
Training Students’ Thinking Skills using Problem-based Learning
Integrated with Virtual Mobile Learning
Insar Damopolii
*
, I. Iwan and Bayu Kurniadi
Biology Education Department, Universitas Papua, West Papua, Indonesia
Keywords: Thinking skill, Problem-based learning, virtual, mobile learning, STEM
Abstract: Learning based on science, technology, engineering and mathematic (STEM) in the 2013 curriculum can be
implemented through the application of a combination of problem-based learning and virtual mobile learning.
This research aimed to train thinking skills of students in SMA Negeri 01 Manokwari through the application
of problem-based learning combined with virtual mobile learning. One-shot case study was operative in this
research. A total of 126 students in the XI
MIA
class of SMA Negeri 01 Manokwari were involved as research
subjects. Data collection techniques include learning achievement tests and thinking skill rubrics based on
SOLO Taxonomy. Data analysis were in the form of percentage of achieving thinking skill and inferential
analysis used Kruskal-Wallis. The results indicate that the students’ level of thinking skills has reached
relational level or level 4, and the highest percentage of thinking skill levels achieved by students was at level
3 or multistructural level. The significant values of the five treatment groups were 0.120 > 0.05, indicating
that there was no differences in the achievement of thinking skills among five treatment groups. The study
has concluded that problem-based learning combined with virtual mobile learning can be deployed to foster
students’ thinking skills.
1 INTRODUCTION
Problem-based learning is a recommended learning
strategy in the 21st century class. The application of
effective learning models in the classroom is expected
to improve students’ learning outcomes and empower
their potential. Teaching is not based on the teacher's
preference, but needs to be determined based on the
students’ competence as well (Damopolii, Nunaki, &
Supriyadi, 2018). Teachers in problem-based
learning (PBL) classes facilitate the learning process
by monitoring their students’ progress and asking
questions to encourage them to excel in problem
solving process (Major & Palmer, 2001). In fact,
students consider problem-based learning effective
learning (Hallinger & Lu, 2011).
Several previous studies show that there is an
influence of learning models based on students'
learning achievement problems on students’
achievement (Demirel & Dağyar, 2016; Günter,
Akkuzu, & Alpat, 2017; Taşoğlu & Bakaç, 2014).
The implementation of PBL empowers students’
critical thinking skills (EL-Shaer & Gaber, 2014;
Gholami et al., 2016; Zabit, 2010), creative thinking
skills (Birgili, 2015; Ersoy & Başer, 2014; Murni &
Anggraini, 2016), problem solving skills (Darma,
2018; Nasution, Yerizon, & Gusmiyanti, 2018;
Sihaloho, Sahyar, & Ginting, 2017), and levels of
structuring concepts (Inel & Balim, 2010). Research
students in the Department of Biology Education in
Universitas Papua have found that there is no
significant effect of PBL implementation on students’
learning achievement (Sogen, Damopolii, &
Kilmaskossu, 2018; Zannah, Iwan, & Damopolii
2018), and fair influence is evident on student attitude
in Science (Batdı, 2014). Some studies acknowledge
the effect of PBL on achieving student learning
objectives, but on the other hand some studies claim
that there is no significant effect. The author also
found that there was no measurement of thinking
skills based on SOLO taxonomy of students in
learning to implement PBL integrated with
technology. As such, it is necessary to deploy a
technology to help students achieve SOLO taxonomy,
where the technology must comply with the demands
of STEM-based curriculum in Indonesia and student
development.
Based on the results of direct observation and
interviews, the researcher has found that SMA Negeri
01 Manokwari is a school with fairly complete ICT
584
Damopolii, I., Iwan, I. and Kurniadi, B.
Training Students’ Thinking Skills using Problem-based Learning Integrated with Virtual Mobile Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0010025100002917
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Social Sciences, Laws, Arts and Humanities (BINUS-JIC 2018), pages 584-589
ISBN: 978-989-758-515-9
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

facility and competent human resources. This can be
seen from the ability of teachers and students who are
skilled enough to operate ICT facilities such as
Infocus, computers, laptops, and smartphones. Of the
331 students in class XIMIA of SMA Negeri 01
Manokwari, there are 302 students or 91% of students
who use Android-powered smartphones. The data
shows that Android-based smartphones are a type of
mobile device that is very popular and most sought
after by the students of class XIMIA SMA Negeri 1
Manokwari. These conditions should strongly
support more innovative learning by utilizing the
available ICT facilities. However, the availability of
fine ICT facilities and competent human resources in
the school has yet to accrue optimal biology learning.
The utilization of ICT in learning is known as e-
learning. The newest branch or part of e-learning is
mobile-based learning or mobile learning (Georgieva,
Smrikarov, & Georgiev, 2005) Mobile learning is
flexible because it can be changed or updated at any
time, particularly if there are changes in material,
especially in the field of science that has improved
with respect to its theory. In principle, mobile
learning aims to facilitate learners anywhere and
anytime according to their place (Wilson & Bolliger,
2013). Mobile learning is virtually accessible from
anywhere, by providing access to various learning
materials.
Mobile devices that can be used for the
development of learning media are smartphones
(smartphones) (Squire, 2009). The use of this
smartphone is put in experiment by Dewanti to
connect smartphone usage with students' learning
achievements, the results of which show that there is
a significant correlation between smartphone usage
and students' learning achievement, where the use of
smartphones positively affects students' learning
achievement, with higher smartphone usage resulting
in higher students’ learning achievement (Dewanti,
Widada, & Triyono, 2016). Good achievement results
from their good thinking skills. One of the thinking
skills is SOLO taxonomy level of thinking skill.
Today, SOLO taxonomy has been used to measure
students' thinking skills (Seiter, 2015). The level of
SOLO taxonomy is divided into five stages, namely
prastructural, unistructural, multistructural, relational
and extended abstract (Wells, 2015), each of which is
used in various subjects (Biggs & Collis, 1982),
including biology (Minogue & Jones, 2009).
A study by Uzunboylu, Cavus & Ercag suggests
the use of mobile learning in large-scale study
(Uzunboylu, Cavus, & Ercag, 2009), In addition, it is
suggested to delve into the more implementation of
PBL in the future (EL-Shaer & Gaber, 2014), and
PBL improvements to previous research. As such,
study focusing on use of mobile-assisted virtual PBL
is expected to accrue good effect in training thinking
skills based on SOLO taxonomy.
2 METHOD
This research was an experimental study using a one-
shot case study. The subjects in the study were
students of XIMIA class at SMA Negeri 01
Manokwari. Five classes were involved as treatment
classes, namely XIMIA3 with 29 students (group 1),
XIMIA5 with 29 students (group 2), XIMIA6 with 20
students (group 3), XIMIA7 with 24 students (group
4), and XIMIA8 with 24 students (group 5). As such,
a total of 126 students were involved in the study. The
research was carried out in the even semester of
2017/2018 school year, starting from March 27 2018
to May 18, 2018.
Learning instruments used in the study included
lesson plan, student worksheets, achievement tests,
and Android-based virtual mobile learning. Learning
instrument was adapted to the 2013 curriculum
applied by SMA Negeri 01 Manokwari. Lesson plan
was constructed and arranged in the form of HOTS
lesson plan (High-Order Thinking Skills Lesson
Plan). Android-based mobile learning media and
student worksheets were implemented in the form of
the syntax of Problem Based Learning (PBL)
activities. Tests of learning outcomes included five
items. This learning instruments were used to assist
the learning process in order to achieve the learning
objectives. To measure thinking skills, a five-level
rubric was used, which comprised of prastructural,
unistructural, mutistructural, relational and extended
abstract.
The production phase of mobile learning
commenced with preparing instrument and materials
used in the process of making Android-based mobile
learning media. The equipment used by researchers
were PC hardware, ACER ASPIRE E5-471-30Q8,
appypie website and Android smartphone OPPO E37.
Materials needed in the process of making android-
based mobile learning media was a good WIFI signal
so that the learning process ran smoothly, Youtube
video URL related to the material of the human
reproductive system, images of human reproductive
system material, various material summaries in the
form of Microsoft Word , and multiple choice quiz
questions in Microsoft Word format. After preparing
the necessary instrument and materials, the researcher
made a storyboard or general description that showed
the storyline and the process of using the instructional
Training Students’ Thinking Skills using Problem-based Learning Integrated with Virtual Mobile Learning
585
media. Storyboard was made in the form of
smartphone display slides. Each slide had different
functions and views with different button as well as
settings, background and animation effects.
Storyboards that had been created were then
processed online at www.appypie.com.
Validity of research data was obtained from the
validation instrument sheet. This validation
instrument sheet applied 1-5 Likert scale with
alternative answers comprising of 1) irrelevant, 2)
less relevant, 3) quite relevant, 4) relevant and 5) very
relevant. Validation sheets were filled in by three
validators, including media expert, material expert
and biology learning practitioner. Validation results
showed that lesson plan, student worksheet,
achievement test, and virtual mobile learning were
valid and applicable for learning process.
Data analysis, in the form of achievement
percentage of each thinking skill level and inferential
analysis using the Kruskal-Wallis test was made
operative to find out any significant differences
among classes and its effect on tinking skill.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Based on the results of the study applying problem-
based learning assisted by virtual mobile learning in
five treatment groups, crucial data have been
garnered in the form of achievement percentage of
each thinking skill level and the analysis of
differences in thinking skills using Kruskal-Wallis.
The following is the data from the analysis:
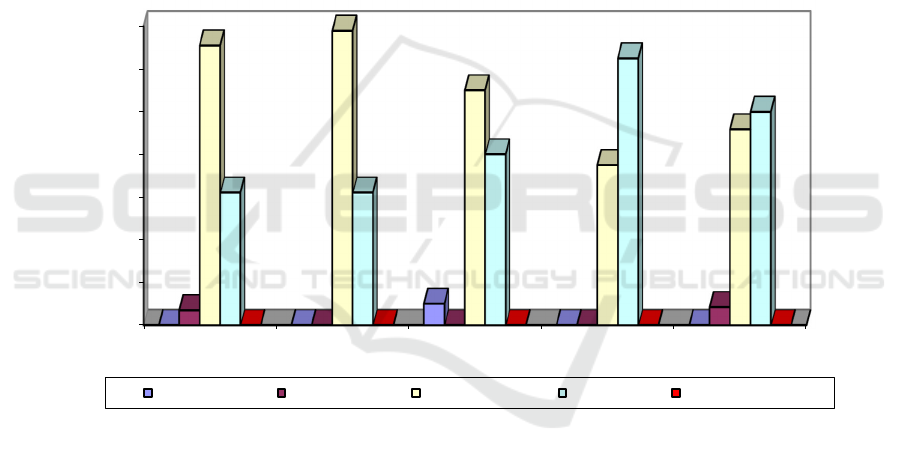
Figure 1: Students’ achievement with to thinking skills based on SOLO taxonomy
Figure 2 demonstrates that each group has different
thinking skill achievements. In all treatment groups,
achieving the thinking skill level is at the relational
level. In groups 1, 2 and 3, the highest level of
thinking skill from students reaches the multistuctural
level, while groups 4 and 5 reaching the highest
achievement at the relational level. The prestige level
in group 3 reaches 5%, while the other groups have
yet to reach this level. Unistructural levels in group 1
reach 3.45% and group 4 reach 4.17%, while the other
groups have not reached the same level. In all groups,
no students have reached the extended abstract level.
When a total of 126 students are taken into
account; 55.56% of students reach the multistructural
level; 42.06% of students reach relational level;
1.59% of students reach an unistructural level; 0.79%
of students reach prestructural level; and 0% of
students reach extended abstract level. These data
conclude that PBL assisted virtual mobile learning
can foster students’ thinking skills to reach relational
levels. The highest percentage of achieving thinking
skills is at the multistructural level.
0,00%
10,00%
20,00%
30,00%
40,00%
50,00%
60,00%
70,00%
Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5
0,00% 0,00%
5,00%
0,00%
0,00%
3,45%
0,00%
0,00%
0,00%
4,17%
65,52%
68,97%
55,00%
37,50%
45,83%
31,03% 31,03%
40,00%
62,50%
50,00%
0,00% 0,00% 0,00% 0,00% 0,00%
Prestructural Unistructural Multistructural Relational Extended Abstract
BINUS-JIC 2018 - BINUS Joint International Conference
586
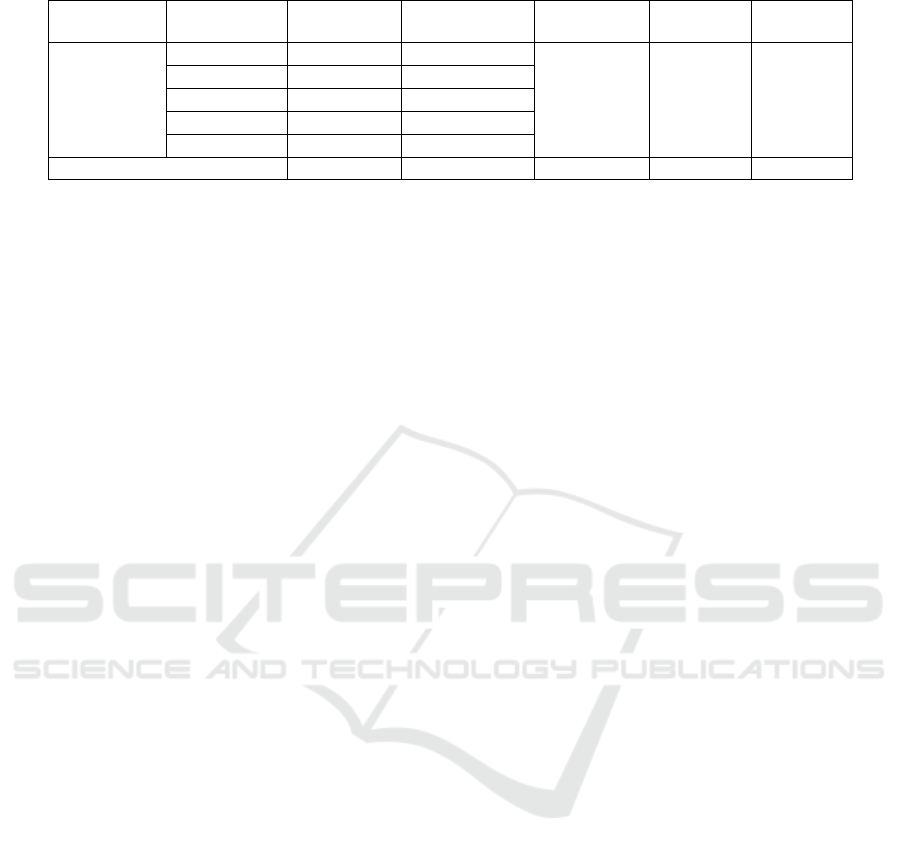
Table 1: Analysis results of Kruskal-Wallis on thinking skills based on SOLO taxonomy
Group N Mean Rank Chi-Square df
Asymop.
Sig.
Thinking
Skills
1
29 56.34 7.238 4 0.120
2
29 57.59
3
20 61.23
4
24 76.94
5
24 67.75
Total 126
Table 1 indicates that there is no difference in the
achievement of SOLO taxonomy level of thinking
skills in the five treatment groups. This shows that the
achievement of SOLO taxonomy level of thinking
skill in each group taught using the problem based
learning model assisted by mobile learning is similar.
Good thinking habits raise questions to direct
students’ learning, by taking into account various and
varied kinds of problems, finding out how to solve
problems through various types of inquiry, and
thinking independently (Chin & Chia, 2006).
Students have positive opinions in learning using
PBL models. This is indicated by their interest in the
problems given by the teacher. Because the problems
given are related to the phenomena of everyday life,
students can be empowered to develop lifelong
learning (Günter et al., 2017; Tseng, Chiang, & Hsu,
2008). Mobile learning is the opposite of learning that
occurs in conventional classes, where it is not just a
machine, but an inseparable instrument (Jinlong,
Zhaolei, & Yawei, 2012; Woodill, 2011).
The combination of problem-based learning with
virtual mobile learning makes learning process better.
The results are found to improve previous research
that indicate influence at medium extent (Batdı,
2014), and some other studies which reveal no effect
of problem-based learning in student learning
achievement (Sogen et al., 2018; Zannah et al., 2018).
With the use of PBL combined with virtual mobile,
students become active and thus can observe objects
of biological learning through pictures and videos
presented in mobile learning. This can also overcome
the limitations in learning due to insufficient
laboratory facilities in schools, support efficient use
of budget, and provide practicality and flexibility for
students. Students can study at home because mobile-
learning that has been designed is stored on their
smartphone. In mobile learning, today’s students are
always connected to the internet. According to Shen
et al., 95% of students are interested in taking distance
learning through internet (Shen, Wang, Gao, Novak,
& Tang, 2009). In mobile learning, there is also a
consultation section if students want to ask questions
about the concept related to a material.
Learning with the use of PBL requires students to
solve problems collaboratively in groups. Mobile
learning is there to help students find the information
they need, because mobile learning is connected to
the internet. In real-world situations, students
individually use mobile learning to support their
learning and increase their understanding, especially
because it is connected to a computer system using
wifi (Ahmed & Parsons, 2013; Chu, Hwang, Tsai, &
Tseng, 2010). Wifi has a great effect on learning
(Roschelle, 2003), which supports learning activities
(Vogel, Spikol, Kurti, & Milrad, 2010).
In the learning process under investigation,
students find it easier to obtain information, because
they do not need to carry heavy textbooks provided
by school libraries. Rather, they can simply use
smartphones for more positive purposes. As a result,
the learning process becomes more enjoyable and
suits the demands of today's generation, and at the
same time reduces the adverse effect of smartphones
being laden with negative content or game related
apps. Survey conducted by Shen et al reveals that
9.5% of mobile phones are used for learning (Shen et
al., 2009). With the innovation allowing instructional
purpose of mobile phone, smartphone becomes even
more useful.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the research results, it can be concluded that
problem-based learning assisted by virtual mobile
learning can foster students’ thinking skills based on
SOLO taxonomy. The students’ achievement with
regard to thinking skill level reaches the relational
level (level 4), and the highest percentage of
achieving SOLO taxonomy level of thinking skills is
at the multistructural level (level 3). Future research
can apply particular learning strategy to excel
student’ thinking skills to reach the extended abstract
level (level 5). It can delve into the relationship
between achieving particular SOLO level of thinking
skill and students’ learning achievement.
Training Students’ Thinking Skills using Problem-based Learning Integrated with Virtual Mobile Learning
587

ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The author would express his gratitude to the
developer of online application Appypie
(https://www.appypie.com/) for the free features
provided to create a virtual mobile learning
application.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, S., & Parsons, D. (2013). Abductive science
inquiry using mobile devices in the classroom.
Computers & Education, 63, 62–72.
Batdı, V. (2014). The effects of a problem based learning
approach on students attitude levels: A meta-analysis.
Educational Research and Reviews, 9(9), 272–276.
Biggs, J. B., & Collis, K. F. (1982). Evaluation the quality
of learning: the SOLO taxonomy (structure of the
observed learning outcome). Academic Press.
Birgili, B. (2015). Creative and critical thinking skills in
problem-based learning environments. Online
Submission, 2(2), 71–80.
Chin, C., & Chia, L.-G. (2006). Problem-based learning:
Using ill-structured problems in biology project work.
Science Education, 90(1), 44–67.
Chu, H.-C., Hwang, G.-J., Tsai, C.-C., & Tseng, J. C. R.
(2010). A two-tier test approach to developing location-
aware mobile learning systems for natural science
courses. Computers & Education, 55(4), 1618–1627.
Damopolii, I., Nunaki, J. H., & Supriyadi, G. (2018). Effect
of problem solving learning model on students
achievement. Journal of Education Research and
Evaluation, 2(1), 1–9.
https://doi.org/10.23887/jere.v2i1.12558
Darma, I. K. (2018). Improving mathematical problem
solving ability through problem-based learning and
authentic assessment for the students of Bali State
Polytechnic. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series
(Vol. 953, p. 12099).
Demirel, M., & Dağyar, M. (2016). Effects of problem-
based learning on attitude: A metaanalysis study.
Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science &
Technology Education, 12(8).
Dewanti, T. C., Widada, W., & Triyono, T. (2016).
Hubungan antara keterampilan sosial dan penggunaan
gadget smartphone terhadap prestasi belajar siswa
SMA Negeri 9 Malang. Jurnal Kajian Bimbingan Dan
Konseling, 1(3), 126–131.
EL-Shaer, A., & Gaber, H. (2014). Impact of problem-
based learning on student’s critical thinking
dispositions, knowledge acquisition and retention.
Journal of Education and Practice, 5(14), 74–83.
Ersoy, E., & Başer, N. (2014). The effects of problem-based
learning method in higher education on creative
thinking. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences,
116, 3494–3498.
Georgieva, E., Smrikarov, A., & Georgiev, T. (2005). A
general classification of mobile learning systems. In
International conference on computer systems and
technologies-CompSysTech (Vol. 8, pp. 14–16).
Gholami, M., Moghadam, P. K., Mohammadipoor, F.,
Tarahi, M. J., Sak, M., Toulabi, T., & Pour, A. H. H.
(2016). Comparing the effects of problem-based
learning and the traditional lecture method on critical
thinking skills and metacognitive awareness in nursing
students in a critical care nursing course. Nurse
Education Today, 45, 16–21.
Günter, T., Akkuzu, N., & Alpat, Ş. (2017). Understanding
‘green chemistry’and ‘sustainability’: an example of
problem-based learning (PBL). Research in Science &
Technological Education, 35(4), 500–520.
Hallinger, P., & Lu, J. (2011). Assessing the instructional
effectiveness of problem-based management education
in Thailand: A longitudinal evaluation. Management
Learning, 42(3), 279–299.
Inel, D., & Balim, A. G. (2010). The effects of using
problem-based learning in science and technology
teaching upon students’ academic achievement and
levels of structuring concepts. In Asia-Pacific Forum
on Science Learning & Teaching (Vol. 11).
Jinlong, G., Zhaolei, S., & Yawei, T. (2012). Mobile
learning research-based intelligent mobile phone and
3G networks. In Instrumentation, Measurement,
Computer, Communication and Control (IMCCC),
2012 Second International Conference on (pp. 1238–
1242).
Major, C. H., & Palmer, B. (2001). Assessing the
effectiveness of problem-based learning in higher
education: Lessons from the literature. Academic
Exchange Quarterly, 5(1), 4–9.
Minogue, J., & Jones, G. (2009). Measuring the impact of
haptic feedback using the SOLO taxonomy.
International Journal of Science Education, 31(10),
1359–1378.
Murni, A., & Anggraini, R. D. (2016). The influence of
applying problem based learning based on soft skill to
increase students’creativity in the subject development
of high school mathematics curriculum. In Proceeding
7th International Seminar on Regional Education (Vol.
3, pp. 1203–1212).
Nasution, M. L., Yerizon, Y., & Gusmiyanti, R. (2018).
Students’ mathematical problem-solving abilities
through the application of learning models problem
based learning. In IOP Conference Series: Materials
Science and Engineering (Vol. 335, p. 12117).
Roschelle, J. (2003). Keynote paper: Unlocking the
learning value of wireless mobile devices. Journal of
Computer Assisted Learning, 19(3), 260–272.
Seiter, L. (2015). Using SOLO to classify the programming
responses of primary grade students. In Proceedings of
the 46th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer
Science Education (pp. 540–545). New York, NY,
USA: ACM.
https://doi.org/10.1145/2676723.2677244.
Shen, R., Wang, M., Gao, W., Novak, D., & Tang, L.
(2009). Mobile learning in a large blended computer
BINUS-JIC 2018 - BINUS Joint International Conference
588

science classroom: System function, pedagogies, and
their impact on learning. IEEE Transactions on
Education, 52(4), 538–546.
Sihaloho, R. R., Sahyar, & Ginting, E. M. (2017). The effect
of problem based learning (PBL) model toward
student’s creative thinking and problem solving ability
in senior high school. IOSR Journal of Research &
Method in Education (IOSR-JRME), 7(4), 11–18.
Sogen, T. W. B., Damopolii, I., & Kilmaskossu, J. P.
(2018). The effect of the problem-based learning model
(PBL) on the students learning outcomes of human
excretory system material. Inornatus, Biology
Education Journal, 1(2).
Squire, K. (2009). Mobile media learning: multiplicities of
place. On the Horizon, 17(1), 70–80.
Taşoğlu, A. K., & Bakaç, M. (2014). The effect of problem
based learning approach on conceptual understanding
in teaching of magnetism topics. Eurasian Journal of
Physics and Chemistry Education, 6(2).
Tseng, K.-H., Chiang, F. K., & Hsu, W.-H. (2008).
Interactive processes and learning attitudes in a web-
based problem-based learning (PBL) platform.
Computers in Human Behavior, 24(3), 940–955.
Uzunboylu, H., Cavus, N., & Ercag, E. (2009). Using
mobile learning to increase environmental awareness.
Computers & Education, 52(2), 381–389.
Vogel, B., Spikol, D., Kurti, A., & Milrad, M. (2010).
Integrating mobile, web and sensory technologies to
support inquiry-based science learning. In Wireless,
Mobile and Ubiquitous Technologies in Education
(WMUTE), 2010 6th IEEE International Conference on
(pp. 65–72).
Wells, C. (2015). The structure of observed learning
outcomes (SOLO) taxonomy model: How effective is
it? Journal of Initial Teacher Inquiry, 1.
Wilson, M., & Bolliger, D. U. (2013). Mobile learning:
Endless possibilities for allied health educators. Journal
of Diagnostic Medical Sonography, 29(5), 220–224.
Woodill, G. (2011). The mobile learning edge: Tools and
technologies for developing your teams. McGraw-Hill
USA.
Zabit, M. N. M. (2010). Problem-based learning on
students’ critical thinking skills in teaching business
education in Malaysia: A literature review. American
Journal of Business Education, 3(6), 19–32.
Zannah, N. L., I. Iwan., & Damopolii, I. (2018). Effect of
Problem Based Learning (PBL) model toward learning
achievement of Senior High School student in
Invertebrate topic. Inornatus, Biology Education
Journal, 1(1).
Training Students’ Thinking Skills using Problem-based Learning Integrated with Virtual Mobile Learning
589
