
Community Resilience Assessment under Public Health Emergencies:
Based on Collaborative Governance
Yixi Wang and Zixiao Li
a
Department of Assets Appraisal, Sichuan Agricultural
University, Chengdu, China
Corresponding author: 1402407361@qq.com
Keywords: Public Health Emergencies, PSR Model-Entropy Method, Community Resilience Assessment, Collaborative
Governance.
Abstract: This paper
embeds collaborative governance
into the
community resilience study of normalized prevention
and control of public health emergencies. Taking the typical epidemic prevention and control community
in Chengdu as the research unit,
Drawing on
the PSR model
and constructing the community resilience
evaluation
system embedded in collaborative
governance, using the entropy method to quantify the
resilience
level of the sample communities at the beginning of 2020, the end of 2020, and
the middle of 2021,
then exploring the evolution of the resilience of the original Covid-19 infected communities in the post
epidemic period, proposing feasible paths and improvement strategies for optimizing community resilience
embedded in collaborative governance.
The results show that: During the study period, the resilience
fluctuation of most sample communities shows a trend of "rising first and then decreasing" or "falling first
and
then rising". The resilience of a small number of communities fluctuates slightly. Overall, 19 sample
communities in Chengdu have
improved
to
a certain extent.
1 INTRODUCTION
The
mutation of COVID- 19 in 2021 warns
mankind
to
face the
persistent challenges
and threats of
the
epidemic. The
normalization prevention
and control
of public
health emergencies represented by the
epidemic situation of infectious
diseases have
become the
top priority of
social governance. As the
basic
unit of social governance, the community is
the first position of "defense
from the outside and
rebound
from the inside". At
the
same
time, as
micro-
level
social
governance, community governance has
the
internal requirements of
collaborative
governance. (Hu, 2016) Facing the
escalation of
epidemic challenges, how to
promote
the formation
of
collaborative governance
patterns, improve the
ability of
the
community in
resilient governance, and
improve the resilience of
human society
in the face
of public health
emergencies has become the key link
to
deal with
public
emergencies
in
China.
As
the focus
of
social
governance
shifts
downward, community resilience has gradually
become the
frontier of
social system research. In the
a
http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9979-9251
earliest
research
on
community resilience,
community resilience
is "the
ability of the system
to
respond
to external shocks
and
still
maintain its
main
structure and function
in
the event
of a crisis".
(Holling, 1973)
At
the
beginning of the
21st
century,
K Magis extended resilience to the adaptability, self-
organization and learning
capabilities of
the
community, and
paid more attention
to the role
of
multi-party
collaboration in crisis
response. (MAGIS,
2010) In
recent research, Lan
Yuxin, a Chinese
scholar, defined
community
resilience
as
"the ability
of communities to
actively respond to risk
disturbances and obtain
more sustainable
capabilities
in the
future through
adaptive
and stress
response".
(LAN, Zhang. 2020).
Collaborative governance under public crisis
means
that with
the support
of
information
technology, the government, social organizations,
enterprises, individual
citizens and
other social
elements participate in cooperation and coordination,
and
take
a series of
control actions
at different
stages
of
crisis development
for
potential
and current
crises,
in
order to effectively
prevent, handle and
138
Wang, Y. and Li, Z.
Community Resilience Assessment under Public Health Emergencies: Based on Collaborative Governance.
DOI: 10.5220/0011342900003437
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2021), pages 138-145
ISBN: 978-989-758-589-0
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

eliminate crises, Finally,
the purpose
of
safeguarding
and
promoting
public interests
to
the
greatest
extent
is achieved. (He, 2008)
Among them,
collaborative
governance includes
three types:
collaboration between governments, the
collaboration between governments
and civil society,
and collaboration between civil
society.
(Sha, Xie.
2010).
Since
the outbreak of COVID- 19,
there has
been
an
explosive
growth
trend in the
study of public
emergencies. Combining
resilience
theory and
collaborative
governance theory has become a new
research direction. However, there are
currently few
empirical
studies
focusing
on
resilience
under
collaborative governance, and
the
integration
of
collaborative governance
theory
into
the
construction
of community
resilience needs further
research.
On
the basis
of
comprehensive
previous studies,
this
paper takes the
typical epidemic prevention
communities in Chengdu as
the
research object.
Collect data from the beginning of 2020, the end of
2020, and the middle of 2021,
and
build
a resilience
evaluation index system under collaborative
governance
from three aspects: pressure,
state,
and
response
to the disturbance
of public
health
emergencies. Analyze
the evolution
process
of
community resilience
embedded
in
collaborative
governance, and
propose an optimized
path for
resilient
community
governance
under the
disturbance
of public
health
emergencies.
2 SURVEY OF RESEARCH
OBJECTS
From the outbreak of the COVID-19 epidemic in early
2020 to August 2021,
Chengdu has encountered
three rounds
of
epidemics at
the
beginning of 2020,
the end of
2020,
and
the middle of 2021. Therefore,
this paper takes all
the
communities in Chengdu
that
have been
disturbed
during
the study period
as
empirical objects
to explore the
timing evolution
of
community resilience in response to public health
emergencies, and
then explore
the process
of
community governance embedded in collaborative
governance. There
are
19
sample communities,
specifically: Lianhua Community,
Shuangbai
Community,
Shuanglin
Community,
Wangping Street
Community, Wangcong
Community, Gaodian
Community,
Jindu
Community,
Pengzhen Guangrong
Community, Yifu
Community,
which
were disturbed
by
the epidemic in
early 2020 Communities,
Tiaodenghe
Community,
Taiping
Village, Yong'an
Village, Pineapple Community,
Jinqiao
Community,
Xichi Community, Babuqiao
Community
that
were
disturbed by
the
epidemic
at
the
end
of
2020,
Qingshuihe Community, Shengxing
Community,
Americas
Garden Community that
were
affected by
the epidemic in
2021 Garden community.
3 DATA AND EVALUATION
METHOD
3.1 Data Source
The data used in this paper are
set
in three-time
gradients: at the beginning
of 2020, the end of 2020,
and the middle of 2021. The data used to establish the
indicators were
obtained
from the government
websites such as
the
Chengdu
Municipal
Comprehensive
Service Supervision Platform for
Grassroots Publicity,
the
Chengdu
Municipal
Public
Enterprises,
and Institutions Office Disclosure
Platform,
the official
website
of the
Chengdu
Municipal
Health
and Health
Commission,
the
official
website of the Chengdu
Municipal
Bureau
of
Statistics, the official websites of the people's
governments of each district and
their communities,
as
well
as
the residents'
questionnaires and
the
offline
interviews with community party-mass
service centers and
community hospitals.
3.2 Construction of Index System
The PSR model
consists of three types
of
indicators:
pressure,
state, and
response.
This
paper
uses
the
PSR
model to decompose the community resilience,
and combines the resilience assessment
model and
the collaborative governance model
to
construct a
community resilience assessment
index system
from
the perspective of
public health
emergencies,
which
then
reflects
its
collaborative governance
ability in
response to
public
health emergencies.
Based
on this, this paper defines "stress
resilience" as
the community
system, especially
the
governance
system,
is
adversely affected
by
public health emergencies and
may
be harmed,
"state resilience"
as the situation and
development
direction
of community system, especially
community governance system, in resisting public
health emergencies, and "response resilience"
as the
ability
of
communities
under
collaborative
governance to prevent public health emergencies,
mitigate
damage, and recover from adaptation.
Community Resilience Assessment under Public Health Emergencies: Based on Collaborative Governance
139

The community
resilience evaluation
index
system
constructed
in
this
paper refers
to
the
assessment framework and indicators of
community
resilience
and
collaborative
governance at
home
and abroad,
and
finally identifies eight specific
indicators at the domain level:
"stress resilience"
includes
environmental and
demographic
risks,
reflecting the impact
on the
community
in the
face
of
public health
emergencies. it
reflects
the
impact
of
community
response to public health
emergencies. The "state
resilience"
includes medical
resource status, the
state of medical
resources,
socio-economic
state, and
community
organization
state, reflecting the
current situation of community
governance
system
reflecting the development
of
the
community
governance
system;
the "response
resilience" is influenced by early warning
capability,
recovery
capability,
and learning and
adaptive
capability, reflecting the
community
governance
system's
ability to respond to public
health
emergencies.
The factors
of "response
resilience" are
early warning
capacity,
recovery
capacity,
and
learning
adaptation
capacity, which reflect the
ability of the community governance system
to
mitigate
shocks in response to
public health
emergencies.
Based on
the
characteristics of
each
domain and
the actual situation
of the sample
communities,
we determines
the
specific indicators
of 24 index layers
and finally
constructed
the
community resilience
assessment
index
system
embedded
in collaborative governance.
3.3 Determine the Weights of
Indicators at All Levels
3.3.1 Measurement Method
Selection-entropy Method
Based
on the community resilience evaluation
index
system of this paper,
to
quantitatively evaluate
the
resilience
level of sample communities
with
multiple
indicators,
it
is
necessary to unify
the units and
dimensions of
each evaluation index, and
standardize the data. The determination of the index
weight will directly affect the
accuracy
of the
evaluation results. Therefore,
the entropy
method
in
the objective
weighting
method
is
used to determine
the index
weight.
3.3.2 Construct the Original Matrix
Construct
a
matrix of
19 (community
samples)
*
24
(indicators). Record
the
value
of
the
jth
index of
the
i-th community
as a formula.
3.3.3 Data Standardization Processing
Since the measurement units of the various indicators
in
the construction of the indicator, system is
not
uniform, and both positive indicators
and
negative
indicators
are
included (the higher the
positive
indicator value, the better,
the
lower
the negative
indicator value, the better). Therefore, it is necessary
to
standardize
and dimensionless the
data
first,
that
is,
convert the
absolute value
of the
index into relative
value,
and homogenize different indicators. The
specific method
is as
follows:
Positive
indicators:
x
=
{
,⋯,
}
,⋯,
,⋯,
(i=1,2…,n;j=1,2,…,m)
(1)
Negative indicators:
x
=
,⋯,
,⋯,
,⋯,
(i=1,2…,n;j=1,2,…,m)
(2)
3.3.4 Calculate the Entropy Value of the j
th
Indicator
𝑃
=
∑
(i=1,2…,n;j=1,2,…,m)
(3)
𝑒
=−𝑘
∑
𝑝
𝑙𝑛𝑝
(i=1,2…,n;j=1,2,…,m)
(4)
Among k=1/ln(n)>0, e
≥0
3.3.5 Calculate the Entropy Redundancy
d
=1−e
(j=1,2,…,m)
(5)
3.3.6 Calculate the Weights of Each Index
W
=
∑
(j=1,2,…,m)
(6)
Finally, using the data from all sample communities,
the weights of the indicators for the resilience
assessment of the sample communities were
calculated. (Table 1)
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
140
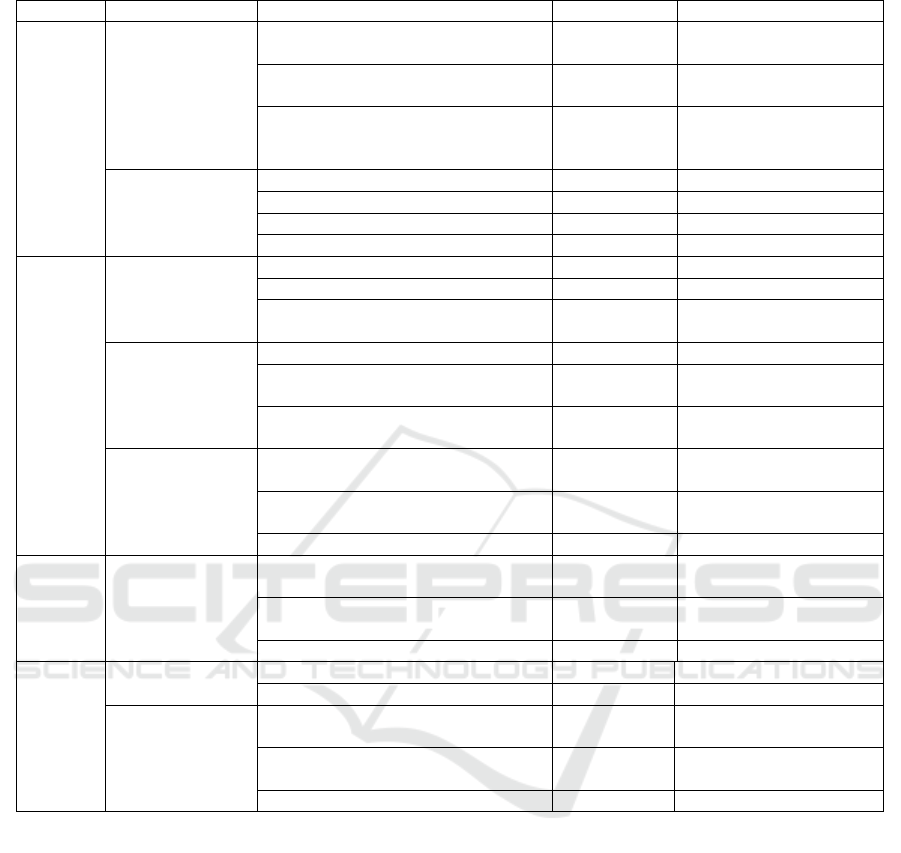
Table 1: Evaluation index
system
of resilience
of sample community
and its weight
value.
Process Domain
la
y
er Index la
y
er Attributes Com
p
rehensive wei
g
ht
Stress
Environmental
characteristic risk
The degree of automatic monitoring
of
ris
k
p
ressure
+ 0.0331
Average
number of community public
mana
g
ers
p
e
r
10,000
p
eo
p
le
+ 0.0857
Average
daily passenger
flow of
surrounding
large passenger
transportation centers
- 0.0104
Demographic
risk
Mobile
p
opulation share - 0.0247
Population densit
y
- 0.0121
De
g
ree of A
g
in
g
- 0.0183
Resident outbrea
k
awareness + 0.0262
Status
Medical information
Index
Medical Information Technolog
y
Index + 0.0316
Numbe
r
of
p
ublic hospitals within 5 k
m
+ 0.0681
Percentage of second-class hospitals
and
above within 15-minute livin
g
circle
+
0.0201
Socioeconomic
status
Percentage of three no compounds + 0.0295
Completeness
of public construction
facilities
+ 0.0239
Number
of small and
micro
enterprises
p
e
r
square
kilomete
r
in
the jurisdiction
+
0.0904
Social organization
status
Information level
of community
organizations
+ 0.0244
Average
number of social organizations
p
e
r
10,000
p
eo
p
le
+ 0.0967
Percentage of resident volunteers + 0.0877
Response
Early warning
capability
Early Warning
System Sensitivity
and
Accurac
y
+ 0.0591
Frequency of daily updates
of public
health information
+ 0.0638
Gri
d
-
b
ase
d
g
overnance effectiveness + 0.0209
Recovery Capability
Resident
p
artici
p
ation + 0.0324
Quarterl
y
avera
g
e financial income + 0.0619
Learning
adapt
ability
Training
informatization and
accessibilit
y
of out
p
ut devices
+ 0.0155
Emergency education and
training
effectiveness
+ 0.034
Governance s
y
ste
m
iteration efficienc
y
+ 0.0297
4 EVALUATION RESULTS AND
ANALYSIS
According to the above calculation steps,
the
data
of
the 19 sample
communities at the beginning of 2020,
the
end of 2020, and
the middle of 2021
are
processed
to
determine
the
weight under the
entropy
method,
while using it
to
calculate the resilience
level and ranking
of
each sample
community,
as
shown in Table 2.
At
the
beginning of
2020,
Shuanglin community
in
Chenghua District has the highest
comprehensive
resilience level,
with a
score
of
0.0926, including 0.0111 for
the
pressure layer,
0.0718 for
the
state layer,
and 0.0098
for
the
response layer.
The 2nd and 3rd places are American
Garden
community and Taiping
Village respectively.
The Jindu,
Gaodian,
and
Xichi communities with
poor
resilience in response
to public health
emergencies
ranked
the last
3 in
the
comprehensive
resilience
score.
At
the end of 2020, the ranking
of the
resilience
levels of the sample communities has
changed
to
some
extent from
the beginning of
2020,
but the
overall
fluctuations are relatively small.
Except
that
the
ranking
of Qingshuihe
community dropped
from
6th
to
14th, and the
ranking
of
Wangcong, Gaodian,
Jinqiao, Babuqiao,
and
Yifu communities fluctuated
Community Resilience Assessment under Public Health Emergencies: Based on Collaborative Governance
141

slightly, the ranking of other communities remained
unchanged.
In the
middle
of 2021,
the
resilience level
of
each sample community
fluctuated greatly
on
the
basis
of the end of 2020. Only
Wangcong
community
and Babuqiao community
did
not change the
status
layer
score
ranking
from the
end
of 2020
to the
middle
of 2021, while the pressure
layer
and response
layer score rankings
level of Shuanglin community
has decreased
significantly.
This
is because
the
impact of external
disturbance on
resilience
has
gradually diminished, and
a
complete
governance
system
has
not
been established within
the
community, which
cannot guarantee the steady
growth of community resilience
in the
post epidemic
era.
The
communities whose comprehensive
resilience
level
showed "
falling first and then rising
"were:
Qingshuihe Community,
Shengxing
Community,
Shuangbai Community, Wangcong
Community, Pineapple
Community, Jinqiao
Community,
and Yifu
Community. Among
them, the
Shengxing
community has
been
affected by the
epidemic,
and its
resilience level has
increased
significantly
from the
middle of 2021
compared to
the beginning
of 2020. Specifically,
the scores of
indicators
such as
"residents'
awareness of the
epidemic
situation", "residents' participation"
and
"effectiveness
of emergency education and training"
have been greatly improved. This shows that even
if
it had COVID- 19
cases
in the
central area
of
2021,
over
the
past year, the community has vigorously
launched
online and offline
emergency education
and
training, which has
effectively
enhanced
residents' awareness
of
prevention
and self-
consciousness and
improved
the cohesion and
enthusiasm of community
residents.
Thanks
to
this,
when
the
community
responded
to
COVID-19, the
resilience level
of the
Shuang
Lin community has not
risen, and it has withstood the test
of public
health
emergencies
to
the
community
governance
system.
In
addition,
the resilience of Tiaodenghe
Community
and babuqiao
community has been
decreasing
during the study period. Among them, the
response resilience of the Tiaodenghe community
declined significantly
from the beginning
of 2020
to
the
end of 2020,
while the
pressure resilience
decreased significantly from
the end of 2020 to the
middle of 2021. This is
because the
Tiaodenghe
community has COVID-19 cases in its jurisdiction
at
the
end of
2020, the
pressure on the community
to
respond to public
health
emergencies has
increased,
and the
community governance system and
governance
capabilities
are
not yet
complete, which
made
it unable to fully
and
effectively
respond to
disturbances.
Specifically, the
scores of indicators
such
as "the number
of social organizations per
10,000
people" and
"the proportion of permanent
volunteers" have
dropped significantly. It can
be
seen that
the community can
not
effectively
respond to
the disturbance of public health
emergencies
and reduce the impact of
disturbance
without the joint participation of multiple subjects
such
as government, autonomous organizations,
and
residents. Therefore, for
the
construction
of
resilient
communities,
collaborative
governance
with
the
participation of multiple
subjects
is indispensable.
In
addition,
the resilience
of Yongan
village and
Pengzhen
Guangrong
community
grew steadily
during
the study
period,
and their
pressure
resilience, state resilience and response resilience
fluctuated
less. It
can be seen that
although
both
Yongan
Village
and
Pengzhen Guangrong
Community have
been
disturbed
by
public
health
emergencies,
their
community
resilience was
less
impacted by the
disturbance
and can
be slightly
improved, indicating
that their
community
governance
system has
sufficient capacity
to
response to disturbances to maintain
the stable
development
of the
community.
5 POLICIES AND SUGGESTIONS
Based
on the
PSR model,
this
paper
constructs a
resilience assessment
index system
embedded in
collaborative governance
from the perspective
of
responding to public health emergencies and
conducts resilience assessment and
empirical analysis
on sample communities disturbed
by the
COVID-19
epidemic
in
Chengdu from
2020
to
2021. Studies
have shown that
the main
influencing factors that
cause the
differences in resilience
fluctuations of
sample
communities are: the
coordination
situation
of the government,
social organizations, residents,
and
other diverse
subjects participating
in community
resilience governance, and
the effectiveness of the
governance system
to
resist
public
health
emergencies
by relying on
information technology.
Therefore,
this
paper believes
that the main
link to
improve
community resilience
is the
improvement of
the
community governance
system.
The
key
measure to strengthen the
effectiveness
of
community
governance
is to build a multi-subject
collaborative governance mechanism. The effective
way
to
improve
the
collaborative level of the
governance system
is to attach
importance
to
intelligent construction.
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
142
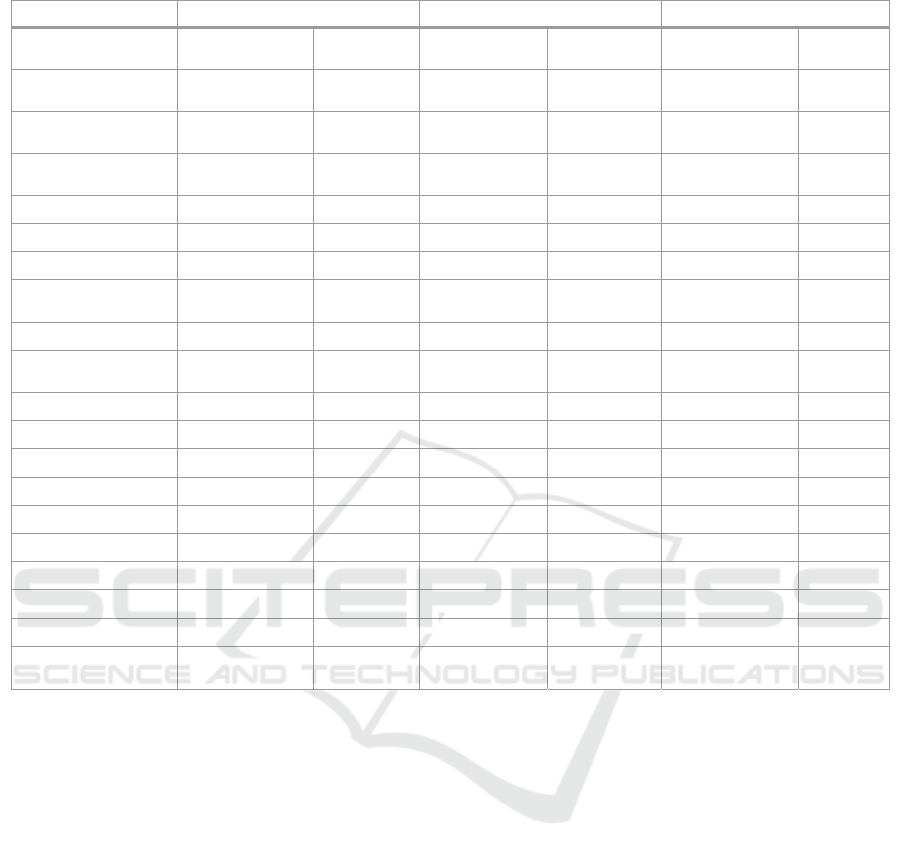
Table 2: Composite resilience score and ranking of sample communities.
Early
2020
End of
2020
Mid-2021
Toughness
score Ranking Toughness
score Ranking Toughness
score Ranking
Qingshuihe
Communit
y
0.0569 6 0.0403 14 0.0508 11
Shengxing
Communit
y
0.0474 12 0.0430 12 0.0533 8
Americas Garden
Communit
y
0.0854 2 0.0964 2 0.0863 1
Lianhua
Community 0.0495 11 0.0535 6 0.0522 10
Lianhua
Community 0.0495 10 0.0466 9 0.0508 12
Shuanglin
Community 0.0927 1 0.0994 1 0.0790 2
Jumping
Stomp
River
Communit
y
0.0657 5 0.0610 5 0.0577 6
Wangping Community 0.0677 4 0.0721 4 0.0717 3
Wangchong
Communit
y
0.0357 16 0.0348 17 0.0361 17
Taiping
village 0.0683 3 0.0727 3 0.0562 7
Yong’an village 0.0516 8 0.0517 8 0.0524 9
Pineapple Community 0.0549 7 0.0525 7 0.0591 5
Gaodian Community 0.0335 18 0.0342 19 0.0333 18
Jinqiao Community 0.0426 14 0.0392 15 0.0445 14
Xichi
Community 0.0298 19 0.0342 18 0.0302 19
Babuqiao Community 0.0379 15 0.0368 16 0.0363 16
Yifu
Community 0.0513 9 0.0439 11 0.0635 4
Jindu
Community 0.0343 17 0.0412 13 0.0374 15
Pengzhen Guangrong
Community
0.0453 13 0.0463 10 0.0492 13
Based
on the above conclusions and from the
perspective
of dealing
with
the disturbance
of public
health
emergencies, this paper puts
forward
the
following
recommendations
for the optimization of
community resilience
governance:
5.1 Establish and Improve the
Community Governance System to
Ensure the Steady Growth of
Resilience
As
the
basic unit
of grassroots
governance, the
community should
establish and improve
the
"one
core
and three governance, collaboration participation
and common interests",
the meaning is
a sound
urban and
rural
grassroots governance
system led by
the Chinese Communist Party that combines
autonomy, rule of law, and rule
of
virtue, which
can
lead
to
effective
community resilience to public
health emergencies and improve the community's
ability to
recover from
emergencies, thereby
ensuring smooth growth in resilience.
5.1.1 Strengthen the Leadership of Party
Building and Promote the
Participation of Diverse Subjects in
Community Governance
With
the continued impact
of the COVID-19
epidemic
New
Crown Pneumonia, how communities
can
achieve
a combination of normalized governance
and abnormal governance has become a
key issue
in
resilient
community building.
And through
the
firm
leadership of the Communist
Party of
China
to
improve
the
community
governance system will
become
an
important measure for resilient
communities to achieve.
The reason
is that
the
community grassroots
government
governance
unit
has
been transformed from
a
neighborhood
committee and
others
to
a
community
public
management
unit integrated with the party-mass
service center, and the
leadership
of the Communist
Community Resilience Assessment under Public Health Emergencies: Based on Collaborative Governance
143

Party
of China building
has become the
foundation
of
the community
governance
system and played its
leading
core role
to
strengthen with
the connection
between community public management
units and
residents,
enterprises
and social
organizations by
taking the Party branch
of
multiple subjects as
the
node. Meanwhile resilient
community under the
leadership
of party-building will drive multiple
subjects
in the community
to
deal
with emergencies
collaboratively
in
the face
of public
health
emergencies
and fully bring into play exemplary
vanguard role
of Party
Members among the
masses
to lead
the
masses
in fighting against
the
impact of
public
health
emergencies, realizing the
sinking of
power
and improving
the
resilience
of the
community
while increasing the
effectiveness of
governance.
5.1.2 Improve the Effectiveness of
Griddization Governance and
Strengthen the Collaborative
Governance of Multiple Subjects
At
present,
there
is
a
general
lack
of professional
management personnel
to
carry
out community
governance work
and professional griddization
management
in
the
community, and
most
of the
community residents serve as
grid members.
And
the
lack
of
professional social
worker talents and
other phenomena,
causing the community to
encounter emergencies that cannot be effectively
responded to. Therefore,
the key to improving
community resilience lies in building grid
management personnel
while
strengthening
the
professional
capacity
training,
and building a
collaborative governance mechanism
for multiple
subjects
to guide
and
absorb
multiple subjects from
within
the
community to participate
in community
governance.
5.2 Strengthen Community Intelligent
Construction and Improve the
Effectiveness of Community
Governance
Under the
attack
of the COVID-19
epidemic,
information
technology has played
an important
role
in the fight against the epidemic, so that intelligent
community is an important means
of effectively
combining normalization and abnormal
governance
in communities and
comprehensively
improving
community resilience. The construction of an
intelligent community not only
requires
the
community to
fully and rationally
apply
various
information resources, optimize
community
resilience
from the physical
level, and improve the
effectiveness of the community governance
system;
But also
requires the construction of a sharing
platform with
the
community public
management
organizations
as the
core,
closely
linking
with
community
residents, autonomous organizations
and
other
multiple subjects
and
promoting
the
active
participation
of
multiple subjects in community
governance. Especially in
the face
of public
health
emergencies, it can effectively
and
timely mobilize
the power of multiple
subjects to relieve the impact
of public emergencies
on
the
community.
For
example, under the normalization of
epidemic
prevention
and
control, big data
technology is
embedded in epidemic prevention
and
control, and
the
community
also
uses
information platforms
such
as "Sichuan E-Zhi Cai"
and residential
WeChat
groups to require multiple
subjects
to participate
in
dynamic
monitoring of
the community, so as to
efficiently carry
out epidemic prevention and
control.
At the same
time,
intelligent communities
as
a
means
of governance
should effectively
make
the
community governance
process
open
and
transparent,
enhance
social
supervision, strengthen
the
effectiveness
of
community governance through
risk monitoring,
financial
revenue and
expenditure
disclosure, etc. and improve community resilience.
In
summary, this
paper
uses
the PSR model
to
disassemble the
details of the
community
response
to
the three
epidemic situations
in Chengdu from
2020 to 2021, determine the sample community by
using the
full
sample
method,
and
analyze
the
improvement
methods of community resilience
embedded
in collaborative
governance, which
is
comprehensive
and scientific. However, due
to
the
lack of time-series
research, more analysis cannot
be made
on
time series, which can’t further
predict
the specific development
direction
of community
resilience.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This
paper is one
of the phased
results of the
Sichuan
Agricultural
University’s
undergraduate
research
National Innovation Training
Program
"Community
resilience
assessment under the
normalized prevention
and
control of public health
emergencies
-- a case study of
Chengdu"
(202110626057).
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
144

REFERENCES
C
S Holling. (1973). Resilience and
Stability
of Ecological
Systems. Annual Review
of Ecology and
Systematics,
Vol. 4:1-23.
He S. (2008).
From
government
crisis
management
to
crisis collaborative governance
--
Also on the
innovation
of
China's
crisis
governance
paradigm.
Journal
of Jiangnan
Social University,
02:23-26.
Hu X. (2016).
From
decentralized governance to
collaborative governance: multiple
subjects
of
community
governance and
their
relationship
construction
[J].
Jiang
han
forum,
4: 41-48.
LAN
Y, Zhang
X. (2020). Community
resilience
and
its
realization
path: from
the
perspective of governance
system modernization. Administration
Reform,
07:
73-
82.
MAGIS
K.
(2010). Community Resilience: An
Indicator
of Social
Sustainability.
Society
and Natural
Resources,235:401-416.
Sha Y,
Xie
Z. (2010).
on
collaborative governance
of public
crisis. Chinese Public Administration,04:73-77.
Community Resilience Assessment under Public Health Emergencies: Based on Collaborative Governance
145
