
The Effectiveness of Learning Activity Based Costing (LABC) in
Teacher Education Institution Based on Science Cluster in Cost
Unification Context
Abubakar Abubakar
Department of Education Administration, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jl. Dr. Setiabudi No.229, Bandung, Indonesia
abubakarditruna@upi.edu
Keywords: Fund, learning activity, effectiveness, productivity index.
Abstract: Learning Activity Based Cost model is applied and adopted in higher education. The prior concept is Activity
based cost. When it based on student learning activity at undergraduate program (S1, the researcher named
this model as LABC. ABC model is developed in higher education and set by directorate general of Higher
Indonesian in calculating cost unification. For higher education. But unfortunately, the problem rose that
teacher education institution in adopting and implementing cost unification(UKT/BKT) still received small
amount and insufficient than by public university. Meanwhile learning portion for learning practices and
theory in this institution used more money than public universities with learning ratio 70:30. For practices
and theory due to this institution developed vocational model. The problem is how department or study
program in every cluster both UPI and UM as a representative of teacher education with smaller money will
able to adopt and implement LABC model effectively suitable with student cost they received and reached
high productivity index. Actually, there is a gap between actual and expected result by every cluster with fund
they received. On the other hand, department or study program face the barrier in implementing LABC due
to university still using money budget and implement LABC inconsistently. The impact is not only tri dharma
unreached the highly level, but also productivity index is low specifically for research and writing academic
journal.
1 INTRODUCTION
Indonesian government set and granted operational
cost for public higher education since year 2012, and
this program continued until now. It ‘s strategic
policy for actualilizing equaity and equality but in
implementing this program university faces the
chalenges. The grants is not only for regular
university but also for autonomuos public university
which open several student recruitment, e.g public
national student selection and local university
selection with different tariff.
Developing higher education is viewed as human
investmen for manpower needs and benefits for
global competitiveness nationwide and international.
Now adays the cheap cost for every citizent to enter
public higher education is the national problem to be
solved. The trend is that cost for public universities
rise every year and higher than private one. It can
be said that private is lower cost than public
universities in general. On the other cases, The
government has differenciated the cost of student
fees for public universities and teacher education
intitutions and it set by ministry of research and
higher education. According to prior research result
that there are gap both of them on cost unification
tariff. For example cost unification in mechanical
engineering program in public university 9 million
rupiahs and 6.5 million rupiahs per smester for
teacher education institution and implied that cost
must be accompanied with more government
subsidies. Implementing operational cost for public
universities is based on ministry of education
regulation number 58, year 2012. Sentence 1, which
Said:
Operational cost of public higher education is
held by government and called BOPTN is as cost
assistant from government was given to Public
higher education for costing the lack of
operational cost by impact of no elevating
education fees in public higher education.
358
Abubakar, A.
The Effectiveness of Learning Activity Based Costing (LABC) in Teacher Education Institution Based on Science Cluster in Cost Unification Context.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences (ICES 2017) - Volume 2, pages 358-361
ISBN: 978-989-758-314-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

The difference of Higher education performance
based on learning activity based cost model both
public universities and teacher education institution is
caused by the portion of practice and learning theory
with ratio 70:30 in teacher education as vocational
institution. It means that a lot of money spent for
buying practice stuff and doing workhsop in student
learning activity. The criteria of adequacy, equity,
appropriateness and effectiveness for costing study
program as a research focus and correlated with
Productivity indeces in every teacher education.
For conceptual framework on analyzing data and
theory, the reseacher hold the financing theory about
cost-quality relationship and the ‘laws’ of higher
education cost from R. Bowen (1981) and its impact
for university productivity (Sulivan, et al, 2012). The
research problem is how LABC implemented
effectively and its impact in improving academic
performance, output profile and productivity indices
from UPI and UM.
2 METHODS
This research used mix method both quantitative and
qualitative as policy evaluation in financing higher
education. This model is related with quantitiatave
and qualitative analysis in reaching policy objectives
to be quit or continue, (Patton Sawicki, 1986:305). It
s also related with making decision (Levin and Mc
Ewan, (2001:10). The Approach in evaluation of
higher education financing policy is the cost oriented
evaluation. It assumed that its government institution
and others has a lot of budget for financing their
porgrams. Two method were used both cost benefit
analysis and cost effectiveness approach and use
cross section and time series data.
Two sample for this research are Universitas
Pendidikan Indonesia (UPI) located in Bandung, west
Java and Univesrsitas Negeri Malang (UM) located in
East Java. Finally, for data analysis the reseacher
compare two sample related to cost effectiveness and
productivy of each institution. Unit analysis for two
sample represented as in table 1.
Table 1: The research sample form two university.
No
Science Cluster
UPI
UM
1
Technology/
Engineering
Architecture
Electric
engineering
2
Science education
Chemistry
science
education
Chemistry
science
education
3
Social education
Economics
Education
Accounting
Education
For analyzing the productivity, the researcher uses
category for measuring Productivity Indexes as in
table 2:
Table 2: Productivity index.
81-100
Very High
61-80
High enough
51-60
Lower
- 50
Very lower
And the productivity Calculation can be broken
down into four steps:
1. Allocate the quality and expenditure data to the
education function.
2. Calculate the change in the quantity data from
periode to periode.
3. Calculate the input index
4. Calculate the productive index, (Sulivan, et al,
2012:69-71)
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
UPI and UM were founded in 1954 as higher
education of teacher education (PTPG). For adapting
the changing these two institutions have became the
University since 1999 and set by govenment
regulation and has wider mandate and cross-
fertalization for science educations program and non
science eduations program. UPI with Leading and
outstanding vision as an autonomous university but
UM still strugle for reaching those status. UM is
positioning his campus with “the learning
university”. Both universities reach own prestige for
academic and non academic manner. The calculating
and implementing of cost unification for study
program in each instituion is deliberately done by
their university. UPI places his status as corporate
university and planed to became World Class
University (WCU). For describing the improvement
of each institution indicated by academic
performance, Output profile and Productivity indices
can be present as follow.
The Effectiveness of Learning Activity Based Costing (LABC) in Teacher Education Institution Based on Science Cluster in Cost
Unification Context
359
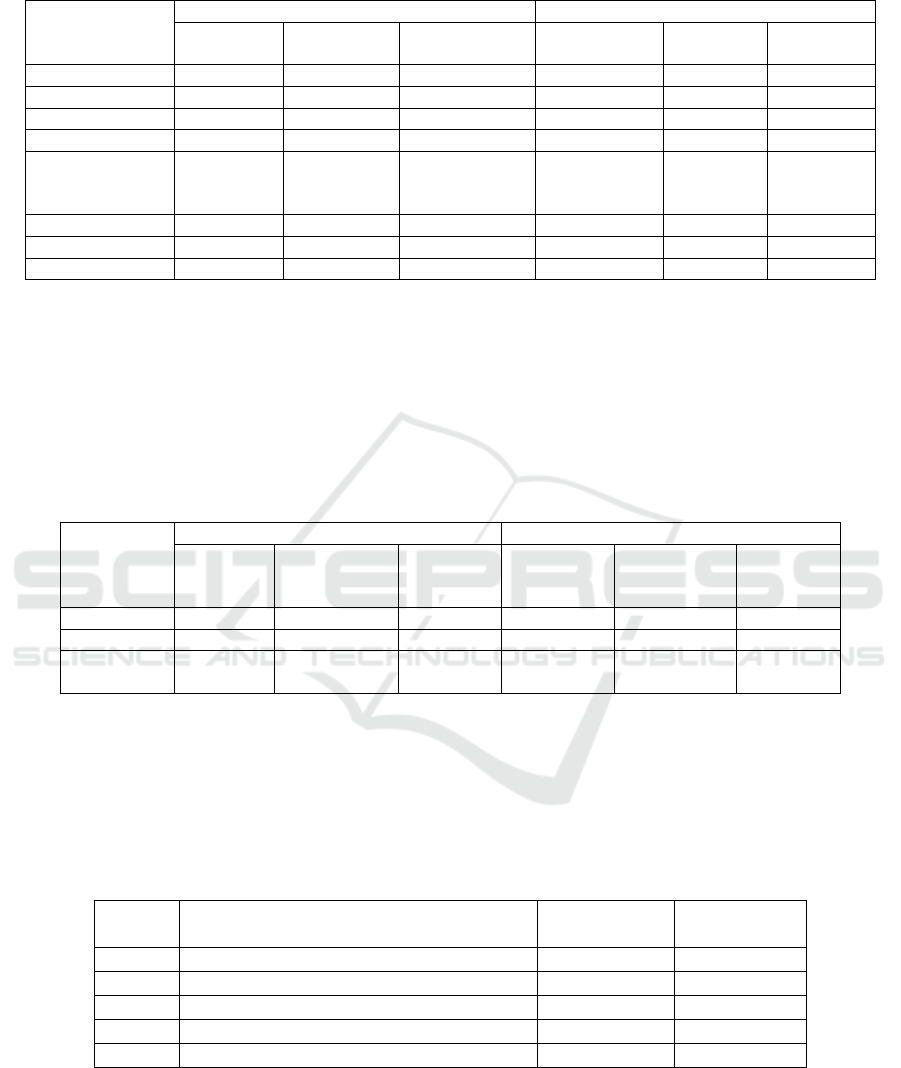
Table 3: Performance gain of two institutions.
Study Program
performance
UPI
UM
Accounting
Architecture
Chemistry
economics
Electric
enginering
chemistry
Accreditation
B
B
A
A
A
B
Research
85
17
30
45
9
15
Journal
65
70
10
60
30
50
Patten
-
-
1
-
1
1
Cooperation and
collaboration
with external
-
80
-
-
20
2
Lecturer
12
12
22
31
36
31
Unification cost
11 million
16 million
17, 6 million
8,4 million
9 million
18 million
Table 3 shows that UPI and UM rearch different
academic performance. Each institution has
accredited from B to A. UM has two A’s and one B
accreditation study program. UPI has two B’s and one
A accrediatation study program. Research and
science journal is vary between two university and
UPI is more productive in doing research and writing
journal. We can analys it from ratio journal and
reseacrh with lecturer from each study program/
department. Cooperation element describe how study
program collaborative with external institution. Cost
unification between university shows the strengh of
learning activity and UPI is higher than UM.
Table 4: Profile of Output between Two Institutions.
Output
Profile
UPI
UM
Accountin
g Ed
Architecture
Ed
Chemistry
Ed.
Economics
Ed
Electric
engineering
Ed.
Chemistry
Ed.
Study time
4 years
5,2 years
4,3 years
4 years
4,7 years
4,2 years
yudisium
3,22
3,22
3,24
3,4
3,23
3,01
Waiting
time
3 months
3 months
2-3 months
3,5-5
months
5 months
4 months
Table 2. shows that three cluster of study program
at UPI and UM rearch academic achievement by each
study program by average of study time range from
4-5,2 years and 4- 4,7 years. It means student finish
their studies from 8 – 10 for UPI and 8-9 smesters for
UM. Average of student yudisium is range from 3,01
– 3,4 at UM and 3,22-3,24 at UPI or good
achievement. Finally, the waiting time to work is
range from 2-3 months for UPI, and 3-5,5 months for
UM. It means the ouput from UPI is relatively faster
than UM to get their jobs (see in table 4).
Table.5: Productivity Index on Tridarma of HE.
NO
Tridharma and support
UPI
(Percent)
UM
(Percent)
1
Educations (teaching)
82
81
2
Research
74
72
3
Public service
76
75
4
Supporting elemen
72
73
5
Cooperation-collaboation
58
55
Table 5 indicates that productivity index for
tridharma achievement of two universities almost the
same. It range from 55-82 percents. It means that
education (teaching) element gain the very high rank.
Research, public service and support element range
72-76 percents or good enough rank, but cooperation
or collaboration between universities is only 55-58
percents or lower. It indicated that cooperation and
collaboration of these clusters with external element
must be elevated and need struggle from the leader of
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
360

study program/department. Tridharma of higher
education both universities show not only the strength
and weakness but also the opportunity and treat.
Teaching element is strong but the others still weak
and treat for competitiveness. Teacher education as
vocational institution use cost by portion 70:30 for
practice and theory learning. Doing pratices need
more resources and need much money. According to
research finding for tridharma shows that study
programs has a problem for budgeting their study
program in their own capacities because of financing
these elements is regulated by university finance
policy. The university grant the funds to all study
program/department and all units in university after
they proposed budget by RKAT (anual plan and
budget) and the funds drop to them periodically.
Every units is monitored and evaluated by internal
auditor just in case they find problem in using money
effectively and efficiently.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Implementing of learning activity based cost (LABC)
in teacher education institution is the new way of
budgeting system that set by ministry of research and
higher education. This budget model generates the
direct cost for academic and indirect cost for
managerial aspect on financing university and also
study program and departement. This model reflects
the managing cost of university that accompanied
with government regulation in operational cost for
HE (BOPTN) for eligible public university and fund
received yearly. On the other hand, teacher education
institution (university) implements cost unification
for managing fund resource from their students.
These new public institution must be race with old
public university. They must be competete their
academic performance, output and productivity with
public university. According to core business of the
institution, intitution budget and fligh hour of
managing university seems to be far different among
them. Cost and productity seems to be corelated and
indicated that there are cost-quality relatinship in
these institution, but their cost effectiveness still
lower. It can be implied that enough and proportional
budget for them can elevate their productivity index
on tri dharma of Higher education. In this case,
teacher education instituion must achieve the higher
achievement but got smaller portion in receiving
grant from government than public university. It
seems to be second level to received the fund from
minstry. Finally, they ordered to be contibuted to
achieve higher rank unversity globally.
REFERENCES
Bowen R., H., 1980. The Cost of Higher Education, HOW
much Do Colleges and Universities Spend per Student
and How Much Should They Spend? Jossey-Bass
Publisher, San Francisco.
Hicks T. D., 1992. Activity –Based Costing for small and
Mid-Sized Businesses, Implementation Guide, New
York: John Wiley and Sons.
Levin., Mc Ewan, 2001. Cost Effectiveness Analysis,
Method and Application (Second Edition), California:
Sage Publications, Inc.
Patton., Sawicki. 1986, Basic Method of Policy analysis
and Planning, New Jersey: Prentice Hall, engglewood
Cliffs.
Sulivan A.T, et.al., 2012, Improving Measurement of
productivity in Higher Education, Washington: The
National Academies Press.
The Effectiveness of Learning Activity Based Costing (LABC) in Teacher Education Institution Based on Science Cluster in Cost
Unification Context
361
