
Why People Decide to Participate in National Health Insurance?
Based on Theory of Planned Behaviour and Technology Acceptance Model
Ernawaty Ernawaty, Cindy Novia Dimantri
Faculty of Public Health, Universitas Airlangga, Mulyorejo, Surabaya, Indonesia
ernawaty@fkm.unair.ac.id
Keywords: Decision, Membership, National health insurance, Technology acceptance model, Planned behaviour
theory.
Abstract: There are many Indonesian have not participated in National Health Insurance (NHI). Preliminary study on
2016 in Faculty of Public Health, Universitas Airlangga showed only 29.5% (102 students) participated in
NHI. From 102 students, only 34.3% paid the premium by their parents for their non-wage workers status
whereas for the rest, the premium was paid by employer or through wage cut. The purposes of this study are
influenced by the combination of planned behavior theory and technology acceptance model. This
observational analytic research with cross-sectional design used stratified random sampling to obtain 242
parents of the student. Result shows that most parents had negative perceived ease of use and perceived
usefulness about NHI. Attitude, subjective norm and perceived behavioral control of parents about NHI are
also negative, whereas regression test shows that perceived ease of use influenced perceived
usefulness. Both perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use influenced attitude on NHI, whereas
intention to participate in NHI was influenced by perceived usefulness, attitude, subjective norm and
perceived behavior control. Conclusion shows, need to improve perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use,
attitude, subjective norm and perceived behavioral control through education on NHI program.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the past 15 years, many countries have adopted
universal health coverage (UHC) as an aspiration for
national policy. In 2010 World Health Report,
universal health coverage is defined as providing
everyone in a country with financial protection from
the costs of using health care and ensuring access to
the health services they need (World Health
Organization, 2010).
The National Health Insurance Program (NHI) is
is a form of government commitment to the
implementation of public health insurance to reach
universal health coverage in Indonesia which
entered into force on 1 January 2014. NHI
membership is mandatory and implemented
gradually over the entire people in Indonesia
referring to Article 4 at the Social Security Act
Constitution in 2004 which is declare that the
principle of compulsory membership is a principle
that requires the entire population to become social
security participants which implemented in stages.
Beside Indonesia, Taiwan also implements
national health insurance to reach universal health
coverage since 1995. Based on research,
participation in Taiwan almost reach 99% because it
is a mandatory health insurance scheme (Wu et al.,
2010).
Meanwhile Indonesia implemented national
health insurance just recently. In 2014, national
health insurance implemented to address growing
disparities in health care and make basic health care
available to entire population of Indonesia. There is
however some evidence of areas where NHI in
Indonesia is underperforming.
One of the problems in Indonesia is the low
participation of citizen in national health insurance
and the participation dominated by the low income
family which their participation is paid by the
government. Community’s decision to participate in
a health insurance scheme is determined by socio-
cultural and socio-economic factors (Fenebga et al.,
2015). There are several factors caused the decision
of citizen to actively participate in national health
insurance. Research showed that intensify
community education and balanced commitment to
technical and perceived quality improvement effort
related to national health insurance are needed to
Ernawaty, . and Dimantri, C.
Why People Decide to Participate in National Health Insurance? - Based on Theory of Planned Behaviour and Technology Acceptance Model.
In Proceedings of the 4th Annual Meeting of the Indonesian Health Economics Association (INAHEA 2017), pages 257-260
ISBN: 978-989-758-335-3
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
257
enhance and stimulate active participation in
national health insurance (Alhassan et al., 2015).
Based on the preliminary survey conducted to
346 students at Faculty of Public Health (FKM),
Universitas Airlangga, showed that only 29.5% (10
+ 2 students) who participate in the program NHI.
Among the 102 students, only 34.3% who pay
premiums independently and classified as Not
Receiver Wage Workers (PBPU). The purpose of
this study was to analyze the factors that influence
parents' decisions to participate in NHI program by
using a combination of planned behaviour theory
and technology acceptance model.
2 METHODS
This is quantitative observational with analytic
design. The sample size on this research is 242
parents of Faculty of Public Health, Universitas
Airlangga’s students. The sampling technique used
stratified random sampling technique. This study
was conducted in December 2016 until May 2017.
Data collected with questionnaire and analysed with
statistical method to analyse the factors influencing
intention to participate in NHI
3 RESULTS
This research showed parents’ perception about
perceived of used, perceived usefulness, attitude
subjective norm and perceived behaviour control of
the National Health Insurance (NHI) program.
Table 1: Perception of parents about Perceived Ease of
Use and Perceived Usefulness of the National Health
Insurance program (NHI)
Perceptions
Perceived Ease
of Use
Perceived
Usefulness
n % n %
Ba
d
93 38.4 87 36
Enou
g
h 79 32.6 84 34.7
Goo
d
70 28.9 71 29.3
Total 242 100 242 100
Table 1 shows that the majority of parents have
poor perceptions of Perceived Ease of Use and
Perceived Usefulness in the National Health
Insurance (NHI) program.
Table 2: Perception of parents about the attitude,
subjective norm, and perceived behavioural control of the
National Health Insurance program
Perceptions
Attitude Subjective norm
Perceived
Behavioural
Control
n % n % n %
Bad 104 43 99 40.9 89 6.8
Enough 53 21.9 77 31.8 75 1
Good 85 35.1 66 27.3 78 2.2
Total 242 100 242 100 242 100
Table 2 shows that most of parents have a bad
perception about the attitude, subjective norm, and
perceived behavioural control of the National Health
Insurance program (NHI).
Table 3: The test results of the influence between
perceived ease of use and parents perceived usefulness on
the NHI program
No. Variable
Standardized
Coefficients (β)
Significance (p)
1.
Perceived
Ease of Use
0.700 0,000 *
Table 3 shows that the parental perception of
perceived ease of use significantly influences the
perceived usefulness with p value of 0.000.
Therefore, there are similarities ratings of perceived
ease of use of the perceived usefulness of students
and parents.
Table 4: The Test Results of the influence of Perceived
Usefulness and Perceived Ease of Use against Student
Parent Attitude
Variable
Standardized
Coefficients
(β)
Significance
(p)
1. Perceived Usefulness 0.236 0,000 *
2.
Perceived Ease of
Use
0.275 0,000 *
* a significant effect, P <0.05
Table 4 shows that perceived usefulness and
perceived ease of use has a significant influence on
the attitude of parents of students on the National
Health Insurance program (NHI).
INAHEA 2017 - 4th Annual Meeting of the Indonesian Health Economics Association
258
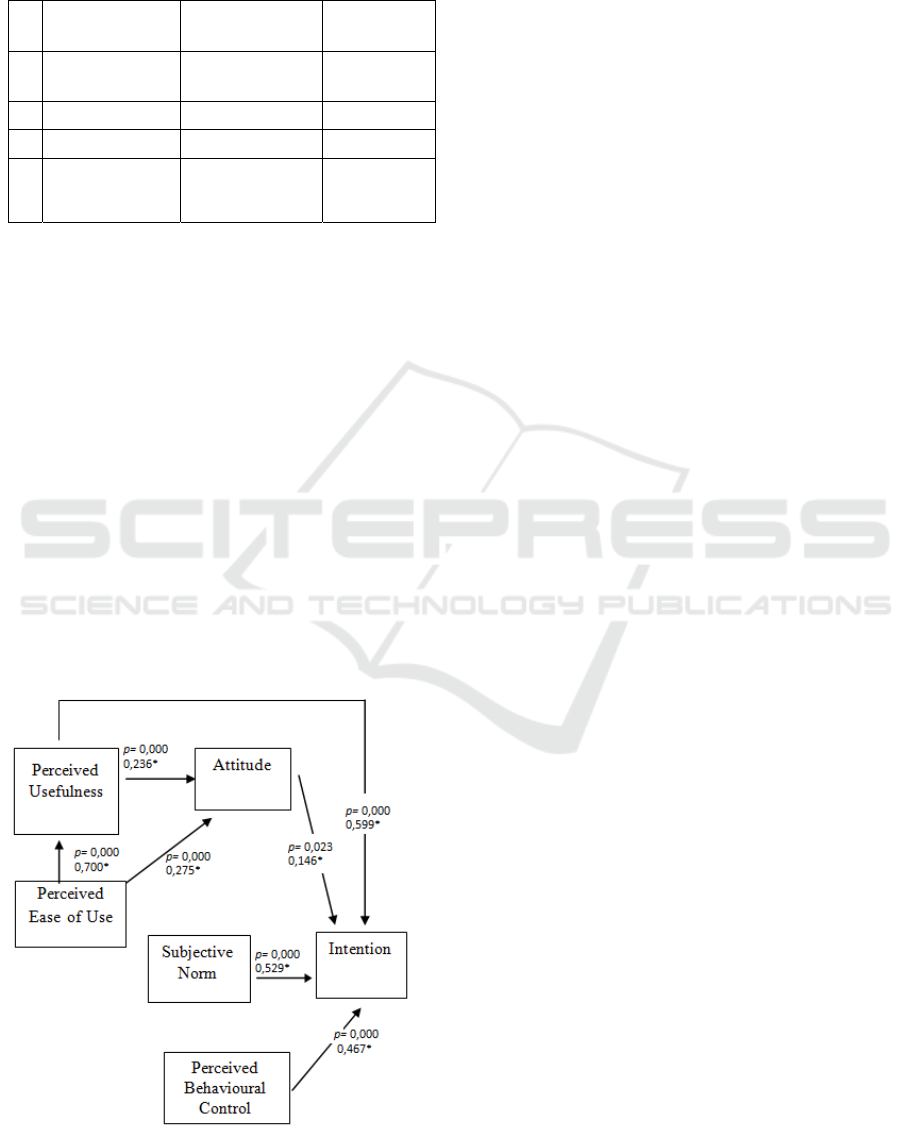
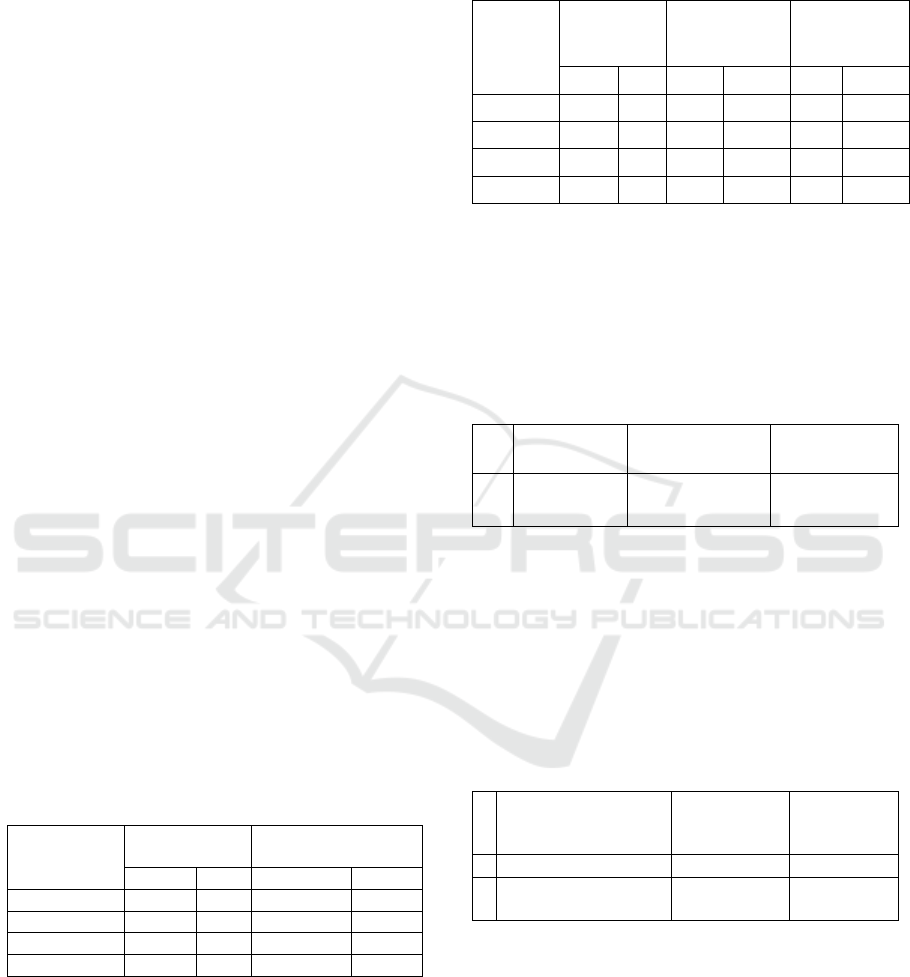
Table 5: Influence Test of Perceived Usefulness, Attitude,
Subjective Norm and Perceived Behavioural Control to
the Student Parent's Intention to the National Health
Insurance Program (NHI).
N
o. Variables
Standardized
Coefficients
(β)
Significance
(p)
1.
Perceived
Usefulness
0.599 0,000 *
2. Attitude 0.146 0,023 *
3.
Subjective Norm
0.529 0,000 *
4.
Perceived
Behavioural
Control
0.467 0,000 *
* a significant effect, P <0.05
According to the table 5, it can be seen that the
perceived usefulness, attitude, Subjective norms and
perceived behavioural control have a significant
effect on the parents' intentions to the National
Health Insurance (NHI) program. Based on the
influence (β), it is known that perceived usefulness
have the greatest influence on parents intention, then
subjective norm and perceived behavioural control.
4 DISCUSSIONS
In this research, there were several variables
analysed to identify its influence towards intention
to participate in national health insurance. The
variables such as perceived of usefulness, attitude,
perceived ease of use and subjective norm. These
variables compiled based on Theory of Planned
Behaviour and Technology Acceptance Model.
Figure 1: Factors affecting intention to participate in NHI
Based on figure 1, there are several factors
affecting, directly and indirectly, towards intention
to participate in NHI program. Perceived usefulness,
attitude, subjective norm, and perceived behavioural
control showed significant and direct influence
towards intention to participate in NHI. Meanwhile,
perceived of use and perceived usefulness also
showed significant and indirect influence towards
intention to participate in NHI.
4.1 Perceived Usefulness
Perceived usefulness is defined as the extent to
which a person believes that NHI program will
provide benefits for student’s parent. Based on the
results of the study shows that most of parents
(36.00%) have poor assessment of perceived
usefulness. It can be interpreted that most of parents
feel that the NHI program does not provide benefits
in life. Results of linear regression analysis showed
that perceived usefulness effect on the attitude of the
parents of students. In tune with the research
Widhiastuti, et al (2015) stated that the perception of
the benefits (perceived usefulness) had a significant
influence with NHI membership.
4.2 Perceived Ease of Use
Perceived ease of use is to measure a person trust
over NHI program will provide students and parents
have health services easily in NHI era. Based on the
survey results, revealed that most of parents
(38.40%) have a perception Perceived ease of use is
bad. This may imply that most of parents feel that
the program is give less benefit to obtain health
services.
4.3 Attitude
Attitudes are a negative and positive response on the
part of a person if they have to perform the
behaviour to be determined, in relation to the
student's parental attitudes toward the acceptability
of the NHI program. Based on the results of this
study is that the most of parents (43.00%) being
negative to the NHI program. Linear regression test
showed that attitudes affect the intentions of the
parents of students participated in NHI. This is in
line with study conducted by Purwaningsih (2016)
which states that there is a significant relationship
between the family head attitude and NHI program
membership.
Why People Decide to Participate in National Health Insurance? - Based on Theory of Planned Behaviour and Technology Acceptance
Model
259

4.4 Subjective Norm
Subjective norm is the perception of social pressure
are used to behave or not behave that can be
influenced by others. Most of parents (40.90%) rate
subjective norm negatively. Linear regression test
showed that the effect on the subjective norm
influenced parents intention to participate in NHI
program. This is in line with previous study by
Takhti, Rahma and Abedini (2013) which describes
the influence of subjective norm to intention.
4.5 Perceived Behavioural Control
Perceived behavioural control is confidence that
individual will ever on never do, which is then
estimated by his ability to do. In this case, the
student's parents will estimate their ability to receive
the NHI program. Linear regression test showed that
perceived behavioural control affect the parents’
intention to participate in NHI program. This is
contrasts with other study conducted by Melinda, et
al (2016) which states that there is no relationship
between behavioural control (perceived behavioural
control) with the participation interest in BPJS.
4.6 Intention
Intention is an indication of the readiness of
individuals to perform certain behaviours that are
assumed to be direct influence of individual
behaviour. Based on the value of the influence of
variables that affect the intention, subjective norm is
the most powerful influencing variable.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Most of student’s parents have perceived ease of use
perceptions, perceived usefulness, attitude,
subjective norm, and perceived behavioural control
is bad against the National Health Insurance
program (NHI). Results of regression analysis
showed that perceived usefulness and perceived ease
of use influence the attitudes of parents toward NHI
program. Parents Intention becomes participants in
NHI influenced by perceived usefulness, attitude,
subjective norm and perceived behaviour control.
The conclusion showed that to improve parents to
participate in the NHI program, we need to increase
the perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use,
attitude, subjective norm and perceived behavioural
control through education about NHI program.
REFERENCES
Alhassan, R.K. et al., 2015. Comparison of Perceived and
Technical Healthcare Quality in Primary Health
Facilities: Implications for a Sustainable National
Health Insurance Scheme in Ghana. PLOS One,
10(10).
Fenebga, C.J. et al., 2015. Social Capital and Active
Membership in The Ghana National Health Insurance
Scheme - a Mixed Method Study. International
Journal for Equity in Health, 14(118).
Melinda, A., Antono, S, 2016. Factors Associated with
Public Interest in Self BPJS Opt In Bener District
Purworejo. Journal of Public Health (e-Journal)
Volume 4, Number 4, October 2016 (ISSN: 2356-
3346).
Purwaningsih, S. 2016. Factors Associated with Public
Participation in National Health Insurance Tegalsari in
the village of Ponorogo, 2015. Essay. Muhammadiyah
Surakarta university.
Takhti, HK, Rahman, ABA & Abedini, S., 2013. Factors
Determining Nurses Hospital Information System
Usage. International Journal of Management &
Information Technology, 3 (3), pp.37-44.
Widhiastuti, IA, Putri, PP, Januraga, DN Wirawan, 2015.
Relationship of Benefit Perceptions with NHI
Participation Self-Helping at Puskesmas I East
Denpasar. Public Health and Preventive Medicine
Archive. Volume 3, No.2, December 2015.
Wu, T.-Y., Majeed, A. & Nuo, K.N., 2010. An Overview
of The Healthcare System in Taiwan. London Journal
of Primary Care, 3(2), pp.115-19.
World Health Organization, 2010. Health System
Financing: The Path to Universal Coverage. Geneva:
World Health Organization.
INAHEA 2017 - 4th Annual Meeting of the Indonesian Health Economics Association
260
