
Wireless Sensor Network for Remote Monitoring
and Detection of Explosives
(W-ReMADE)
Simi S. and Maneesha V. Ramesh
Amrita Centre for Wireless Network and Applications, Amrita School of Engineering
Amrita University, Ettimadai, Coimbatore, India
Abstract. Recent years have shown a worldwide increase in terrorist bombings.
Continuous monitoring for the presence of explosives in public places can
improve security of the public and infrastructure. The objective of this research
work is to reduce, control, and warn about the forthcoming terrorist activity by
precise and quick detection of explosives. This paper proposes a wide area
monitoring system using a multi phase wireless sensor network design. W-
ReMADE uses multiple wireless sensor nodes integrated with different types of
sensors to identify the explosives. Based on diverse orthogonal techniques, the
system collects data from the sensing nodes, dynamically aggregates the data
and forward to the sink node for further analysis. A mobile node has been
introduced to further confirm the suspected objects, thus offering an enhanced
target tracking mechanism that reduces number of false alarms. W-ReMADE
provides an effective warning mechanism for security threats in public places so
that immediate action can be taken against bomb threats.
1 Introduction
In today’s world terrorism is a main threat to the security of the world. Continuous
monitoring systems can improve the security of infrastructure and general public in
urban areas. A wireless sensor network is a solution for continuously monitoring and
identifying explosive materials. Currently, effective systems were not developed to
operate remotely in open environments over a wide area. The difficulty with the
existing techniques is that the suspected items have to bring nearer to the detecting
instrument. This involves more human involvement in the detection and cannot be
continuously monitored. Here comes the significance of remotely detecting the
explosives were the process of detection is taking place at a reasonable distance from
the suspected material without affecting the other people occupied in suspected area.
This paper mainly concentrates on detection of explosive materials in public
places with the help of wireless sensor network technology [1-2]. The area under
study is monitored in real time, collect data, aggregate it and send to the sink node.
The main constituent of explosives is chemical components. By analyzing the
chemical signatures, it is almost possible to predict whether a material is explosive or
not. In an open environment, a single type of sensor may not be adequate in
confirming the explosive material presence. Also the concentration of these materials
S. S. and Ramesh M..
Wireless Sensor Network for Remote Detection of Explosives.
DOI: 10.5220/0003116300600071
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Semantic Sensor Web (SSW-2010), pages 60-71
ISBN: 978-989-8425-33-1
Copyright
c
2010 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

will be very less in the atmosphere because of its well packing. These may cause
wrong alarms and destroy the usefulness of the system. To meet this limitation, the
W-ReMADE uses more than one mutually independent technology for the detection
scheme. As the signal strength is less in field, the system uses a mobile node to reach
the suspected area, collect signals and confirm the presence of explosives and thus
provide an enhanced target tracking. Sensor nodes of the wireless sensor network are
planned to deploy in Indian airports. Multiple sensors of varying type are deployed in
such a way that the network can cover the whole region. Sensed data is send to the
sink node for processing.
According to global terrorism data base [3], the terrorist attacks are increasing in
recent years. In terms of total terrorist attacks between 1970 and 2007, India is ranked
in the fifth position in the list of top ranking countries. It is also found that nearly 50%
of weapons used were explosives. The explosives used were readily available,
especially dynamite, grenades, and improvised devices placed inside vehicles. The
security measures in airport are not much effective to detect the presence of
explosives. W-ReMADE is designed to set up not only in the inside areas of airports,
but also to provide an effective way to identify the presence of explosives outside the
rooms. Even if it is designed for this particular scenario, this can be applicable to
other public places such as railway stations, bus stations, parks, embassies, hotels etc.
with slight design modifications.
The paper is organised as follows: Section 2 describes a brief review of the related
works. Section 3 and 4 presents the proposed system model and network architecture.
The algorithms used in the system are described in section 5. Section 6 deals with the
advantages of the system followed by the conclusion.
2 Related Work
In conventional systems, biosensors like dogs and honey bees were used to detect
explosives. But they have restricted attention span and are very expensive. So, various
instruments have been developed. The problems with those approaches were the
complexity and bulk size. Several existing detection methods that can be utilized for
remote explosive detection are mentioned in [4]. The development of explosive
detection with Micro Electro Mechanical Systems(MEMS) technology was briefly
reviewed in [5] MEMS is a micro fabrication technology that combines mechanical
elements, sensors, and electronics in a chip. For commercial application of potential
MEMS based explosive detectors, require high sensitivity and excellent selectivity.
Here also standoff distance is a main problem to apply in open environments.
In [6] authors developed a technique for stand-off detection of trace explosives
using infrared photo-thermal imaging. They used a set of infrared quantum cascade
lasers which is tuned to the absorption bands of explosive traces .When the lasers
illuminate the object, an infrared camera detects the small increase in thermal signal.
The main problem with this approach is the standoff distance limit. Also in a noisy
environment, it is very difficult to detect the increase in thermal energy. The authors
of [7] utilize terahertz technology for explosive detection. The system uses very low
levels of non ionizing radiation to detect and identify objects hidden under clothing.
Many chemical substances and explosive materials exhibit characteristic spectral
61

responses at THz frequencies that can be used for threat object identification. This
technique is able to sense through several layers of clothing with the help of safe non
ionizing radiations. As the maximum standoff distance that can be achieved from this
method is 1m, in an open environment it is difficult to apply this method.
Some of the stand-off methods currently developed is focused on chemical
identification. The main challenge includes the distances from which effective
detection can be conducted in presence of various interferences from environments.
Bourzac, Katherine describes a method to detect explosive materials using magnetic
sensors developed for use in the battlefield [8]. The National Institute of Standards
and Technology (NIST) have developed magnetometer for detecting the presence of
magnetic materials [9]. But it does not consider the information about the chemicals
used in explosives and it cannot be applied to scenarios where more metallic presence
is found. German researchers developed a sensor system [10] to monitor people
carrying explosive in public places. The system consists of two separate sensor
networks to find chemical properties and kinetic information of the person. They are
using their own chemical sensors for the sensor network. The cost of developing such
type of sensors is comparatively high. In the proposed design, the system uses already
existing components for sensing purpose. As one type of sensor is not sufficient to
detect the explosive presence, the proposed design utilizes more than one independent
technology. Also W-ReMADE allows to continuously monitoring the area without
affecting the passengers going through the monitoring area.
3 W-ReMADE System Design
3.1 Sensing Components
As the system is using more than one technique is used to identify the explosive and
the joint result is used for decision making, the probability of false alarms are
comparatively less. Even if one of the sensor readings is wrong, the system can work
well by selecting the correct reading from other sensors. An explosive material can
be identified chemically, magnetically, thermally and electrically. But thermal and
electrical measurements will not improve performance because of the noisy
environment. So the proposed design utilizes the chemical and magnetic properties
of the material. W-ReMADE combines imaging technology, optical technology and
chemical as well as magnetic identification techniques.
In W-ReMADE, we used a set of image sensors to locate unattended objects.
Theses image sensors will capture the pictures of the scene periodically and send to
the image analyzing server to identify unattended objects. To support chemical
identification of the explosives, W-ReMADE makes use of vapor sensors to collect
the vapour concentration present in the air. An air collecting system and a filter is
used to collect large volumes of air and to filter the commonly present particles of
air. The vapour sensor is connected to the mote using an interface board and it can
transmit the sensed data for analysis. To magnetically identify the explosives, the
system used the MicaZ magnetometer. The system also employs an optical
technique in which it uses a LIDAR emitting infra red radiations that will excite the
molecules of air and reflected back. To collect the response patterns, the system is
62
equipped with additional light collectors and detectors. The corresponding
frequencies of vibration are calculated and send to the sink node for further analysis.
3.2 System Architecture
The proposed wide area monitoring system is applicable to any public places such as
railway stations, airports, bus stations, supermarkets, embassies etc. Even if the
system is applicable to all urban areas, this project mainly focuses on the airports in
India. The area under testing is equipped with LIDAR, image sensors, magnetic
sensors and chemical sensors. These sensing components are deployed in the roof of
the passenger areas. The system will continuously monitor the area and if the strength
of signal collected from the sensors is greater than a particular threshold, the system
will immediately give indication to the security personnel through internet or mobile
network. If the collected signal strength is less than the predefined threshold, the
system will perform second phase operations for the confirmation. The following
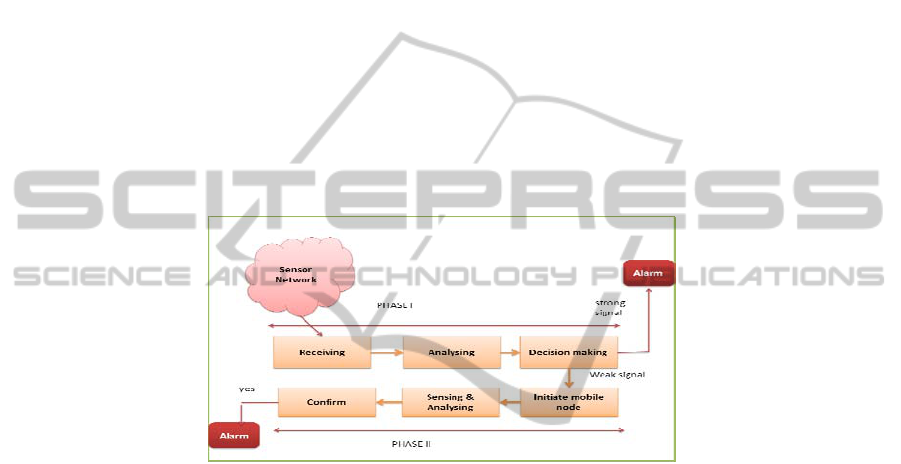
figure 1 gives an overview of the system.
Fig. 1. Overview of the system.
Phase 1
To monitor the presence of explosives, W-ReMADE uses vision based method,
chemical identification and magnetic identification. All these methods are done in
parallel in order to provide more precise results and to reduce number of false alarms.
The system will compares the data collected from different techniques and make an
appropriate decision whether any of the data is false or not. Even if the result from
one technique is wrong, the system is able to distinguish it by using the correlation
between historical data and data from sensors using a different technique. Image
sensors will periodically take pictures of the scene and send to the image analysing
server. The background images of the test area are already stored in the server. By
running the object identification algorithm, the system is able to find out unattended
objects. If any unattended object is found, the area under that image sensor will be
close monitored by initiating phase II operations for the confirmation of suspected
object.
The concentration of explosive molecules may be low in the test environment. To
get more concentrated vapors of the air, W-ReMADE uses a vacuum system which
will collect large volume of air from the test area. These air molecules are filtered
63
using a concentrator and fed to a vapour sensor. From the concentrated air molecules,
the vapour sensor can effectively find the chemical composition of particles present in
that air sample. The sensed data is send to the sink for analysis. Using a
magnetometer, the system will find the metallic presence in the area. The laser beam
from the LIDAR scans the entire area with the IR beam and excites the particles
present in air. The system is equipped with additional light collectors and detectors to
capture the response patterns. These response patterns are fed to a vibration sensor
tuned to the resonant frequency of chemicals in the explosive. From the vibrations of
the sensor, the system will find the corresponding wavelength. These detected
wavelengths are forwarded to the sink for further analysis. Sink node contains a data
base that stores the chemical signatures of the already known chemicals present in the
explosives. Sink node will compare the received chemical signature with one in the
data base and take appropriate decisions by considering all other measurements.
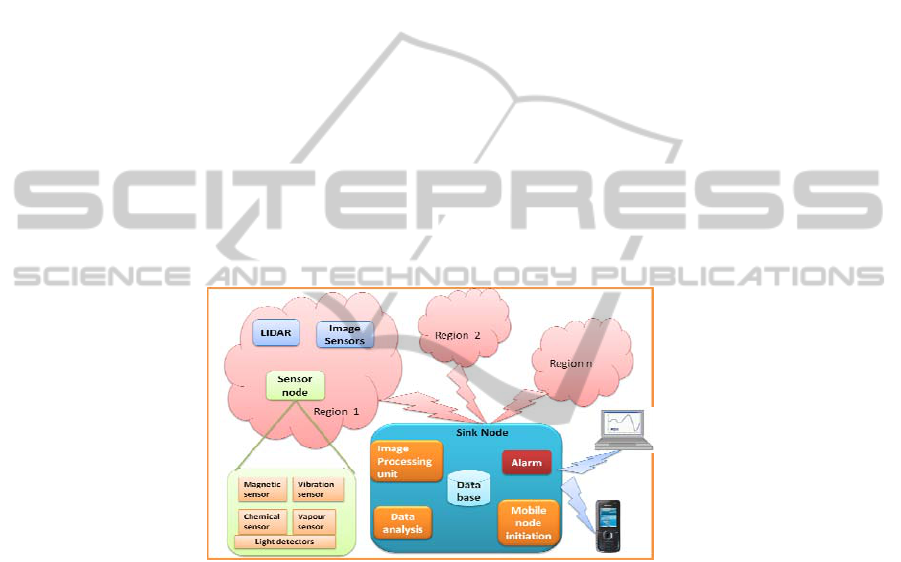
The system uses two thresholds to process strong and weak signals. A strong
signal is identified by a high threshold t
high
and to discard the weak signal the system
uses a low threshold t
low.
If the sensed data is greater than the high threshold t
high
, it
will give immediate indications to the security personnel’s. If the comparison result is
less than t
high
and greater than t
low
, it will initiate phase II operations for the
confirmation of presence or absence. If the calculated result is less than t
low
, the
system will ignore the data. .Figure.2 gives the design details of W-ReMADE.
Fig. 2. W-ReMADE system design.
Phase II
Operations in phase II will be initiated whenever the sink node receives some
suspicious data. Then sink node initiates a mobile node with more sensitivity for close
observation. A special track made of steel rope is provided in the roof for the
uninterrupted movement of mobile node. To deploy such a path is cheap in test area
like airports. This node will reach the suspected area and scan the area for explosives.
The sensed data is immediately sent to the sink for verification of suspicious data. If
the sink node confirms the presence of explosives, it will give indications to the
security personnel through e-mail or internet or sms services so that they can take
immediate actions. This mobile node can also be utilized, if any anonymous phone
call about bomb threats is received.
64
4 W-ReMADE Algorithm Design
4.1 Network Topology
For efficient routing of packets within the network, the entire area is divided into a
number of clusters. Based on the communication range, the sensing nodes will
create clusters. The proposed design uses a hierarchical architecture. In a cluster,
there are multiple sensors of same type. Even if the data collected from one sensor is
erroneous, the system can effectively calculate correct results by using data from
alternate sensor. W-ReMADE will correlate the data coming from the sensors in a
particular area, find the deviations of data and can ignore data accordingly. This
allows the system to reduce wrong data processing. Also if any one of the sensor is
not working properly, the remaining set of same type sensors can contribute data and
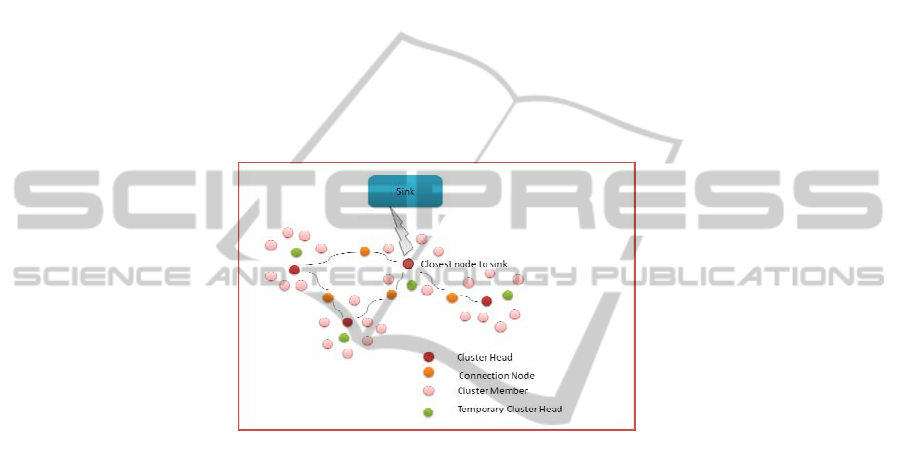
can manage sensor faults. The following figure 3 illustrates the network topology.
Fig. 3. Network Topology.
There are mainly four types of nodes in a cluster. These nodes are cluster member
node, cluster head, temporary cluster head and connection node. The low level nodes
which sense the data are called cluster members. Each cluster is associated with a
special node with more computational capacity called cluster head. The main
functions of these nodes are to aggregate the data coming from cluster members and
to forward to sink node. A small number of alternative cluster heads are provided to
the network which can be shared among clusters to handle cluster head failures if any.
Connection nodes in the network act as communication link between two clusters.
4.2 Algorithms
Cluster Generation Phase
This phase mainly focuses to generate clusters of sensor nodes for effective
communication. The algorithm will select one of the available special nodes as cluster
head for each region. Initially, in each cluster head, the administrator of the network
will load the number of hops from that cluster head to the sink node. This is for
computing the shortest route to the sink node from each cluster head. To set up a
65

cluster, the nodes in the network will exchange a set of messages. These messages are
invitation message, response message, confirmation message, negotiation message
and acknowledgement. Invitation message is a broadcast message used by the cluster
heads to invite other nodes in its communication range to create clusters. This
message contains the ID of the cluster head. Response message is send by the nodes
who receives invitation message. This is an indication that the node is reachable from
the cluster head and it is ready to join the cluster. The message includes the node ID,
number of invitations, and the IDs of inviting nodes and corresponding signal
strengths. Negotiation message is transferred between the cluster heads to
compromise the number of cluster members and link nodes in each cluster. This
maintains a minimum and maximum limit in the number of nodes in the cluster.
Confirmation message is send by the cluster heads to confirm the membership in the
cluster by specifying the ID of the cluster head. After receiving confirmation
message, the cluster members will send an acknowledgement to the cluster head.
In the cluster generation process, cluster heads will broadcast an invitation
message to all the neighboring nodes. The nodes receiving invitation will send a
response message to all the inviting nodes. If the signal strength of any of the
invitation message is less then it will ignore the invitation otherwise send a response.
The cluster head will store the details of response messages in a table. The nodes
receiving invitation from more than one cluster head are the candidate of a connection
node which is a bridge between the communications of two cluster heads. Using any
one of the connection nodes, the neighboring cluster heads will communicate with
each other to make an agreement between numbers of cluster members and
connection nodes. The network design supports only at most two connection nodes
between two clusters in order to avoid energy wastage of these nodes. Depending on
the total number of cluster members of neighboring cluster heads, the extra
connection nodes will be changed to cluster members of any one of the cluster head
and update the cluster table. The cluster heads will send a confirmation message to all
nodes in its cluster table. By receiving this confirmation message, the member nodes
will store the ID of cluster head and send an acknowledgement to the cluster head. If
the cluster head is not receiving the acknowledgement after the timeout period, it will
retransmit the confirmation message. All cluster heads in the network knows the
number of hops to the sink node from that node. These cluster heads have to forward
the aggregated data to the sink node. For fast and effective forwarding, the number of
hops travelled by the packet should be less. We used Dijkstra’s shortest path
algorithm [11] to find the shortest path from each cluster head to sink node. It uses
number of hops to the sink as metric of the algorithm. The shortest path information is
added to the routing table of each cluster head and connection node.
Communication Phase
In this phase, the actual communication between nodes takes place. The cluster
members will send the sensed the data periodically to the cluster head. The sampling
rate can be changed by the sink node in case of any suspect in that particular area.
Cluster heads aggregates the data coming from different sensors and forwards it to the
sink. The sink will receive the aggregated message from all cluster heads and analyze
the data. The messages exchanged in this phase are synchronization message, data
message containing sensed data from cluster members and aggregated data message
that is to be forwarded to the sink node.The cluster members will send the data
66

message to the cluster heads. Cluster heads will check the message type when it
receives a packet. If the message is a data message from one of its cluster member, it
will store the data for further processing, aggregate data, create a packet destined for
sink, find the shortest path node to sink, and forward the data. If the message type is
an aggregated message to the sink, the node will find next shortest path node to the
sink and forward the aggregated message. If it is a synchronization message, the node
will reset its clock and forward to neighboring cluster heads.
Data Aggregation Phase
All the cluster members will collect data periodically and send to the cluster head.
The main function of cluster head is to aggregate the data. There is multiple numbers
of varying types of sensors in a cluster. Based on the timestamp, the cluster members
will store the data from all type of sensors and create a vector. The number of such
vectors in cluster heads will be different based on the number of sensing nodes in a
cluster. It will compute the correlation between each vector using the following Karl
Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
n∑x
y
∑x∑
y
∑
∑
∑
∑
(1)
If r>=0.8 or r <=-0.8, then there is a strong correlation between the vectors. So it is
not required to send all the incoming data, only one vector is sufficient. This will
reduce the communication cost of the system. If the correlation coefficient is less than
0.5, it is required send the differing vectors. Cluster head will add a time stamp and
forward the aggregated vector to the sink by selecting the shortest route in the routing
table.
Data Analysis Phase
The chemical and magnetic signatures of already known explosives are stored in the
database of sink node. In the sink node, the received aggregated data is compared
with the signatures stored in the database. If the recieved data is less than the
threshold t
low,
, the system will ignore the data. If the incoming data is in between t
low
and t
high
, the sink node will initiate a mobile node for the confirmation of explosives in
the suspected area. If the data is greater than t
high
, then the system immediately give
indication to the concerned people.
Advanced Sensing Phase using Mobile Node
If the output of data analysis phase is in between t
low
and t
high,
we cannot surely say an
explosive content in the area and cannot disseminate an alarm. It may be an
erroneous/noisy data. In this situation, W-ReMADE uses an enhanced target tracking
phase to confirm the presence or absence of explosive and to avoid wrong alarms. The
sink node will localize the area using the node ID of incoming packets. The area
under monitoring is equipped with a steel rope on the roof. The sink node will initiate
a mobile which can traverse though this path and can reach the area under suspect.
This node is equipped with high sensitivity components which carry out the detection
process more close to the target. The mobile node will send the sensed data
immediately to the sink node for the confirmation of suspected target.
Localization of Suspected Area
In case of suspicious data, the sink node will initiate a mobile node for the confirma-
67

tion of suspected object. The sink node will look up the distance to the corresponding
cluster head from where the suspected data is obtained. It initiates the mobile node fed
with the location information. Also it sends a message to the cluster head to indicate
that, the sink node initiated a mobile node and it will reach the cluster head with in t
seconds. The cluster head knows the location of static cluster members. It checks the
previous packets and finds the coordinate position of the sensor nodes from which the
suspicious data was obtained. Then it uses triangulation technique to find the
approximate location of suspected target. After t seconds, the cluster head will
broadcast a message with the location information, which can be received by the
mobile node. By receiving this message, the mobile node is able to go more close to
the suspected object. It will sense the data forwards to the sink node and provide a
better tracking mechanism.
Alarm Dissemination Phase
If the presence of explosive material is confirmed by the sink node, then the system
will provide an early warning to the concerned persons. For the indication of
explosive material presence, it uses existing mobile network and internet. The system
will automatically give sms alerts and e-mail alerts to the important security officials.
The authorized persons can view all the sensed data from the sensor network in the
internet in real time. Depends on the variations in the sensed data, the officials can
take immediate actions. In the case of threat messages or calls, the administrator can
configure the system to change the sampling period and threshold limits so that the
system can provide improved results.
Time Synchronization
In a sensor network, there may be propagation delay of the packets due to some
environmental factors. The sensors have to coordinate their actions for the
aggregation of data. If there is no time synchronization, the aggregated data may be
an erroneous. Each sensor node is associated with a clock based on its oscillator
frequency. Due to atmospheric conditions such as temperature, pressure, there may be
slight difference in the oscillating frequency and in turn result in a drift from original
clock. But the network protocol requires a common clock to avoid erroneous data. In
W-ReMADE, The clock in all the nodes of the network is synchronized with respect
to the clock of sink node. Sink node uses a spanning tree algorithm to find connected
components of network graph. It will send a synchronization message with current
clock time to the cluster heads. To handle the difference in clock value due to the
delays in the network, we calculated an estimate of delay of packets. Here we
considered only the transmission delay and propagation delay. Also it is assumed that
the distance between two communicating nodes is a constant r. The propagation delay
between two communicating nodes depends on the distance between them and the
signal propagation speed. The propagation delay (prop_delay) is computed as the
ratio of distance between nodes to the speed of light. Also we calculated the
transmission delay, trans_delay as the ratio of number of bits to the transmission rate.
prop_delay = r / c. (2)
trans_delay = packet length / transmission rate. (3)
delta = prop_delay + trans_delay. (4)
68

The cluster heads knows the number of hops required to reach the sink node.
Whenever the cluster head receives such a synchronization message, it will multiply
the number of hops and the delay factor to calculate propagation delay. This
propagation delay will be added to the incoming clock data and the local time will be
updated. After the synchronization of cluster heads, the will create a synchronization
packet with updated data and broadcast to cluster members. They will add the delay
factor and update the clock time.
4.2.1 Selection of Frequency of Transmission
As the sensed data in W-ReMADE is more sensitive, it is required to prevent the
unauthorized capturing of data in flowing through the network. To provide security to
the data transmission, we are using frequency hopping [12]. The available bandwidth
is divided into a number of bands. The network operates between 2400MHz and
2483.5 MHz. It is divided into 12 nonoverlapping channels. The channel allocation
algorithm randomly selects a particular channel and used for transmission. The
receiver is also using the same algorithm and seed for the generation of frequency. As
the algorithm randomly selecting the channel, it is very difficult for the intruder to
find the sequence of frequencies used for transmission and thus provides security for
the transmission.
5 Implementation
To implement W-ReMADE, we used MicaZ motes and ZigBee technology. The
sensor nodes and gateway in the system are using CC2420 RF transceiver. Each
cluster member in the system can sense the data and communicate to higher level
nodes. Also they can receive synchronization messages and other control messages
from higher level nodes in the hierarchy. The transmission and reception of the
messages are through MicaZ mote embedded with ZigBee compatible RF transceiver
.It uses a communication frequency between 2400MHz and 2483.5 MHz. With the
help of MicaZ expansion connector, the system can connect to other sensors, data
acquisition boards and gateway. MIB600CA is used to connect the wireless network
to wired network for streaming the sensed data to the internet. TinyOS is the
operating system used for the development. The components and interfaces of
TinyOS are used to communicate messages in the network.
To evaluate the performance of the proposed system, we simulated the
functionality in National Instruments Lab View – Real Time software. For each type
of sensor, we plotted the received data. Due to atmospheric interference, there may be
noise in the collected data and it may cause wrong alarms. To reduce number of
wrong alarms, W-ReMADE uses a confirmation phase where a mobile node can
move closer to the suspected object and can sense data. So the data is more accurate
compared to the stationary sensor data. We assumed that the noise in the stationary
sensor data follows a Gaussian distribution. Due to error factors, the stationary sensor
data crosses above or below the predefined thresholds causing wrong alarms. As the
mobile sensor is getting more accurate data, the probability of wrong alarms are
reduced. The following graph in Figure 4 shows that the probability of wrong alarms
69
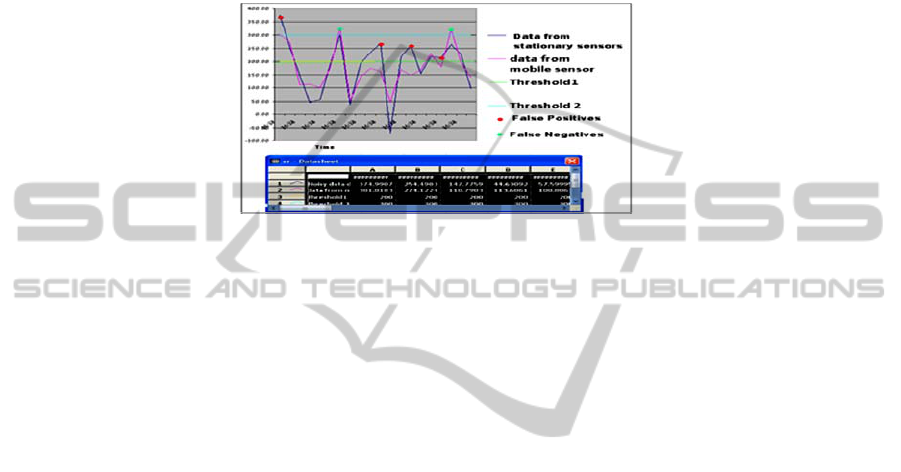
is significantly reduced when we use the confirmation phase. We created a test bed in
a closed air conditioned room. Sensors are placed on the roof and at the air exhausts.
The sensed data is forwarded to the sink node and can be viewed in the internet. We
gradually changed the metallic and chemical concentration in the room. Then the
network was able to give results which exceed the threshold value. A sensor node was
placed more close to the target. The data obtained from that sensor was more exact
compared to the other readings.
Fig. 4. Performance improvement using confirmation phase.
6 Advantages
The W-ReMADE system is applicable to any wide and highly populated areas. The
detection process involves continuous monitoring with minimal human involvement
and without affecting the routines of passengers. As the system uses a confirmation
phase and data from more than one mutually independent technique, the probability of
wrong alarms are significantly reduced. With the help of frequency hopping the
network provide security to the data available in the network. The security officials
need not visit the site for getting details; instead it is available in the network. W-
ReMADE provides facilities for authorized persons to view the sensed data through
the internet in real time.
7 Conclusions and Future Scope
W-ReMADE utilizes wireless sensor network technology to detect explosive
materials present in urban areas. This is a wide area, continuous, remote monitoring
system with minimal human involvement. The system can be deployed to any public
places such as railway stations, airports etc. for the safety of general public and
infrastructure. The accuracy and reliability of the system is maximized, and false
alarms are reduced, by the use of multiple sensors of varying types ensuring coverage
of the wide area. Enhanced target tracking is achieved by using a confirmation phase
with the help of a mobile node. If the system confirms the presence of explosives, the
concerned people are informed via the existing mobile network and internet. One of
the future developments of the system is in reducing the high degree of noise, in
outdoor environments, that can cause performance degradations.
70

References
1. Akyildiz I, Su W, Sankarasubramaniam Y, Cayirci E, A survey on sensor networks, IEEE
Communications Magazine, 43(5), 102–114, 2002.
2. Pottie G J, Kaiser W J. Embedding the Internet: Wireless integrated network sensors.
Communication of the ACM,,43(5), pp.51~58, 2000 DOI= http://www.ee.ucla.edu/~pottie/
papers/nae_01.pdf.
3. Gary LaFree and Laura Dugan “Introducing the Global Terrorism Database,” Political
Violence and Terrorism 19:181-204. 2007 DOI =http://www.ccjs.umd.edu/faculty/
userfiles/23/FTPV_A_224594.pdf.
4. National Research Council, Existing and Potential Standoff Explosives Detection
Techniques The National Academies Press, Washington, D.C., 2004.
5. Deyi Kong “MEMS Based Sensors for Explosive Detection” in Proc. 3rd IEEE Int. Conf.
On Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems January 6-9, 2008, Sanya, China.
6. Robert Furstenberg “Stand-off Detection of Trace Explosives by Infrared Photo-thermal
Spectroscopy” DOI =http://
ieeexplore.ieee.org/iel5/5159754/5168000/05168074.pdf
7. C. Baker, T. Lo, W. R. Tribe, B. E. Cole, M. R. Hogbin, and M. C. Kemp Detection of
Concealed Explosives at a Distance Using Terahertz Technology Vol. 95, 0018-
9219/_2007 IEEE No. 8, August 2007 Proceedings of the IEEE 1559-1565.
8. Bourzac, Katherine. “Tiny, Sensitive Magnetic-Field Detectors: Arrays of cheap magnetic
sensors could detect improvised explosive devices.” Technology Review, Massachusetts
Institute of Technology 16 November 2007.
9. Subpicotesla atomic magnetometry with a microfabricated vapour cell DOI =
http://tf.nist.gov/ timefreq /general/ pdf/2219.pdf.
10. “Hidden sensor network to detect explosives” DOI=http://www.theengineer.co.uk/news/
hidden-sensor-network-detects-explosives/1000515.article.
11. Thomas H.Coreman and Charles E. Leiserson , Z ( 2001) Introduction to Algorithms(2
nd
ed.) London: MIT Press and McGraw-Hill.
12. William stallings (1981). Data and computer Communications (2
nd
ed.), mexico: Prentice
Hall.
71
