
The Influence of Firm Performance to Corporate Social
Responsibility Disclosure
Case Study of Sharia Banks in Indonesia
Ria Yanuari Pramono
Faculty of Economics and Business, Airlangga University Surabaya, Indonesia
riayanuaripramono@gmail.com
Keywords: Capital Adequacy Ratio, Asset Growth, FDR, CSR Disclosure, Shariah Enterprise Theory.
Abstract: The development of CSR disclosure has a positive impact on Islamic economy which is characterized by the
concept of Shariah Enterprise Theory. Profitability of the company shows the company succeeded in
obtaining profit as measured by Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR), Asset Growth and Financing Deposit to Ratio
(FDR). This research is an explanation research in which the researcher explains the relationship between the
variables through hypothesis testing. The research variables include three independent variables is CAR,
Asset Growth, FDR and then CSR Disclosure as a dependent variable. The population of the study was all
Sharia Banks operate in Indonesia and have published annual financial reports during the period 2012-2014.
The data source is secondary data. The study used multiple regression analysis and processed using SPSS.
The result of the study concluded that there are significant influences between firm performance and Islamic
Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure. This research gives a suggestion for further research to use other
measure variables of financial performance to get a more comprehensive model.
1 INTRODUCTION
Market participants consider that companies that have
a sustainable social concern have a good reputation
and better opportunities than other companies that do
not have it. The strengthening of the principles of
Environmental Management Accounting, Good
Corporate Governance such as fairness, transparency,
accountability, and responsibility has encouraged
broader accounting concepts using accounting tools
and practices to support internal corporate
management decision-making on environmental
issues and their impact on corporate performance
(Doorasamy 2015).
Corporate social responsibility (Corporate Social
Responsibility) is one of the several corporate
responsibilities to stakeholders. Stakeholders, in this
case, are people or groups who can influence or be
influenced by various decisions, policies, and
operations of the company, Inoue, Funk, and
McDonald (2017). The tendency of globalization and
increased demand from stakeholders for companies to
carry out the role of social responsibility and
disclosure encourages the involvement of companies
in practice EMA. Sees the practice of EMA emerged
CSR as evidence of activity from EMA. According to
Lopatta, Reemda and Chen (2017) CSR is a general
statement which indicates the company's obligation to
utilize its economic resources in operations to provide
and contribute to internal and external stakeholders.
Profitability of the company is often highlighted
because it shows the success of the company in
obtaining profit, to measure the extent to which the
company gains profit can be seen from capital
measured by Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) ratio.
According to Li, Chen, Chien, Lee, and Hsu (2016).
CAR ratios are able to show how far all bank assets
that contain risks (credit, investments, securities, bills
with other banks) participate in financing from the
bank's own capital funds in addition to obtaining
funds from sources outside the bank, such as funds
from the community, and loan.
Aset is an asset used for corporate operational
activities. The large operating results generated by the
company, the increase in assets followed by increased
operating results will further increase the confidence
of outsiders of the company.
While the company's liquidity reflects the
condition of the company in carrying out its
operational activities and the appropriate measure of
corporate liquidity in this research is the ratio of
Financing Deposit to Ratio (FDR) because this ratio
shows the finance of sharia banking companies,
152
Pramono, R.
The Influence of Firm Performance to Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure - Case Study of Sharia Banks in Indonesia.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business, and Philanthropy (ICIEBP 2017) - Transforming Islamic Economy and Societies, pages 152-156
ISBN: 978-989-758-315-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

especially related to the liquidity aspect which shows
the customer deposit funds and used in meet the loan
request (loan request) of its customers. Companies
with high profits, growth and liquidity levels will get
a lot of attention especially from the public and
investors so that the spotlight has more value in the
eyes of the public and investors, the company tends
to disclose Social Responsibility (CSR Disclosure).
In Indonesia the development and disclosure
activities of CSR received government support, it was
proven after the House of Representatives passed the
Act on social and environmental responsibility or
CSR as a Limited Liability Company in Article 74 of
Law No.40 of 2007 on Limited Liability Company
(UUPT) on July 2007. It is mentioned that a limited
liability company that carries on business in the field
or concerned with natural resources is obliged to
carry out social and environmental responsibility
(Article 74 paragraph 1). According to Pramono
(2015), the reason companies, especially in the field
of banking, do social reporting is due to a change of
responsibility paradigm, from management to
shareholders to management to all stakeholders.
In addition, according to Isnanisa 2016, the
challenge to maintain a corporate image in the
community is the reason why a bank in Indonesia
conducts social reporting. One type of bank that plays
an important role in the disclosure of social
responsibility is sharia bank. According to Meutia
(2010), Islamic banks should have more spiritual
dimension. This spiritual dimension not only requires
non-usury business but also able to provide welfare
for the wider community, especially for the weak
economic community. According to Yusuf (2010),
the position of sharia banks as financial institutions
that already exist at the national and international
level should be a pilot financial institution in moving
the CSR program. Implementation of Islamic bank
CSR program is not only to fulfill the mandate of the
law, but furthermore that the social responsibility of
Islamic banks is built on the basis of the philosophy
and tasawwur (picture) of Islam is strong to become
one of the financial institutions that can prosper the
community. Looking at the above demands, public
companies in Indonesia that make CSR reporting
separately have increased by 60% by 2014 compared
to 2012. In addition, the rapid development of
Indonesia's sharia banking industry makes research
on social responsibility at banks sharia is required.
The statistics of the development of sharia banking up
to December 2016 shows that sharia banking services
are increasingly widespread throughout the
archipelago with 12 Sharia (BUS), 37 Sharia
Business Unit (UUS) and 154 BPRS. Total assets of
sharia banking have reached 130.5 trillion rupiahs or
grew 47.5% year on year (yoy). The high growth of
sharia banks is able to increase its share to 3.7% of
total national banking assets.
The development of EMA practice not only has a
positive impact on the development of the
conventional economy, but also the Islamic economy.
It is characterized by the emergence of CSR with the
concept of Shariah Enterprise Theory.Shariah
Enterprise Theory is an Enterprise Theory that has
been internalized with Islamic values to produce
transcendental and more humanist (Triyuwono,
2007). According to Meutia (2010), the most
appropriate theory to express corporate social
responsibility is Shariah Enterprise Theory (SET).
This is because in the Shariah Enterprise Theory God
is the source of the main mandate. While the
resources possessed by the Stakeholders are the
mandate of Allah in which it attaches a responsibility
to use in the manner and purpose set by the Giving of
the Trust.
CSR reporting is a practice established on the
basis of norms in the community. In the sharia
banking sector, the values of norms used are Islamic
religious values, or also called the values of sharia.
This research intends to explain how the reporting of
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is based on
Sharia values.
Research that examines the influence of CSR has
been done. Susilowati (2013) examines the effect of
profitability, growth and firm size on the disclosure
of corporate social responsibility information from
manufacturing companies listed in Indonesia Capital
Market Directory, using partial least square against an
inner model of ERC direct influence, firm size and
growth on CSR showing influence not significant
(significant). While inner model test for direct
influence of profitability to CSR showed significant
result. Isnanisa, Kartika and Suryan (2016), analyzed
the effect of profitability and growth on disclosure of
social responsibility according to Shariah Enterprise
Theory at Syariah Commercial Bank in Indonesia.
The result of research by using multiple linear
regression shows that profitability variable measured
by ROE have positive effect to CSR Disclosure and
growth variable have negative effect to CSR
Disclosure.
Based on the results of previous research, several
independent variables affecting Corporate Social
Responsibility research Kusumawardhany (2014) and
Isnanisa, Kartika and Suryan (2016) have differences
where the results of this study are contradictory where
profitability negatively affect the disclosure of social
responsibility in the mining industry, while
profitability have a positive effect on disclosure of
social responsibility in Sharia banks industry both
previous research equally use ROE to measure
profitability so that research this time using CAR.
According to Li, et.al (2016) the CAR ratio shows
The Influence of Firm Performance to Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure - Case Study of Sharia Banks in Indonesia
153

how much the total assets of banks that contain risks
that come funded from their own capital in addition
to obtaining funds from sources outside the bank so
that the increase in profitability positively affect the
disclosure of social responsibility (CSR Disclosure).
In addition to the research of Isnanisa, Kartika and
Suryan (2016) by taking 7 research samples indicated
that growth by using Assets Growth had negative
effect on the disclosure of social responsibility, this
study investigated whether growth positively
influences CSR Disclosure by researching the entire
population of Sharia Commercial Banks registered in
Islamic Banking Statistics. None of the previous
research has used liquidity to measure the financial
performance of sharia banks in Indonesia by using
Shariah Enterprise Theory. Seen from the results of
previous research the researchers used three basic
theories (agency theory, the theory of legitimacy and
stakeholder theory) which has been frequently used in
research with the theme of CSR.Previous research
using profitability variables with ROA and ROE
proxy as a measuring tool to see the performance
corporate finance as well as variable growth and
company size to assess the company's financial
performance. There is little research using CAR
(Capital Adequacy Ratio) proxy to measure the
profitability of a company, growth by using Assets
Growth proxy and liquidity by using FDR (Financing
to Deposit Ratio) proxy as variable to measure
company's financial performance. In addition, the
practice of CSR disclosure is more often seen from
the CSD index or GRI index, whereas still not much
explored by researchers is how the practice of CSR
disclosure is seen from the CSRI index according to
Shariah Enterprise Theory.Therefore this study was
conducted on the annual report all sharia banks
registered in Islamic Banking Statistics due to the use
of CSRI index according to Shariah Enterprise
Theory as appropriate to see how far the disclosure of
social responsibility of Sharia Commercial Banks in
Indonesia.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Shariah Enterprise Theory
Shariah Enterprise Theory is an Enterprise Theory
that has been internalized with Islamic values to
produce a transcendental and more humanist theory.
Enterprise Theory according to Triyuwono (2007), is
a theory that recognizes the existence of
responsibility not only to the owners of the company
but to the broader stakeholder group. Enterprise
Theory is able to accommodate the plurality of
society (stakeholders), things that can not be done by
proprietary theory and entity theory. This is because
the concept of enterprise theory shows that economic
power is no longer in one hand (shareholders), but is
in many hands, that is stakeholders.
2.2 Relationship Profitability to
Corporate Social Responsibility
Disclosure (CSR Disclosure) on
Sharia Bank
Profitability in this study is measured by Capital
Adequacy Ratio (CAR) which is a capital indicator
used as a variable affecting CSR Disclosure based on
the level of bank risk. This capital adequacy ratio is
an indicator of the ability of sharia banks to cover the
decline in their assets as a result of sharia bank losses
caused by risky assets Dendrawijaya (2003). So with
the increased capital itself, the bank's health-related
with the capital ratio (CAR) is increasing and with
large capital, the company is very flexible to perform
the disclosure corporate social responsibility in social
media.
2.3 Relationship Growth to Corporate
Social Responsibility disclosure
(CSR Disclosure) on Sharia Bank
Company growth can show improvement of
company's financial performance. Maria Ulfa (2009)
states that growth is a company's growth rate as
measured by the company's sales growth. The growth
of the company is one of the considerations of
investors in investing. Companies with high growth
opportunities are expected to provide high
profitability in the future, expected earnings more
persistent, so investors will be interested to invest in
the company. Companies with high growth will get a
lot of spotlights so that predicted companies that have
a higher growth opportunity tend to do more
disclosure of corporate social responsibility (CSR
Disclosure). Growth in this study was measured by
Asset Growth which is a growth indicator used as a
variable affecting CSR Disclosure based on the level
of productivity and sustainability of sharia banks.
2.4 Relationship Liquidity to Corporate
Social Responsibility disclosure
(CSR Disclosure) on Sharia Bank.
The Financing Deposit to Ratio (FDR) measures the
extent to which a bank can meet its short-term
liabilities, such as repaying its depositors' funds at the
time of billing and sufficient credit requests. The
amount of credit disbursed will determine the bank's
ICIEBP 2017 - 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business and Philanthropy
154
profit. If the bank is not able to disburse credit while
the funds that collected a lot will cause the bank loss.
The higher the FDR, the liquidity of the company is
increasing with the assumption that the bank is able
to channel credit effectively, so a number of bad loans
will be small so that the positive effect on the
disclosure of social responsibility (CSR Disclosure).
3 METHODS
In this research, there are four observation variables
related to three of them as the independent variable
that is profitability measured by Capital Adequacy
Ratio (CAR), growth measured by Asset Growth and
liquidity as measured by Financing Deposit to Ratio
(FDR) and a dependent variable that is CSR
Disclosure. The dependent variable in this research is
CSR Disclosure in company's annual report measured
by corporate social responsibility index (CSRI). The
CSRI measurement instrument to be used in this
study is based on Shariah Enterprise Theory, which
classifies CSR disclosures into five categories, God
(2 items), Customer (17 items), Employees (10
items), Communities (9 items), and Nature (9 items).
The population in this study is the Sharia
Commercial Bank according to the Islamic Banking
Statisticsin Indonesia (11 Islamic Banking Statistics),
which are listed on Sharia Banking Statistics and have
published the annual financial statements for the
period 2012-2014.
Table 1: Name of Sharia Banks in Indonesia.
Name of Sharia Banks
PT. BNI Syariah
PT. Bank Muamalat Indonesia
PT. Bank Syariah Mandiri
PT. Bank Syariah Mega Indonesia
PT. BCA Syariah
PT. BRI Syariah
PT. Bank Jabar Banten Syariah
PT. Bank Panin Syariah
PT. Bank Syariah Bukopin
PT. Bank Victoria Syariah
PT. Bank Maybank Syariah Indonesia
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 2: Results of Multiple Linear Regression Analysis.
Dependent
Variable
Independent
Variable
ß
CSR Disclosure
(Y)
Konstanta
0,567
CAR (X1)
-0,004
Asset Growth (X2)
0,002
FDR (X3)
0,000
R = 0,557
Adjusted R² = 0,239
Obtained by regression model of variable relation
ratio of sharia public bank consisting of sub-variable
of CAR, Asset Growth, and LDR to CSR Disclosure
as follows:
Y = 0,567 + -0,004 + 0,002 + 0,000 (1)
Where:
X : CAR
X : Asset Growth
X : FDR
The interpretation of the regression model is as
follows:
b = 0,567 means if the variables X , X
,
dan X
are zero, then the variable Y will be worth 0.567
units.
b = -0.004 means if CAR (X ) increases by unit
and variable other constant, then variable Y will
decrease by 0,004 unit.
b = 0.002 means if Asset Growth (X )
increases by unit and other variables are
constant, then variable Y will increase of 0.002
units.
b = 0,000 means if FDR (X ) increases by unit
and variable other constant, then the variable Y
will increase by 0.000 unit.
The coefficient of determination (Adjusted R²) is
a measure of the suitability of the regression line. In
addition Adjusted R² can also be used to measure the
proportion of total diversity that can be explained by
the regression line.
KD = Adjusted R² x 100%
= 0.239 x 100%
= 23.9%
Thus, the value of Determination Coefficient of
23.9% indicates meaning that if CAR (X ), Asset
Growth (X ), and FDR (X ) gives a simultaneous
effect of 23.9% toward CSR Disclosure (Y). While
the rest equal to 76.1% influenced by other factors
that are not observed.
The Influence of Firm Performance to Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure - Case Study of Sharia Banks in Indonesia
155
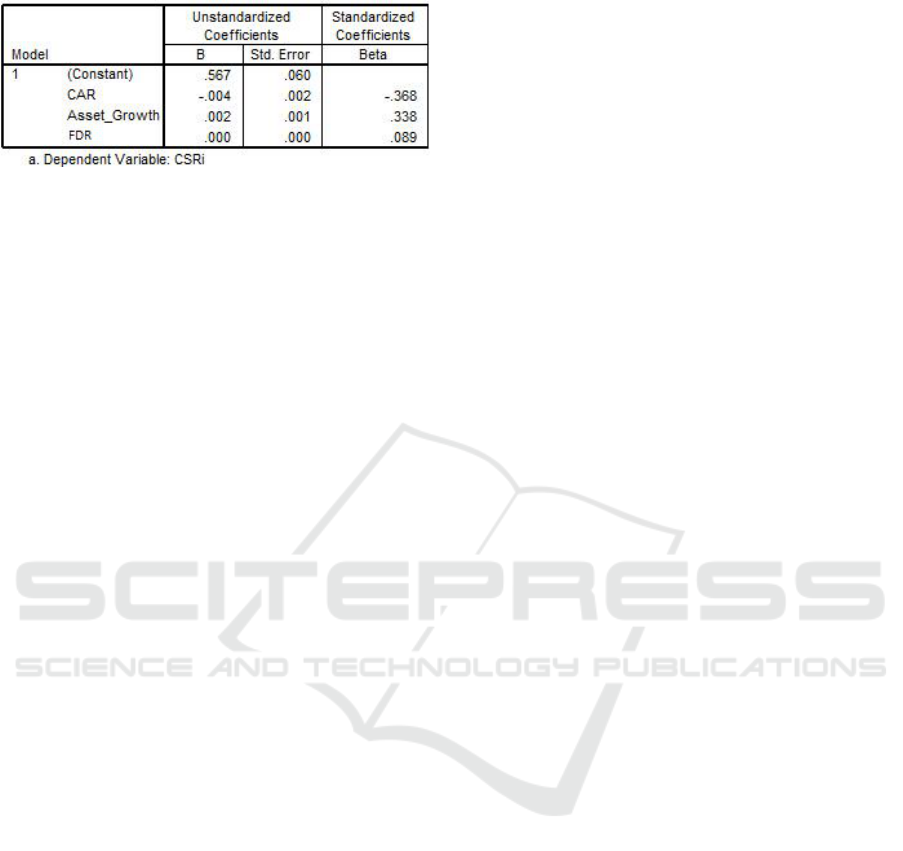
Table 3: The Test Results on Hypothesis.
This study is a population study so that partial
test t is not required to test the hypothesis, hypothesis
test on population research seen from the coefficient
value ß. The interpretation results from Table 4.2 are
as follows:
1. The negative CAR coefficient of (-0.004) shows
that CAR negatively affect CSR Disclosure.
2. The result of positive Asset Growth coefficient
of 0.002 indicates that Asset Growth has a
positive effect on CSR Disclosure.
3. The coefficient of FDR of 0,000 has the
meaning that the FDR is not effect on CSR
Disclosure.
5 CONCLUSION
By considering the analysis relating to the
formulation of the problem in this study, it can be
concluded that Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) has a
negative effect on corporate social responsibility
disclosure (CSR Disclosure) of sharia banks in
Indonesia. This indicates that if the CAR value
increases then the company tends to decrease the
disclosure of corporate social responsibility because,
with high profitability, the funds are allocated to the
capital adequacy of the company used to bear the risk
of financing by the company.
Asset Growth has a positive effect on corporate
social responsibility disclosure (CSR Disclosure) of
sharia banks in Indonesia. This indicates that if the
value of Asset Growth increases then the company
increases CSR Disclosure because the existence of
the company can grow and sustain by conducting
disclosure of social responsibility.
Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR) does not affect the
disclosure of corporate social responsibility (CSR
Disclosure) of sharia banks in Indonesia. This
indicates that if a high or low LDR will not affect
corporate social responsibility disclosure, CSR
Disclosure is not affected by liquidity seen from LDR
ratio and quality in CSR disclosure is not easy to
measure.
REFERENCES
Doorasamy, Mishelle. 2015. Theoretical Developments In
Environmental Management Accounting And The Role
And Importance Of MFCA. Foundations of
Management 7.1: 37-52.
Isnanisa, Clara Hagya, Kartika Dewi Sri Susilowati, and
Suryan Widati. 2016. Factors affecting csr disclosure
according to shariah enterprise theory. Journal of
Management Accounting Students 2.3.
Inoue, Yuhei, Daniel C. Funk, and Heath McDonald. 2017.
Predicting behavioral loyalty through corporate social
responsibility: The mediating role of involvement and
commitment. Journal of Business Research 75: 46-56.
Kusumawardhany, Sayekti Indah. 2014. The Effect of
Profitability and Leverage on Disclosure of Corporate
Social Responsibility of Mining Registered at Indonesia
Stock Exchange 2010-2012. Unpublished.
Li Y, Chen YK, Chien FS, Lee WC, Hsu YC. 2016. Study
of optimal capital adequacy ratios. Journal of
Productivity Analysis. 2016 Jun 1;45(3):261-74.
Lopatta, Kerstin, Reemda Jaeschke, and Chen Chen. 2017.
Stakeholder Engagement and Corporate Social
Responsibility (CSR) Performance: International
Evidence. Corporate Social Responsibility and
Environmental Management 24.3 (2017): 199-209.
Maria Ulfa. 2009. The Influence of Corporate
Characteristics on Social Responsibility. Unpublished.
Meutia, Inten. 2010. Menata Pengungkapan CSR di Bank
Islam (Suatu Pendekatan Kritis). Jakarta: Citra Pustaka
Indonesia.
Meutia, Inten. 2010. Shari’ah Enterprise Theory sebagai
Dasar Pengungkapan Tanggungjawab Sosial Bank
Syariah. 2010. Unpublished.
Pramono, R. Y. 2015. Pengaruh Profitabilitas,
Pertumbuhan dan Likuiditas terhadap Pengungkapan
Tanggung Jawab Sosial (CSR Disclosure) Menurut
Shariah Enterprise Theory (Studi Kasus pada Bank
Syariah di Indonesia). 2015. Unpublished.
Susilowati, Kartika Dewi Sri. 2013. Kemitraan Strategis
dalam Implementasi CSR (Studi Kasus Pada Produk
‘Kecap Bango’ PT Unilever Indonesia, Tbk.
Unpublished.
Triyuwono, Iwan. Mengangkat ”sing liyan ” untuk
Formulasi Nilai Tambah Syari’ah. Simposium
Nasional Akuntansi X Unhas, 26-28 Juli 2007. 1-21.
Yusuf, yasir. 2010. Aplikasi CSR pada Bank Syariah: Suatu
Pendekatan Maslahah dan Maqasid Syariah. EKSIBISI,
Vol 4, No 2, juni 2010.98-115.
ICIEBP 2017 - 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business and Philanthropy
156
