
Development of Malay Culture-Based Dance Learning Model to
Enhance Early Childhood Students’ Creativity
Nurlita Nurlita
1
, Ahmad Zain Sarnoto
2
, and Miratul Hayati
2
1
Universitas Riau, Pekanbaru Riau, Indonesia
2
Institut PTIQ Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia
litamartison@gmail.com, elbanyumasi@yahoo.co.id, miratul.hayati@uinjkt.ac.id
Keywords: Malay Culture, Dance Learning Model and Early Childhood Students’ Creativity.
Abstract: Dance can be conceptualized as human behavior composed of purposeful, intentionally rhythmical, and
culturally influenced sequences of nonverbal body movements. This study aims to develop a Malay Culture-
based dance learning model to enhance early childhood students’ creativity. Method of 3D-1I development
model (Define, Design, Development and Implementation) of research methods has been utilized to develop
Malay Culture-based dance learning model. The number of respondent involved in this study 8 early
childhood students of Early Childhood Laboratories School Unversitas Riau. The data was collected by
instrument test that developed Ennis’s framework and adapted in dance creativity. The result indicated that
fluency creativity indicator with make various kinds of limb poses classification got high score improvement,
16-point score. It can be concluded Malay Culture-based dance learning model effectively to enhance early
childhood students’ creative.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to Gilbert (2003), we learn well through:
the approach of various sensors (through listening,
seeing, saying, and doing); real teaching material;
emotional attachment; challenging but still
achievable materials; positive feedback; and sequent
and comprehensive learning. Dance is one of the best
ways to learn for young children. Through dance,
children learn meaningfully. Dance also stimulate
brain so performing optimally (Karpatu et al., 2015).
Dance is creative and constructive activity which
emerge emotional intensity and meaning (Grammer
et al., 2011). As an expression of art, dance can
communicate with its lover through phases of
expressive movements. So the dance is a branch of art
which use body movement as a tool of expression.
The dance, for early childhood becomes interesting if
the dance express ideas, feelings, and experiences of
the child. The dance activity should involve children
actively and give them chance to express their
creativity. Teacher has to be capable to choose an
active dance education model in order to guiding the
children to express their creative idea (Farquhar,
2016). For teacher, it will help them to explore the
children creativity.
Dance can be conceptualized as human behavior
composed of purposeful, intentionally rhythmical,
and culturally influenced sequences of nonverbal
body movements and stillness in time and space and
with effort and the movements are mostly not those
performed in ordinary motor activities but may refer
to them (Hanna, 2014). Dance learning model for
early childhood should use a “free”, “open”, and
“children center” approach. The concern is in the
process not the product, considered to the limitation
of their movement ability, unlike the dance
movement of an adult. The dance learning should
become fun experience and meaningful for children,
not as force or become a burden.
The creative talents in every child have to be
known, maintained, and developed through an exact
stimulation to create their creativity (Arnott et al.,
2016). Their mind set and behavior have to be
developed since early stage, because most of creative
child could solve their own problem from childhood
and more when they grow. when physical
performance is required in an environment where
learners are used to sitting in chairs to receive
information, it can provoke emotions and feelings. In
fact, children center approach in the dance leaning is
far from expectation. Most of the dance learning is
teacher center, the children become a passive
316
Nurlita, N., Sarnoto, A. and Hayati, M.
Development of Malay Culture-Based Dance Learning Model to Enhance Early Childhood Students’ Creativity.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences (ICES 2017) - Volume 1, pages 316-319
ISBN: 978-989-758-314-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

learning, they just follow the teacher instruction or the
teacher movements which is not creative, uncritical,
and not innovative.
Dance have big role in cultural. Pekanbaru have a
bold Malay culture. Since childhood, the children
there have been introduced to the Malay culture, so
that the Malay dance was not strange to them at all.
Contextual learning is one of the way so that learning
has a big influence and get good results. This article
aims to develop a Malay Culture-based dance
learning model to enhance early childhood students’
creativity.
2 METHODS
The 3D-1I model (Define, Design, Development and
Implementation) of research methods has been
utilized to develop Malay Culture-based dance
learning model (Hermita et al., 2017). The define step
was done by study case in some early childhood
schools to raised kind of dance learning model, the
design step was construct Malay Culture-based dance
learning model, the develop step was done by
validating Malay Culture-based dance learning model
that has been constructed in design step.
Implementation step was conducted Malay Culture-
based dance learning model in Early Childhood
Laboratories School Unversitas Riau. The number of
respondent was 8 early childhood student.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Malay Culture-based dance learning model have been
constructed by Three-D and One-I model (Define,
Design, Development and Implementation). For
comprehensive analysis, we are going to pronounce
follows.
3.1 Define
In define step has analyzed dance learning model in
early childhood. It aimed to construct a conceptual
framework that is procedural in the form of a pattern
or design that can be used as a study in the
development of a program of play activities for young
children. Concrete model development in this
research is a manifestation of child development
theory, learning and learning theory and play theory
for early childhood which refers to creative dance
approach.
3.2 Design
The design step was design Malay culture-based
dance learning model and instrument test. The
scheme of instrument test has been created to measure
early childhood students’ creativity. It was developed
from Ennis’s framework and adapted in dance
creativity and divided by some criteria as table 1 and
assessment criteria as table 2.
Table 1: creativity dance indicators.
Indicators
Descriptor
Classification
Duration
(second)
Fluency
Demonstrate
various poses
Make various
kinds of limb
poses
30
Reorganize the
movement
Interpret the
movement made
by the instructor
and make the
movement back
using other limbs
30
Form a series
Make movement
consisting of
movement of
head, hand, and
foot in standing
position
30
Form a series
head, hands,
and motion
feet at low
levels
Make movements
consisting of head
movements,
hands, and feet
with body position
low, such as
squatting, sitting
on the floor, lying
down, and others
30
The
arrangement of
motion is
themed
Make themed
movements with
opposite traits that
are savage-not
savage, funny-not
funny, and quiet
not calm
30
Flexibility
Structure of
movement with
properties i.e.
brooms and
fan
Make a move from
the property that
has been provided
i.e. broom and fan
by the way of
using these objects
unusually
30
Elaboration
Movement
sequence
demonstration
themed with
music
Create and
develop themed
motion with
musical
accompaniment
30
Originality
Unusual
movements
(unique)
Make more
different kinds of
motion than usual
30
Responding to
motion sounds
30
Development of Malay Culture-Based Dance Learning Model to Enhance Early Childhood Students’ Creativity
317
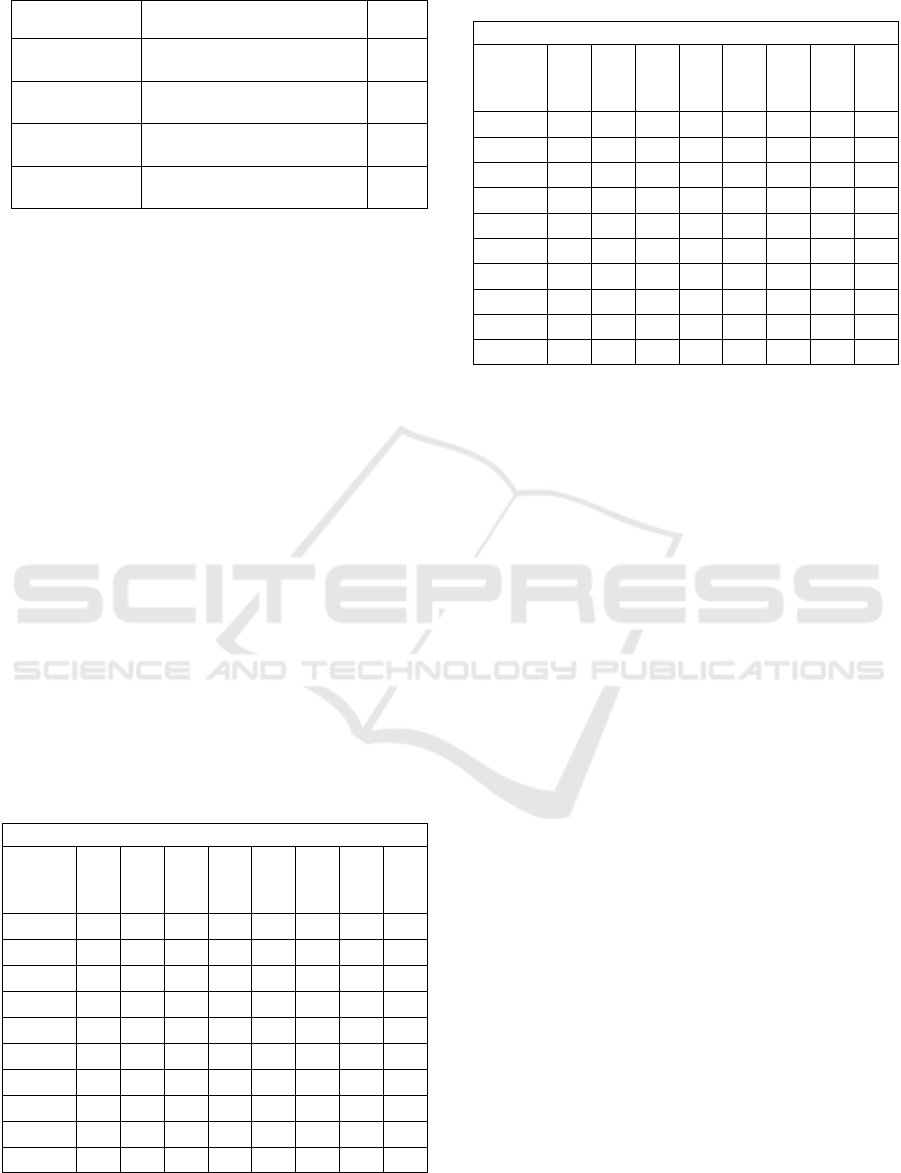
Table 2: Assessment criteria of dance creativity.
Movement of
Dance
Criteria
Score
Consistent
The observed behavior occurs
more than 6 times
4
Often Appear
The observed behavior appears
5-6 times
3
Began to Appear
Observed behavior occurs 3-4
times
2
Not yet seen
Observed behaviors are very
rare
1
3.3 Development
Development phase validated lesson plan and
instrument test of Malay Culture-based dance
learning model. And the result of validating as
follows
The contents of the model, especially its
relevance to the development of children's
creativity;
Clarity of thinking framework or research flow
(content and systematic);
The methods used;
Learning process to be run.
3.4 Implementation
Implementation was real step to implement Malay
Culture-based dance learning model. It was
conducted by 8 early childhood students in Early
Childhood Laboratories School Unversitas Riau. The
result of implantation Malay culture-based dance
learning model shown table 3 and table 4.
Table 3: pre-test score of implementation Malay
Culture-based dance learning model.
Number of Respondents
Number
of
Criteria
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
2
2
1
1
1
1
2
1
2
2
2
2
1
1
2
3
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
2
4
1
2
1
1
2
2
2
2
5
1
1
1
2
1
2
1
1
6
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
7
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
1
8
2
2
2
2
2
1
2
1
9
2
1
1
2
2
1
2
1
Total
13
15
13
15
14
13
13
12
Table 4: Post-test score of implementation Malay culture-
based dance learning model.
Number of Respondents
Number
of
Criteria
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
3
4
3
4
3
3
3
4
2
4
3
3
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
4
3
3
3
3
3
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
5
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
6
3
4
3
3
3
3
3
2
7
3
4
3
3
3
3
3
2
8
3
3
3
3
3
2
3
2
9
3
3
3
3
3
2
3
2
Total
29
30
28
29
28
25
27
22
The result in implementation stage will be
explained every creativity indicators as follows.
3.4.1 Fluency
In fluency indicator has 5 calcifications of creative
dance movements. Results of the pretest and posttest
score got the highest increasing was on classification
make various kinds of limb poses. It increased 16
score point between pretest and posttest.
3.4.2 Flexibility
In this indicator has one classification, make a move
from the property that has been provided i.e. broom
and fan by the way of using these objects unusually.
It got increasing score earned posttest score of 15
points.
3.4.3 Flexibility
For this indicator or category makes a movement
consisting of head, hand, and foot movements in a
standing position got a 14-point boost from the pretest
and posttest scores. at posttest, students get perfect
score only one but others students also experience
improvement from pretest score.
3.4.4 Originility
This indicator has two descriptors. One of them got
high score in responding to motion sounds. It got
increasing score 12 point from pretest and posttest.
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
318

4 CONCLUSIONS
Has been successfully develop Malay culture-based
dance learning model and instrument test. The
development learning model has shown a good
function in measuring early childhood students’
creativity on creativity dance movement with four
indicators.
REFERENCES
Arnott, L., Grogan, D., Pauline D., 2016. Lessons from
using iPads to Understand Young Children’s Creativity.
Contemporary Issues in Early Childhood. 17(2): 157-
173.
Farquhar, S., 2016. Time in early childhood: Creative
possibilities with different conceptions of time.
Contemporary Issues in Early Childhood. 17 (4): 409-
420.
Gilbert, A. G., 2003. Toward Best Practices in dance
Education Through the Theory of Multiple
Intelligences. Journal of education. 3 (1): 28-33.
Hanna, J. L., 2014. A Nonverbal Language for Imagining
and Learning: Dance Education in K–12 Curriculum.
Educational Research. 37 (8): 491-506.
Karpatu, F. J., Giacosa, C., Foster, N. E. V., Penhune, V.
B., Hyde, K. L., 2015. Dance and The Brain: A Review.
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences: The
Neurosciences and Music. 1337: 140-146.
Grammer, K., E. Oberzaucher, I. Holzleitner, 2011. Dance:
the human body as a dynamic motion system, Imprint
Academic. Exeter.
Hermita, N., Suhandi, A., Syaodih, E., 2017. Constructing
and Implementing a Four Tier Test about Static
Electricity to Diagnose Pre-service Elementary School
Teacher’ Misconceptions. Journal of Physics:
Conference Series.
Development of Malay Culture-Based Dance Learning Model to Enhance Early Childhood Students’ Creativity
319
