitivity of BPSA. The purpose of
BPSA was to inhibit the growth of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa making the identification of
Burkholderia species easier to characterize because
of the typical morphology of the colony Howard,
et.al, 2005).
The sensivity was equal between ASA and
BPSA based on their sensitivity ratio, although
BPSA selectivity was found to be lower than ASA
medium. Culture from 86 of 155 clinical specimens
showed growth in at least one selective medium
(range, 1 to 4 positive samples per patient) (Peacock
et.al, 2005). BPSA has advantages in showing
typical morphology such as crinkled and undulating
colonies, while in ASA media it was seen to be
smooth surface and convex colonies. Both media did
not show any significant difference overall (Howard,
et.al, 2005). ASA media supported the growth of
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
584

Burkholderia species including Burkholderia mallei
and suitable for screening during situation when
Burkholderia pseudomallei and/or Burkholderia
mallei were suspected (Peacock et.al, 2005).
ASA media has an important role to support
the diagnosis of melioidosis at the University
Hospital of North Sumatra. This study findings
demonstrated that to use only the current routine or
nonselective media as the standard diagnostic tools
of culture was definitely not enough to establish the
diagnosis of melioidosis from clinical samples. The
use and application of ASA as standard culture
media in clinical microbiology laboratory routine
services to support and establish the challenging
diagnosis of melioidiosis from clinical samples
collected from patients suspected with melioidosis
was imperative.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This study showed that the use of ASA media was
necessary especially in clinical microbiology
laboratory settings and has high selectivity rate for
Burkholderia. In this study, 7 of 10 types of bacteria
that had successfully grown on ASA media were
found to be Burkholderia species (5 of Burkholderia
cepacia and 2 of Burkholderia pseudomallei).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors are gratefully acknowledged to the
Research Institute of Universitas Sumatera Utara for
providing the funds from TALENTA 2018 based on
the scheme of Research Development of University
of Sumatera Utara Hospital (PPRSU) with contract
number: 72/2.3.1/PPM/ KP-TALENTA USU/2018.
REFERENCES
Estrada-De Los Santos, P., Bustillos-Cristales, R. and
Caballero-Mellado, J., 2001. Burkholderia, a genus
rich in plant-associated nitrogen fixers with wide
environmental and geographic distribution. Applied
and Environmental Microbiology. American Society
Micorbiology.
Cheng, A.C. and Currie, B.J., 2005. Melioidosis:
epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management.
Clinical Microbiology Reviews. US National Library
of Medicine National Institutes of Health.
Currie, B.J., Ward, L. and Cheng, A.C., 2010. The
epidemiology and clinical spectrum of melioidosis:
540 cases from the 20 year Darwin prospective study.
PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. US National
Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health.
Wiersinga WJ, van der Poll T, White NJ, Day NP,
Peacock SJ. 2006. Melioidosis: insights into the
pathogenicity of B.pseudomallei. Nature Review
Microbiology. US National Library of
Medicine National Institutes of Health.
Howard, K and Inglis TJJ. 2003. Novel Selective Medium
for Isolation of Burkholderia pseudomallei. Journal of
Clinical Microbiology. American Society
Micorbiology.
Peacock, SJ., Chieng, G., Allen, C., Cheng., Dance, D.,
Amornchai, p.,1 Wongsuvan, G., Teerawattanasook,
N. Chierakul, W., Day, NP and Wuthiekanun, V.
2005. Comparison of Ashdown’s Medium,
Burkholderia cepacia Medium, and Burkholderia
pseudomallei Selective Agar for Clinical Isolation of
Burkholderia pseudomallei. Journal of Clinical
Microbiology. American Society Micorbiology.
Edler, C.,
Derschum, H., Kohler, M., Neubauer,
H., Frickmann, H and Hagen, RM. 2017. Comparison
of Mast Burkholderia Cepacia, Ashdown +
Gentamicin, and Burkholderia Pseudomallei Selective
Agar for the Selective Growth of Burkholderia Spp.
European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology.
US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of
Health.
Role Selective and Nonselective Media for Isolation of Burkholderia Species from Patients with Suspected Melioidosis
585
