
The Influence of Time Personality on the Persuasive Effect of
Brainwashing Advertisements
Junfeng Liao
1,2
, Zhengyan Yang
1
, Ying Pan
1
and Chaohua Zhao
3
1
Department of Electronic Business, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
2
College of Economics and Management, Kashi University, Kashi, Xinjiang, China
3
Beijing chalk tianxia education technology co., ltd. Beijing, China
Keywords: Time Personality, Brainwashing Advertising, Purchase Intention, Brand Cognition.
Abstract: This paper discusses the persuasion effect of different time personality on brainwashing advertising, and
analyzes the questionnaire by SEM, Draw the following conclusions: brand familiarity (pre advertising brand
attitude) has a positive and significant impact on advertising cognitive response and brand cognitive response;
advertising cognitive response has a positive and significant impact on brand cognitive response and
advertising attitude; brand cognitive response and advertising attitude have a positive and significant impact
on brand attitude; brand attitude has a positive and significant impact on purchase intention; advertising style
and time Interpersonal personality plays a moderating role in the influence of brand cognition, advertising
attitude and brand attitude on purchase intention.
1 INTRODUCTION
The core of advertising is "creative." Research shows
that advertising has a positive effect on corporate
performance in the long run, and can also expand its
brand effect (Huang 2018). Therefore, more and more
enterprises are trying to make their products and
services stand out in the fierce homogeneous
competition through a large amount of investment in
advertising. However, in the early years, there
appeared a batch of "brainwashing" TV commercials
that used "violent repetition" without creativity and
innovation, which left a deep impression on viewers
and brought huge profits to the products they
promoted. Although the survey shows that most
people are disgusted with repetitive "brainwashing"
advertisements, the above advertisements still bring
substantial growth in product sales and significant
increase in website popularity and visits. In China's
advertising environment, brainwashing advertising
does not necessarily have a negative impact on brand
image, and to a certain extent can still cause sales
growth to achieve the effect of advertising (Li 2019).
However, in today's precision marketing
environment, it is not suitable for enterprises to
simply use brainwashing advertising strategy and
"violent repetition" means to put circular advertising
images and advertising words into the minds of all
audiences. Because potential consumers have
different time personalities, that is, their time insight,
time urgency, time consciousness and time
motivation are also different, brainwashing
advertisements may also produce different persuasive
effects for consumers with different time
personalities. From the past achievements of
brainwashing advertising and the research on the
influence of existing brainwashing advertising on
brand image, brainwashing advertising is not
undesirable. However, in order to achieve precise
marketing and rationally allocate resources, the first
thing to do is to accurately place advertisements, and
then it is very important to find potential consumers
who can accept brainwashing advertising.
Therefore, this research is based on the
application of TRA's model theory and advertising
persuasive effect model to clarify the current research
status of time personality, the characteristics of
brainwashed advertising, and accurately identify
these potential consumers. Secondly, based on the
comparative research results of the difference
between the persuasive effect of brainwashing
advertising and non-brainwashing advertising, it
provides marketing method recommendations for
advertising investment in commercial activities.
490
Liao, J., Yang, Z., Pan, Y. and Zhao, C.
The Influence of Time Personality on the Persuasive Effect of Brainwashing Advertisements.
DOI: 10.5220/0011188200003440
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management (BDEDM 2022), pages 490-496
ISBN: 978-989-758-593-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Attitude and Cognitive Response
before Advertising
According to Lutz (1977) and other scholars' theory,
brand attitude before advertising will affect
consumers' brand cognitive response, and brand
attitude before advertising may even have an impact
on advertising cognitive response or attitude. Thus,
we propose: H1a:brand attitude before advertising
has a significant positive impact on advertising
cognitive response. H1b: brand attitude before
advertising has a significant positive impact on brand
cognitive response.
2.2 Advertising Cognition Response
and Brand Cognition
Advertising persuasion refers to the process that
consumers understand and accept the content of
advertising information that advertisers intend to
send out (Richard 1977). In the extension of the two
mediating hypothesis model of advertising
persuasion, consumers' cognition of advertising
affects their advertising attitude, which in turn affects
their brand cognition and brand attitude, and the
hypothesis that advertising cognitive response will
affect brand cognitive response has been confirmed
(Cai 2016). Thus, we propose: H2: advertising
cognitive response has a significant positive impact
on brand cognitive response.
2.3 Brainwashing Advertising and
Cognitive Response
In the process of advertising, repetitive brainwashing
advertising and elegant non-brainwashing advertising
will make consumers have different cognitive
reactions to advertising and the corresponding brand.
Advertising will affect consumers' purchase intention
through emotion and cognition (Meng 2019). Thus,
we propose: H3: Advertising style has a significant
positive impact on advertising cognitive response.
H4: Advertising style has a significant positive
impact on brand cognitive response.
2.4 Cognitive Response and
Post-advertising Attitude
According to the affective transfer hypothesis,
advertising attitude influences individual behavior
intention through brand attitude (Scott 1986).
Combined with the double mediation model, we
propose: H5: advertising cognitive response has a
significant positive impact on advertising
attitude. H6:
brand cognitive response has a significant positive
impact on brand attitude. H7: advertising attitude has
a significant positive impact on brand attitude.
2.5 Brainwashing Advertising and
Post-advertising Attitude
In the process of accepting advertisements,
consumers may have different cognitive reactions to
brainwashing advertising and non-brainwashing
advertising, and cognitive response will affect
consumers' attitudes. Thus, we propose: H8:
advertising style has a significant positive impact on
consumer's advertising attitude. H9: advertising style
has a significant positive impact on consumer brand
attitude.
2.6 Post-advertising Attitude and
Behavioral Intention
According to the rational behavior theory (TRA),
consumer attitudes affect their behavior. Drawing on
the assumptions of cognitive response and post-
advertising attitude, thus, we propose: H10: post-
advertisement attitude has a significant positive
impact on purchase intention. H11: post-advertising
brand attitude has a significant positive impact on
purchase intention.
2.7 Brainwashing Advertising and
Behavioral Intention
Different advertising styles affect consumers'
cognition of advertising content, information
reception and emotional attitude towards advertising,
thus affecting consumers' purchase intention. H12:
advertising style has a significant positive impact on
purchase intention.
2.8 The Regulating Effect of Time
Personality
Time personality can control the individual's
response to time-related situations. Because
The Influence of Time Personality on the Persuasive Effect of Brainwashing Advertisements
491
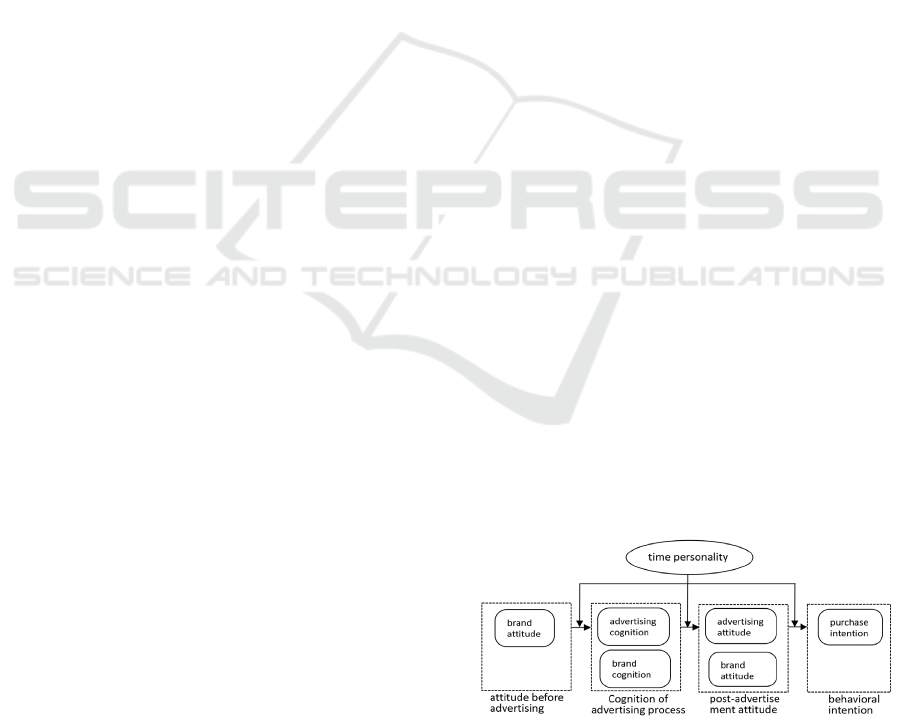
brainwashing advertising is a video advertising with
time length, when consumers receive advertising
information, their time personality may have an
impact on it. This paper selects four dimensions of
linear economic time, time orientation, time
compliance and time duration to describe consumers
' time personality. Thus, we propose:
1) the influence of linear economic time on the
persuasive effect of brainwashing advertising
H13a There is a significant difference in
consumers' advertising cognitive response between
economic time and non-organized time when they
accept brainwashing advertising.
H13b There is a significant difference in
consumers' brand cognitive response between
consumers in economic time and non-organized time
when they accept brainwashing advertising.
H13c There is a significant difference in
consumers' advertising attitude between economic
time and non-organized time when they accept
brainwashing advertising.
H13d There is a significant difference in
consumers' brand attitude between economic time
and non-organized time when they accept
brainwashing advertising.
H13e There is a significant difference in
consumers' purchase intention between economic
time and non-organized time when they accept
brainwashing advertising.
2) the influence of time orientation on the
persuasion effect of brainwashing advertising
H14a There is a significant difference in
consumers' advertising cognitive response between
the past trend and the future trend when they accept
brainwashing advertising.
H14b There is a significant difference in
consumers' brand cognitive response between the
past trend and the future trend when they accept
brainwashing advertising.
H14c There is a significant difference in
consumers' advertising attitude between the past
trend and the future trend when they accept
brainwashing advertising.
H14d There is a significant difference in
consumers' brand attitude between the past trend and
the future trend when they accept brainwashing
advertising.
H14e There is a significant difference in
consumers' purchase intention between the past trend
and the future trend when they accept brainwashing
advertising.
3) the influence of time compliance on the
persuasive effect of brainwashing advertising
H15a There is a significant difference in
consumers' advertising cognitive response between
time compliance and time-anxious consumers when
they accept brainwashing advertising.
H15b There is a significant difference in
consumers' brand cognitive response between time
compliance and time-anxious consumers when they
accept brainwashing advertising.
H15c There is a significant difference in
consumers' advertising attitude between time
compliance and time-anxious consumers when they
accept brainwashing advertising.
H15d There is a significant difference in
consumers' brand attitude between time compliance
and time-anxious consumers when they accept
brainwashing advertising.
H15e There is a significant difference in
consumers' purchase intention between time
compliance and time-anxious consumers when they
accept brainwashing advertising.
4) the influence of time duration on the persuasive
effect of brainwashing advertising
H16a There is a significant difference in
consumers' advertising cognitive response between
time-tough and fast-returning consumers when they
accept brainwashing advertising.
H16b There is a significant difference in
consumers' brand cognitive response between time-
tough and fast-returning consumers when they accept
brainwashing advertising.
H16c There is a significant difference in
consumers' advertising attitude between time-tough
and fast-returning consumers when they accept
brainwashing advertising.
H16d There is a significant difference in
consumers' brand attitude between time-tough and
fast-returning consumers when they accept
brainwashing advertising.
H16e There is a significant difference in
consumers' purchase intention between time-tough
and fast-returning consumers when they accept
brainwashing advertising.
Figure 1: Research models.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
492
3 RESEARCH DESIGN
3.1 Research Object
This study selects the Internet brand "boss direct
employment network" as the experimental material.
"Boss direct employment" is a recruitment tool for
employers and job seekers to chat and communicate
directly under the brand. Its platform covers
mainstream cultural media, Internet companies,
finance, real estate and other industries. According to
the video advertising characteristics of the "boss
direct employment" brand adopted in this study, the
following criteria are followed when selecting the
respondents: the respondents themselves or their
relatives and friends may need to apply for a job now
or in the future, pay attention to and understand the
job information, so as to ensure the accuracy and
authenticity of the collected data.
3.2 Questionnaire Design and Data
Collection
This questionnaire is divided into seven parts: the
first part is the basic information of the sample. The
second part is about the evaluation of consumers'
attitude before advertising, which is measured by
Algesheim (2005) brand familiarity scale. The third
part is the broadcast of online video ads. the
respondents need to watch a 15s video ad in the
questionnaire. The video ads embedded in volume A
are brainwashing ads, and volume B are non-
brainwashing ads. The fourth part is about the
evaluation of consumers' cognitive response in the
advertising process, namely, advertising cognitive
response and brand cognitive response. The fifth part
is about the evaluation of consumers' post advertising
attitude, namely advertising attitude and brand
attitude. The sixth part is about the evaluation of
consumer behavior intention, namely purchase
intention. The above three parts all refer to the scale
of CAI Peier (2016) which studies the brand
persuasion effect under Internet video patch
advertising. The seventh part is the evaluation of
consumer's time personality, which adopts the Likert
seven scale proposed by usunier.
225 questionnaires were collected in the pre-test,
and the Cronbach's alpha less than 0.5 was deleted. A
total of 700 questionnaires were collected and 584 of
them were valid, including 289 in volume a and 295
in volume B. the effective rate was 83.4%.
4 RESULTS & DISCUSSION
The Cronbach's α value of the overall reliability of the
questionnaire is 0.929, and the α value of each
variable of the questionnaire is greater than 0.8. The
kmo values of volume a and volume B were 0.933
and 0.922 respectively. In Bartlett spherical test, the
significance probability was 0.000, which met the
condition of factor analysis. Principal component
analysis and Kaiser standardized orthogonal rotation
method were used for factor analysis. Four common
factors were extracted by principal component
analysis. The cumulative contribution rates of
common factors were 72.567% and 68.134%
respectively. The common factors extracted could
explain the variables better. The number of factors
after orthogonal rotation is less than the number of
variables assumed in the model, but the factor load is
all greater than 0.4, almost no double load situation,
indicating that the scale has good construction
validity. In addition, the model x2 / DF = 3.114, GFI
= 0.942, RMSEA = 0.086, NFI = 0.876, CFI = 0.912,
RFI = 0.859, TLI = 0.900, PNFI= 0.765, PCFI =
0.800) shows that the model has good fitting effect
and is suitable for subsequent analysis.
4.1 Main Effect Test
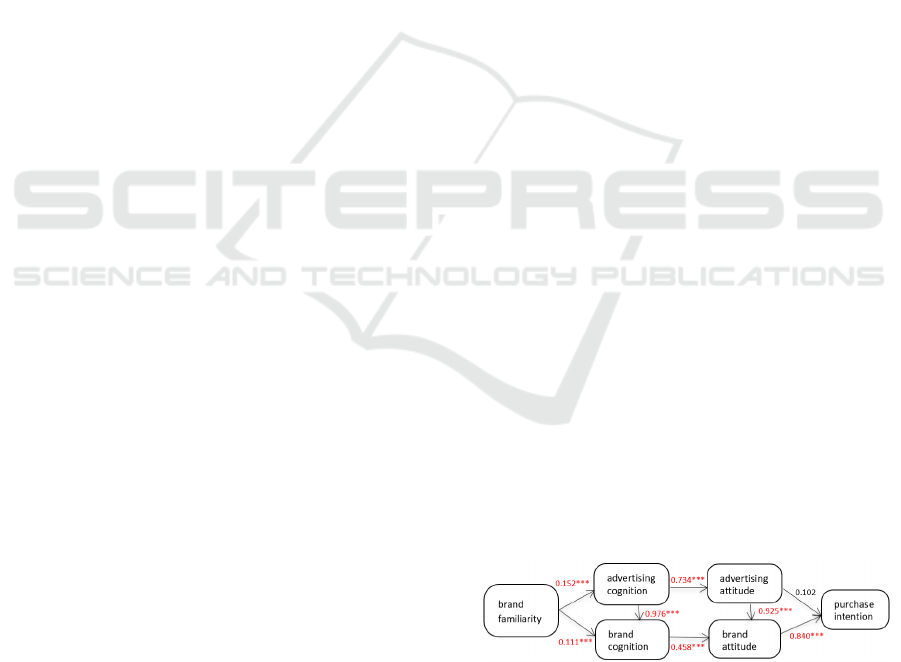
The path coefficient of the overall model
standardization is shown in the figure, and H1a, H1B,
H2, H5, H6, H7 and H11 are all verified. Brand
familiarity (brand attitude before advertising) has a
significant positive impact on advertising cognitive
response and brand cognitive response; consumers'
brand cognition and advertising attitude are
dependent on the level of advertising cognitive
response. If the advertising design is complex and
consumers' advertising cognitive response is low,
then consumers' cognition and advertising attitude to
the brand will be poor, which will lead to consumers'
dissatisfaction Brand attitude and purchase intention
also decreased.
Figure 2: Results of testing hypotheses for the total sample.
The Influence of Time Personality on the Persuasive Effect of Brainwashing Advertisements
493
4.2 The Difference of Persuasion Effect
between Brainwashing and Non-
Brainwashing Advertisements
In this paper, independent sample t-test method is
used to verify whether the persuasion effect of
different advertising styles is different. The results
are shown in Table 1. H4, H8, H9 and H12 are
verified. Brainwashing advertising has a more
significant positive impact on brand cognitive
response and advertising attitude. Non- brainwashing
advertising has a more significant positive impact on
brand attitude and purchase intention. There is no
significant difference between the two types of
advertising cognitive response. H3 is not valid.
Therefore, in order to achieve the final sales goal,
enterprises should invest more in non-brainwashing
advertising.
Table 1: Persuasion Effect of Brainwashing and Non-
Brainwashing Advertisements.
t
Mean
difference
Standard
erro
r
Cad 1.646(0.1000) 0.0099 0.0060
Cb 22.551***(0.0000) 0.1323 0.0059
Aad 8.920***(0.0000) 0.0439 0.0049
Ab -14.498***(0.0000) -0.1055 0.0073
PI -18.568***(0.0000) -0.1501 0.0081
*** means significant at the level of 0.1%
4.3 The Effect of Time Personality on
Persuasion of Brainwashing
Advertisements
Independent sample t-test is also used to test the
influence of time personality on the persuasion effect
of brainwashing advertising. The results are as
follows.
4.3.1 The Test of the Influence of Linear
Economic Time on the Persuasion
Effect of Brainwashing
Advertisements
As shown in Table 2, there is a more significant
positive effect of economic time consumers'
cognitive response to brainwashing advertising, and a
more significant positive effect of non-organizational
time consumers' attitude to brainwashing advertising.
H13a and h13c are verified.
Table 2: The Effect of Linear Economic Time on
Persuasion of Brainwashing Advertisements.
t
Mean
difference
Standard
erro
r
Cad -2.197*(0.029) 0.0099 0.0060
Cb -1.814(0.071) 0.1323 0.0059
Aad -2.072*(0.039) 0.0439 0.0049
Ab -0.489(0.625) -0.1055 0.0073
PI 0.018(0.986) -0.1501 0.0081
* means significant at the level of 5%
However, there is no significant difference in
brand cognitive response, brand attitude, purchase
intention between economic time and non-
organizational time.
4.3.2 The Test of the Influence of Time
Orientation on the Persuasion Effect of
Brainwashing Advertisements
As shown in Table 3, there are no significant
differences between the past and future trends in
consumers' cognitive response, brand cognitive
response, advertising attitude, brand attitude and
purchase intention to accept brainwashing
advertisements, so the hypotheses are not verified.
Table 3: Time Orientation on Persuasion Effect of
Brainwashing Advertising.
t
Mean
difference
Standard
erro
r
Cad 0.562(0.575) 0.0051 0.0090
Cb 0.422(0.674) 0.0042 0.0100
Aad 0.435(0.664) 0.0033 0.0076
Ab -0.761(0.447) -0.0067 0.0088
PI -0.531(0.596) -0.0049 0.0093
4.3.3 The Test of the Influence of Time
Compliance on the Persuasion Effect
of Brainwashing Advertisements
As shown in Table 4, there is a more significant
positive impact of time-abiding consumers on the
purchase intention of the brand promoted by
brainwashing advertising. H15e was verified.
However, there is no significant difference in the
cognitive response, brand cognitive response,
advertising attitude and brand attitude between the
time-abiding and time anxious consumers.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
494
Table 4: Time Compliance on Persuasion Effect of
Brainwashing Advertising.
t
Mean
difference
Standard
erro
r
Cad -0.471(0.638) -0.0043 0.0090
Cb 0.36(0.719) 0.0036 0.0100
Aad 0.061(0.952) 0.0005 0.0076
Ab 1.3(0.195) 0.0114 0.0088
PI 2.058*(0.04) 0.0189 0.0092
* means significant at the level of 5%
4.3.4 A Test of the Influence of Time
Duration on the Persuasive Effect of
Brainwashing Advertisements
As shown in Table 5, fast return preference
consumers have a more significant positive impact on
brand attitude of brainwashing advertising, and h16d
is verified. However, there are significant differences
in advertising cognitive response, brand cognitive
response, advertising attitude and purchase intention
between time tough consumers and quick return
consumers.
Table 5: The Effect of Time Duration on Brainwashing
Advertising Persuasion.
t
Mean
difference
Standard
erro
r
Cad -1.625(0.105) -0.0146 0.0090
Cb -0.75(0.454) -0.0075 0.0100
Aad -1.075(0.283) -0.0081 0.0076
Ab -2.324*(0.021) -0.0202 0.0087
PI -1.52(0.13) -0.0140 0.0092
* means significant at the level of 5%
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper selects the brand of "boss direct
employment" Internet recruitment platform to study
the effect of advertising persuasion and the influence
of advertising style and time personality on it.
Through empirical analysis, we draw the following
conclusions: brand attitude before advertising has a
positive impact on consumers' advertising cognitive
response and brand cognitive response. If consumers
have a knowledge of the brand before contacting the
corresponding advertising, then consumers can be
more confident Good understanding of the
corresponding advertising information and brand
information. In addition, advertising cognitive
response is an important factor affecting consumers'
brand cognitive association, which is an important
premise for consumers to produce
advertising attitude;
good brand cognitive response and advertising
attitude will enhance brand attitude and purchase
intention. For brainwashing advertising, consumers
have higher brand awareness and advertising attitude,
while non-brainwashing advertising has higher brand
attitude and purchase intention. For enterprises, non-
brainwashing advertising has higher conversion rate.
Time personality has a differential impact on the
effect of brainwashing advertising. Specifically,
economic time consumers have higher advertising
cognitive response, non-group advertising The
consumers with time weaving preference and quick
return preference have better advertising attitude and
brand attitude respectively, while the consumers with
time following preference have stronger purchase
intention to the brand promoted by brainwashing
advertisement.
According to the conclusion of this paper, the
following suggestions are put forward for enterprises.
1: When consumers come into contact with the brand
advertising again, the level of advertising cognition
and brand cognition will be better. 2: When choosing
advertising strategies, advertisers should focus on the
impact on consumers' advertising cognition and
attitude, which will directly affect consumers' brand
attitude and final purchase intention. 3: When
choosing the advertising style, we should not only
seek to improve the advertising attitude
of consumers,
but blindly choose brainwashing advertising, in order
to improve the advertising communication effect and
ignore the sales effect of advertising. Non-
brainwashing advertising is a better choice as the
mainstream advertising of brand promotion. At the
same time, a small amount of brainwashing
advertising flow is used to improve consumers'
advertising attitude, in order to achieve the best
advertising persuasion effect. 4: If the advertising
mainly chooses brainwashing advertising, in order to
make the advertising persuasion effect better, the
target audience can choose consumers with the
following time personality: non- organizational time
personality under the linear economic
time dimension,
time compliance personality under the time
compliance dimension, and quick return preference
personality under the time persistence dimension.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thanks for the support from The National Social
Science Fund of China (18BGL110).
The Influence of Time Personality on the Persuasive Effect of Brainwashing Advertisements
495

REFERENCES
Cai pei'er, Sha Zhenquan. Brand persuasion effect
underInternet video patch advertising [J]. Journal of
Management, 2016, (10): 1525-1533.
Huang Qixing, Wen Wen. Advertising expenditure,
industry competition and corporate performance [J].
Journal of Management, 2018, (12): 1838-1845.
Li Zhengfeng, Zhang Lijun, Hu Yueqin. The effect of trial
information on advertising persuasion: a study based on
progressive new products [J]. China Circulation
Economy, 2019, (04): 100-110.
LUTZ R J, SWASY J L. Integrating Cognitive Structure
and Cognitive Response Approaches to Monitoring
Communications Effects [J]. Advances In Consumer
Research,1977,4 (1): 363-371.
MACKENZIE S B, LUTZ R J, BELCH G E. The Role of
Attitude Toward the Ad as a Mediator of Advertising
Effectiveness: A Test of Competing Explanations [J].
Journal of Marketing Research, 1986, 23 (3): 130 / 143.
Meng fanxi Research on the influencing factors of online
video patch advertising on audience purchase intention
[D] Beijing University of Posts and
telecommunications, 2019.
BDEDM 2022 - The International Conference on Big Data Economy and Digital Management
496
