
The Effects of Chinese Medicine Lianhua Qingwen on Inhibiting the
Replication of Covid-19 Virus
Hongzhu Ji
Fordham University FCLC, New York, U.S.A.
Keywords: Chinese Medicine, Lianhua Qingwen, Covid-19, Virus Replication.
Abstract: Lianhua Qingwen, a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine, has been used to treat fever and respiratory
infections for many years including SARS. Recent studies have shown that it can also be used as a COVID-
19 treatment. The goal of this work is to test if Lianhua Qingwen fights against coronavirus by reducing virus
replication? The antiviral activity of Lianhua Qingwen against SARS-CoV-2 was assessed in infected cells
from patients using CPE assay and plaque reduction assay. There are six possible results: they are based on if
Lianhua Qingwen shows positive, no, or negative inhibition on the CPE inhibition assay and weather it gives
us an inhibitory effect on the formation of plaque of the virus or not, and we will say Lianhua Qingwen
significantly inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication in cells which partially supports our hypothesis, or it partly
supports our hypothesis and these results wouldn't give a clear answer to our research question, or it
contradicts our hypothesis. The result of our study will provide important information for how Lianhua
Qingwen helps to treat COVID-19, and it will help us with controlling the COVID-19 pandemic. Future
studies should focus on more potential effects of Lianhua Qingwen and vivo experiment is needed.
1 INTRODUCTION
COVID-19 is a highly contagious respiratory
infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory
syndrome coronavirus‐2 (SARS‐CoV‐2)(Xia et
al. 2020). It's an animal transmission disease that is
likely originated from bats and spread dramatically in
humans, and now it has widely spread around the
world. By now there are more than 115 million cases
and 2.55 million deaths. This COVID-19 pandemic
not only severely damaged people's life and health,
but also harmed social, economic, and political. The
symptoms of it are fever, dyspnea, nasal congestion,
sore throat, asthenia, dry cough, multiple organ
dysfunction, and death. China has successfully
controlled the pandemic with its strict policy and
traditional Chinese medicine including Lianhua
Qingwen.
Additionally, by analyzing COVID-19 infected
patients’ clinical records from Wuhan Ninth Hospital
and CR & WISCO General Hospital, researchers
found the Lianhua Qingwen combination could allay
fundamental symptoms significantly and shorten the
progress and development of it (Li et al. 2020).
Lianhua Qingwen, the classic traditional Chinese
Medicine, is still commonly used today as a treatment
for inflammatory fever and respiratory infectious
diseases. It was used to fight against SARS in China
from 2002 to 2003, and it was included in the
Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Novel
Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Pneumonia (On Trials, the
Fourth/Fifth/ Sixth/Seventh Edition) issued by the
Chinese government. Lianhua Qingwen consists a
total of 13 different herbs: Lian Qiao, 255 g; Ma
Huang, 85 g; Jin Yin Hua, 255 g; Ban Lan Gen, 255
g; Mianma Guanzhong, 255 g; Bo He, 7.5 g; Shi Gao,
255 g; Guang Huo Xiang, 85 g; Hong Jing Tian, 85
g; Yu Xing Cao, 255 g; Da Huang, 51 g; Ku Xing Ren,
85 g; and Gan Cao, 85 g (Hu 2020). Previous studies
had shown using conventional drugs with the addition
of Lianhua Qingwen is a treatment with bright
potential for both pneumonia and the COVID-19
virus, and by using Lianhua Qingwen the healing
period of COVID-19 is shortened and several
symptoms like fever, cough, fatigue, sputum, muscle
aches, difficulty breathing, chest tightness and
pulmonary imaging can be improved (Hu et al. 2020).
These studies have shown that Lianhua Qingwen
relieved symptoms of the COVID-19 remarkably, but
research about the fundamental mechanism is
elusive.
284
Ji, H.
The Effects of Chinese Medicine Lianhua Qingwen on Inhibiting the Replication of Covid-19 Virus.
DOI: 10.5220/0011292900003438
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare (ICHIH 2022), pages 284-288
ISBN: 978-989-758-596-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Therefore, my research question is: Is the use of
Lianhua Qingwen block the replication of the
COVID-19 virus? And my hypothesis is I predict that
Chinese Medicine Lianhua Qingwen helps to block
replication of COVID-19. I will treat lung cells from
COVID infected human patients with an increasing
amount of Lianhua Qingwen (0mg/mL which is the
buffer solution, 0.1 mg/mL, 0.3 mg/mL, 0.5 mg/mL,
0.7 mg/mL, and 1 mg/mL) for the various durations
(12h, one day, three days, and seven days) and
measure it by CPE inhibition assay and plaque assay
with 10 replicates.
2 METHOD
2.1 Materials
This experiment will use COVID-19 infected cells
(experiment cells) from patients, and the growth of
cells was supported at 37 °C by Dulbecco’s Modified
Eagle’s medium (DMEM) along with fetal bovine
serum at the concentration of 10 %. The infection
experiments were conducted in a biosafety level-3
laboratory for safety concerns. Lianhua Qingwen
capsules were obtained and the black powder of it
was removed from the capsules. The black powders
were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide first to 200
mg/mL. Next, at room temperature mix the solution
by shake or stir it for 30 minutes, and prepare the
stock solution by diluting the Lianhua Qingwen
solution with serum-free DMEM to the concentration
of 0.1 mg/mL, 0.3 mg/mL, 0.5 mg/mL, 0.7 mg/mL
and 1 mg/mL, and at the temperature of −20 °C
reserve it. Additionally, preparing Remdesivir
solution with a similar method by dissolved in
dimethyl sulfoxide and mix to the concentration of
100 mM and stored at −20 °C with the Lianhua
Qingwen solution, and the dilution buffer that used in
later experiments is prepared by DMEM with 2%
fetal bovine serum. Materials like 96-well plates,
0.6 % agar, timer, thermometer, and microscope are
also needed in the following experiment.
2.2 Cytopathic Effect (CPE) Inhibition
Assay
The cytopathic effect is observable abnormalities
such as structural changes in host cells that are caused
by the viral invasion, and different viruses infect
different types of cells will cause different cytopathic
effects. CPEs are important aspects of a viral
infection in diagnostics. The CPE assay is used to test
if a compound exhibits any antiviral efficacy or not.
CPE assay is a cost-effective and time-efficient assay
that we used to evaluate test articles' ability to inhibit
CPE. Many combinations of cells and viruses can be
used to measure interferon activity via CPE assay.
And by using the dose-response assay we are able to
tell the selected antiviral efficacy range (Britannica
2019).Put experiment cells in monolayers inside
separate 96-well plates. To explore the effectiveness
against experiment virus of Lianhua Qingwen, in the
experiment group, the infected cells were incubated
with Lianhua Qingwen solution at various
concentrations for different durations (12h, one day,
three days, and seven days). Then, the positive
control group was developed at the different
concentrations of Remdesivir solution mentioned
before. As for the negative control group, grow the
experiment cells with indicated concentrations of
solely buffer solution (which contains 0 mg/mL of
Lianhua Qingwen). After various times of incubation
in these different solutions, the infected experiment
cells will show full CPE under the microscope
(100%). Next, the CPE at different percentages in all
three groups with different solutions treated cells
were recorded. Also, 10 replicates will be done for
this experiment, and by using the Reed-Muench
method we will be able to calculate IC50 which is the
half virus-induced CPE of inhibition concentration
for all the experiments and the calculated IC50 will
be compared later (Li et al. 2020).
2.3 Plaque Reduction Assay
Plaque assay is a way of measuring virus quantity that
is used to test the concentration of virus’s dose of
infection, and it specifies the quantity of appeared
units of plaque in the test sample of viruses. A
monolayer of infected cells at different
concentrations and covered with a semi-solid
medium (we will use agar in this experiment), to
forestall the infection of virus from spreading
randomly. When a certain virus passes infection to a
cell monolayer the infected cell area will create a
plaque. The culture will then be stained with a dye,
which stains only viable cells. We will use 1% crystal
violet in this experiment. As a result, the plaque (the
dead cells) will appear unstained against the colored
background for researchers to count (Kaufmann,
Kabelitz 2002). The SARS-CoV-2 infected cells were
put in monolayers and were put in 96-well plates
separately. And for all three groups, the plates were
all covered with 0.6 % agar, 2% fetal bovine serum.
Next, for each of the individual groups, the plate was
covered with the different concentrations of either
The Effects of Chinese Medicine Lianhua Qingwen on Inhibiting the Replication of Covid-19 Virus
285

Lianhua Qingwen (0.1 mg/mL, 0.3 mg/mL, 0.5
mg/mL, 0.7 mg/mL, and 1 mg/mL), Remdesivir, or
buffer (0.6 % agar, 2% fetal bovine serum together
with either one of these three are all considered as
agar overlays). Then incubated all plates with 5%
CO2 at 37 °C for different durations (12h, one day,
three days, and seven days). Following, removed the
agar overlays for each plate. And, fixed the cell
monolayer with 10 % formalin, stained with 1%
crystal violet. This experiment will be done with 10
replicates. Lastly, the plaques for all groups were
counted carefully and photographed (Li et al. 2020).
2.4 Statistical Analysis
The statistical significance of all numerical data
gathered through the Reed-Muench method will be
analyzed using the student’s T-Test on GraphPad
Prism® at (p <0.05).
3 RESULT
SARS-CoV-2 infected cells from patients were
supported by DMEM as specified in the method part.
To conduct an inquiry into the effectiveness of
Lianhua Qingwen against the virus, the cells were
incubated with Lianhua Qingwen at different
concentrations for about 72 h. And the positive and
negative control groups followed a similar method
with Remdesivir which is the positive control group
and buffer solution (DMEM with 2% fetal bovine
serum) as the negative control. Calculating the IC50
number for the virus-induced CPE of these three
experiments by the Reed-Muench method compared
the results to test our hypothesis. For the Cytopathic
effect inhibition assay, the positive control
experiment with Remdesivir would show positive
inhibition and the negative control experiment with
the buffer (0% of Lianhua Qingwen solution) would
show negative inhibition. Lianhua Qingwen could
show positive inhibition, no inhibition, or negative
inhibition. If the experiment with Lianhua Qingwen
solution shows positive inhibition or no inhibition,
we will conduct that Lianhua Qingwen inhibited the
tested virus replication in experiment cells (because
the negative control will give negative results of virus
inhibition) which agrees with our hypothesis.
Lianhua Qingwen inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication
significantly in infected cells will be represented as a
"+" sign in Table#1. For the Plaque reduction assay,
after counting the plaques for all groups Remdesivir
would show less plaque which indicates positive
inhibition and the negative control experiment with
the buffer would show more plaque which shows
negative inhibition. And if Lianhua Qingwen inhibit
or reduced effects of the plaque appearing of the
virus, it will be represented as a "+" sign in Table#1,
and it agrees with our hypothesis.
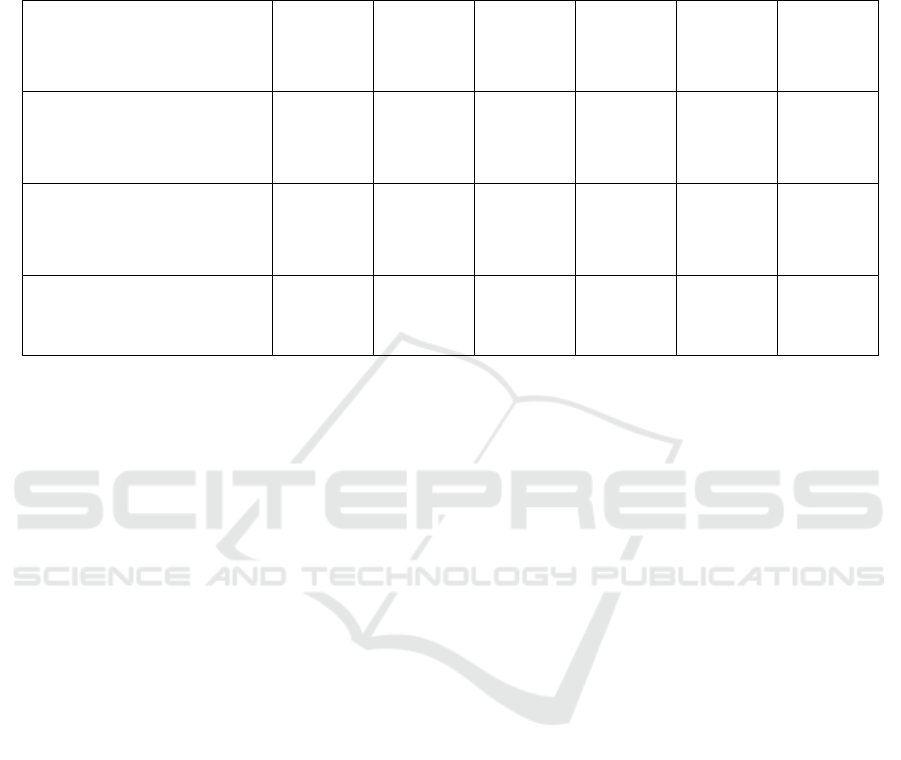
There are six possible results: (1). If Lianhua
Qingwen shows positive inhibition on the CPE
inhibition assay and it prevents the plaque formation
of the virus, we will say Lianhua Qingwen
appreciably prevent the COVID-19 virus replication
in experiment cells which agree with our hypothesis.
(2). If Lianhua Qingwen shows no inhibition on the
CPE inhibition assay and it gives us the same effect
as the first result, and we also say the replication of
the virus in cells was invited by Lianhua Qingwen
remarkably which agree with our hypothesis. (3). If
Lianhua Qingwen shows negative inhibition on the
CPE inhibition assay and inhibitory effect was given
to us on the formation of plaque in cells, the results
of the CPE and plaque reduction assay contradicted
each other, which partly proves our hypothesis and
these results wouldn't give a clear answer to our
research question. (4). If Lianhua Qingwen shows
positive inhibition on the CPE inhibition assay and it
gives us no inhibitory effect on plaque formation of
the SARS-CoV-2 virus, we will the results of the CPE
and plaque reduction assay contradicted each other,
which partly proves our hypothesis and these results
wouldn't give a clear answer to our research question.
(5). If Lianhua Qingwen shows no inhibition on the
CPE inhibition assay and it shows no inhibitory effect
on plaque formation of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, we
say the results of the CPE and plaque reduction assay
contradicted each other, which partly supports our
hypothesis and these results wouldn't give a clear
answer to our research questions. (6). If Lianhua
Qingwen shows negative inhibition on the CPE
inhibition assay and it gives us no inhibitory effect on
plaque development of the virus, which means
Lianhua Qingwen did not significantly inhibit the
tested virus replication in cells and it disagrees with
our hypothesis.
4 DISCUSSION
Previous studies had shown Lianhua Qingwen
together with drugs that are currently used is a
potential bright treatment for COVID-19, and by
using it the healing period of COVID-19 is shortened
and improves several symptoms. Research has also
shown Lianhua Qingwen inhibits virus replication in
both Vero E6 and Huh-7 cells, and it has a dose-
dependent effect of inhibition on the formation of
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
286
plaque. This study will use infected lung cells from
patients to verify if Lianhua Qingwen fights against
coronavirus by reducing virus replication. Our
hypothesis is consistent with previous studies and it
predicts that Lianhua Qingwen helps to block
replication of COVID-19.
Table 1: All Possible Results.
Antiviral activity of Lianhua
Qingwen on SARS-CoV-2 in
vitro
Result 1 Result 2 Result 3 Result 4 Result 5 Result 6
Cytopathic effect (CPE)
inhibition assay
positive
inhibition
(
+
)
no
inhibition
(
+
)
negative
inhibition
(
-
)
positive
inhibition
(
+
)
no
inhibition
(
+
)
negative
inhibition
(
-
)
Plaque reduction assay
positive
reduction
(+)
positive
reduction
(+)
positive
reduction
(+)
no
reduction
(-)
no
reduction
(-)
no
reduction
(-)
Agree or disagree with the
hypothesis
agree agree
partly
agree
partly
agree
partly
agree
disagree
Possible results one and two are consistent with
previous studies investigating Lianhua Qingwen, and
they are most likely to happen. Both of these results
show inhibition on the CPE inhibition assay and it
gives us an negative growth effect on plaque
formation of the virus, and they agree with our
hypothesis. The difference between these two results
is result 1 shows a stronger ability of the inhibition on
coronavirus. In result 2, Lianhua Qingwen shows no
inhibition on the CPE inhibition assay but it gives us
an inhibitory effect on plaque formation. This result
is still significant because showing no inhibition still
means Lianhua Qingwen succeeded in slowing or
even stopping the virus replication. This is essential
in controlling the pandemic and it could help save
thousands of lives. Based on previous research,
between these two results, result 1 is even more likely
to happen. These results show how Lianhua Qingwen
helps to treat COVID-19 by inhibiting the rapid virus
replication, and future studies should focus on more
potential effects of Lianhua Qingwen and vivo
experiment is needed. Research could also be done
about the differences between recovered cells that
were treated with different drugs (for example
shapes, size, viability, etc.). Also, even these results
prove Lianhua Qingwen inhibits virus replication,
studies could also find other possible mechanisms
that Lianhua Qingwen may use to fight the COVID-
19 virus.
Possible results three, four, and five partly prove
our hypothesis and these results are controversial and
wouldn't give a clear answer to our research question.
These results show contradictions between the CPE
inhibition assay and the plaque reduction assay, and
if there are no errors in operation that caused these
contradictions we should design more experiments on
the effects of Lianhua Qingwen on virus replication.
Future studies should focus on why these two assays
give different results and find more ways to test the
inhibition effects of Lianhua Qingwen on virus
replication. Also, studies that find other possible
ways that Lianhua Qingwen could use to fight the
COVID-19 virus.
The possible results six contradicts with the
current understanding of Lianhua Qingwen's effects
on the SARS-CoV-2 virus, this result indicates that
Lianhua Qingwen did not inhibit SARS-CoV-2
replication in cells dramatically and it disagrees with
our hypothesis. This result is unlikely to happen since
there has already been much research that proves
relief of clinical symptoms of coronavirus and the
inhibition effect that Lianhua Qingwen has on the
virus. However, since the mechanism of antiviral
effects on coronavirus is new and hard to find, there
could be other ways Lianhua Qingwen helps treat
coronavirus. Future studies should review the
existing researches that are not consistent with this
result and focus on finding other mechanisms that
Lianhua Qingwen could help fighting coronavirus.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study explores the effect of Lianhua Qingwen in
The Effects of Chinese Medicine Lianhua Qingwen on Inhibiting the Replication of Covid-19 Virus
287

the inhibition of the COVID-19 virus. The result of
our study will indicate whether or not Lianhua
Qingwen fights against coronavirus by reducing virus
replication. The possible results that are likely to
happen prove our hypothesis that Lianhua Qingwen
inhibits virus replication which supports that
combines Lianhua Qingwen with existing therapies
to help to treat COVID-19 in clinical. The possible
controversial results on the infected lung cells from
patients will also indicate the inhibition effects of
Lianhua Qingwen on coronavirus, and we need to
find out what caused these two assays to give us
contradicted results. Future studies need to be
investigated in clearer details and find other
mechanisms that Lianhua Qingwen could help
fighting coronavirus and trying to validate this further
by conducting vivo experiments.
REFERENCES
Britannica, (2019) The Editors of Encyclopaedia.
"Cytopathic effect". Encyclopedia Britannica,
https://www.britannica.com/science/cytopathic-effect.
Hu, Caiyun, et al. (2020) Efficacy of Lianhua QINGWEN
Compared with Conventional Drugs in the Treatment
of COMMON Pneumonia and COVID-19
PNEUMONIA: A Meta-Analysis.
www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2020/5157089/.
Kaufmann, S.H.; Kabelitz, D. (2002). Methods in
Microbiology, Immunology of Infection. Academic
Press., ISBN 0-12-521532-0.
Li, Runfeng, et al. (2020) “Lianhuaqingwen Exerts Anti-
Viral and Anti-Inflammatory Activity against Novel
Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2).” Pharmacological
Research, Published by Elsevier Ltd.,
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7102548/.
Xia, Qi‐Dong, et al. (2020) “Network Pharmacology and
Molecular Docking Analyses on Lianhua Qingwen
Capsule Indicate Akt1 Is a Potential Target to Treat and
Prevent COVID‐19.”
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/cpr.12949.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
288
