
The Role of Digital Marketing in Increasing SMEs’ Competitiveness
Rui Pedro Silva
1a
, Henrique Mamede
2b
and Arnaldo Santos
2c
1
Universidade de Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro, Vila Real, Portugal
2
Universidade Aberta, Lisbon, Portugal
Keywords: Digital Marketing, Digital Transformation, Small and Medium Enterprises, Content Management, Online
Engagement.
Abstract: With the significant increase of technology-based newer competitors and the digital economy reshaping the
global economic environment, it is undoubtful that the market is becoming aggressively more demanding for
small and medium enterprises, which is a strong driver of their need to adopt new digital technologies and
transform their businesses. Events such as the COVID-19 pandemic have accelerated the online engagement
of consumers, and that also means that digital transformation might not only be about the digitalisation of
internal processes and reshaping of business models but as well, and not least relevant, the Strategies used by
SMEs to position themselves in the market and maximise the value of digital marketing to regain
competitiveness and reposition their products.
1 INTRODUCTION
For SMEs (Small and Medium-sized Enterprises),
embracing digital transformation is not about
changing internal processes or adopting new
technologies; it fundamentally changes business
models (Loebbecke & Picot, 2015). At the same time,
the digitalisation process is reshaping the way
consumers and businesses interact (Taiminen &
Karjaluoto, 2015). However, we see SMEs struggling
and facing increased difficulties in adopting the
newer digital technologies, mainly due to their
limitations in resources and skills to fully
comprehend the value they can get (Giotopoulos et
al., 2017). For example, in a study carried out by
Ramukumba (2014), it was identified that lack of
funding, management skills, and investments in
newer technologies are ranked as the highest factors
in the failures of SMEs in South Africa.
On the other hand, SMEs have a few essential
positive aspects that support potential successes:
flexibility, faster, and less constrained (Barann et al.
2019), and their flat organisational structure enables
and supports more accessible communication and
close control of what is happening within the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4827-7944
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5383-9884
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5139-6728
company, which are factors that reduce risk of
failures (Prause, 2019).
With SMEs playing such a vital role, there is a
need to look at digital transformation and
digitalisation with more concrete strategies (Hulla et
al., 2021).
Lemon and Verhoef (2016) stated that
digitalisation pushes companies to develop a
seamless experience with customers across multiple
channels and touchpoints, which are possible ways to
get competitive in the re-shaped way consumers and
businesses interact.
Research such as Vial (2019) and Matarazzo
(2021) demonstrate the trend of SMEs using digital
technologies to improve their relationship and
proximity with customers through different channels.
At the same time, the use of technology in B2B
marketing is gaining momentum (Schultz & Good,
2012; Rapp et al., 2013; Agnihotri et al., 2016;
Guesalaga, 2016)
With the context of the relevance of SMEs for
the global economy, the impact that digital
technologies have on their competitiveness, and the
critical role digital marketing likely plays in
improving customer relationships, this work aims to
Silva, R., Mamede, H. and Santos, A.
The Role of Digital Marketing in Increasing SMEs’ Competitiveness.
DOI: 10.5220/0011118000003280
In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Smart Business Technologies (ICSBT 2022), pages 93-100
ISBN: 978-989-758-587-6; ISSN: 2184-772X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
93
answer the research question (RQ1): Is the digital
marketing strategy a well-defined factor in increasing
SMEs' digital economy competitiveness?
2 METHODOLOGY
Through a systematic literature review (SLR), we will
break down the research question into three different
categories:
1. SMEs & Digital Transformation success
factors
2. The technology developments in digital
marketing
3. SMEs’ competitiveness and digital
economy
We will use the database Science Direct
(Elsevier) to identify the relevant articles, following
the search strings indicated in Table 1.
Table 1: Query strings for step 1 in each category.
Category Query String
SMEs & Digital
Transformation success
factors
((SME OR "small and
medium enterprises")
AND (("digital
transformation") AND
(("success factors") OR
("success reasons") OR
("success strategies" ))))
The technology
developments in digital
marketing
(("SME" OR "small and
medium enterprises")
AND ("digital
marketing") AND
("technologies"))
SMEs competitiveness
and digital economy
(("SME" OR "small and
medium enterprises")
AND (("digital
economy") AND
(("competitiveness") OR
("winning markets") OR
("gain market share" ))))
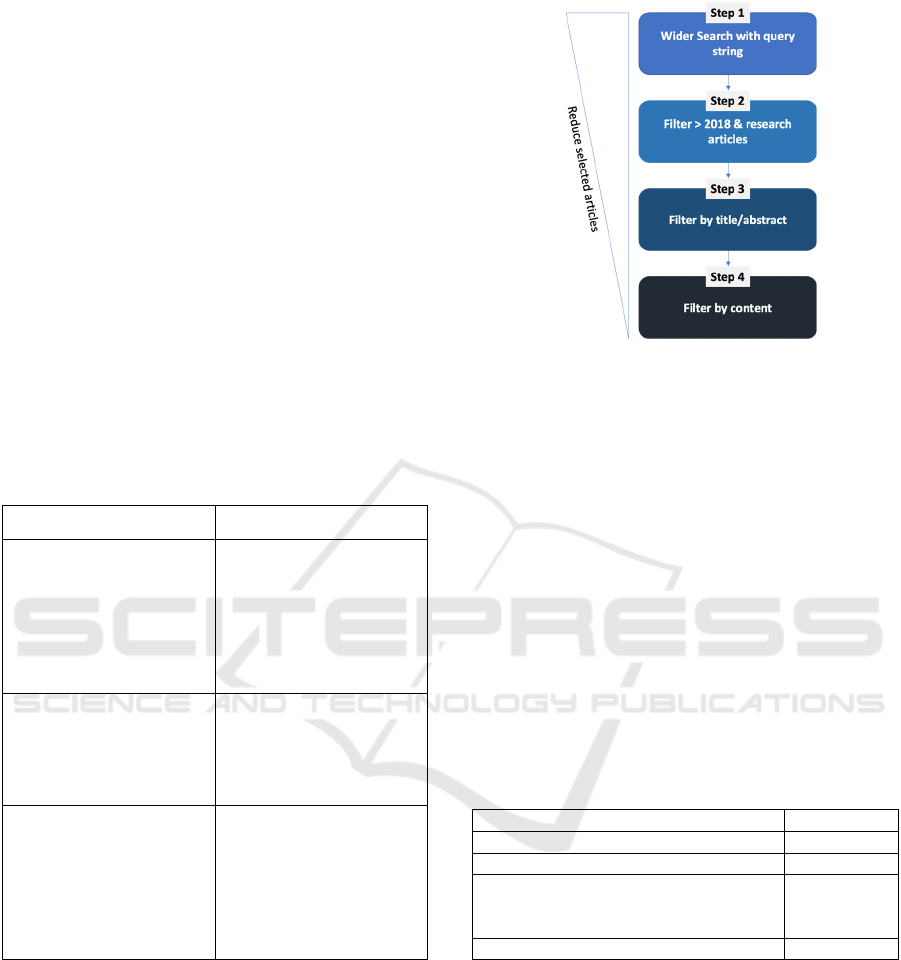
Our process consists of four steps (as illustrated in
Figure 1):
- Step 1: Search by the defined query string in all
the article content.
- Step 2: Limit the results from 2018 onwards (to
get the most up-to-date) and only research
articles.
- Step 3: Reduce the results further and filter by
title/abstract relevant keywords.
- Step 4: Analyse the shortlisted articles in step 3
and choose the relevant ones in the review
category.
Figure 1: Literature filtering process.
After finalizing step 4, we will document each
article identifying the relevant contribution to the
category and listing the keywords used by the author.
Per category, we will show a graph with the used
keywords in all the articles analysed in step 4.
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
3.1 SMEs & Digital Transformation
Success Factors
For category 1, we have analysed 16 articles and
selected 7, as identified in Table 2.
Table 2: The process of identifying relevant literature for
category 1.
Ste
p
Results
1
(
search b
y
q
uer
y
strin
g)
121 articles
2
(
onl
y
> 2018 & onl
y
research articles
)
96 articles
3 (filter title/abstract (("SME" OR
"small and medium enterprises") AND
("digital")))
16 articles
1 (search by query string) 7 articles
Daxhammer et al. (2019) analysed the potential of
implementing multi-sided platforms (MSP) through
SMEs and how this type of business model can foster
innovative strategies in this type of company.
Through their analyses of 36 companies, the
authors have concluded that this model is not yet
highly implemented within SMEs, identifying some
reasons to limit its rollout.
To this category, a few are of importance: (1) The
digitalisation is not yet at the core of companies'
competencies; (2) Daily operations consume much of
the companies' time, leaving no space to innovate; (3)
ICSBT 2022 - 19th International Conference on Smart Business Technologies
94

The benefit of business models such as MSP is not
apparent for SMEs; (4) The implementation of this
type of innovative model cannot be supported by
internal tech staff; (5) Organization's management
does not fully support it.
Author's Defined Keywords: Innovation
Management, Business Models, Multi-Sided
Platforms
Löcklin et al. (2021) presented a concept to
manage the transfer of datasets between organisations
(Data Administration Shell), addressing a very
relevant topic: The lack of resources that SMEs must
manage data-related projects and their need to often
rely on external providers in the field of data science.
Author's Defined Keywords: Data Science,
Development, Artifact Management
Turkyilmaz et al. (2020) assessed the context of
SMEs in Kazakhstan and the challenges and
opportunities those companies face with digital
transformation in Industry 4.0.
They identify the key strengths such as flat
organisations, strong entrepreneurial spirit, or quick
responses to market changes. On the other hand, the
authors also identify weaknesses: lack of knowledge
of Industry 4.0, lack of qualified personnel, absence
of well-defined strategy, and limitations/constraints
in resources.
The authors also identify opportunities such as
obtaining support from governments, or entering
global value chains, while facing threats such as a low
level of R&D and lack of proper IT ßor infrastructure.
Author's Defined Keywords: Industry 4.0,
Digitization in SME, Drivers and Opportunities for
SMEs, Challenges of SMEs
Hulla et al. (2021) developed research on some of
the challenges of SMEs (within the Manufacturing
sector) in the context of digitalisation and the
competencies needed.
The authors identified five key challenges: (1)
Lack of strategy/roadmap; (2) Not recognising the
value of digitalisation; (3) Lacking the necessary
digital skills and needed competencies; (4) Lacking
resources; (5) Employees not embracing digital.
The authors have as well, identify a few needed
competencies to improve the results of the
digitalisation: (1) Process Know-How; (2) Recognise
the potential of digitalisation; (3) Define a digital
roadmap; (4) Data analysis; (5) Communication; (6)
Basic knowledge on digital technologies.
Author's Defined Keywords: Digitalization,
manufacturing, production, competency
development, SMEs, learning factories, training.
Wang et al. (2021) investigated how digitalisation
activities, integrated with strategic actions, can help
an organisation in a decline turnaround. Data from
Chinese companies from 2012 to 2019 identified
asset retrenchment, cost retrenchment, and new
products as having a significant impact on turnaround
success. The authors also refer to internal and external
digitalisation as two activities with a moderately
positive impact, with external digitalisation
supporting the positive effects of the relationship
between introducing new products and turnaround
success rate.
Their overall study results fully support the
relevance of digitalisation in accessing knowledge
and information that facilitate the effectiveness of a
company's turnaround.
Author's Defined Keywords: Decline,
Turnaround performance, Knowledge-based view,
digitalisation, Retrenchment action, Strategic action.
In their work, Bouwman et al. (2019) examined
whether SMEs in the digital transformation process
get better results when allocating more resources to
experiment with new business models and strategic
discussions.
This work theoretically contributes to a better
understanding of business model innovation
(experimentation) in the context of digital
transformation, showing that technology-based
dynamic capabilities, with organisational agility,
bring a significant improvement in the company's
competitive performance, as well as that policies are
encouraging SMEs to leverage technology, should
drive the usage of tech such as big data or social
media as a tool to experiment new business models
and rolling out new strategies. Quite a significant
contribution when knowing that new technologies
such as IoT, Artificial Intelligence, or machine
learning will expose SMEs to the need to re-thinking
some of their business models.
Author's Defined Keywords: Big Data, Business
model experimentation, Business model innovation,
digitalisation, SME, social media.
Scuotto et al. (2021), in their research, contribute
to the confirmation of the high degree of relevance of
individual digital capabilities in SMEs' growth and
their innovation. The authors assert that SMEs' ability
to innovate highly depends on employees' digital
capabilities to maximise digital technologies.
Author's Defined Keywords: Digital
Transformation, Individual digital capabilities,
Microfoundations, Labor-intense SME, innovation.
Through the 16 analysed articles, we could
identify more than 25 different keywords, with
Digital Transformation, SMEs, and Industry 4.0
being at the top of the used words (as illustrated in
Figure 2).
The Role of Digital Marketing in Increasing SMEs’ Competitiveness
95
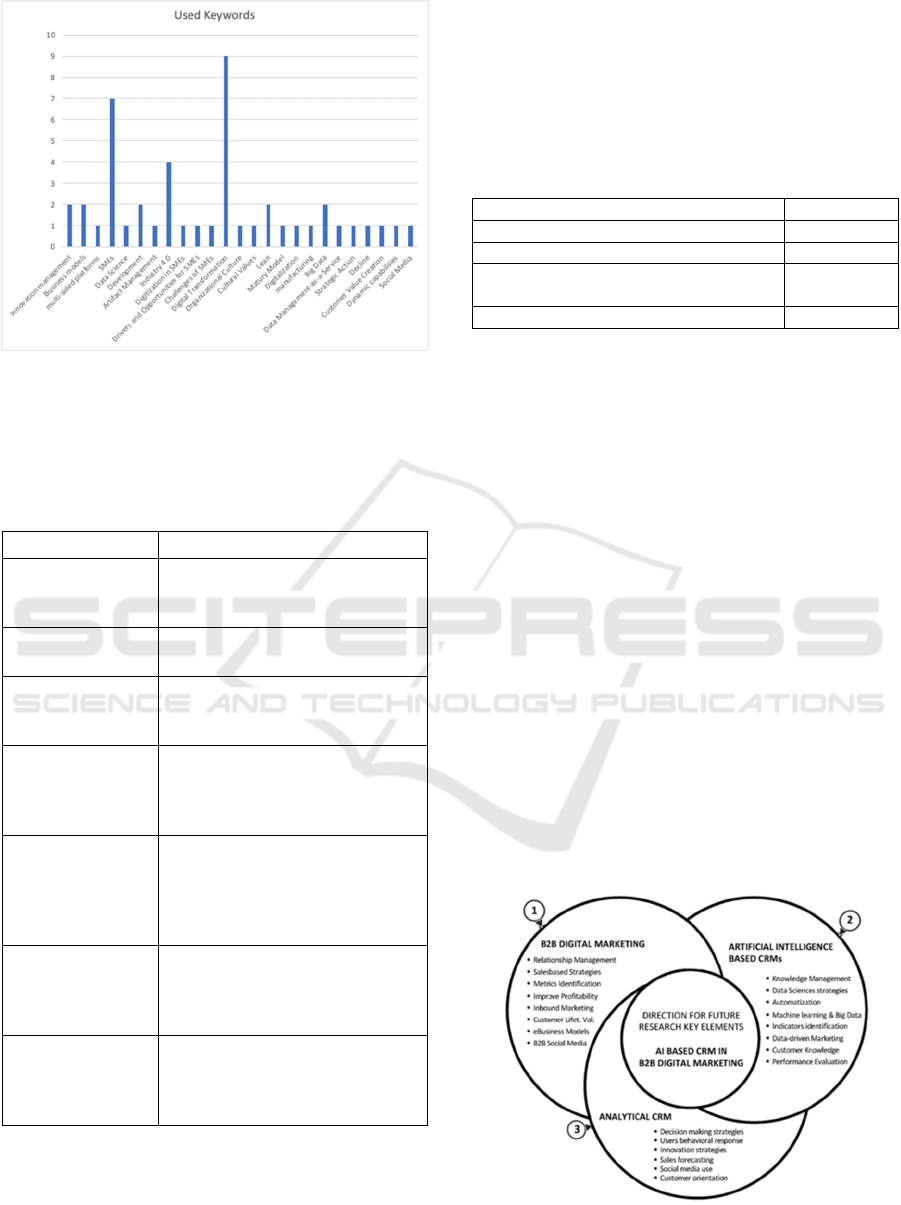
Figure 2: Literature filtering process.
Table 3 summarizes the keywords explicitly used
by the selected authors/articles.
Table 3: Keywords summary of the reviewed articles in
category 1.
Step Results
Daxhammer et al.
(2019)
Innovation Management,
Business Models, Multi-Sided
Platforms
Löcklin et al.
(2021)
Data Science, Development,
Artifact Management
Turkyilmaz et al.
(2020)
Industry 4.0, Digitization in SME,
Drivers and Opportunities for
SMEs, Challenges of SMEs
Hulla et al. (2021)
Digitalisation, manufacturing,
production, competency
development, SMEs, learning
factories, training
Wang et al.
(2021)
Decline, Turnaround
performance, Knowledge-based
view, digitalisation,
Retrenchment action, Strategic
action
Bouwman et al.
(2019)
Big Data, Business model
experimentation, Business model
innovation, digitalisation, SME,
social media
Scuotto et al.
(2021)
Digital Transformation,
Individual digital capabilities,
Microfoundations, Labor-intense
SME, innovation
While we cannot draw any conclusions from the
keywords used, there is a clear pattern in studies in
Industry 4.0, while there are more limited findings in
SMEs outside of that sector (for example, in
services).
3.2 The Technology Developments in
Digital Marketing
For category 2, we have analysed 14 articles and
selected 6, as identified in Table 4.
Table 4: The process of identifying relevant literature for
category 1.
Step Results
1 (search by query string) 196 articles
2 (only > 2018 & only research articles) 137 articles
3 (filter title/abstract “digital
marketing”)
14 articles
4 (filter by relevance after reading it) 6 articles
Cartwright et al. (2021), through a systematic
literature review (SLR), contribute to the
understanding that in the B2C, social media has
emerged as a successful marketing platform, while in
B2B remains to be established at the same level. The
SLR shows that social media channels revolutionize
B2B marketing through strategic platforms in
facilitating sales, integrated communication, and
employee engagement.
This work also highlights the role of organizations
in guaranteeing:
1. Sales employees shall social media
successfully, developing relationships with
customers.
2. Employees play a role in creating and
disseminating content.
3. Employees play an active role in social media
strategy.
Author's Defined Keywords: B2B marketing, social
media, Digital marketing, strategic marketing.
Saura et al. (2021) looked at the main applications
of Artificial Intelligence-based CRMs in B2B Digital
Marketing (summarised in Figure 3).
Figure 3: Summary of characteristics per main uses in AI-
based CRMs in B2B Digital Marketing (Saura et al., 2021).
ICSBT 2022 - 19th International Conference on Smart Business Technologies
96
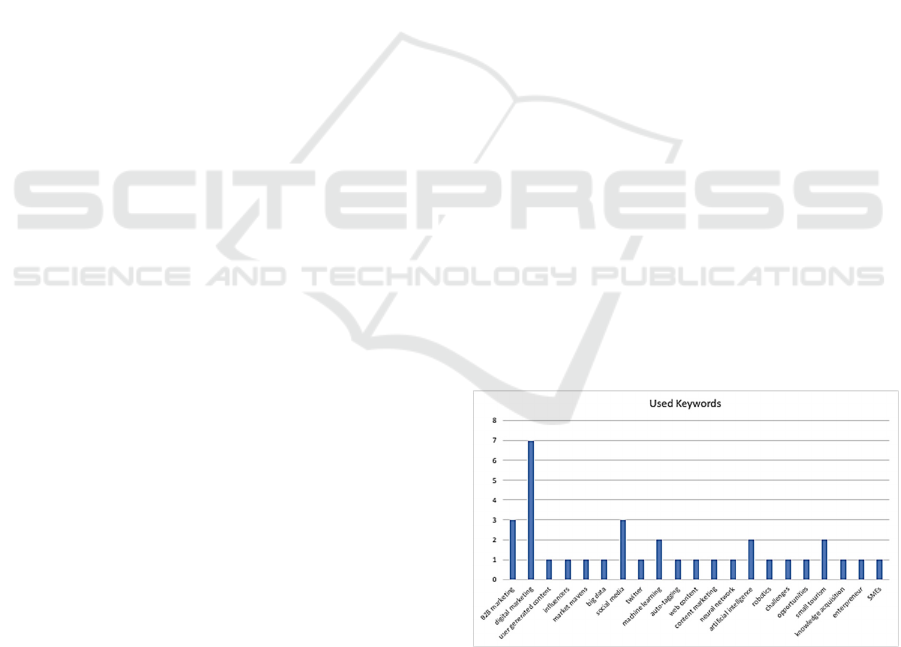
The authors have also identified five research
propositions of relevance:
- "Well-defined B2B digital marketing strategies
using AI-based CRMs would determine success
and growth in marketing."
- "The efficiency of AI-based CRMs in B2B
digital marketing when corporate strategies are
focused on lead generation should be explored."
- "Clearly defined uses of AI-based CRMs in B2B
digital marketing would benefit online brand
building."
- "Well-defined key guidelines and actions to
optimise AI-based CRMs would determine
success in using customer experience/journeys
on B2B digital marketing."
- "Innovation development protocols in B2B
digital marketing when using AI-based CRMs
should be developed, tested, and proposed as
business innovation models. "
Author's Defined Keywords: B2B digital
marketing, Artificial intelligence-based CRMs,
Multiple correspondence analysis
Boddu et al. (2021) analyzed the role of machine
learning, robotics, and artificial intelligence in digital
marketing. Their findings conclude that Artificial
Intelligence has a more significant influence on the
future of marketing. SMEs should make that
adoption, being at greater risk if not getting into that
path. They highlight that companies need solid
foundations in technology, data, processes, and
organization (people, skills, and culture) to maximize
the adoption of these technologies. They also
highlight the positive impact of robots in
collaboration with digital marketeers and machine
learning-driven analytical tools in digital marketing.
Author's Defined Keywords: Artificial
Intelligence, Machine Learning, Digital Marketing,
Robotics, Marketing, Management, Organization.
Salminen et al. (2019) compared three different
state-of-the-art algorithms for tagging online website
content and establishing cross-platform applicability.
They concluded that neural network performs better
for multilabel classification, and the model they
developed was able to perform near to a human-to-
human agreement when applied on YouTube.
Author's Defined Keywords: Machine Learning,
Auto-tagging, Web content, Content marketing,
Neural network, Digital marketing.
Sharma et al. (2020) wanted to explore the use of
digital tools by small travel agencies and their
perceived challenges and motivations.
Within this industry, there is a similar pattern of
the growing relevance of social media; at the same
time, websites and e-email still play a crucial role in
digital marketing. Social Media tools such as
Facebook, WhatsApp, and Instagram as the most
used.
Digital Marketing is seen as an essential piece for
small travel agencies as it allows them to get closer to
the customers and improve engagement. However,
they face challenges, especially fierce competition
security issues (fake profiles, scams, …). Some small
travel agencies avoid the digital channels to protect
the client relationships due to the digital ability to
provide more comprehensive comparison and
benchmarking.
Author's Defined Keywords: Digital marketing,
Small travel agencies, Motivations, Challenges.
Chatterjee & Kar (2020), having the Indian
market as the base, explore the key factors affecting
SMEs' social media marketing and how social media
marketing impacts SMEs. Their research fully
supports the point that social media marketing
positively impacts SMEs' business.
They refer to the exponential growth of social
media marketing adoption within SMEs and how it
positively contributes to their business growth.
They refer to the new technologies such as
"Social-CRM" gaining traction due to capturing
information that enables better interaction with
customers. SMEs adopt this strategy with less
complexity, less cost, and remarkable effectiveness.
Author's Defined Keywords: Digital marketing,
Social media marketing, technology impact, SME.
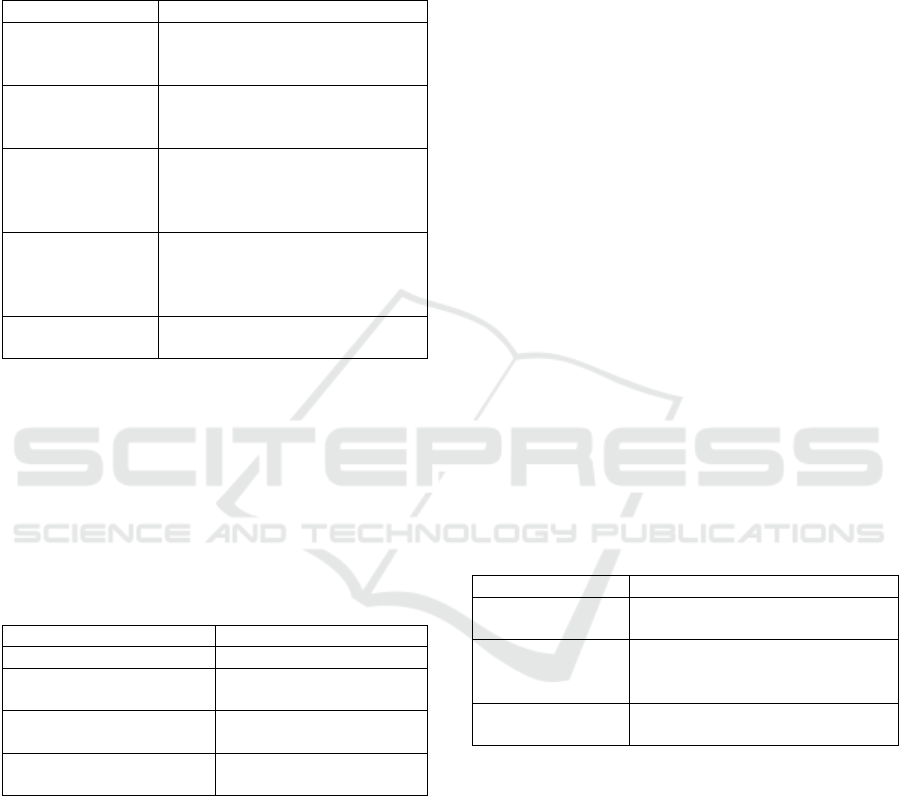
The analysed literature, through 14 articles, does
show a pretty heterogeneous set of keywords (as
illustrated in Figure 4) with a few taking relevances:
Digital Marketing in 7 articles, b2b marketing, and
social media with three articles.
Figure 4: Keywords used in analysed literature of category
2.
While the keywords do not draw any conclusion,
it reflects that digital marketing and social media are
coming together in some of the articles.
The Role of Digital Marketing in Increasing SMEs’ Competitiveness
97
When referring to SMEs, B2B marketing has
been more investigated recently. Table 5 summarises
the keywords explicitly used by the selected
authors/articles.
Table 5: Keywords summary of the reviewed articles in
category 2.
Step Results
Cartwright et al.
(2021)
B2B marketing, social media,
Digital marketing, strategic
marketin
g
Saura et al. (2021)
B2B digital marketing, Artificial
intelligence-based CRMs,
Multi
p
le corres
p
ondence anal
y
sis
Boddu et al.
(2021)
Artificial Intelligence, Machine
Learning, Digital Marketing,
Robotics, Marketing,
Mana
g
ement, Or
g
anization
Salminen et al.
(2019)
Machine Learning, Auto-tagging,
Web content, Content marketing,
Neural network, Digital
marketing
Sharma et al.
(
2020
)
Digital marketing, Small travel
a
g
encies, Motivations, Challen
g
es
3.3 SMEs´ Competitiveness and Digital
Economy
For category 3, we have analysed 22 articles and
selected 1. Additionally, we chose two articles from
category 2 (with a total of 3), as it suits category three
better, as identified in Table 6.
Table 6: The process of identifying relevant literature for
category 1.
Step Results
1 (search by query string) 355 articles
2 (only > 2018 & only
research articles)
187 articles
3 (filter title/abstract
“di
g
ital econom
y
”
)
22 articles
4 (filter by relevance after
readin
g
it
)
1 (plus 2 from category 2)
Through a systematic literature review, Hossain
et al. (2021) assessed the impact of COVID-19 and
some of the strategies followed by SMEs to remain
competitive.
The authors state the relevance of technology and
digital marketing as means for SMEs to survive. They
intensify the critical value of cloud-based
technologies to allow firms to navigate crises while
highlighting the vital importance of digital marketing
to increase SMEs' competitiveness. They state that
"Enterprises that made the best use of the digital
platform through the adoption of technology, digital
marketing, and innovations secured the peak of
success and profitability."
Author's Defined Keywords: SME, SLR
Setkute & Dibb (2022) bring very relevant
research to this field. They highlight some constraints
in rolling out digital marketing in SMEs, especially
limited resources and marketing-related skills.
The work gives a significant contribution to
identifying the more important role that digital
marketing can play in B2B SMEs, especially when
stating that introducing a digital channel is unlikely to
increase sales or competitiveness on its own, and that
is where digital marketing can play an active role
creating that competitiveness.
Author's Defined Keywords: Digital marketing, B2B
marketing, SME marketing, Marketing practice.
Hong et al. (2021) bring an interesting perspective
of the advantages of digital technology to managing
the supply chain as an effective model to improve
communication, coordination, and collaboration
across organizations.
Author's Defined Keywords: Supply chain
platforms, SMEs, platforms
While the initial search identified 22 articles, it
led to a minimal number of articles addressing the
competitiveness factors of SMEs in the digital
economy space.
Table 7 summarizes the keywords explicitly used
by the selected authors/articles.
Table 7: Keywords summary of the reviewed articles in
category 3.
Step Results
Hossain et al.
(
2021
)
SME, SLR
Setkute & Dibb
(2022)
Digital marketing, B2B
marketing, SME marketing,
Marketing practice
Hong et al. (2021)
Supply chain platforms, SMEs,
p
latforms
4 DISCUSSION
Our literature review shows that SMEs have some
advantages, especially in their flexibility and ability
to change faster (Turkyilmaz et al.,2020). On the
other hand, these companies are exposed to their
limitations, especially lacking the needed resources
and strategies (Löcklin et al., 2021; Turkyilmaz et
al.,2020).
Our research also identifies a few behaviors that
might potentially help SMEs to increase their
competitiveness, such as more focus on
ICSBT 2022 - 19th International Conference on Smart Business Technologies
98

experimenting with new business models (Bouwman
et al., 2019), being open to different types of digital-
first models such as multi-sided platform models
(Daxhammer et al., 2019), or still, investing in their
talent and organization, increasing their level of
acceptance and capabilities to the digital technologies
(Hulla et al., 2021; Scuotto et al.,2021; Turkyilmaz et
al.,2020).
The role of digital is not only a step to change the
technology but also a way to increase company
competitiveness (Hossain et al.,2021) or create a
turnaround in their business (Wang et al.,2021).
The role of digital marketing is widely
researched, especially in the space of B2C. This work
also contributes to linking digital marketing to the
competitiveness of SMEs.
We could identify literature that identifies the role
of digital marketing and social media as factors that
support organisations in gaining competitiveness and
improving their relationship with customers
(Cartwright et al., 2021; Chatterjee & Kar, 2020;
Hossain et al.,2021; Setkute & Dibb,2022).
The relevance of digital marketing, significantly
the increase of social media marketing due to its
flexibility and reduced cost (Chatterjee & Kar, 2020),
is also visible in the technological developments we
see happening. Digital marketing is not an only
website and e-mail (Sharma et al., 2020) approach but
somewhat being significantly improved by newer
technologies such as machine learning (Boddu et al.,
2021; Salminen et al., 2019), artificial intelligence
(Boddu et al., 2021; Saura et al., 2021), or even the
platforms like "Social-CRM" (Chatterjee & Kar,
2020). Those technologies are accompanied by
heavier use of social media platforms such as
Facebook, Instagram, or WhatsApp (Sharma et al.,
2020), increasing SMEs' ability to get closer to their
customers and better position their products.
We couldn't find much relevant literature
analysing the position of SMEs in the digital
economy context and how these companies could
remain competitive while competing with new
entrants with potential more advanced technology.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Our research looked at the three different pillars: (1)
SMEs & Digital Transformation success factors; (2)
The technology developments in digital marketing;
(3) SMEs’ competitiveness and digital economy,
being able to identify clear patterns of factors that
influence SMEs to maximise our of their digital
transformation.
We also found relevant literature regarding the
different technologies that positively impact the
efficiency of digital marketing. A relevance is
because digital marketing has been identified as
positively influencing companies' performance.
If we go back to our research question (RQ1), "Is
the digital marketing strategy a well-defined factor in
increasing SMEs' digital economy competitiveness?"
our research couldn't fully answer it.
We found evidence that digital marketing is
indeed a factor in improved performance in SMEs,
which ultimately increases their competitiveness in a
more general form (Cartwright et al., 2021; Chatterjee
& Kar, 2020; Hossain et al.,2021; Setkute &
Dibb,2022), we couldn't though find evidence that
can ultimately put this in the context of the digital
economy. In reality, we could find evidence that
SMEs aren't yet fully embracing newer digital
business models such as multi-sided platforms
(Daxhammer et al., 2019), which could be an
indicator that though digital marketing can help
SMEs in the short term, it might not be enough in the
future if the SMEs products can't compete.
5.1 Limitations
This research work is based on the ScienceDirect
literature, limiting its conclusions. While the
collected literature provides clear evidence, it can't be
considered definitive due to the limitation of the
source database.
5.2 Opportunities for Further
Research
Our research identifies the relevance of digital
marketing for SMEs (Cartwright et al., 2021;
Chatterjee & Kar, 2020; Hossain et al.,2021; Setkute
& Dibb,2022), mainly social media (Chatterjee &
Kar, 2020); there is though, limited research
regarding the execution of digital strategies in SMEs
and how to make it work while facing limitations in
resources (Löcklin et al., 2021; Turkyilmaz et
al.,2020). It would be interesting to investigate further
how to leverage artificial intelligence, machine
learning, or big data to create less resource-heavy and
more machine-based strategies.
REFERENCES
Agnihotri, R., Dingus, R., Hu, M. Y., & Krush, M. T.
(2016). Social media: Influencing customer satisfaction
The Role of Digital Marketing in Increasing SMEs’ Competitiveness
99

in B2B sales. Industrial Marketing Management, 53,
172–180.
Barann, B., Hermann, A., Cordes, A. K., Chasin, F., &
Becker, J. (2019). Supporting digital transformation in
small and medium-sized enterprises: a procedure model
involving publicly funded support units. In Proceedings
of the 52nd Hawaii International Conference on
System.
Bouwman, H., Nikou, S., & de Reuver, M. (2019).
Digitalisation, business models, and SMEs: How do
business model innovation practices improve
performance of digitalising SMEs?
Telecommunications Policy, 43(9).
Cartwright, S., Liu, H., & Raddats, C. (2021). Strategic use
of social media within business-to-business (B2B)
marketing: A systematic literature review. Industrial
Marketing Management, 97, 35–58.
Chatterjee, S., & Kumar Kar, A. (2020). Why do small and
medium enterprises use social media marketing and
what is the impact: Empirical insights from India.
International Journal of Information Management, 53.
Daxhammer, K., Luckert, M., Doerr, M., & Bauernhansl, T.
(2019). Develop a strategic business model framework
for multi-sided platforms to ensure sustainable
innovation in small and medium-sized enterprises.
Procedia Manufacturing, 39, 1354–1362.
Giotopoulos, I., Kontolaimou, A., Korra, E., & Tsakanikas,
A. (2017). What drives ICT adoption by SMEs?
Evidence from a large-scale survey in Greece. Journal
of Business Research, 81, 60–69.
Guesalaga, R. (2016). The use of social media in sales:
Individual and organisational antecedents, and the role
of customer engagement in social media. Industrial
Marketing Management, 54, 71–79
Hong, J., Guo, P., Deng, H., & Quan, Y. (2021). Adopting
supply chain service platforms for organisational
performance: Evidence from Chinese catering
organisations. International Journal of Production
Economics, 237.
Hossain, M. R., Akhter, F., & Sultana, M. M. (2022). SMEs
in Covid-19 Crisis and Combating Strategies: A
Systematic Literature Review (SLR) and A Case from
Emerging Economy. Operations Research
Perspectives, 9, 100222.
Hulla, M., Herstätter, P., Wolf, M., & Ramsauer, C. (2021).
Towards digitalisation in production in SMEs - A
qualitative study of challenges, competencies and
requirements for trainings. Procedia CIRP, 104, 887–
892.
Lemon, K., & Verhoef, P. (2016). Understanding customer
experience throughout the customer journey. Journal of
Marketing, 80(6), 69–96.
Loebbecke, C., & Picot, A. (2015). Reflections on societal
and business model transformation arising from
digitisation and big data analytics: A research agenda.
The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24(3),
149–157.
Löcklin, A., Vietz, H., White, D., Ruppert, T., Jazdi, N., &
Weyrich, M. (2021). Data administration shell for data-
science-driven development. Procedia CIRP, 100,
115–120.
Matarazzo, M., Penco, L., Profumo, G., & Quaglia, R.
(2021). Digital transformation and customer value
creation in Made in Italy SMEs: A dynamic capabilities
perspective. Journal of Business Research, 123, 642–
656.
Prause, M. (2019). Challenges of Industry 4.0 technology
adoption for SMEs: The case of Japan, Sustain. 11.
Ramukumba, T. (2014). Overcoming SMEs Challenges
through Critical Success Factors: A Case of SMEs in
the Western Cape Province, South Africa. The
University of Ljubljana, 16(1), 19–38.
Rapp, A., Beitelspacher, L. S., Grewal, D., & Hughes, D.
E. (2013). Understanding social media effects across
seller, retailer, and consumer interactions. Journal of
the Academy of Marketing Science, 41(5), 547–566.
Saura, J. R., Ribeiro-Soriano, D., & Palacios-Marqués, D.
(2021). Setting B2B digital marketing in artificial
intelligence-based CRMs: A review and directions for
future research. Industrial Marketing Management, 98,
161–178.
Salminen, J., Yoganathan, V., Corporan, J., Jansen, B. J., &
Jung, S. G. (2019). Machine learning approach to auto-
tagging online content for content marketing efficiency:
A comparative analysis between methods and content
type. Journal of Business Research, 101, 203–217.
Sarath Kumar Boddu, R., Santoki, A. A., Khurana, S.,
Vitthal Koli, P., Rai, R., & Agrawal, A. (2021). An
analysis to understand the role of machine learning,
robotics, and artificial intelligence in digital marketing.
Materials Today: Proceedings.
Schultz, R. J., Schwepker, C. H., & Good, D. J. (2012). An
exploratory study of social media in business-to-
business selling: Salesperson characteristics, activities,
and performance. Marketing Management Journal,
22(2), 76–89.
Sharma, A., Sharma, S., & Chaudhary, M. (2020). Are
small travel agencies ready for digital marketing?
Views of travel agency managers. Tourism
Management, 79.
Setkute, J., & Dibb, S. (2022). "Old boys' club": Barriers to
digital marketing in small B2B firms. Industrial
Marketing Management, 102, 266–279.
Taiminen, H. M., & Karjaluoto, H. (2015). The usage of
digital marketing channels in SMEs. Journal of Small
Business and Enterprise Development, 22(4), 633–651.
Turkyilmaz, A., Dikhanbayeva, D., Suleiman, Z.,
Shaikholla, S., & Shehab, E. (2020). Industry 4.0:
Challenges and opportunities for Kazakhstan SMEs.
Procedia CIRP, 96, 213–218.
Wang, J., & Bai, T. (2021). How digitalisation affects the
effectiveness of turnaround actions for firms in decline.
Long Range Planning.
ICSBT 2022 - 19th International Conference on Smart Business Technologies
100
