
Afferent GPi and Efferent from RMTg to VTA of LHb for Reward
Omission
Ziqing Zu
Nanjing Foreign Language School International Centre, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210018, China
Keywords: Reward Omission, Globus Pallidus Internal Segment (GPi), Lateral Habenula (LHb), Glutamatergic Neurons,
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (Gabaergic) Neurons, Rostromedial Tegmental Nucleus (RMTg).
Abstract: Reward omission is an essential part in reinforcement learning that has not been fully appreciated, as most of
the studies have been focused on the positive reward prediction error (RPE). Therefore, this thesis investigates
into the globus pallidus internal segment (GPi), an important afferent of the lateral habenula (LHb), that is
responsible for reward omission coding. First, destroying the GPi enables us to find out whether it is the only
input for reward omission into the LHb, which is the main area for negative RPE. Then, it will be determined
whether Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAergic) neurons also involve in the omission signal transmission
besides glutamatergic neurons by optogenetically inhibiting GPi glutamatergic neurons. Furthermore, a
comparison between the efferent GABAergic neurons of the LHb in the rostromedial tegmental nucleus
(RMTg) and the ventral tegmental area (VTA) will be made.
1 INTRODUCTION
Numerous researches have already been done on the
investigation of understanding how brain neurons
code for RPE, which simply means the discrepancy
between expected and actual rewards signaled by the
dopamine (DA) neurons in the VTA (Schultz, Dayan,
Montague 1997). Also according to Schultz et al.
(Schultz, Dayan, Montague 1997, Schultz, Apicella,
Ljungberg 1993), when actual reward is greater than
expected, DA neurons will be activated (positive
RPE), while they will be depressed if reward is less
than the predicted reward (negative RPE). Despite the
fact that the entire neural circuit for RPE is still
unclear, there have been a myriad of researches into
the circuitry involved in positive RPE (Keiflin, Janak
2015), and even punishment prediction (Mattfeld,
Gluck, Stark 2011). However, as the other type of
negative prediction error besides punishment
prediction, the reward omission seems to be
neglected by many. Reward omission can be
understood as unexpected reduction in actual reward.
This is crucial for survival, since it also shows the
ability to update the reinforcement learning behavior
to adapt to changes in the environment (Bromberg-
Martin, Matsumoto, Hong, Hikosaka 2010).
Previous researches (Stamatakis, Van Swieten,
Basiri, Blair, Kantak, Stuber 2016, Lecca et al 2017,
Tooley et al 2018, Li, Pullmann, Jhou 2019) have
shown that ventral pallidum (VP), hypothalamus
(HT), and the GPi all project to the LHb, which is the
major region for the coding of reward omission
(Matsumoto, Hikosaka, 2007, Tian, Uchida 2015).
Furthermore, the VP (Tooley et al 2018) and the HT
(Stamatakis, Van Swieten, Basiri, Blair, Kantak,
Stuber 2016, Lecca et al 2017) are both proved to be
responsible for the punishment prediction, while the
GPi is not (Lazaridis et al 2019). However, in the
Lazaridis paper (Lazaridis et al 2019), the GPi, co-
releasing glutamatergic/GABAergic neurons, is said
not to encode negative value or develop a prediction
signal for any negative events. However, actually this
outcome is one-sided because he only mentioned the
aversion, leaving out omission entirely. As a result, it
is certain that the GPi codes for reward omission
(Hong, Hikosaka 2008), as many other research
articles have also come to the same positive
conclusion. What we do not know yet is whether the
GPi is the only input to the LHb for omission, or the
VP and the HT are also involved, apart from their
roles for punishment prediction.
Moreover, Shabel et al. (Shabel et al. 2012)
identified that both the excitatory glutamatergic
neurons and inhibitory GABAergic neurons from the
810
Zu, Z.
Afferent GPi and Efferent from RMTg to VTA of LHb for Reward Omission.
DOI: 10.5220/0011296800003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 810-816
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
GPi send projections to the LHb. Actually, in 2008,
neurons in the GPi had already been classified into
two types, the positive type and the negative type, by
Hong and Hikosaka (Hong, Hikosaka 2008). The
negative type, which will be activated when no
reward is presented, shows extremely similar firing
pattern to neurons in the LHb. As a result, presumably
it is the GPi glutamatergic neurons, that mainly, if not
entirely because of the coexisting GABAergic
neurons, send signals to its downstream LHb when
reward is omitted.
Apart from the afferent of the LHb, there have
been large amount of studies about its efferent. It has
been proved the RMTg, the immediate downstream
of the LHb, responsible for negative RPE (Jhou et al
2009), is mediated by the LHb glutamate
neurotransmitters during negative RPE (Graziane,
Neumann, Dong 2018). After that, the VTA-
projecting GABAergic neurons from the RMTg will
send inhibitory inputs (Eshe et al 2015) directly to
depress the DA neurons (Tian, Uchida 2015). While
other pathways from the LHb to the VTA DA neurons
including dorsal raphe nucleus etc. have also been
mentioned in Tian and Uchida paper (Tian, Uchida
2015), my focus is the GABAergic projection from
the RMTg to the VTA, making a comparison with the
GABAergic neurons in the VTA. Because the RMTg
is a small area close to the VTA, not many people
regard its GABAergic neurons as a distinct region
from the VTA GABAergic neurons. Nevertheless,
one of the differences between their functions can be
revealed by the coding of reward omission. As
mentioned above, the RMTg will be activated during
negative RPE (Graziane, Neumann, Dong 2018),
while the GABAergic neurons in the VTA show no
significant modulation by reward omission (Cohen et
al 2012). Therefore, understanding the circuitry will
give a brighter view of how RPE is regulated in the
main region VTA and others, hence increasing our
understanding about the complicated brain works, as
well as learning behavior.
The thesis will look deeply into the neural circuit
of omission, mainly the GPi input to the LHb to
determine whether it is the only input to the LHb for
reward omission, as well as what kind of
neurotransmitters are involved in the signaling
process. Additionally, the efferent pathway of the
LHb from the RMTg to the VTA during reward
omission will also be examined to provide a
comparison between the GABAergic neurons in the
RMTg and the VTA.
2 RESULTS
2.1 Positive Results
2.1.1 GPi is the Only Input into the LHb
Coding for Reward Omission
To determine the significance of GPi in reward
omission response, the GPi will be destroyed by
passing electricity through. Then, mice of the lesion
and control group that have already learnt the
association between the odour cue and water reward
will again be presented with the same odour cue, but
without the following water as reward (Figure 1A).
During this reward omission period, extracellular
recording of firing patterns will be taken at the LHb
and will be sorted afterwards (Figure 1B).
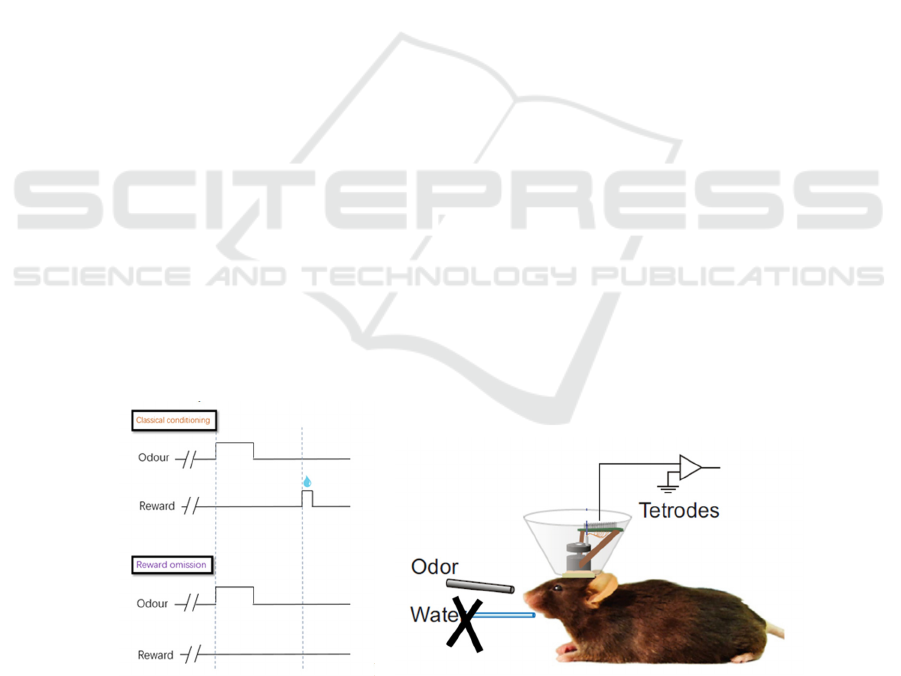
A B
Figure 1: Basic experimental procedure for the GPi lesion experiment. (A) Mice will first be trained to associate the odour
cue with the following water reward through a classical conditioning task. Then, during the experimental period, only the
odour cue will be delivered, while the actual result will be omitted. (B) Extracellular recording of the LHb will be made
during reward omission.
Afferent GPi and Efferent from RMTg to VTA of LHb for Reward Omission
811
As shown in Figure 2, the population spike of
neurons in the LHb of the control and lesion group of
mice responds differently to reward omission.
Normally, the excitatory glutamatergic neurons will
transmit the excitation elicited by the omitted reward
to the LHb, where the neurons will be also be
activated (Hong, Hikosaka 2013), as shown by the
control group (Figure 2A). However, on the contrary,
neurons in the LHb show no activity during reward
omission in the lesion group (Figure 2B), indicating
that they do not receive any signals for coding reward
omission.
The entirely disappeared response in the LHb
reveals that destroying the GPi has a complete effect
on reward omission coding, i.e. none of the other
neurons that project into the LHb send omission
signals. Hence, it can be concluded that the GPi is the
only input into the LHb coding for reward omission.
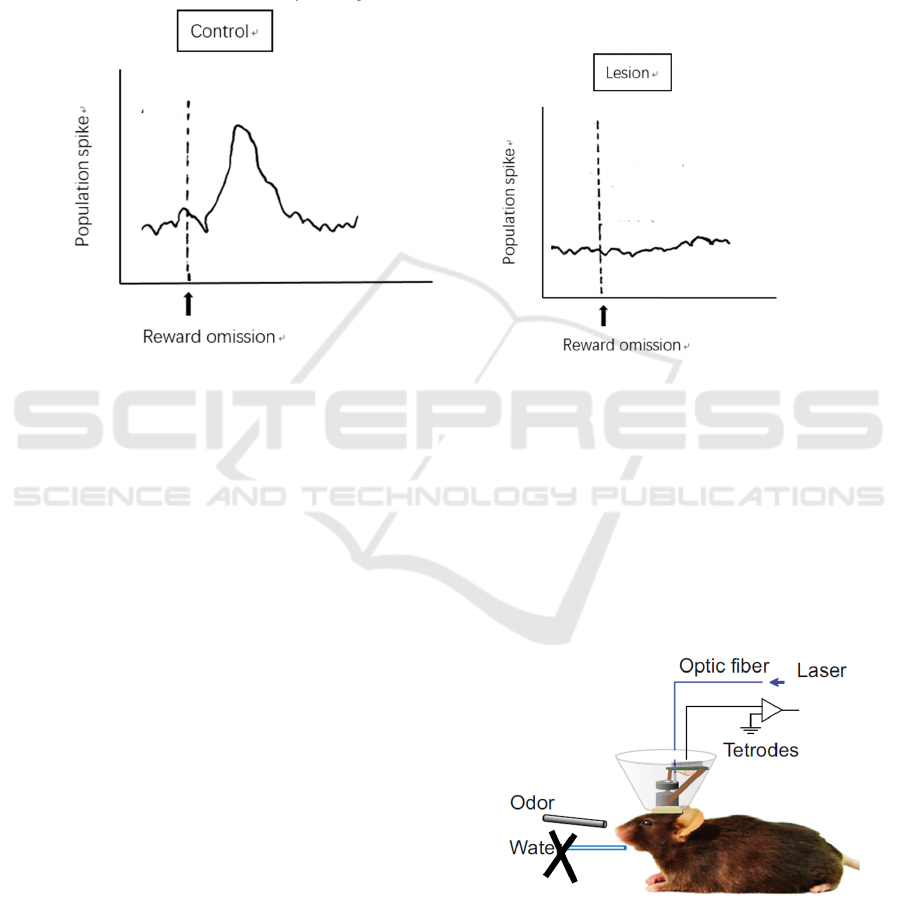
AB
Figure 2: Expected result from the control group and the GPi lesion group of reward omission. (A) Unaffected population
spikes at the LHb during reward omission is recorded. (B) No firing of excitation is detected when no reward is presented to
the group of mice with lesioned GPi.
This result is anticipated according to the major
role of the GPi for reward omission (Matsumoto,
Hikosaka, 2007, Tian, Uchida 2015), and of the VP
and the HT for punishment prediction (Stamatakis,
Van Swieten, Basiri, Blair, Kantak, Stuber 2016,
Lecca et al 2017, Tooley et al 2018), which are
distinct and different. Therefore, it is not expected
that one brain region is responsible for more than one
coding process to ensure effectiveness and accuracy.
2.1.2 Neuron-type Determination in the GPi
for Reward Omission Coding
As mentioned above, the excitatory glutamatergic
neurons are estimated to be the only neuronal type
responsible for reward omission (Hong, Hikosaka
2008). To verify the correctness of this hypothesis,
we would like to let only the GABAergic neurons in
the GPi work when reward is omitted, while
inhibiting the glutamatergic ones. Then whether
neural activities will be detected can confirm whether
the GABAergic neurons are also involved in the
reward omission coding.
In this neuron-type determination experiment,
virus and the Cre-loxP system will be included for the
inhibition of neurons. Halorhodopsin (HR), a light-
gated anion channel, will specifically be expressed in
glutamatergic neurons (see Method). Then the reward
omission task (Figure 1A) will be performed again
after inhibiting the glutamatergic neurons in the GPi
via optogenetics, and neural activities at the LHb will
be recorded during omission (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Laser shone through the optic fibre for
optogenetically inhibit the GPi glutamatergic neurons, and
tetrodes for detecting neural activity at the LHb.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
812
Only Glutamatergic Neurons in the Gpi Respond
to Reward Omission. If no neural activity is detected
at the LHb (Figure 4A), then it is clear that the
GABAergic neurons do not respond to reward
omission signals. This will lead to further
consideration of what is the purpose of the GPi
GABAergic neurons. It may suggest another circuit
including various downstream of the GPi, which
certainly needs plenty of researches into this field,
because it is unlikely that one distinctive type of
neuron is present in brain without any actual purpose.
Both Glutamatergic Neurons and Gabaergic
Neurons in the Gpi Respond to Reward Omission.
The other possible outcome is that depression is
recorded at the LHb because of the only activation of
GABAergic neurons (Figure 4B). This indicates that
the GABAergic neurons will also respond to reward
omission. Therefore, the interpretation of this
phenomenon may be the counterbalance of the co-
releasing neurotransmitters to prevent the neurons
being too activated.
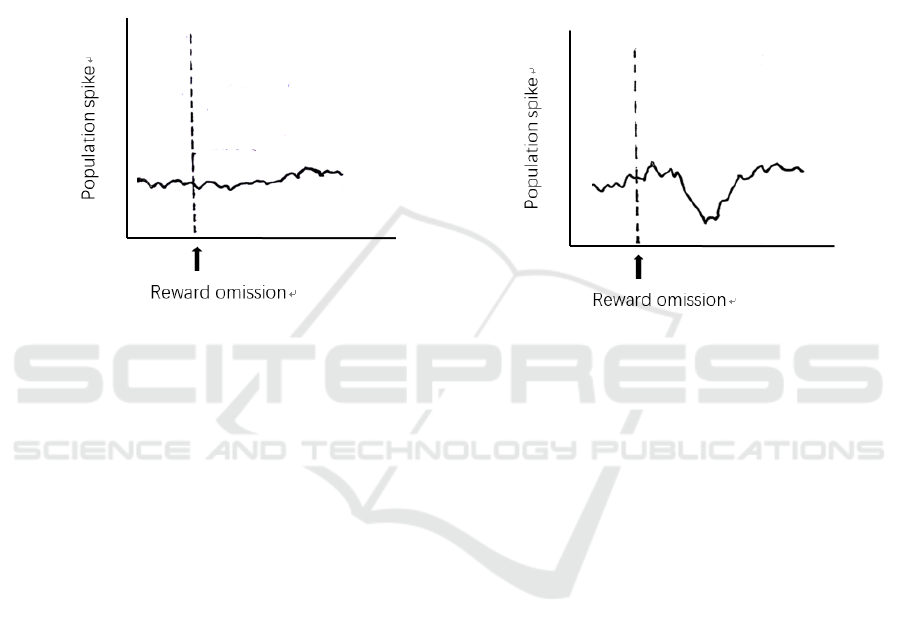
A B
Figure 4: Neural activities detected at the LHb. (A) Only glutamatergic neurons code for reward omission in the GPi, deduced
by undetected neural activity induced by GABAergic neurons. (B) Both glutamatergic neurons and GABAergic neurons code
for reward omission in the GPi, deduced by a depression response of GABAergic neurons when reward is omitted.
2.2 Negative Results
2.2.1 GPi is Not the Only Input into the
LHb Coding for Reward Omission
Using the same method described, the result may also
be that still there are action potentials at the LHb,
which means the GPi is not the only upstream of the
LHb responsible for reward omission, and other
regions like the VP and the HT may also play a
nonnegligible part. Hence researches into the VP and
the HT regarding reward omission require to be done.
However, this outcome means a limitation for the
experiment that determines the neuron types in the
GPi. If it is true that other regions are also involved
in reward omission response, this means that even
inhibiting glutamatergic neurons in the GPi will not
get the expected recording, since other regions will
also be activated during reward omission. Therefore,
the neural activities in the LHb that are singly induced
by the GABAergic neurons in the GPi cannot be
detected, because of the interference from neurons of
other brain regions. It is also not practical to destroy
both the VP and the HT, because it almost means
destroying the entire system, which may lead to the
dysfunction of other brain works, such as learning
behavior and memory.
2.3 Difference in Functions of the
Gabaergic Neurons in the RMTg
and the VTA Regarding Reward
Omission
One aspect to distinguish the RMTg GABAergic
neurons from the VTA GABAergic neurons is their
different responses to reward omission signals. To test
excitations induced by omission signals from the LHb,
extracellular recording at the RMTg is done during
this period. As for detecting neurons in the VTA,
H129-ΔTK-tdT will be used to anterogradely label the
VTA neurons from the RMTg, and the DA neurons in
the VTA will be fluorescently labeled by AAV
carrying Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) (see
Method).
By comparing the overlapping of the tdTomato-
labeled neurons and the GFP-labeled neurons, it is
expected that they are exactly the same, according the
Cohen et al. (Cohen et al 2012) that only DA neurons
Afferent GPi and Efferent from RMTg to VTA of LHb for Reward Omission
813

in the VTA respond to actual reward omission. The
consistency shows that no other neurotransmitter apart
from DA is responsible for reward omission in the
VTA. In the meantime, excitation of GABAergic
neurons in the RMTg should be recorded (Graziane,
Neumann, Dong 2018). Therefore, one of the
differences between the RMTg GABAergic neurons
and the VTA GABAergic neurons is that the former
codes for reward omission while the latter does not.
Hence it will be incorrect if one confuses the two
together.
However, if the labeling does not overlap with
each other entirely, one proper interpretation may be
that the VTA-projecting GABAergic neurons in the
RMTg are also involved in other brain activities like
punishment prediction. As a result, a more
considerate design of experiment to test this
hypothesis should be conducted in the future.
3 DISCUSSION
Because of the lack of investigation of reward
omission from previous researches, the thesis
explained some designed experiments regarding GPi
in reward omission coding and explained the
functional difference between GABAergic neurons in
the RMTg and the VTA.
The ‘blocking’ experiment will be used, i.e.
destroying the GPi to see whether there are still
responses in the LHb. If yes, then the GPi is not the
only input into the LHb coding for reward omission.
Hence further researches should look into the VP and
the HT to test their functions and responses in reward
omission, but not only limited to the punishment
related signals (Stamatakis, Van Swieten, Basiri,
Blair, Kantak, Stuber 2016, Lecca et al 2017, Tooley
et al 2018). Brain regions coding for reward omission
should not be neglected, because this is an
irreplaceable part of reinforcement learning.
If no, it can be concluded that the GPi fully
influences the activity of the LHb neurons in reward
omission. Only if the GPi has been proved to be the
only input into the LHb activated by reward omission
signals, then the optogenetics can be used to inhibit
the GPi glutamatergic neurons and record firing
patterns at the LHb to see whether GABAergic
neurons in the GPi also code for omission (Hong,
Hikosaka 2008, Hong, Hikosaka 2013). Some
reconsideration about how to determine the involved
neurons if the GPi is not the only source should be put
into the limitation. In addition, the results will elicit
more questions, for example, the role of GABAergic
neurons. Do they really help code for omission just to
ensure the neurons do not get too activated? Since
they cannot exist without any purpose, is it possible
that they lead to a whole new pathway into the VTA?
These are presently only guesses without evidence.
As for the efferent of the LHb, although the
RMTg is closely linked to the VTA, the function of
its GABAergic neurons should not be confused with
those in the VTA. One of the differences elaborated
here is the difference in coding for reward omission.
Certainly more considerate experiments should be
done to reveal their functional differences, since this
interpretation only partially considered the omission
response based on previous researches.
Large areas in reinforcement learning, including
reward omission coding, remains unexplored.
Therefore, hypotheses are expected to be made and
tested, and hopefully this thesis will be of some help.
4 METHODS
4.1 Animal
20 adult male mice will be used for the GPi lesion
experiment, 10 of which are used as lesion group, and
the rest are used as control group, containing 5 of
sham-lesion and 5 of no operation. The mice belong
to the sham-lesion and no operation group show no
difference in responding behavior at postsurgical
tests, so they will be regarded as the same in the
experiments. Mice in the lesion group and sham-
lesion group will be verified by histology.
For the neurotransmitter-determination
experiment, 10 adult male transgenic mice with
SLC17A6-Cre will be used.
For the GABAergic-neuron comparison
experiment, 10 adult male transgenic mice with
DAT-Cre will be used.
All animals were singly housed on a 12-hour
dark/12-hour light cycle.
4.2 Surgery
Electrolytic lesions will be made using a stainless-
steel electrode. The head plate that will be attached to
the skull are going to be used as the anode. After 10
days of training on the conditioned task, the 20 normal
mice will be chosen randomly to become either lesion
group or control group. Electricity will be delivered to
destroy the GPi (from bregma: -0.7mm posterior,
1.8mm lateral, 3.95 mm depth) in the lesion group,
while the sham-surgery group will have no current
delivered. During surgery, mice will be anesthetized
and placed in a stereotaxic frame. For the best result
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
814

of the surgery, monitoring the mice’s breathing rate
and maintaining the temperature of the mice are
necessary. Additionally, after recovery, all the mice
that go through the surgery will be presented with the
odour cue that they learnt in the association task
before. If the licking frequencies of mice remain high,
then they are ready for the experiment since their
memory has been tested unharmed by the surgery.
As for transgenic SLC17A6-Cre mice group, the
optic fibre will be implanted, together with the
electrode for the mimic stimulations, into the GPi, so
that light can be shone through to activate the HR.
4.3 Viral Injection
During the same surgery, adeno-associated virus
(AAV), carrying the transcription stop gene flanked
by double loxP sites with the same orientation and a
following HR, will be injected into the GPi region of
the transgenic SLC17A6-Cre mice.
The same method should be used to inject AAV,
carrying the transcription stop gene flanked by double
loxP sites with the same orientation and a following
GFP, into the VTA (from bregma, AP: −2.9 to −3.1
mm; ML: +0.35 mm; DV: −4.65 mm) of the
transgenic DAT-Cre mice.
Meanwhile, H129-ΔTK-tdT will be injected into
the RMTg (coordinate relative to bregma: AP −6.8
mm; ML ± 0.3 mm; DV −8.4 mm) for anterograde
monosynaptic tracing (Zeng et al 2017).
The expression of AAV in specific neurons is
highly selective and efficient, and both the HR and
the GFP expression is uniform across specifically
targeted neurons. The amount of virus injected should
be accurately controlled, so that the virus cannot
diffuse into nearby brain regions.
4.4 Behavior Task
Before the surgery, all mice will be trained in a
classical conditioning task. The task will be a head-
fixation one, so the animals will be head-restrained
using a head plate and habituated for 15 minutes for
1-2 days before training. Each behavioral trial begins
with an odour cue (CS) for 1 second, followed by a
1-second delay and a drop of water as the reward
(US). After training, mice will perform the licking
behavior during the delay between the cue and
reward, indicating that they have learned the
association between the odour and water. When the
lick rates constantly reaches a standard frequency, the
surgeries can be conducted.
After the surgery and recovery (about 10 days),
mice will be water-deprived for the experiments. The
body weight was maintained above 85% of their full
body weight. Licks were detected by breaks of an
infrared beam placed in front of the water tube.
4.5 Electrophysiology
After 10 days of resting, the recording tetrode will be
implanted to the normal and the transgenic
SLC17A6-Cre mice through the craniotomy above
the LHb to a depth of 1.8mm below bregma. For the
transgenic DAT-Cre mice, the recording tetrode
should be implanted to the RMTg (coordinate the
same as above). All electrode wires are connected to
an electrode interface board for relaying
electrophysiological signals to the data system. For
the extracellular recording, spikes will be sorted via
specific softwares for analysis.
4.6 Histology
After the experiments, 2 mice from the lesion group
and 2 from the sham-surgery group will be sacrificed.
Their brains will be examined for the extent of lesion
by histology. Basically, coronal brain slices will be
made, and the area influenced will be recorded.
5 CONCLUSION
By observing the afferent and efferent circuitry of the
LHb, we hope to gain a better understanding about
the mechanism coding for reward omission. It is
identified whether the GPi is the only input coding for
reward omission, and whether its GABAergic
neurons, apart from the glutamatergic neurons, are
also involved in omission signal transmission.
Additionally, to help distinguish the difference
between the GABAergic neurons in the RMTg and
the VTA, their functional difference regarding reward
omission response was presented.
However, it is certain that more considerate and
further researches should be done to investigate into
the field of RPE, including reward omission. As there
are still many unidentified parts and new questions
elicited by the experiments in this thesis, which were
mentioned above, improvements and more profound
considerations are expected to be made.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I thank professor Kunes, and teaching assistance
Wang and Zhang for the helpful discussion they
provide for completion of this thesis.
Afferent GPi and Efferent from RMTg to VTA of LHb for Reward Omission
815

REFERENCES
Bromberg-Martin, E. S., Matsumoto, M., Hong, S., &
Hikosaka, O. (2010). A pallidus-habenula-dopamine
pathway signals inferred stimulus values. Journal of
neurophysiology, 104(2), 1068–1076.
https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00158.2010
Cohen, J. Y., Haesler, S., Vong, L., Lowell, B. B., &
Uchida, N. (2012). Neuron-type-specific signals for
reward and punishment in the ventral tegmental area.
Nature, 482(7383), 85–88. https://doi.org/10.1038/
nature10754
Eshel, N., Bukwich, M., Rao, V., Hemmelder, V., Tian, J.,
& Uchida, N. (2015). Arithmetic and local circuitry
underlying dopamine prediction errors. Nature,
525(7568), 243–246. https://doi.org/10.1038/
nature14855
Graziane, N. M., Neumann, P. A., & Dong, Y. (2018). A
Focus on Reward Prediction and the Lateral Habenula:
Functional Alterations and the Behavioral Outcomes
Induced by Drugs of Abuse. Frontiers in synaptic
neuroscience, 10, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/
fnsyn.2018.00012
Hong, S., & Hikosaka, O. (2008). The globus pallidus
sends reward-related signals to the lateral habenula.
Neuron, 60(4), 720–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.neuron.2008.09.035
Hong, S., & Hikosaka, O. (2013). Diverse sources of
reward value signals in the basal ganglia nuclei
transmitted to the lateral habenula in the monkey.
Frontiers in human neuroscience, 7, 778.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00778
Jhou, T. C., Fields, H. L., Baxter, M. G., Saper, C. B., &
Holland, P. C. (2009). The rostromedial tegmental
nucleus (RMTg), a GABAergic afferent to midbrain
dopamine neurons, encodes aversive stimuli and
inhibits motor responses. Neuron, 61(5), 786–800.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.02.001
Keiflin, R., & Janak, P. H. (2015). Dopamine Prediction
Errors in Reward Learning and Addiction: From
Theory to Neural Circuitry. Neuron, 88(2), 247–263.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.08.037
Lazaridis, I., Tzortzi, O., Weglage, M., Märtin, A., Xuan,
Y., Parent, M., Johansson, Y., Fuzik, J., Fürth, D.,
Fenno, L. E., Ramakrishnan, C., Silberberg, G.,
Deisseroth, K., Carlén, M., & Meletis, K. (2019). A
hypothalamus-habenula circuit controls aversion.
Molecular psychiatry, 24(9), 1351–1368.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-019-0369-5
Lecca, S., Meye, F. J., Trusel, M., Tchenio, A., Harris, J.,
Schwarz, M. K., Burdakov, D., Georges, F., &
Mameli, M. (2017). Aversive stimuli drive
hypothalamus-to-habenula excitation to promote
escape behavior. eLife, 6, e30697.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30697
Li, H., Pullmann, D., & Jhou, T. C. (2019). Valence-
encoding in the lateral habenula arises from the
entopeduncular region. eLife, 8, e41223.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.41223
Matsumoto, M., & Hikosaka, O. (2007). Lateral habenula
as a source of negative reward signals in dopamine
neurons. Nature, 447(7148), 1111–1115.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05860
Mattfeld, A. T., Gluck, M. A., & Stark, C. E. (2011).
Functional specialization within the striatum along
both the dorsal/ventral and anterior/posterior axes
during associative learning via reward and
punishment. Learning & memory (Cold Spring
Harbor, N.Y.), 18(11), 703–711.
https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.022889.111
Schultz, W., Apicella, P., & Ljungberg, T. (1993).
Responses of monkey dopamine neurons to reward and
conditioned stimuli during successive steps of learning
a delayed response task. The Journal of neuroscience:
the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience,
13(3), 900–913.
https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-
00900.1993
Schultz, W., Dayan, P., & Montague, P. R. (1997). A
neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science
(New York, N.Y.), 275(5306), 1593–1599.
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.275.5306.1593
Shabel, S. J., Proulx, C. D., Trias, A., Murphy, R. T., &
Malinow, R. (2012). Input to the lateral habenula from
the basal ganglia is excitatory, aversive, and
suppressed by serotonin. Neuron, 74(3), 475–481.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.02.037
Stamatakis, A. M., Van Swieten, M., Basiri, M. L., Blair,
G. A., Kantak, P., & Stuber, G. D. (2016). Lateral
Hypothalamic Area Glutamatergic Neurons and Their
Projections to the Lateral Habenula Regulate Feeding
and Reward. The Journal of neuroscience: the official
journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 36(2), 302–
311. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1202-
15.2016
Tian, J., & Uchida, N. (2015). Habenula Lesions Reveal
that Multiple Mechanisms Underlie Dopamine
Prediction Errors. Neuron, 87(6), 1304–1316.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.08.028
Tooley, J., Marconi, L., Alipio, J. B., Matikainen-Ankney,
B., Georgiou, P., Kravitz, A. V., & Creed, M. C.
(2018). Glutamatergic Ventral Pallidal Neurons
Modulate Activity of the Habenula-Tegmental
Circuitry and Constrain Reward Seeking. Biological
psychiatry, 83(12), 1012–1023. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.01.003
Zeng, W. B., Jiang, H. F., Gang, Y. D., Song, Y. G., Shen,
Z. Z., Yang, H., Dong, X., Tian, Y. L., Ni, R. J., Liu,
Y., Tang, N., Li, X., Jiang, X., Gao, D., Androulakis,
M., He, X. B., Xia, H. M., Ming, Y. Z., Lu, Y., Zhou,
J. N., … Luo, M. H. (2017). Anterograde
monosynaptic transneuronal tracers derived from
herpes simplex virus 1 strain H129. Molecular
neurodegeneration, 12(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.1186/
s13024-017-0179-7
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
816
