
Cloning, Expression and Purification of Glutathione Peroxidase of
Antarctic Yeast Rhodotorula mucilaginosa AN5
Hai Yu
1a
, Cuijuan Shi
2b
, Xiujun Gao
2c
and Guangfeng Kan
2,* d
1
Weihai Science and Technology Innovation Development Center, Weihai, Shandong, China
2
School of Marine Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology at Weihai, Weihai, Shandong, China
gfkan@hit.edu.cn
Keywords: Antarctic Yeast, Glutathione Peroxidase, Cloning and Expression, Protein Properties.
Abstract: Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) is a key enzyme in glutathione antioxidant enzyme system, which can remove
H2O2 and other oxidants in organisms. In this study, the GPx gene was cloned, sequence analyzed,
prokaryotic expressed and purified from Antarctic yeast Rhodotorula mucilaginosa AN5. The GPx gene
sequence was amplified successfully by PCR and named RmGPx (GenBank No. KX164292). The open
reading frame (ORF) of RmGPx was 498 bp and encoded 165 amino acids. The predicted molecular weight
of the protein was 18268.6 Da and the theoretical isoelectric point was 8.37. The recombinant expression
plasmid pET-28a-RmGPx was successfully constructed and transferred to E. coli. The protein expression
was the optimum when induced by 0.2 mM IPTG at 37 ℃ for 4 hours. The protein was purified by an
elution buffer of 100 mM imidazole in Ni NTA column. All study results supply the theoretical foundation
for the functional analysis and application of GPx protein.
1
INTRODUCTION
1
Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) catalyzes the
reduction of hydrogen peroxide by GSH and was
first discovered in bovine erythrocytes (Mills 1957).
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are chemically
active small molecules formed in the process of
aerobic respiration and substrate oxidation. They
participate in many biological processes, such as
stimulating signal transduction, mediating cell
apoptosis and defending against pathogen invasion
(Bathige et al 2015). Trace ROS is indispensable in
many biochemical processes, while excess ROS will
cause cellular damages, such as DNA strand
breakage, protein oxidation, polysaccharide
depolymerization, membrane peroxidation and
signal trans-duction damage (Zhang et al 2015). In
order to remove excess ROS and maintain redox
balance in cells, aerobic organisms have evolved
various non-enzymatic and enzymatic antioxidant
systems including GPx (
Matés 2000
).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7829-8578
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9563-1259
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5008-4789
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5357-7204
GPx can scavenge free radicals, participate in
signal transduction and immune response, and plays
an important role in biological stress adaptation
(Zhang et al 2018, Li et al 2021). In Arabidopsis
and yeasts, the growth is inhibited by H
2
O
2
produced by environmental stress, while catalase,
ascorbate peroxidase and GPx can eliminate them
and maintain metabolism balance (Smirnoff and
Arnaud 2018). Zhang et al discovered that in corn
(Zea mays L.) seedlings treated with polystyrene
nanoplastics, the antioxidant enzyme activity of
superoxide dismutase and GPx increased obviously,
which indicated glutamate metabolic pathways
appear to be closely related to plant mechanisms for
tolerance/detoxification of nanoplastics (Zhang et al
2021).
As well known, Antarctic behaves in harsh
environmental conditions. With the changes of air
temperature and snow cover, sea ice is highly
variable by strong gradients in temperature, salinity,
space, and light (
Thomas, Dieckmann, 2002
).
Sea-ice microorganisms suffer huge environmental
stresses, which result in the cellular metabolism
imbalance and active oxygen generation. So, polar
organisms frequently produce more antioxidants or
antioxidases to maintain the redox equilibrium
Yu, H., Shi, C., Gao, X. and Kan, G.
Cloning, Expression and Purification of Glutathione Peroxidase of Antarctic Yeast Rhodotorula mucilaginosa AN5.
DOI: 10.5220/0011232500003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 553-557
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
553

(
Núñez-Pons et al 2018
). In this study, GPx gene
was amplified by PCR from Antarctica yeast AN5.
The recombinant expression plasmid was
constructed, and the optimum induction expression
and purification conditions of recombinant protein
were analyzed. The study lays a foundation for the
properties and functions analysis of GPx protein,
and provides a reference for revealing
environmental adaptation mechanisms of extreme
organisms.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Microorganisms and Growth
Antarctic yeast R. mucilaginosa AN5 was isolated
from Antarctic sea ice collected by the 23
th
Chinese
Antarctic Scientific Expedition. Yeast AN5 was
grown in YEPD medium at 20 °C in an orbital
shaker of 120 rpm. E. coli were kept in LB medium
at 37 °C.
2.2 Cloning and Sequencing of GPx
Gene
The yeast cells were collected by centrifugation and
ground with a mortar and pestle in liquid nitrogen.
Total RNA was extracted following the instruction
of total RNA extractor and then removed the
possible DNA contamination with gDNA eraser.
The RNA was examined in 1.0% (w/v) agarose gel.
The first strand cDNA was prepared by the
manufacturer’s instruction of the PrimeScript RT
reagent kit. The primers RmGPx-F1
(5’-ACGACCTCACAACGCTCAG-3’) and
RmGPx-R1
(5’-GTGGGAAAGGCGAGGATATT-3’) were used
for PCR amplification with cDNA. The PCR
product was sequenced by Sangon Biotech.
2.3 Expression of the Recombinant
Protein
According to the sequencing result of GPx gene, the
forward primer RmGPx-F2 (5'-
CGCGGATCCACCAGCGTCGCCTCTTTC -3')
contained a BamHI restriction site (underlined
nucleotides) and reverse primer RmGPx-R2 (5'-
CCCAAGCTTTGCGGACTCGGCGAGCG -3')
contained a HindIII restriction site (underlined
nucleotides) were designed to amplify the
corresponding open reading frame (ORF). After
PCR was performed, the product was purified,
digested with BamHI and HindIII and cloned into
the same restriction enzyme sites of pET28a
expression vector. The recombinant plasmid was
transformed into E. coli BL21 cells. The
transformants were selected on LB plates with 100
μg/ml kanamycin. Plasmid DNA in the positive
clones was extracted with SanPrep column plasmid
mini-preps kit and digested with BamHI and HindIII.
The cloned gene was verified by PCR reaction.
2.4 IPTG Induction Expression of GPx
Gene
For the expression of GPx gene,
isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was
added to LB medium containing 1 mM kanamycin.
For the determination of the optimum induction
time, every two hours, 5 ml culture cells were
collected and mixed with 5x protein sample buffer,
and boiled for 4 min. After a short centrifugation,
the mixtures were conducted to SDS-PAGE
electrophoresis to detect the expression of target
protein. The electrophoresis was run at 120 V with
12.5% separating gel, and stained with Coomassie
staining solution for 1 h followed by destaining in
destaining solution.
For the determination of the optimum
concentration of IPTG induction, when the
transformants grew to mid-log phase, IPTG was
added to the medium to the final concentration of
0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1.0 mM, respectively.
After incubation for 2 h, cells were collected by
centrifugation and subjected to SDS-PAGE analysis.
2.5 Purification of the Recombinant
Protein
The recombinant protein was expressed by 0.1 mM
IPTG induction for 2 h. The collected cells were
resuspended with cold 0.05 M phosphate buffer (pH
7.0) and broken by the ultrasonic technique for 10
min. After centrifugation, the precipitate was
dissolved with 8 M urea. SDS-PAGE
electrophoresis was used to detect protein
expression in the supernatant and precipitate.
The recombinant protein was purified by Ni
2+
column affinity chromatography. The sample was
firstly washed with 5 bed volumes of washing
buffer to remove contaminating proteins, and then
the target proteins were eluted by elution buffer. The
elution was detected by A
280
value and SDS-PAGE
assay.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
554
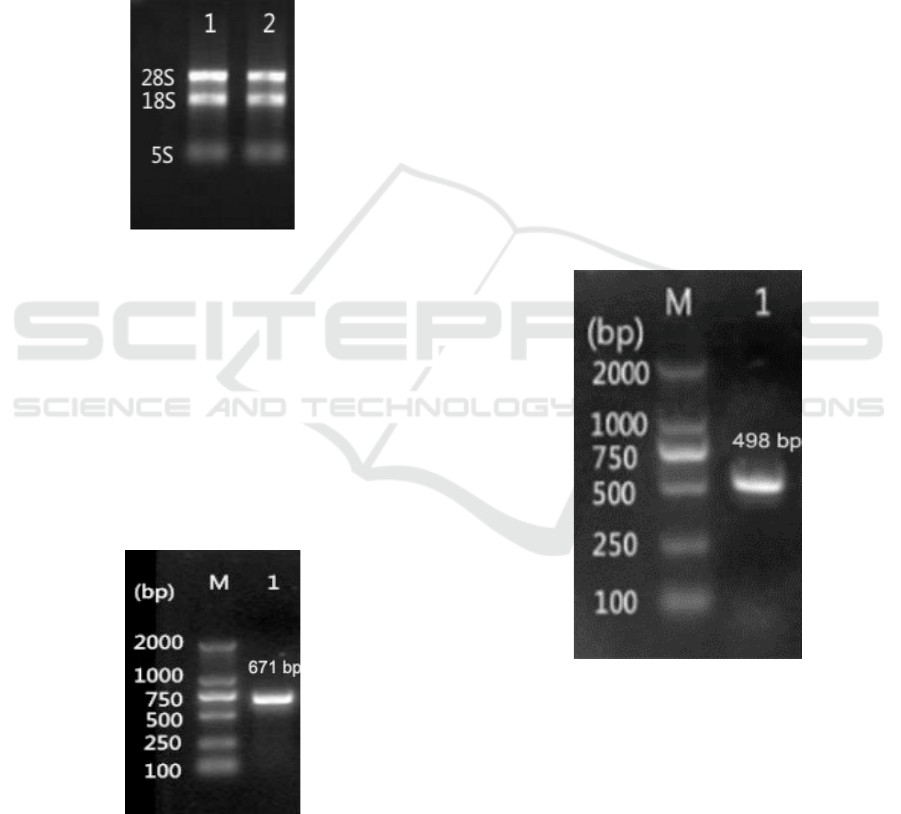
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Cloning of RmGPx Gene
3.1.1 RNA Extraction
The total RNA of Antarctic yeast AN5 was
extracted with the total RNA extractor kit, and
electrophoretic detection is shown in Fig. 1. It can
be seen that the extracted RNA has three obvious
bands of 28s, 18S and 5S rRNA, indicating that the
RNA is not degraded.
Figure 1: RNA analysis of Antarctic yeast AN5
3.1.2 PCR Amplification of RmGPx
The extracted RNA was reverse transcribed into
cDNA by reverse transcription kit. Using cDNA as
template, PCR amplification was performed with
primers RmGPx-F1 and RmGPx-R1, and
electrophoretic detection was shown in Fig. 2.
According to the primer design, the target fragment
was 671 bp, which was consistent with the expected
size, and sequencing results showed the PCR
product was correct sequence.
Figure 2: Gel electrophoresis analysis of target gene PCR
product M, DNA Marker; Lane 1, PCR product.
3.2 Bioinformatics Analysis of RmGPx
PCR amplification and sequencing showed that the
open reading frame of RmGPx gene was 498 bp,
encoding 165 amino acids. The gene sequence was
submitted to GenBank database with the sequence
login number of kx164292. RmGPx protein
predicted that the theoretical molecular weight was
18268.6 Da and the isoelectric point was 8.37,
belonging to cytoplasmic protein. Blastp analysis of
RmGPx protein showed that the similarity of
RmGPx was the highest with GPx sequences of
Rhodotorula sp. jg-1b (KWU44177), followed by
Rhodotorula toruloides NP11 (EMS25797) and
Rhodotorula graminis.
3.3 Construction of Plasmid
Pet-28a-RmGPx
3.3.1 PCR Amplification of RmGPx
Using the cloned RmGPx gene fragment as the
template, PCR amplification was carried out with
primers RmGPx-F2 and RmGPx-R2. The
electrophoresis results (Fig. 3) showed that the
target fragment is 498 bp, and the size is consistent
with the expected value.
Figure 3: PCR amplification of RmGPx gene.
3.3.2 Identification of Positive Clone
RmGPx gene and vector pET-28a(+) were
respectively digested by restriction enzymes BamHI
and HindIII. After purification and recovery, the
digested fragments were connected in proportion,
and then converted to DH5α competent cells.
Positive clones were screened by colony PCR, and
the results indicated that the target gene RmGPx was
inserted in the plasmid successfully (Fig. 4).
Cloning, Expression and Purification of Glutathione Peroxidase of Antarctic Yeast Rhodotorula mucilaginosa AN5
555
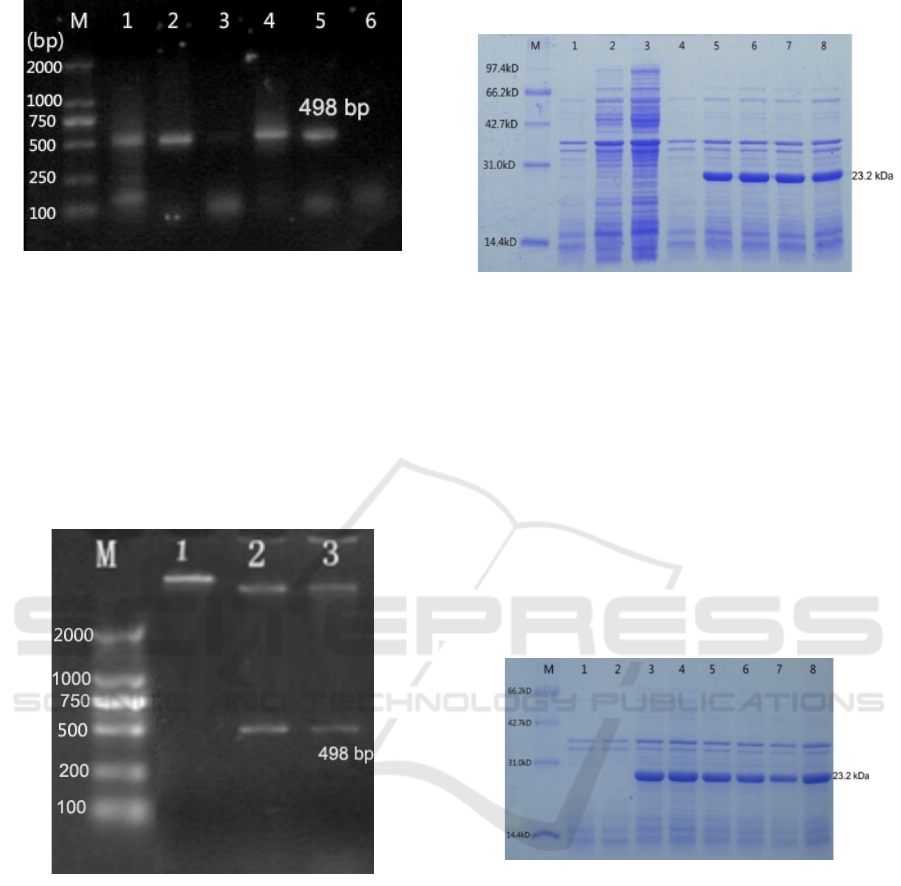
M, DNA Marker DL2000; 1, 2, 4 and 5, Positive clones
Figure 4: Screening of positive clones.
3.3.3 Identification of Recombinant Plasmid
The plasmid of positive clone was extracted and
then identified by double enzyme digestion. The
results in Fig. 5 indicated that the band size of 500
bp was consistent with the expected value, which
proved that the recombinant expression plasmid was
successfully constructed.
M, DNA Marker; 1, recombinant plasmid; 2 and 3,
Enzymatic product.
Figure 5: Gel electrophoresis analysis of enzymatic
products of recombinant plasmid.
3.4 Expression of Recombinant GPx
3.4.1 Optimizing of IPTG Induction Time
E. coli BL21(DE3) transformed with
pET-28a-RmGPx was induced with 1 mM IPTG at
37 ℃. The protein electrophoresis results in Fig. 6
showed that an obvious new protein band was
appeared, which was consistent with the expected
value of 23.2 kDa. After band density detection,
protein expression of Lane 6 was the highest, which
indicated that 4 h was the optimum induction time.
M, protein Marker; Lane 1-3, IPTG induction of wild
bacteria at 0 h, 2 h and 4 h; Lane 4-8, IPTG induction of
recombinant bacteria at 0 h, 2 h, 4 h, 6 h and 8 h
Figure 6: Expression of recombinant protein induced by
IPTG at different time.
3.4.2 Optimizing of IPTG Induction
Concentration
E. coli BL21(DE3) transformed with
pET-28a-RmGPx was induced 4 h at 37 ℃ with
different IPTG concentrations of 0.1-1.0 mM,
respectively. The results shown in Fig. 7 indicated
that Lane 6 was the highest density value, which
demonstrated that 0.2 mM was the optimum
induction concentration of IPTG.
M, protein Marker; Lane 1, Wild bacteria without IPTG;
Lane 2, Recombinant bacteria without IPTG; Lane 3-8,
recombinant bacteria with IPTG induction of 0.1, 0.2, 0.4,
0.6, 0.8 and 1.0 mM
Figure 7: Expression of recombinant protein induced by
different IPTG concentration.
3.5 Purification of Recombinant GPx
The recombinant protein was added to the Ni
column, and the protein impurity was washed off
with binding buffer. Then the binding protein was
eluted with elution buffer containing 50 mM, 100
mM and 200 mM imidazole respectively. The eluted
samples were collected and concentrated, and then
detected by electrophoresis, and the results were
shown in Fig. 8. It could be seen that the elusion
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
556
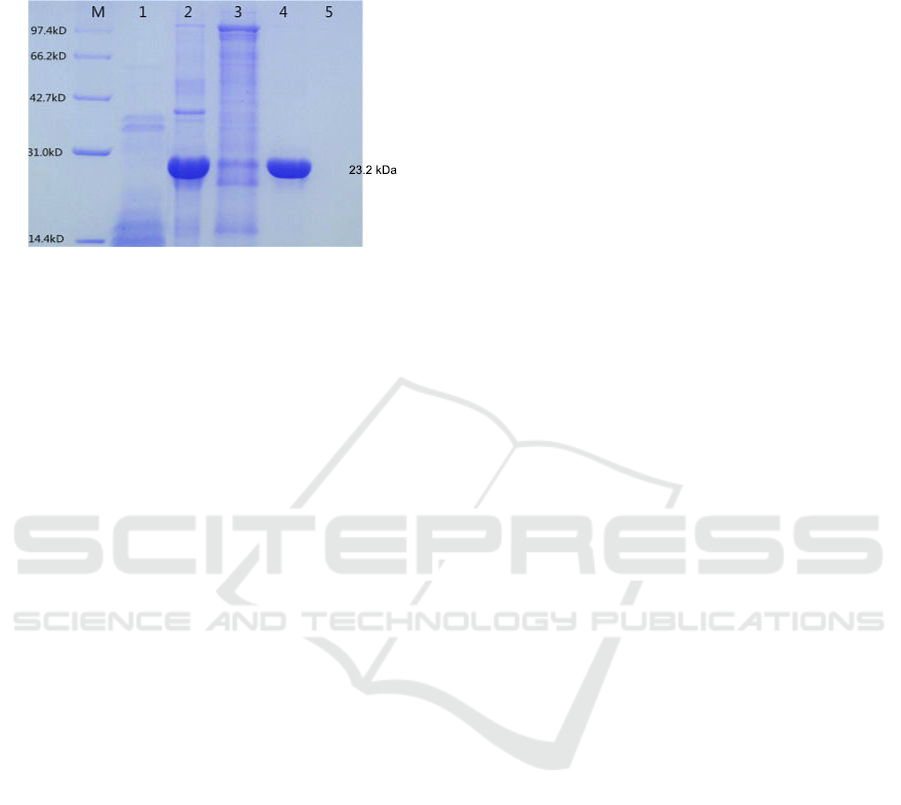
buffer containing 50 mM imidazole could wash off
the protein impurity, and 100 mM imidazole could
elute GPx protein.
M, Protein marker; Lane 1, Recombinant bacteria without
IPTG induction; Lane 2, Total protein of IPTG induced
bacteria; Lane 3-5, Effluent fraction with 50, 100 and 200
mM imidazole buffer respectively
Figure 8: Purification of recombinant RmGPx.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, the RmGPx gene was cloned,
expressed and purified from Rhodotorula
mucilaginosa AN5. The ORF of RmGPx was 498 bp
encoding 165 amino acids. The predicted molecular
weight was 18.3 kDa and the theoretical isoelectric
point was 8.37. The optimum expression conditions
were 0.2 mM IPTG at 37 ℃ for 4 hours. The
protein was purified by elution buffer of 100 mM
imidazole in Ni NTA column. All study results
supply the theoretical foundation for the functional
analysis and application of GPx protein.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Nature and Science
Foundation of Shandong [ZR2021MC180].
REFERENCES
Bathige, S.D.N.K., Umasuthan, N., Godahewa, G.I., et al.
(2015) Two variants of selenium-dependent
glutathione peroxidase from the disk abalone Haliotis
discus discus: Molecular characterization and immune
responses to bacterial and viral stresses. Fish Shellfish
Immunol., 45: 648-655.
Li, W., Huai, X., Li, P., et al. (2021) Genome-wide
characterization of glutathione peroxidase (GPX)
gene family in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) revealed
their role in multiple abiotic stress response and
hormone signaling. Antioxidants (Basel), 10(9): 1481.
Matés, J.M. (2000) Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the
molecular control of reactive oxygen species
toxicology. Toxicology, 153: 83–104.
Mills, G.C. (1957) Hemoglobin catabolism. I. Glutathione
peroxidase, an erythrocyte enzyme which protects
hemoglobin from oxidative breakdown. J. Biol.
Chem., 229: 189–197.
Núñez-Pons, L., Avila, C., Romano, G., et al. (2018)
UV-protective compounds in marine organisms from
the Southern Ocean. Mar. Drugs, 16(9): 336.
Smirnoff N., Arnaud, D. (2018) Hydrogen peroxide
metabolism and functions in plants. New phytol.,
doi:10.1111/nph.15488
Thomas, D.N., Dieckmann, G.S. (2002) Antarctic Sea
ice--a habitat for extremophiles. Science, 295(5555):
641-644.
Zhang, L., Wu, M., Yu, D., et al. (2018) Identification of
glutathione peroxidase (GPX) gene family in
Rhodiola crenulata and gene expression analysis
under stress conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 19(11):
3329.
Zhang, Y., He, Y., He, L., et al. (2015) Molecular cloning
and characterization of a phospholipid hydroperoxide
glutathione peroxidase gene from a blood fluke
Schistosoma japonicum. Mol. Biochem. Parasit., 203:
5-13.
Zhang, Y., Yang, X., Luo, Z.X., et al. (2021) Effects of
polystyrene nanoplastics (PSNPs) on the physiology
and molecular metabolism of corn (Zea mays L.)
seedlings. Sci. Total Environ., 13:150895.
Cloning, Expression and Purification of Glutathione Peroxidase of Antarctic Yeast Rhodotorula mucilaginosa AN5
557
