
Discussion on the Construction of Public Security Data Management
Capability Maturity Model
Qianqian He and Lin Jiang
Chongqing Medical and Pharmaceutical College, Chongqing, China
Keywords: Public Security Data, Management Ability, Maturity Model, Construct Strategy.
Abstract: At present, in the research process of security data management capability maturity model, the research work
of data management process is mainly completed. At the same time, it is necessary to fully grasp the research
status and application of the public security data management capability maturity model, analyze the
characteristics of the maturity model, and construct the public security data management capability maturity
model according to the specific types of public security data. We can use the capability maturity model to
effectively evaluate various problems in the process of public security data management, which is of great
help to improve the public security data management capability.
1 INTRODUCTION
As a new interdisciplinary subject, public security
data management involves a lot of contents in the
research process. The main purpose is to explore the
specific needs of public security governance activities
in information space in physical space and social
space, and to analyze the laws and characteristics of
public security data. We should use the knowledge of
data science and public security to fuse the data
problems in public security governance activities, pay
attention to the management of public security data
itself, and dig deep into the application value of data
in public security governance. Effective data
management generally requires long-term
management planning, and at the same time, it is
necessary to use corresponding management
activities at appropriate nodes to carry out
collaboration among personnel, institutions,
resources and key events. In this management
process, the data management model is an important
bridge connecting management strategy and
management practice, and plays a fundamental role.
Based on the related research contents in the field of
scientific data management and government data
management, the related models of data management
have been put forward, and the data management
infrastructure model and data management capability
maturity model have been formed. These typical
models can play a visual role in the application
process, clarify the complex process of data
management, and decompose the data management
process into different stages. They can identify and
explain the roles of participants, responsibilities of
management activities, processes, important events
and other key elements in different stages. Through
effective data management activities, the
corresponding model can also be optimized.
2 RESEARCH SIGNIFICANCE OF
PUBLIC SECURITY DATA
MANAGEMENT CAPABILITY
MATURITY MODEL
Under the background of continuous social
development and change, the public security situation
is becoming more and more complicated, and
traditional security accidents are characterized by
frequent occurrences and non-traditional security
threats, which will seriously affect social stability and
the level of economic development. From data
production to data analysis, it is necessary to carry out
data analysis and collation based on the demand of
security public decision. We should realize that this
process has the characteristics of long-term and
complexity, and the level of public security data
management can be improved through reliable data
information. In the process of developing and
managing public security data, it is necessary to
strengthen government regulation and guidance, and
He, Q. and Jiang, L.
Discussion on the Construction of Public Security Data Management Capability Maturity Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0011343900003437
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2021), pages 321-326
ISBN: 978-989-758-589-0
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
321
fully tap the application value behind public security
data.
In 2015, China has put forward an action plan to
promote the development of big data, and different
provinces and cities in China are also carrying out big
data management according to the corresponding
plan. In the concrete work, we need to sort out the
public data and strengthen the data quality
management and research work. Building a unified
data management platform can improve the
efficiency of data sharing and play a certain role in
ensuring the comprehensive utilization rate of public
data. We need to pay attention to the scientific and
reasonable public security data management
mechanism according to the specific regional
characteristics in the process of public security data
management. Because of the different economic
bases in different regions, there are some differences
in the cognition of public security data management.
At present, China has not formed a unified path and
goal for the development of public security data
management, nor has it scientifically evaluated the
level of public security management, which leads to
the inability of relevant departments to optimize and
adjust relevant mechanisms according to the situation
of public security data management, and to a certain
extent, affects the formulation and implementation
effect of data management plans and solutions. In this
research process, we mainly analyze the capability
maturity model, and discuss the specific application
value of the capability maturity model in the process
of public security data management. Structured data
management plays a prominent role in determining
the evaluation method of public security data
management capability, which can provide clear
management capability improvement goals and
directions for government departments and related
institutions(Ye 2015).
3 CHARACTERISTICS OF
CAPABILITY MATURITY
MODEL
When building the capability maturity model of
public security data management, it is necessary to
fully grasp the characteristics of the capability
maturity model. The primary function of capability
maturity model is to evaluate the management
capability in the process of software development.
After the capability maturity model is put forward, its
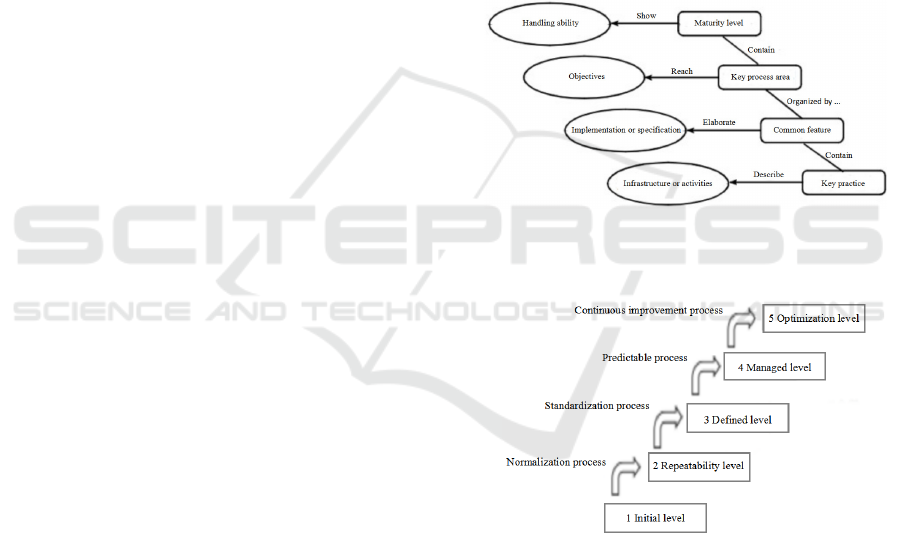
basic structure remains unchanged (Figure 1), which
mainly includes key process areas, specific
objectives, specific practices, common objective,
common practice, common features and capability
levels (Xiong 2020). Among them, the key process
area is the problem that must be solved when realizing
the management goal. The original capability
maturity model consists of 22 key process areas, and
specific objectives and practices refer to specific
objectives and practices in a key process area.
Common objectives and common practices can be
applied in several key process areas. Each key process
area is organized according to public attributes,
including implementation regulations,
implementation capabilities, implementation
activities, measurement and analysis, and
experimental verification. In the research process of
capability maturity model, it includes five steps as
shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the capacity maturity
structure.
Figure 2: Capacity maturity model ladder.
4 ANALYSIS OF PUBLIC
SECURITY DATA TYPES
Public security data refers to all kinds of data
generated in the process of public security
governance. Generalized public security data
includes all kinds of data in all public security fields.
The main function of public security data is to reflect
the concrete phenomena of public security
governance activities, and to obtain the characteristics
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
322

and laws of public security governance activities from
various data, so as to optimize and improve the
corresponding management decisions. The main
characteristics of public security data are huge
amount of data, low application value density,
diversification and obvious big data characteristics.
At present, there is no unified classification standard
for public security data, because the amount of public
security data is relatively large, and there are public
security data in different industries, different
organizations and different data terminals.
When studying public security data, there will be
some differences in the definitions of different
researchers: (1) Researchers think that the public
security data of cities mainly include different
categories of urban public basic data, social situation
and public opinion data, physical environment and
disaster monitoring data, urban operation data,
departmental business data, human behavior data,
emergency handling data and public security
knowledge data. Different categories cover different
types of specific data. (2) Some researchers directly
divide urban big data into sensor system data, user-
generated data, government data, private sector data,
art and humanities data and other mixed data. (3)
Some researchers believe that public security data
simply refers to national security big data. These data
are distributed in the information space, physical
space and social space where people and things are
highly integrated in various complex correlation
forms(Sun 2019).
Because public security in a broad sense refers to
all external environments and orders related to social
life security, including environmental security, public
health security, economic security, information
security, food security, production security, workplace
security and so on. The data generated in these fields
are all public security data. In this research, it is
necessary to scientifically evaluate the maturity of
public security data management ability from the
commonality of data in different security fields.
Public security data is mainly a mixed
environment formed by the integration of Internet,
communication network and sensor network,
including physical space, social space and virtual
network coupling space. The data spaces stripped
from these spaces can all be called public security data
spaces. Physical objects in space are the main carriers
of public security data, including data of key
infrastructure, road traffic structure and semi-
structured infrastructure, as well as unstructured
multimodal data such as environmental physical
parameters and videos sensed by large-scale sensing
devices in human living space. In addition, individuals
and organizations in social space are also the main
producers of public security data, including basic
demographic data, individual or group personality
characteristics, emotional representation, cognitive
decision-making and other psychological data and
behavioral data. Virtual network coupling space refers
to the data generated in the overlapping coupling of
network space, physical space and social space. The
main carrier of these data is the Internet or mobile
terminal devices, including data and information risk
data processed by basic networks and different types
of application systems in information construction, as
well as some unstructured and semi-structured data
such as news reports, forum posts and blog posts.
In a word, the sources of public security data are
complex and the number is huge, and its obvious
feature is that the data of different industries have
strong connections. Because the public security
governance activity itself is continuous, it determines
that the generation and acquisition of public security
data have strong continuity. For example, the business
systems of government departments will constantly
update the corresponding data. In addition, public
security data are complex, diverse and interrelated.
The data of different fields, different sources and
different structural types are relatively large in scale
and growing at a relatively fast rate. There is a certain
connection between public security data of different
fields, and public security governance activities
involve different departments, industries and fields.
Therefore, the generated public security data also have
obvious correlation. Public security data involves a
wide range of subjects, and the production
management and use of public security data involve
different participants such as government
organizations, enterprises, the public and researchers.
These data characteristics determine that the
management of public security data is extremely
complex and difficult.
5 CONSTRUCTION OF PUBLIC
DATA MANAGEMENT
CAPABILITY MATURITY
MODEL
5.1 Model Design
When building the maturity model of public security
data management capability, we must clearly grasp
the public security data management practice and key
practice processes. Based on this, the key process area
can ensure the effectiveness of the maturity model of
Discussion on the Construction of Public Security Data Management Capability Maturity Model
323
public security data management capability, and
based on the maturity model, the level of public
security data management capability can be
scientifically divided. In CNKI, database data
supervision, data guarantee, data fusion and so on
should be used as key words to search for literature.
When searching documents, we should eliminate the
data with low correlation with public security data,
such as medical, financial and energy data, and
identify and sort out the documents highly related to
public security data management. After importing the
identified files into Nvivo software, extract and
encode the data. There are inconsistencies in the
codes, which need to be discussed in groups to
determine the final result. Data management practice
extraction is the key content that must be paid
attention to in the coding process. When extracting
data management practice, it is necessary to combine
similar contents, organize data management practice
into key practice processes, and form key process
areas based on key practice processes. In order to
ensure the application effect of the public security
data management capability maturity model, when
designing the model, we should bring the key
practices and key process areas into the model index
system and carry out the grading work. In this study,
it is necessary to explain the levels of capability
maturity, and accurately describe the characteristics
of different key process areas in each level to form the
classification of public security data management
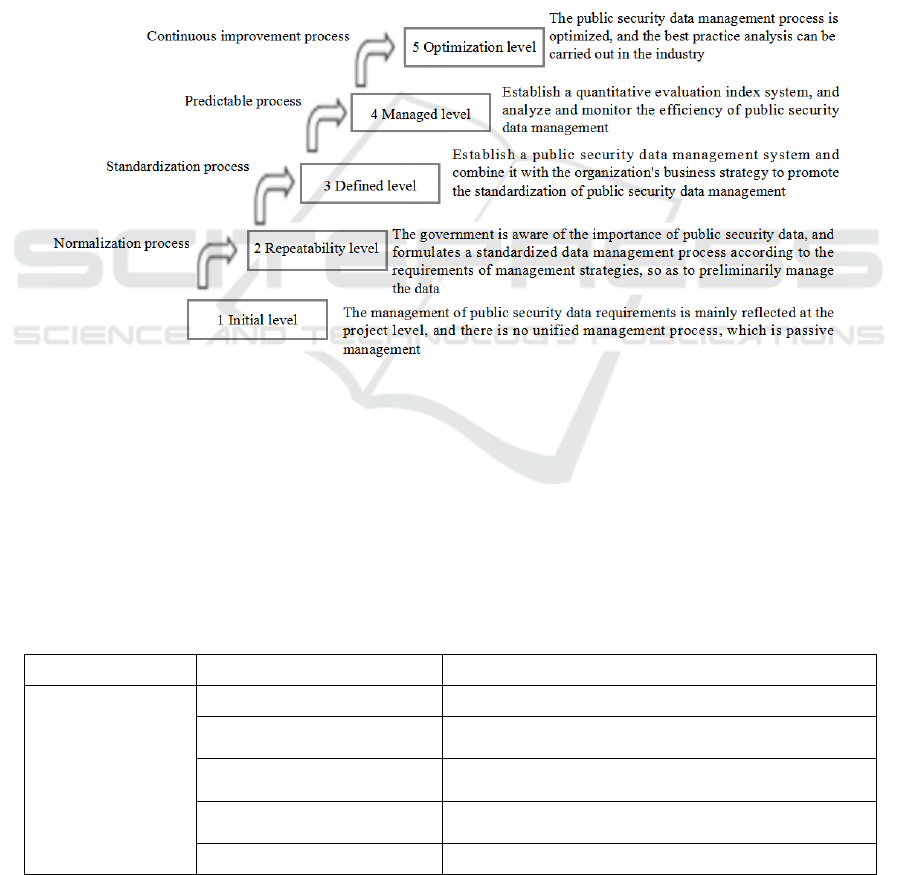
maturity levels, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Schematic diagram of the public security data management capacity maturity level classification
5.2 Management Process and Practice
Construction
In the design of key process areas and key practices
of public security data management, we can use
Nvivo files for coding, summarize the key practices
of public security data management capabilities, and
combine similar practices to obtain integrated data.
According to the goal of key practice, four key
process area indicators can be determined, such as
data acquisition and quality control, data classified
storage and security management, data mining and
analysis, data opening and sharing. In the specific
process of information extraction and mining, it is
necessary to know about researchers and research
years, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Key process areas and key process research years and researchers.
Key process areas Key process Research years and researchers
Data acquisition and
quality control
Clear data source 2010 Zhao Chunyan, 2014Wen Bowei
Determine the data acquisition
metho
d
2012 Chen Beiqing, 2014 Tian Yuchi, 2016 Hu Yu
Determine the data collection
s
p
ecifications
2014 Wang Ting, 2018 Yang Jiangyong
Data acquisition
2008 Dong Rencai, 2014 Wang Ting, 2018 Yang
Jiangyong, Li Guanhua
Data quality management 2015 Li Weibin, 2018 Yang Jiangyong
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
324
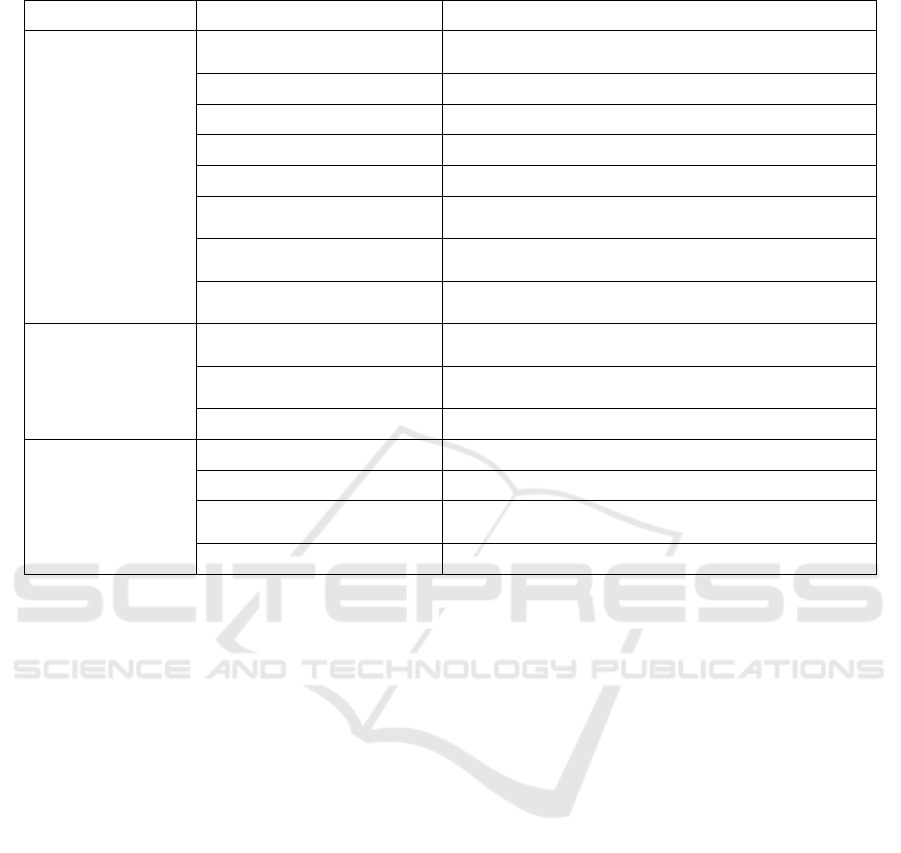
Table 1: Key process areas and key process research years and researchers (cont.).
Key process areas Key process Research years and researchers
Data classification,
storage, and security
management
Establish a data storage
p
latfor
m
2012 Du Hongyue, 2016 Hu Yu, Jin Hui
Data preservation 2013 Liu Jun, 2015 Wang Weibin, 2016 Hu Yu
Data security management 2013 Liu Jun, 2014 Tian Yuchi, 2018 Yang Jiangyong
Authorization management 2005 Xu Yonggang, 2016 Hu Yu, Zhang Shuai
Data backup 2005 Xu Wei, 2014 Zheng Xiufen
Data maintenance and update
2010 Zhao Chunyan
2016 Hu Yu, 2018 Li Guanhua
Determine the data standard
system
2015 Li Xiaohong, Wang Weibin, 2016 Hu Yu, 2017 Wu
Xianhua
Data classification
2010 Zhao Chunyan, 2015 Jin Hui, 2016 Zhang Shuai, Hu
Yu
Data mining and
analysis
Clear the data usage
re
q
uirements
2015 Deng Lan
Data analysis
2012 Du Hongyue, 2015 Wang Weibin, 2017 Wu
Xianhua, 2018 Yang Jiangyong
Visualization processing 2011 You Hong, 2013 Hu Pian, 2014 Wen Bowei
Data opening and
sharing
Fusion data 2008 Dong Rencai, 2014 Wen Bowei, 2017 Wu Xianhua
Build a shared platform 2010 Zhao Chunyan, 2012 Du Hongyue
Develop a data sharing
mechanis
m
2010 Zhao Chunyan, 2012 Du Hongyue
Complete data sharing 2014 Wen Bowei, Wang Ting, 2016 Hu Yu
5.3 Maturity Construction of Public
Security Data Management
Capability
After obtaining the key process areas, it is necessary
to build a maturity model of public security data
management based on the key process areas. Based
on the maturity level of capability maturity model, it
is considered that the practice of public security data
management, through temporary management to fine
planning, is constantly improving the formation
system in China. The characteristics of different key
process areas are different with different maturity
levels. First, in the initial stage, the public security
management system is relatively scarce, and the
whole management process has not been
scientifically defined, nor has a unified standard
management process been formulated. Public
security data is in a disorderly situation, with data
islands and low data utilization rate. Second, in the
repeatable stage, it has been possible to establish
basic system and procedural standards according to
public security data management. In addition, it is
necessary to optimize and adjust the data
management process based on the current situation of
public security data management, which improves the
standardization level of data management to a certain
extent, can carry out public security data management
according to certain rules and standards, and can meet
specific needs and ensure the application effect of
public security data. Third, the level has been defined.
This means that the public security data management
process is relatively perfect. In the process of public
security data management, its standardization is
relatively strong, and a data demand response
mechanism that can meet the requirements of public
security data management has been formed, which
can ensure that the public security data management
can meet the specific needs. Fourth, the management
stage. To determine the relevant indicators of public
security data management, and to ensure the quality
and efficiency of public security data management. At
this stage, the public security data management
mechanism is also relatively perfect, and the public
security data analysis model base has been
completed, and research and analysis work can be
carried out according to the public security data
management work. Comprehensive analysis of public
security data can quantify the analysis results of
public security data, thus supporting public security
management decision-making. Fifthly, in the
optimized stage, the public security data management
has a standardized process, and the management
quality is guaranteed. In addition, with the increase of
Discussion on the Construction of Public Security Data Management Capability Maturity Model
325

data utilization rate, data fusion and analysis can be
carried out in time according to the specific situation
of public security data, especially when dealing with
public crisis events, and its response speed is
relatively fast(Niu 2019).
5.4 Model Application
In the construction of public security data
management capability maturity model, it is
necessary to base on the specific situation of public
security data management in China. Comprehensive
research on key process areas such as key practices,
data acquisition quality control, data mining and
analysis, data opening and sharing, data classification
and storage, and security management, etc., and use
this as the main index to complete the construction of
public security data management capability maturity
model. After the completion of the construction, the
maturity level should be scientifically divided, and its
value is prominent in the process of model
application, mainly in the following aspects: First, the
maturity model of public security data management
capability can be used to scientifically evaluate public
security data management capability, and provide
more scientific and perfect data support and
corresponding information services for the
formulation of public security data management
scheme. In the application process of the model, key
process areas and key practices are important
indicators when establishing the model. Government
agencies or related organizations can make use of the
public security data management capability maturity
model to deeply analyze the situation of public
security data management, compare it with the
indicators in the model, and master the effect of
public security data management capability based on
the level division of the capability maturity model,
which can make relevant government agencies and
organizations clear the shortcomings in the process of
public security data management, and help promote
the healthy development of public security data
management. Secondly, the application of the model
can improve the standardization of public security
data management. The development stage defined in
the model itself belongs to the continuous
management promotion process, while different
organizations carry out data security management
based on the model, and take different development
stages as the main criteria for data management
planning of public security, which is conducive to
ensuring the standardization of data security
management. Third, we can compare and analyze the
quality of public security data management in
different institutions. For example, when evaluating
the public security data management capabilities of
different county and city governments, we can use the
key practice areas as the reference benchmark, and
through horizontal comparison and analysis, make the
institutions with low capabilities learn from those
with higher capabilities (Zhou 2020).
6 CONCLUSIONS
To sum up, the construction of public security data
management capability maturity model can provide
perfect information services for the government and
related organizations in public security data
management to a great extent. The key practices and
key process areas put forward in the application of the
model are important contents to ensure that the
capability maturity model can fully play its role.
However, in the application and research process of
this model, it is still in the preliminary exploration
and research stage, and more attention is paid to the
data creation process in the application of this model.
This requires an in-depth analysis of the current
situation of public security data management and
continuous improvement and optimization of the
capability maturity model according to the actual
capabilities of public security data management, so as
to provide more reliable information support for the
improvement of public security data management
capabilities.
REFERENCES
Niu, Chunhua, Wu, Yanyan, Liu, Hongbing. (2019).
Construction of Public Data Management Capability
Maturity Model.Library & Information,(4):7.
Sun, Hui, Wu, Ting. (2019). Security Management of
Government Sensitive Data Assets. 2019 National
Symposium on Public Security Communication.
Xiong, Yachao. (2020). Research on the Maturity and
Improvement Strategy of Urban Residents' Public
security Cognitive Ability.China University of Mining
and Technology.
Ye, Lan. (2015). Analysis of Data Management Capability
Maturity Model.Document,Information & Knowledge,
(2):9.
Zhou, Linxing, Han, Yongji. (2020). Research on the
Maturity Model Construction of Data Security
Governance Capability.CHINA ARCHIVES,
No.566(12):68-68.
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
326
