
Leadership Improvement in Public Crisis Management: A Study of
China Petrochemical Corporation
Dongming Cao
1a
, Zhengyuan Wang
2b
, Hongfei Yang
3c
and Jie Li
4d
1
Dept. of Human Resources, Sinopec Guangdong Sales Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China
2
General Manager's Office, Sinopec Guangdong Sales Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China
3
Dept. of Synthetic Resin, Sinopec Chemical Sales South China Branch, Guangzhou, China
4
School of Finance and Trade, Guangdong Industry Polytechnic, Guangzhou, China
Keywords: Public Crisis Management, Information Analysis, Leadership, The Main Paths, The Effective Execution
Power.
Abstract: In the current society, public crises are everywhere, and public crisis management has become a hot spot of
public concern. Exploring and improving the leadership improvement path in public crisis management is
conducive to reducing the degree of harm of public crises. This paper is based on 437 survey samples of China
Petrochemical Corporation (Sinopec Group), centering on the category of crisis leadership, using an ordered
logistic regression model to test 9 measurement variables such as personal charm, context sensitivity, system
thinking, crisis communication, action interaction, team inspiring, shared vision, changing opportunity and
organization learning are significantly related to the improvement of crisis leadership, and analyze the
problem of the improvement path of leadership in public crisis management. In this way, we summarize the
core power and effective execution power of leadership in public crises, and points out the main paths from
the management concept to the collaborative governance concept, the establishment of a collaborative
governance structure, and the shaping of a collaborative governance mechanism. In order to reduce the losses
caused by public crises, provide theoretical basis and practical reference.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the frequent occurrence of various
public emergencies has caused serious threats to
China's economic development and is not conducive
to long-term stability of society. As the main body of
public crisis management, leading cadres are
particularly important for the handling of public
crises (Orazi, Turrini, & Valotti 2013). The
emergence of different types of emergencies has
raised many new challenges for leadership
improvement. The adjustment and emergency
response capabilities of leading cadres need to be
further improved (Wang 2013). At the same time, in
the context of economic globalization, the frequency
of public crises is getting higher and higher, and the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9142-8472
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2087-1834
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0379-5529
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3520-9651
scale of the spread is also continuing to expand, and
the harm generated is also growing (Yao, & Gong
2012). In the process of China's social and economic
development and progress, development is the top
priority, and safety is the first responsibility (Wang,
2014). Gradually exploring and improving the public
crisis management method, optimizing the leadership
structure, and having certain scientific and effective
in public crisis management are of great significance
for public crisis management (Zhao, & Li 2011), and
the improvement of leadership can greatly reduce the
number of public crises, reduce the scale of public
crises, and contribute to the long-term stability of
society(Amabile, Schatzel, Moneta, & Kramer 2004).
In this context, this paper deeply studies the
leadership improvement methods in public crisis
management, which has important practical and
Cao, D., Wang, Z., Yang, H. and Li, J.
Leadership Improvement in Public Crisis Management: A Study of China Petrochemical Corporation.
DOI: 10.5220/0011161000003437
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2021), pages 81-89
ISBN: 978-989-758-589-0
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
81

theoretical significance for improving leadership
execution and accelerating China's economic
development.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
We refer to the comprehensive literature research
method of Chen & Lin (2020), use Web of Science
(WoS) as the citation database, and select SCI-
EXPANDED, SSCI, A&HCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH,
ESCI in the WoS core collection as data retrieval
Source, using the keywords "Public Crisis
Management" AND "Leadership" (including the
researcher keyword "DE", and the research content to
add the keyword "ID"), the literature accumulation
time span is 1994-2021, obtained from the subject
search. There are 674 documents and 9 highly cited
documents. Different from the large volume growth
shown in the domestic literature, WoS published
research results on public crisis management and
leadership related topics and the degree of attention
has been increasing year by year after 2006. See the
citation report for details (see Figure 1).In the era of
human society, crises and conflicts exist in all
aspects, and crisis management has become the focus
of public attention. Along with the economic
integration and political integration, the process of
gradually advancing to the global community, and the
gradual acceleration of the pace of economic
development, the crisis of civilization has become the
main product of China's economic development and
adjustment, from the government to the individual.
Master public crisis management methods and
effectively deal with public crises (Zhu 2013). In
recent years, China's public crisis has occurred
frequently, and various crises have gradually
emerged diversely. Some sudden crises pose a serious
threat to human security and social stability. Public
crisis management not only tests the organizational
communication ability, decision-making ability and
activity execution ability of department leaders, but
also tests the psychological endurance of leaders to a
certain extent, and poses a greater challenge to the
improvement of leaders' ability. The ability of
relevant leaders to improve and leadership has
become the key to the management of public crisis
(Wang 2010). In the management of public crisis, the
response to the crisis first needs to understand the law
of the development of the crisis and the source of the
occurrence. The learning of the crisis effect becomes
a prerequisite for crisis management. Among them, in
the process of public crisis management, action
learning as an advanced learning method has
undoubtedly become the management method with
the greatest practical value of crisis management. In
the process of public crisis management, the action
learning process is a two-cycle process focusing on
action and learning. Relevant government
departments can improve leadership, rational
strategic planning, reshape organizational culture,
and improve social public crisis management
capabilities(An 2013). Nowadays, countries around
the world have begun to study leadership
improvement methods and specific practices. And
with the gradual complication of adjustments, the
relevant institutions have proposed new tasks and
tasks for leadership improvement. By considering the
global crisis and the challenges faced, we will analyze
the problems that may be faced by future leadership
improvement, and propose that future leadership
improvement should focus on social phenomena and
improve all aspects of leadership from different
dimensions (Wu, & Zhang 2014). The rapid
transformation of Chinese society requires the
inclusion of public leadership in specific education
development plans. By defining the specific concepts
of public management capacity, and from the
perspectives of supervision and implementation,
crisis management, strategic decision-making,
communication and collaboration, and innovation,
this paper discusses the main ways to improve public
management capacity. On this basis, the six foreign
universities are the main research objects, and the
comparative analysis of leadership training and
promotion methods is carried out. It is found that,
these different approaches also lead to unique
leadership development approaches, while
highlighting leadership development. Moreover, the
use of public leadership in public crisis management
has a significant regulatory effect on public crises
and, to a certain extent, reduces the number of public
crises (Peng, Wang , Xue et al. 2015).
3 PRELIMINARY
Once a crisis occurs, it will have a more serious impact
and bring some adverse effects to the public. In
general, public crises suddenly erupt, and it is difficult
to predict before the crisis erupts, and there is no law
at all. If the relevant leaders did not do the relevant
preventive measures in advance, or did not foresee the
occurrence of the crisis before the crisis, this would
bring unimaginable consequences after the crisis.
In social life, some public crises have certain control
ability, and some are beyond control (Peters 2021).
Before
the public crisis occurs, raise the awareness
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
82
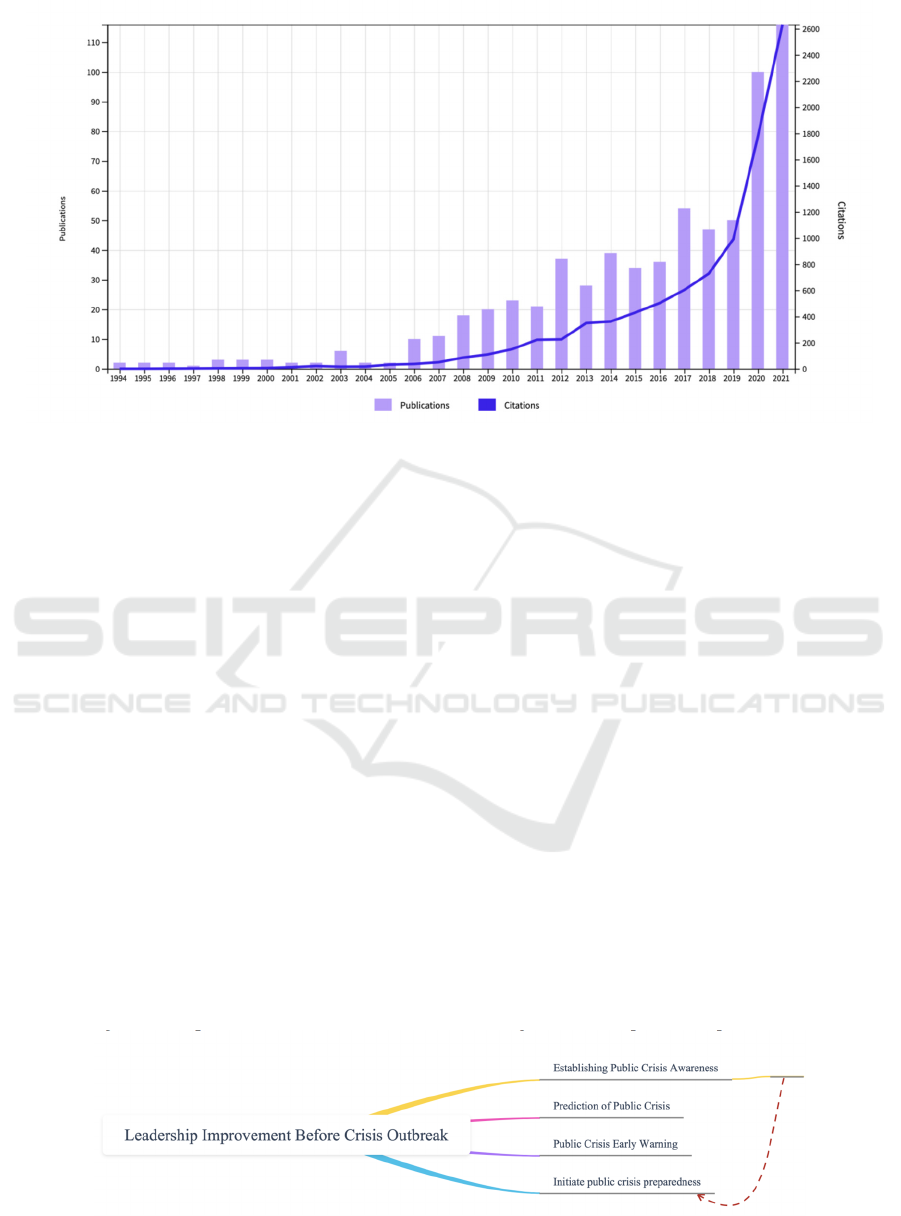
Figure 1: Citation report of research on topics related to public crisis management and leadership.
of public crisis led by relevant departments. Public
crisis forecasts should be made in advance. Preparing
in advance before the crisis is also conducive to the
relevant departments in the prior to all precautions.
At present, after the public crisis, the government that
dominates the public crisis is generally the
government department. Before the crisis broke out,
government leaders led a thorough crisis response
plan. In the event of a crisis, the public will see the
leadership of departmental leaders, all of whom want
to minimize the damage caused by public crises.
Therefore, before the crisis occurs, it is the primary
task of the government leaders to make good
preparations in advance to avoid the crisis.
Before the crisis broke out, there were four main
tasks that government leaders needed to do, as shown
in Figure 2. Establishing public crisis awareness is the
premise of public crisis management, which is the
basis of leadership improvement before the crisis. At
present, China is in a period of stable development,
and the frequent occurrence of natural disasters has
gradually increased the difficulty of public
management. Therefore, government leaders need to
have a strong sense of public crisis, be sensitive to
public crises, and avoid overconfidence leading to
public crises. Moreover, relevant leaders should also
adapt to the development needs of the situation,
continue to learn the corresponding public crisis
knowledge through relevant channels, understand the
causes of some public crises, and understand the
prevention and control measures of public crises in
advance, so as to solve the public crisis. Do the
appropriate preparations.
The occurrence of public crises has a very large
uncertainty, which may have a greater impact on the
public after the outbreak. In addition to public crisis
awareness, government leaders need to make public
crisis predictions. In order to reduce the public crisis
after the outbreak of many harm. Relevant leaders
must use statistical information to make appropriate
crisis predictions within the corresponding time
frame. Moreover, in this process, the leader can
understand the information about the public crisis on
some self-media platforms, and can capture and judge
the time and place where the crisis may occur
according to the clues of some crises. Then,
combined with past experience in public crisis
management, anticipate some public crises that may
Figure 2: Ways to Improve Leadership before the Outbreak of Public Crisis.
Leadership Improvement in Public Crisis Management: A Study of China Petrochemical Corporation
83

occur in advance, and infer the development trend of
future public crises. According to the judgment
results, the pre-preparation of the crisis warning is
prepared by collecting the information related to the
previous or existing public crisis, and the degree of
public crisis harm is minimized, and do the following
two aspects:
3.1 Establishing a Sense of Public
Crisis is a Starting Point for
Leadership Advancement before
the Outbreak
In the process of public crisis management,
leadership transforms consciousness into a
corresponding mechanism by maintaining a certain
sense of public crisis and then using relevant practical
activities. In this process, leaders are required to
make public crisis warnings. In the course of a crisis,
leaders should deploy relevant strategic work through
the situation on the ground to clarify the possible
hazards that may occur after the crisis. Such results
may be related to ways to prevent crises. Through a
certain forward-looking and public crisis warning,
the department leaders can reduce the losses caused
by the public crisis to the public. Of course, before
the leader plans, there are many dynamic
environments that need to be faced. In the process,
the leadership's perception of some environments will
affect the implementation of the entire plan. Doing a
good job of public crisis warning can effectively
prevent and even resolve the emergence of public
crises and reduce the harm of public crises. Moreover,
department leaders should do public crisis warning,
be able to coordinate the specific work of the
department, save a lot of people, goods and financial
resources, which is conducive to maintaining social
order, and it’s conducive to the government's
leadership.
3.2 Prevention is the Best Way to Deal
with Public Crisis Management
Relevant prevention work is in place, and in the event
of a public crisis, it can be faced in a more relaxed
way to resolve the crisis. Doing a good job in public
crisis plans can help the public to take appropriate
measures to deal with public crises before the public
crisis. In this process, government leaders should
attach great importance to the preparation of public
crisis plans, and comprehensively consider the local
situation, and prepare corresponding plans for the
possible situation of different crises. When preparing
the plan, it needs to be meticulous and accurate, and
must not miss any information that may cause public
hazards. At the same time, public crisis plans can also
provide some public crisis management methods to
control public crises in detail.
4 EMPIRICAL TEST
4.1 Operational Definition
We adopt the maturity scale of Cui (2014) and take 9
operational definition indicators, including personal
charm, context sensitivity, system thinking, crisis
communication, action interaction, team inspiring,
shared vision, changing opportunity, and organization
learning as observation variables. To test the relevance
of this dependent variable in crisis leadership
promotion. We use the Likert 8-point scale to measure
the efficiency of crisis leadership. The larger the
value, the more we agree with the impact of crisis
leadership.
Refer to the Peer Esteem Snowballing Technique
(PEST) sampling method of Chen and Lin (2020), and
use the staff at or above the level of section manager
or team lead of China Petrochemical Corporation
(Sinopec Group) as of December 31, 2020 as the
sample frame. 100 respondents were sent via WeChat
push, and the questionnaire was sent to each
respondent within 1 hour of getting the first response.
Among the 100 interviewees, 34 interviewees
participated in the survey and the interview invitation
was forwarded to others in the sample frame they
knew. The invitation letter is verified through
guidelines and settings to minimize isomorphism, and
the invitation letter is requested to be forwarded to
other groups of people in the sample frame as much as
possible. Within half a year (January 1, 2021-June 30,
2021), a total of 468 questionnaires were received.
After the samples were inspected and screened, the
total number of samples was 437.
4.2 Descriptive Analysis
4.2.1 Response Deviation Test
Since the questionnaire survey lasted for 180 days,
this study first conducted a response bias test on the
samples based on the recommendations of Chen et al.
(2020). The top and bottom 27% of the samples were
divided into high and low groups, using SPSS 25.0 for
MAC software, running descriptive statistics (see
Table 1), independent sample t-test (see Table 2) and
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
84

other operations, based on the argument that delayed
responders and non-responders are more similar than
initial responders, according to the time series of
sample recovery, The independent sample's t test
method was used to calculate the degree of
discrimination. The non-response deviation was
evaluated by comparing the initial responders and late
responders. The independent sample t-test results
showed that there was no significant response
deviation and the sample was acceptable. Sample
statistics description:
Table 1: Group statistics.
Group Statistic
Repeated sampling
a
Deviation Mean
difference 95% confidence interval
Lower Upper
Initial response
N 118
Avera
g
e 5633.143 -.0321 6.434 5351.476 5914.790
S.D. 31.089 -.218 5.891 29.535 32.643
Delayed
response
N 118
Avera
g
e 5732.141 .0318 6.053 5445.534 6018.748
S.D. 32.172 -.230 5.291 30.563 33.781
a.Based on 1000 repeated samples
Table 2: Independent sample verification.
Class
Levene's test for
equality of variance
T-test for the equality of means
F Sig. t df
Sig.(two-
tailed)
M.D S.E
difference 95% confidence
interval
Lower t Upper
Sum
with equal 116.677 .001 43.133 132 .000 6.166 0.180 3.124 7.244
No equal 43.133 132 .000 6.166 0.180 3.124 7.244
4.2.2 Demographic Information
Table 3: Demographic information.
SN Position Frequency %
1
Section manager/
Team lead
124
28.375%
2
Manager/
Senior Staff Engineer
97
22.197%
3
Senior Manager/
Principal Engineer
76
17.391%
4 Director
67
15.332%
5 Senior Director
56
12.815%
6 Vice President
11
2.517%
7
CEO/President/
General Manager
6
1.373%
Total
437
100.00%
4.2.3 Descriptive Statistics
1) The Cronbach Alpha coefficient is between 0.901-
0.977, and the coefficient will not increase if any item
is excluded. The correlation coefficients between the
factors are all less than the square root of AVE,
showing high discriminative validity.
According to the Kaiser (1960)
criterion, the
factors were eliminated, the cumulative variance
explanation rate was 76.314%, and the item
standardized factor load was between 0.745-0.910;
the critical ratio significance verification showed that
the p-values < 0.001, significant at the 1% level.
Leadership Improvement in Public Crisis Management: A Study of China Petrochemical Corporation
85

4.3 Regression Analysis
4.3.1 Establishment of Measurement Model
In order to further answer the question of "leadership
improvement path in public crisis management", we
designed an empirical model, focusing on the factors
that influence leadership improvement in public crisis
management. The empirical model constructed using
the ordered logistic regression model is as follows
(See Formula 1):
Among them, y represents the efficiency of
leadership improvement in public crisis management;
j represents the quantitative level of the influence
factors of leadership improvement in public crisis
management (j=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8); i represents the
first i samples; Pi, j represents the cumulative
probability of y of the i-th sample taking the first j
values; x represents the independent variable of the
leading factors in public crisis management; ε
represents the random error term; α is the constant
term; β is the variable coefficient; PC means Personal
Charm, CS means Context Sensitivity, ST means
System Thinking, CC means Crisis Communication,
AI means Action Interaction, TI means Team
Inspiring, SV means Shared Vision, CO means
Changing Opportunity, and OL means Organization
Learning. At the same time, the model also controls
the gender (Gender) variable of the sample. We
conduct empirical analysis through ordered logistic
regression. If the regression coefficient β of the
independent variable should be significantly positive,
it indicates that the influence of the factors that
influence the improvement of leadership in public
crisis management is more obvious.
Logic
(
P
i, j
)
=α
j
+
β
1
PC
i+
β
2
CS
i+
β
3
ST
i+
β
4
CC+β
5
AI+β
6
TI+β
7
SV+β
8
CO+β
9
OL+β
10
Gender+ε
i, j
Formula 1.
4.3.2 Analysis of Ordered Logistic
Regression Results
Table 4 shows the orderly logistic regression analysis
results of leadership improvement efficiency in
public crisis management. The models M1-M10 in
Table 4 reflect the test results of the factors that
influence the efficiency of leadership in public crisis
management. M1 reflects the influence of control
variables on the efficiency of leadership
improvement in public crisis management. It can be
seen from Table 4 that gender is not significantly
related to the improvement of leadership efficiency in
public crisis management. M2 reflects the influence
of Personal Charm on the improvement of leadership
efficiency in public crisis management. It can be seen
that Personal Charm has a significant positive impact
on the improvement of leadership efficiency in public
crisis management, that is, the greater the degree of
Personal Charm, the better the improvement of
leadership in public crisis management. obvious. By
analogy, we can find that six independent variables
such as Context Sensitivity, Crisis Communication,
Action Interaction, Team Inspiring, Changing
Opportunity, and Organization Learning reflect the
influence of leadership improvement in public crisis
management in M5, M6, M7, M9, and M10.
Significantly positive correlation. The regression
results of M2, M4, and M8 show that Team Inspiring
and Shared Vision have no significant impact on the
efficiency of leadership improvement in public crisis
management. However, we also found that in M3,
System Thinking has a significant negative impact on
the efficiency of leadership improvement in public
crisis management.
5 ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
After the outbreak of the public crisis, the decision-
making and execution of leadership is crucial
(Brooke, Irina, & Emina 2020). Government leaders
need to be able to make quick decisions in a short
period of time based on the situation generated by
public crises. They need to have crisis identification
capabilities, rapid decision-making capabilities, and
decision-making research capabilities. The level of
leadership decision-making ability in this process
will directly affect the treatment effect of public
crisis. At the same time, after the leaders make
relevant decisions, the specific tools and tools
adopted at the moment will also affect the quality of
previous decisions. As far as the public crisis breaks
out, the leadership's decision-making process mainly
includes public crisis identification ability, public
crisis information analysis ability, public crisis
decision-making ability, public crisis coordination
ability and public crisis decision-making research
ability (as shown in Figure 3).
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
86
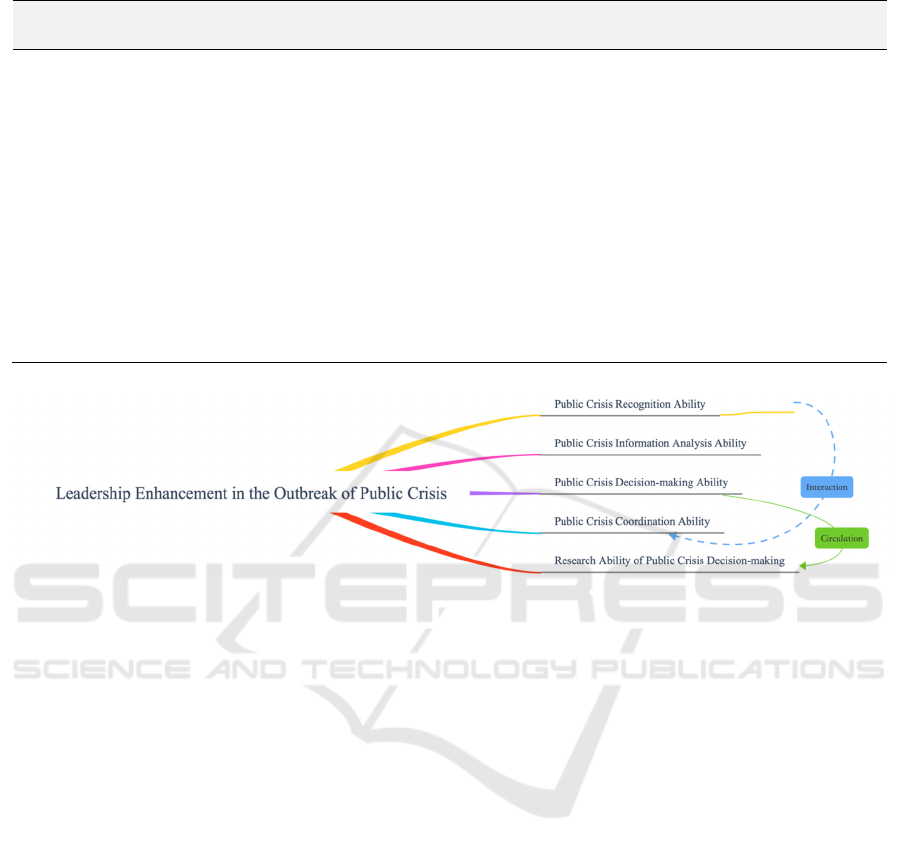
Table 4: Ordered Logistic regression analysis.
Independent
variable
M1 M2 M3 M4 M5 M6 M7 M8 M9 M10
Personal Charm 0.210
Context Sensitivity -0.371**
System Thinking 0.194
Crisis
Communication
0.520***
Action Interaction 0. 638***
Team Inspiring 0.579***
Shared Vision 0.314
Changing
Opportunity
0.462**
Organization
Learning
0.534***
Gender 0.312 0.164 0.093 0.246 0.194 0.210 0.083 0.305 0.144 0.288
*, **, *** indicate significance at the level of 5%, 1%, and 0.1%, respectively.
Figure 3: Leadership Improvement Path in the Outbreak of Public Crisis.
5.1 Public Crisis Identification
Capabilities
Before the different departments, in response to the
public crisis, a corresponding monitoring system will
be established. In the event of a public crisis, the
relevant department leaders can use the decision-
making system to use the relevant information within
the system, combined with the current situation of the
public crisis, to identify the various symptoms of the
public crisis, and then prevent the possible public
crisis. Prevent and effectively resolve public crises.
Government leaders have strong public crisis
identification capabilities and can play a preventive
role in the crisis. This also requires leadership and has
certain decision-making experience and strong crisis
identification capabilities.
5.2 Public Crisis Information Analysis
Capabilities
Information plays an important role in the public
crisis. Because the public crisis will bring certain
difficulties to the government leadership decision-
making. Therefore, public crisis information analysis
capability is also a key link in the public outbreak
process. Leaders need to keep collecting and
analyzing relevant information and maintain certain
sensitivity to some information. Moreover, in view of
the causes and specific conditions of the public crisis,
relevant leaders should collect, screen and analyze
some public crisis information. At this stage, with the
rapid development of scientific information
technology, the time for people to capture
information is getting shorter and shorter. The most
obvious feature is that the spread of the Internet has
gradually accelerated. This requires government
leaders to effectively combine some of the latest
information, make scientific decisions in a short
period of time, and then deal with public crises.
5.3 Public Crisis Decision-making
Ability
After the outbreak of the public crisis, the decision-
making ability that best reflects leadership is the
ability to make decisions. Once the crisis erupts, each
time the time is extended by one minute, the loss
caused to the public will increase by one point,
requiring government leaders to make decisions
Leadership Improvement in Public Crisis Management: A Study of China Petrochemical Corporation
87

quickly and form a public crisis management plan.
On the one hand, leaders need to make corresponding
decisions in a short period of time and lead the people
into crisis management. On the other hand, leaders
need to make decisions and take the overall direction
and manage public crises rationally under the
conditions of insufficient information.
5.4 Public Crisis Coordination Ability
When leaders make clear decisions, they also need to
coordinate the operation of relevant decisions. Under
the uncertain state of high public crisis, the leaders
coordinate their work horizontally and vertically, and
quickly organize relevant personnel to make
important changes within a certain period of time to
minimize the degree of public crisis damage. The
nature of coordinated action is a political activity. The
leader is not a decision maker, but a designer,
protector and facilitator. By learning from the crisis,
the relevant personnel can help to deal with the crisis.
5.5 Public Crisis Decision Making
Research Capabilities
After the crisis has occurred in the crisis research, the
manager should organize the public to resolve the
corresponding crisis by calling the resources of all
parties. In this process, leaders need to develop public
crisis plans, gather relevant information, and conduct
public crisis research. In the research process, leaders
need to analyze the causes, processes and solutions of
public crises from a professional perspective, laying
the foundation for the next crisis prevention.
6 CONCLUSION
Through a series of treatments after the outbreak of
the crisis, society will enter a certain gradual stage,
but at the same time it will enter the stagnation period
of the next crisis. Therefore, after the outbreak of the
public crisis, it is necessary to assess the leadership
improvement behavior of public crisis management.
First, there is a need for leadership accountability in
the public crisis recovery period. That is to say,
accountability is required, and it is necessary to
analyze the consequences of leading cadres’ defaults
and consequences. Second, it is necessary to
strengthen the construction of administrative
accountability culture.
There must be certain objective reasons for the
outbreak of public crises, strengthen the construction
of administrative accountability culture, break the
traditional thinking of "official standard", standardize
the rights and responsibilities of leadership, and
improve the public responsibility consciousness of
leadership by improving the accountability
mechanism. Finally, leadership assessment in public
crisis management. After accountability, it is
necessary to conduct a job evaluation of some well-
performing leaders and give corresponding rewards.
In addition, a leadership learning system should be
constructed to disseminate information about public
crises with appropriate systems to prepare for the next
public crisis prevention.
REFERENCES
Amabile, T. M. , Schatzel, E. A. , Moneta, G. B. , &
Kramer, S. J. . (2004). Leader behaviors and the work
environment for creativity: perceived leader support.
Leadership Quarterly, 15(1), 5-32.
An Z.F. (2013). Action Learning: A New Way to Improve
the Government's Crisis Management Ability, Journal
of Jilin Institute of Business and Technology, 29(4),82-
85.
Brooke F. L., Irina A. I., Emina H.. (2020) Leadership under
Fire: How Governments Manage Crisis
Communication. Communication Studies 71:1,128-
147.
Cui X. M.. (2014). Research on the Influence Mechanism
of Crisis Leadership on Crisis Management
Performance. Fudan University.
Chen, Y., Lin, Z.(2020). Business Intelligence Capabilities
and Firm Performance: A Study in China[J].
International Journal of Information Management,
102232.
Kaiser, H. F.(1960) The application of electronic computers
to factor analysis. Educational and Psychological
Measurement, 20(1): 141-151.
Orazi, D. C. , Turrini, A. , & Valotti, G. . (2013). Public
sector leadership: new perspectives for research and
practice. International Review of Administrative ences,
79(3), 486-504.
Peng Z.C., Wang Y.L., Xue L., et al. (2015). Public
Leadership Improvement: A New Exploration of the
Orientation of MPA Education in China, Public
management review, 12(3),135-148.
Peters, B. G. . (2021). Governing in a time of global crises:
the good, the bad, and the merely normal. Global Public
Policy and Governance, 1(1), 4-19.
Wang S.D. (2013). Challenges and Path Choices of Leading
Cadres' Emergency Management Capability in the New
Period, Learning forum, 29(12),59-61.
Wang S.J. (2014). Talking about the Leadership of Chinese
Government under the Public Crisis, Charm China,
10(2),381-381.
Wang F.M. (2010). Analysis on the Leaders in Public Crisis
Management and Their Ability Improvement, Journal
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
88

of Xiamen Special Economics Party School, 22(2),77-
80.
Wu J., Zhang M. (2014). Responding to Public Crises and
Challenges Building Future-oriented Leadership,
Chinese leadership science, 1(1),32-35.
Yao N., Gong Z. (2012). Research on Leadership in Cross-
border M&A——Based on the Perspective of
Agglomeration Advantage, Hubei Social Sciences,
26(10),54-59.
Zhao Z.H., Li P. (2011). The use of leadership emotional
intelligence in public crisis response, Leadership
science,27(3),27-29.
Zhu Z.F. (2013). Leadership Research in Crisis
Management, Party and government forum, 29(5),44-
46.
Leadership Improvement in Public Crisis Management: A Study of China Petrochemical Corporation
89
