
Factors That Leads to Financial Management and Their Implications
to Local Government Performance: What Should Be Done?
Sumbawati Sumbawati
,
Lalu Hamdani Husnan
and Busaini Busaini
Mataram University (Universitas Mataram), Mataram, West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Keywords: Control, Accessibility, Transparency, Accountability, Performance.
Abstract: The aims of this paper is to examine the factors that leads to transparency and accountability financial
management and their implication to local government performance. Type of this paper was causative
research. The population in this study are internal and external stakeholders, with purposive sampling
technique, and involving 50 respondents. The result of this test using Smart PLS 3.0 shows that Government
internal control system and financial report accessibility has positive effect to transparency. Government
internal control sys-tem has positive effect to accountability, while accessibility has no effect. Local financial
management accountability has implication to local government performance, while transparency has no
implication. The results of this study can contribute to knowledge and development of accountancy literature
especially public sector accountancy associated with local financial management and their implication to local
government performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
The performance of government agencies is closely
linked to accountability and transparency. The
implementation of various existing laws and
regulations related to the application of the concept of
accountability and transparency in financial
management is expected to realize the management
of good local government and stand on its people.
Implementation of accountability and transparency in
local financial management is expected to improve
the performance of local governments. Local
governments need to implement an internal control
sys-tem in local financial management, and facilitate
accessibility for stakeholders in obtaining
information on local financial report to create
transparency and accountability in local financial
management. This can add to the trust and support
from various parties including the local government
apparatus working more vigorously and discipline.
Based on the Evaluation Result Report (ERR) of
the Ministry of Administrative Reform and
Bureaucracy Reform (PAN-RB) on the account-
ability performance of the Civil State Apparatus
(ASN) in 2016, the Government of Central Lombok
regency obtains the CC title. “The CC / Less score
indicates that there are many things that do not in sync
between the program / activity and the results
achieved. That is, there are still many implemented
activities that are useless. This is a challenge for local
governments to keep improving their performance,”
Abnur (2017).
The CC predicate is not in line with the opinion of
the audit of LKPD by the Supreme Audit Agency
(BPK), that the government of Central Lombok
regency obtains unqualified opinion in 5 (five)
consecutive years from 2012 until 2016. The
Government of Central Lombok Regency must
continue to improve internal control system,
compliance with statutory regulations, and
accessibility of financial statements to maintain WTP
opinion.
The current phenomenon of financial
accountability is the Audit Result Report (LHP) of
BPK for fiscal year 2016, there are 4 (four)
weaknesses of the internal control system and there
are 6 (six) findings of non-compliance with laws and
regu-lations. This has a financial impact resulting in
a loss to the financial statements of the local
government of Central Lombok Regency.
One of the efforts of the local government of
Central Lombok Regency in realizing transparency
and accountability of regional financial management
is through website http://lomboktengahkab.go.id/. On
the website there are some important data’s related to
718
Sumbawati, S., Husnan, L. and Busaini, B.
Factors That Leads to Financial Management and Their Implications to Local Government Performance: What Should Be Done?.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 718-723
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

the management of regional finances such as APBD
report of Fiscal Year 2016, LPSE link (e-
procurement) which still cannot be accessed until
now. (Accessed Friday 30 June 2017).
Several studies have been conducted to ex-amine
the effect of SPIP and the accessibility of financial
statements on transparency and accountability of
local financial management. Researchers testing
SPIP's influence on transparency of local financial
management are Rakhman (2013) proving positive
results, while Azizah (2014) concludes that SPIP has
no effect on transparency. Hehanusa (2015) proved
empirically that the accessibility of financial
statements has a positive and significant impact on
the transparency of financial statements. Re-searchers
who examine the influence of SPIP on the
accountability of local financial management that are
Kartika (2013), Aramide et al (2015), Lelly and Ke-
wo (2017) show different results. The influence of
financial statement accessibility to the accountability
of local financial management is done by Sande
(2013) that the accessibility of local financial report
has a positive and significant influence on the
accountability of local financial management.
Research on the effect of transparency and
accountability of local financial management on local
government performance by Auditiya (2013) proves
that transparency and accountability of local financial
management have a positive and significant impact
on local government performance. In the other hand,
Astuti (2013) concluded that the transparency and
accountability of local financial management do not
bring effect on the performance of local governments.
The difference of this study with previous
researchers is that there is no researcher who explores
the factors that influence transparency and
accountability of regional financial management that
is the internal control system of government and
accessibility of financial report and its implication to
local government performance.
The motivation to do this research is because there
is still a research gap from previous research and the
phenomenon of BPK auditor's findings on the
weakness of internal control system, non-compliance
with legislation from internal stakeholder
perspectives and external stakeholders on the
application of government internal control system
and financial statement accessibility.
Based on the explanation above, the problem in
this research are formed as follows: the factors that
leads to transparency and accountability financial
management and their implication to local
government performance?
The objectives of this research are: The aims of
this paper is to examine the factors that leads to
transparency and accountability financial
management and their implication to local
government performance.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Literature Review
According to Jensen and Meckling (1976) describes
the agency relationship (Agency Theory) is a contract
made by the shareholders (principals) and managers
(agents) in which the shareholders (principal)
authorizes the manager (agent) decision making to the
agent. Furthermore, Zimmerman (1977), agency
problems, occurred also in government organization,
not just occur in the private sector. Society regarded
as principles that mandate / authority to the
government as an agent, in performing the duties of
government to improve people's welfare.
Spence (1973) as the inventor of the signalling
theory (Signalling Theory) states that by providing a
signal, the sender (owner of the information) seeks to
provide relevant information utilized by the recipient.
The receiving party will then adjust his behavior
according to his understanding of the signal.
According to Mahsun (2006: 77): "Performance
is a description of the level of achievement of the
implementation of an activity / program / policy in
realizing the goals, objectives, mission and vision
organization contained in strategic planning of an
organization.
According to Chabib (2010: 10), the financial
management needed to control the local financial
policy include: 1. Accountability 2. Value for money
3. Honesty in managing public finances 4.
Transparency 5. Control.
Transparency is to provide open and honest
financial information to the public based on the
consideration that the public has the right to know
openly and thoroughly the government's
accountability in the management of the resources
entrusted to it and its compliance with legislation,
Nordiawan (2006: 131).
Accountability of local financial management is
the responsibility of financial integrity, disclosure and
compliance with laws and regulations. The targets are
financial statements that include the receipt, storage
and financial expenditures of local government
agencies (LAN and BPKP, 2003).
PP 60 of 2008 establishing the existence of the
internal control system control that should be
Factors That Leads to Financial Management and Their Implications to Local Government Performance: What Should Be Done?
719
implemented at the level of central and local
government. COSO (2013); Arenas et al (2014: 315);
Kamath (2002:205); Whittington (2001:242)
mentioned components of internal control consist of
five components, namely: 1. Environmental control;
2. Risk Assessment; 3). Activity Control; 4)
Information and Communication; 5) Supervision.
This opinion is also supported by Government
Regulation No 60 of 2008; Dinapoli (2007:9);
Harison (2013:235).
In Law Number 33 Year 2004 regarding Financial
Balance between Central Government and Local
Government article 103, it is stated that the in-
formation mentioned in Regional Financial
Information System (SIKD) is open data which can
be known, accessed and obtained by the citizen.
In an open democracy, this access provided by the
media, such as newspapers, magazines, radio,
television stations, and websites (internet); and
forums that provide direct attention or incentives that
encourage government accountability to the citizen.
(Shende and Bennet, 2004).
2.2 Conceptual Frame
Signal theory is used to explain the effect of SPIP on
transparency and accountability of local financial
management. Application of SPI is a form of
government (agent) to the people (principal).
Implementation of a good internal system, can be
used as a means to provide a good signal to the
citizen. The control system is designed to gain
sufficient confidence in achieving the objectives of
financial statement reliability and compliance with
laws and regulations. Moreover, this theory explains
the effect of transparency and accountability of
financial management to government performance.
To reduce asymmetry information, the government
creates integrity and reliable and financial statements.
The financial statements are then audited by the
Inspectorate and BPK to be submitted to the DPRD
as a form of accountability to the people.
Agency theory also states that agents are
opportunistic and tend to dislike the risk of
stakeholder trust toward government. The
responsibility that local governments show as the
executive is how they are able to provide access for
users of financial statements. Using financial reports
reported by the agency as their responsibility, the
principal may assess, measure, oversee transparent
and accountable local financial management.
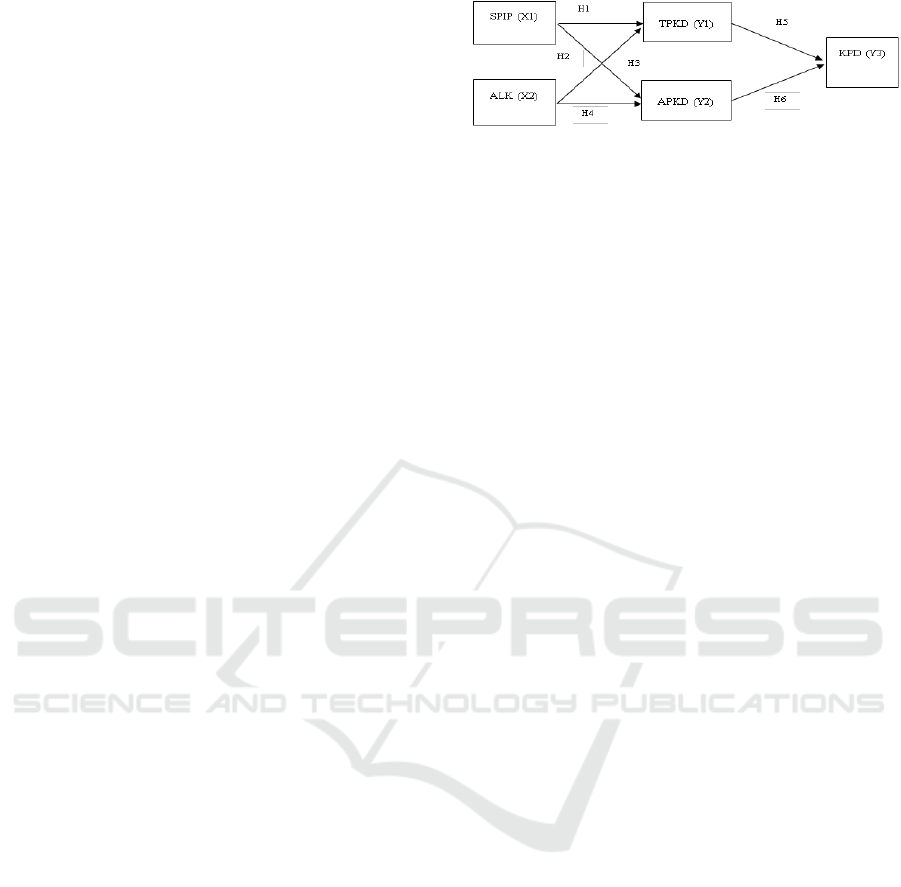
The conceptual framework of this research can be
drown as follows:
Figure 1: Research method.
Note:
SPIP : Government Internal Control System
ALK : Accessibility Financial Report
TPKD : Local Financial Management
Transparency
APKD : Local Financial Management
Accountability
KPD : Local Government Performance
2.3 Hypothesis Development
In the signal theory, the government (agent) will try
to give a good signal to the citizen (principal) with the
implementation of control systems to achieve goals.
The research conducted by Azizah et al (2014) and
Rakhman (2013) conclude different results. Rakhman
(2013) proves the influence of the government's
internal control system on the transparency of local
government financial statements is significant and
positive. Based on the description, it can be put
hypothesis as follows: H1: The government's internal
control system has a positive effect on the
transparency of local financial management.
In the agency theory, agents are usually
opportunistic and tend to dislike risk (risk averse).
The responsibility of the government represents as an
agent is how they are able to provide access for users
of financial statements. According to Mardiasmo
(2009: 171): "the citizen as a trusting party toward the
government has the right to know and the right to be
informed financial report." Hehanussa (2015)
empirically prove that the accessibility of financial
statements has a positive and significant impact on
the transparency of local financial management.
Based on the explanation, the hypothesis would be:
H2: The accessibility of financial statements has a
positive and significant impact on the transparency of
local financial management.
The signal theory can help the government
(agent), the citizen (principal), and outsiders reduce
the asymmetry information by producing a financial
report with integrity to believe the reliability of
information submitted by the agent, need to get
opinions from others who freely give opinion about
the financial statements. Research on the influence of
internal control system on financial accountability
was conducted by Kartika (2013) that SPI does not
has direct effect on the accountability of local
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
720

financial management, in contrast to conclusion of
Aramide et al (2015), Lelly and Kewo (2017). The
results showed that the internal control system has a
significant positive effect on financial accountability.
Based on the description, it can be made a hypothesis:
H3: Internal Control System has a positive and
significant effect on the accountability of local
financial management.
In agency theory, there is an assumption that
agents act opportunistically against principals. Sande
(2013) concluded that the accessibility of financial
statements has a positive and significant impact on
the accountability of local financial management.
Based on the description, it can be made a hypothesis:
H4: Accessibility of local financial reports has a
positive and significant impact on the accountability
of local financial management.
The signal theory explains that the government as
a party given the mandate of the citizen de-sires to
show the signal to society by means of transparency
of local financial management through the website
that can be accessed by users of local financial
statement information. Auditiya (2013) concluded
that the transparency of financial management has a
positive and significant impact on performance. This
is a different result with researchers Astuti’s (2013).
Based on the description, then made a hypothesis: H5:
The transparency of local financial management has
a positive and significant impact on the performance
of local government.
The Signal Theory can help local governments as
agents in reducing the asymmetry information of
local financial by producing good and integrity
financial information. This signal indicates that the
local government has carried out its duties and
responsibilities as the citizen's caretaker (Puspita and
Martini, 2010). Auditiya’s research (2013) states that
the accountability of local financial management has
a positive and significant influence on the
performance of the local government work unit.
Unlike Astuti’s (2013). Based on the description, it
can be made a hypothesis: H6: The accountability of
local financial management has a positive and
significant impact on the performance of local
government.
3 METHODS
The type of research used is associative re-search.
The population in this test is 200 people, consisting
of all SKPD in Central Lombok District Government,
which is referred to as internal stakeholders. Those
included 31 SKPD, Auditor Inspectorate and external
stakeholders consisting of members of DPRD,
NGO/foundation, and entrepreneur. The study was
conducted in March 2017 to April 2017. Sampling
technique is taken based on purposive sampling
technique. Sample in this re-search are Sub-Head of
Finance Unit of SKPD 9 people, Finance Staff of
SKPD 9 people, Auditor Inspectorate 8 people, 8
members of DPRD, 8 NGOs, and Entrepreneur 8
persons, therefore the sample number is 50 people.
Methods of data collection is done by filling the
questionnaire. The variable, measured by Likert
scale. Data analysis used in this research is Smart PLS
program version 3.0.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Outer Models Evaluation
The outer model evaluation is done to assess the
validity and reliability of the model. The result of the
evaluation of the first phase outer model is 18
statements declared that it does not to meet the
convergent validity because it has the loading factor
value <0.6 and 46 statements stated to meet the
convergent validity because it has a loading factor
value> 0.6. Statements that do not meet convergent
validity are 12 of the SPIP Variables, 6 of the
Variables APKD. The invalid statement is excluded
from the model, PLS Algorithm analysis is performed
again for phase II of testing. The result of outer
evaluation of phase II model shows that all statements
have loading factor value above 0.6, therefore, that
stated convergent validity.
Moreover, to fulfil the required loading factor
value, the AVE value of the construct also meets the
requirements of convergent validity is AVE value>
0.5. PLS algorithm report also shows that all variable
constructs have good reliability because they have
composite reliability value> 0.7.
4.2 Inner Model Evaluation
Based on the R-square value generated from the inner
model evaluation, it was concluded that the variable
of transparency of local financial management
(TPKD) can be explained by SPIP variable and 60.7%
financial statement accessibility, while 39.3% is
explained by other un-researched variables.
Local Government Financial Management
Accountability (APKD) can be explained by
Government Internal Control System (SPIP) and
Accessibility of Financial Statement (ALK) as much
Factors That Leads to Financial Management and Their Implications to Local Government Performance: What Should Be Done?
721

as 62,3%, while 37,7% is explained by other
unexamined variables. Local Government
Performance Variables (KPD) can be explained by
variable TPKD and APKD equal to 27,0%, while
equal to 73,0% explained by other unexamined
variables.
Besides R-Square, inner model evaluation
through the bootstrapping menu also generates T-
statistics values that will be used to test the
hypothesis. The criteria are T-statistic> 1.64 (5%
alpha value, one tail).
4.3 Discussion
4.3.1 Interpretation of Results
4.3.1.1 Effect of Government Internal Control
System on Transparency of Regional
Financial Management
The results of the first hypothesis testing, through
PLS shows that the value of T-statistics> t-table is
7,170> 1.64. This shows that the internal control
system has a positive and significant impact on the
transparency of local financial management. The
Government of Central Lombok Regency has
implemented SPIP integrally and thoroughly so that
local financial management can be implemented
transparently.
4.3.1.2 Effect of Accessibility of Financial
Statements on Transparency of Regional
Financial Management
Results of testing the second hypothesis, through PLS
shows that the value of T-statistics> t-table is 4.371>
1.64. This shows that the accessibility of financial
statements has a positive and significant impact on
the transparency of local financial management. By
providing easy access for users of financial
statements, it will enable the operation of a good
control function on the accountability of the use of
local assets as well as control over the financial
policies taken by the government, whether controlled
by external user or internal financial statements.
4.3.1.3 Influence of Government Internal
Control System on the Accountability of
Regional Financial Management
The result of the third hypothesis testing, through PLS
shows that the value of T-statistics> t-table is 12,870>
1.64. This shows that the government's internal
control system has a positive and significant effect on
the accountability of local financial management. The
Government of Central Lombok Regency has
implemented SPIP integrally and thoroughly so that
the financial management of the region can be
accounted for.
4.3.1.4 Effect of Financial Statement
Accessibility to Local Financial
Management Accountability
The results of the fourth hypothesis testing, through
the PLS shows that the value of T-statistics <t-table is
0.915 <1.64. This shows that ease of ac-cessing
financial statements does not affect the accountability
of local financial management. The results of this
study due to the publication of financial statements
through the Internet media is less effective. This is
caused by the society’s apathetic condition toward
information technology. While the publication of the
principle of easy and cheap through the newspaper
media is not published by the government.
4.3.1.5 Influence of Transparency of Regional
Financial Management to Local
Government Performance
The results of the fifth hypothesis testing, through the
PLS shows that the value of T-statistics <t-table is
0.262 <1.64. This shows that the transparency of local
financial management does not has implications for
local government performance. The result of this
research is caused by untransparency of local
financial management which is published through
newspaper media. Newspaper media is the most
inexpensive and easy media. Public ignorance of
financial statements causes a lack of community
control over local government performance.
4.3.1.6 Effect of Regional Financial
Management Accountability on Local
Government Performance
The results of testing the sixth hypothesis, through
PLS shows that the value of T-statistics> t-table is
3.153> 1.64. This indicates that the account-ability of
local financial management has implications for the
performance of local governments. This can be
proved from the opinion of the WTP from the BPK
that the Central Lombok Regency Government
achieved 5 times in a row.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The conclusions that can be drawn from this study is
the government's internal control system and the
accessibility of financial statements have a positive
and significant impact on financial management,
which in turn has implications for the performance of
local governments. The results of this study can
contribute to knowledge and development of
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
722

accountancy literature especially public sector
accountancy associated with local financial
management and their implication to local
government performance. And the results of this
study can be used as a consideration for decision
makers in the local government.
The proposed suggestions are: Indonesian
Government has to be aware of applied the role and
regulation toward evaluation of local government
performance. This is cause by different part of local
government will have different approaches. As result
of this research found that was not all of 58
determinant factors could be used as an evaluation for
performance of local government. Result of this
research will be precisely acceptable if these
determinants factor been found has to test further by
using bigger respondent and loading factor score >
0.7 as suggested by Chin (1998).
REFERENCES
Abnur, A., 2017. Banyak Daerah Bernilai Rendah, Menpan
RB Ancam Potong DAK. Available from:
http://cdp.khoirilanwar.com.
Aramide, Sanusi Fasilat, Mustapha Muhammed Bashir.
2015. The Effectiveness of Internal Control System and
Financial Accountability at Local Government Level in
Nigeria. Impact: International Journal of Research in
Business Management (IMPACT: IJRBM) ISSN (E):
2321-886X; ISSN (P): 2347-4572. Vol. 3, Issue 8, Aug
2015, 1-6.
Arenas, A. A., Elder, R. J., Beasly, M. S., 2014. Auditing
and Assurance Service: An Integrated Approach, 12 th
Edition, Pearson, Prentice Hall Inc.
Astuti, R. M., 2013. Pengaruh Akuntabilitas, Transparansi
Dan Fungsi Pemeriksaan Intern Terhadap Kinerja
Pemerintah Daerah (Studi Kasus Pada Dinas
Pendapatan Pengelolaan Keuangan Dan Aset Daerah
(DPPKAD) Kabupaten Grobogan. Tesis. Fakultas
Ekonomi dan Bisnis. Universitas Muhamadiyah
Surakarta.
Auditiya, L., Husaini, Lismawati. 2013. Analisis Pengaruh
Akuntabilitas dan Transparansi Pengelolaan Keuangan
Daerah terhadap Kinerja Pemerintah Daerah. Jurnal
Fairness. Vol.3 No. I, 21-41.
Azizah, Nur, Junaidi, Achdiar Redy Setiawan. 2014.
Pengaruh Penyajian dan Aksesibilitas Laporan
Keuangan Serta Sistem Pengendalian Intenal
Pemerintah Terhadap Transparansi Dan Akuntabilitas
Pengelolaan Keuangan Daerah. Tesis. Universitas
Trunojoyo Madura.
Chabib, S., Heru Rochmansjah. 2010. Pengelolaan
Keuangan dan Aset Daerah. Fokusmedia. Bandung.
Chin, W.W., 1998. The Partial Least Square Approach for
Structural Equation Modelling. In G.A. Marcoulides
(Ed), Modern, Modern Methods for Business Research
(pp.295-358). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Dinapoli. 2007. Standard for Internal Control in New York
State Government.
Harrison. 2013. Financial Accounting. 9 th Edition.
Pearson.
Hehanussa, S. J., 2015. Pengaruh Penyajian Laporan
Keuangan Daerah dan Aksesibilitas Laporan
Keuangan Daerah Terhadap Transparansi dan
Akuntabilitas Pengelolaan Keuangan Daerah Kota
Ambon. Jurnal Bisnis, Akuntansi dan Manajemen.
ISSN 2302-9791. Vol.2 No. 1 May 2015
Jensen, M., Meckling W.H., 976. Theory of the Firm:
Managerial Behavior, Agency Cost, and Ownership
Structre, Journal of Financial Economics, 3,305-360.
Kartika, I., 2013. Pengaruh Sistem Pengendalian Intern
Pemerintah (SPIP) terhadap Kualitas Laporan
Keuangan dan Impilkasinya terhadap Akuntabilitas
Keuangan (Penelitian pada Realisasi Anggaran di
Pemerintah Daerah Kabupaten Wilayah Provinsi Jawa
Barat). Skripsi. Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia.
Kamath, L. F., 2002, Auditing Concepts and applications,
A Risk-Analysis Approach, 5th Edition, West
Publishing Company.
Lelly, Cecilia, Kewo, 2017. The Influence of Internal
Control Implementation and Managerial Performance
on Financial Accountability Local Government in
Indonesia. International Journal of Economics and
Financial Issues, 2017, 7(1), 293-297.
Mahsun, M., 2006. Pengukuran Kinerja Sektor Publik.
BPFE. Yogyakarta.
Mardiasmo. 2009. Akuntansi Sektor Publik. Andi.
Yogyakarta.
Nordiawan, D., 2006. Akuntansi Sektor Publik. Salemba
Empat. Jakarta.
Puspita, R., Martini, D., 2010. Analisis Pengaruh Kinerja
Dan Karakteristik Pemda Terhadap Tingkat
Pengungkapan Dan Kualitas Informasi Dalam Website
Pemda. Universitas Indonesia.
Rakhman, M. A. 2013. Pengaruh Pengendalian Intern
terhadap Transparansi Pengelolaan Keuangan Daerah
Kabupaten Bandung Barat. Tesis. Universitas
Pendidikan Indonesia.
Sande, P., 2013. Pengaruh Penyajian Laporan Keuangan
Daerah dan Aksesibilitas Laporan Keuangan terhadap
Akuntabilitas Pengelolaan Keuangan Daerah. Tesis.
Universitas Negeri Padang.
Shende, S., Tony Bennet. 2004. Concept Paper 2:
Tranpararency and Accountability in Public Financial
Administration. UN DESA.
Spence, M., 1973. Job Market Signalling. The Quarterly
Journal of Economics. Vol. 87, No.3. http//jstor.org
Whittington O. R., Pany Kurt, 2001, Principles of Auditing
and Other Assurance Services, Thirteenth Edition,
McGraw-Hill Companies Inc.
Zimmerman, L. J., 1977. The municipal accounting maze:
An analysis of political incentives. Journal of
Accounting Research Vol 15, 107-144.
Factors That Leads to Financial Management and Their Implications to Local Government Performance: What Should Be Done?
723
