
Study on Dynamic Evaluation of River Health based on Theme
Service
Xu Zhang
1
, Xiao Zhang
1,*
, Jianhong Yang
2
, Jiancang Xie
1
, Wentao Shi
1
and Dan Yuan
1
1
State Key Laboratory of Eco-hydraulics in Northwest Arid Region, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an 710048,
Shaanxi, China
2
Shaanxi Provincial Water Resources and River Bank Dispatch Center, Xi’an 710004, Shaanxi, China
Keywords: Dynamic evaluation, River health, Theme service
Abstract: In view of the shortcomings of traditional river health evaluation, such as fixed indexes and poor adaptability,
the information technology was applied to the evaluation, and a dynamic evaluation mode of river health
based on theme service was proposed. First, determine the evaluation themes which based on river health
issues. Second, establish the river health dynamic evaluation process which based on the theme service. Third,
construct the evaluation index database and componentize the evaluation method. Finally, draw the
knowledge map of the evaluation theme on the synthesis integrated platform and build the river health
dynamic evaluation system. A case study was carried out to evaluate the river health in the Xianyang-Xi'an
section of the main stream of Weihe River from two themes: river ecological environment quality and river
social service function capacity. The results show that the dynamic evaluation of river health based on the
theme service can be achieved quickly and from multiple angles, and the results are more credible, which can
better meet the needs of decision makers compared with the traditional evaluation methods. The results are
of great significance for promoting the construction of river ecological civilization and have practicability and
popularization value.
1 INTRODUCTION
River health evaluation is a description and
assessment of the current situation of the river. It is of
great significance to propose effective river
protection measures and scientific water resources
allocation schemes for the sustainable development
of the river, the ecological environment construction
of the basin and the rational utilization of water
resources (Pinto & Maheshwari, 2014). Many
scholars at home and abroad have carried out study
on river health and achieved many beneficial results.
In the early stage of research, biological monitoring
methods such as Australian River evaluation Plan,
South Africa's scoring system and Fish Aggregate
Integrity Index (FAII) were widely used to evaluate
the health of rivers (Chen et al., 2014). However, river
not only have biological integrity but also their
specific physical structure integrity, and the overall
situation of rivers cannot be comprehensively
evaluated only by the damage of river organisms
(Wang et al., 2019). After that, comprehensive index
methods such as River Habitat Survey (RHS) (Raven
et al., 1998), RCE score (Petersen, 1992) and Index
of Stream Condition (ISC) in Australia (Anthony et
al., 1999) have become a new research direction.
China also put forward the indexes, standards, and
methods of river health evaluation (for pilot projects)
in 2010 to guide the pilot projects of national river
health evaluation and provide an important reference
for river health evaluation in China. Li et al. (2016)
established the river ecosystem health evaluation
index system of Huaihe River Basin (Henan Section)
based on four indexes: hydrological characteristics,
water quality, biological conditions, and geomorphic
characteristics. Gu et al. (2018) established the North
Canal River ecosystem health evaluation index
system based on four indexes: hydrology, water
quality, aquatic organisms, and habitat status. Chen et
al. (2019) comprehensively considered the feasibility
condition of Lhasa River, established a multi-level
and multi-index evaluation system based on the
characteristics of ecological environment, social and
economic development of Lhasa River, to provide
reference for the management and protection of Lhasa
River Basin. Previous studies on river health
Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Yang, J., Xie, J., Shi, W. and Yuan, D.
Study on Dynamic Evaluation of River Health based on Theme Service.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Water Resource and Environment (WRE 2021), pages 341-350
ISBN: 978-989-758-560-9; ISSN: 1755-1315
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
341
evaluation mainly focus on the construction of index
system or the selection of evaluation model, but there
are some problems such as the fixed evaluation index
system, and the evaluation model is difficultly to
adapt to dynamic changes.
Aiming at the complex river health problems, this
paper proposes a dynamic evaluation mode of river
health based on Theme Service (Xie et al., 2015) to
carry out dynamic evaluation of river health, the
purpose is to solve the problems of fixed indexes and
weak adaptability in traditional river health
evaluation. By constructing the evaluation index
database, the deviation of traditional evaluation
caused by less evaluation indexes are avoided. By
componentizing the evaluation method, the rapid and
accurate river health evaluation service is provided.
The evaluation process is visualized based on the
synthesis integrated platform, which improves the
credibility of the evaluation, can quickly modify the
evaluation indexes and methods, and provide
dynamic and feedback correction evaluation services.
Taking the Xianyang-Xi'an section of the main
stream of Weihe River as an example, based on field
research, two evaluation themes were finally
determined, a river health dynamic evaluation system
based on theme service was established, and dynamic
evaluation was carried out for each theme. The
research results of this paper are of great significance
to reasonably formulate the health protection
measures, maintain the normal natural and social
functions and promote the construction of ecological
civilization of Weihe River.
2 DYNAMIC EVALUATION OF
RIVER HEALTH
2.1 Support of Dynamic Evaluation
Theme Service
The synthesis integrated platform is an information
platform to realize component customization and call,
evaluation model integration, knowledge map
drawing and editing, knowledge accumulation and
retrieval, and decision-making discussion (Lian et al.,
2019). The platform system framework is designed
based on Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA). The
biggest difference from the traditional evaluation
system is that there is no specific business function.
All applications are built through knowledge map and
components, and specific decision evaluation
application systems can be gradually built through
application combinations (Xie & Luo, 2010). It
makes the application system have strong flexibility.
It is the foundation and support for the realization of
dynamic evaluation theme service. The synthesis
integrated platform can establish and improve the
feedback mechanism for the participation of decision
makers and experts in the decision-making process
and give full play to their experience and wisdom.
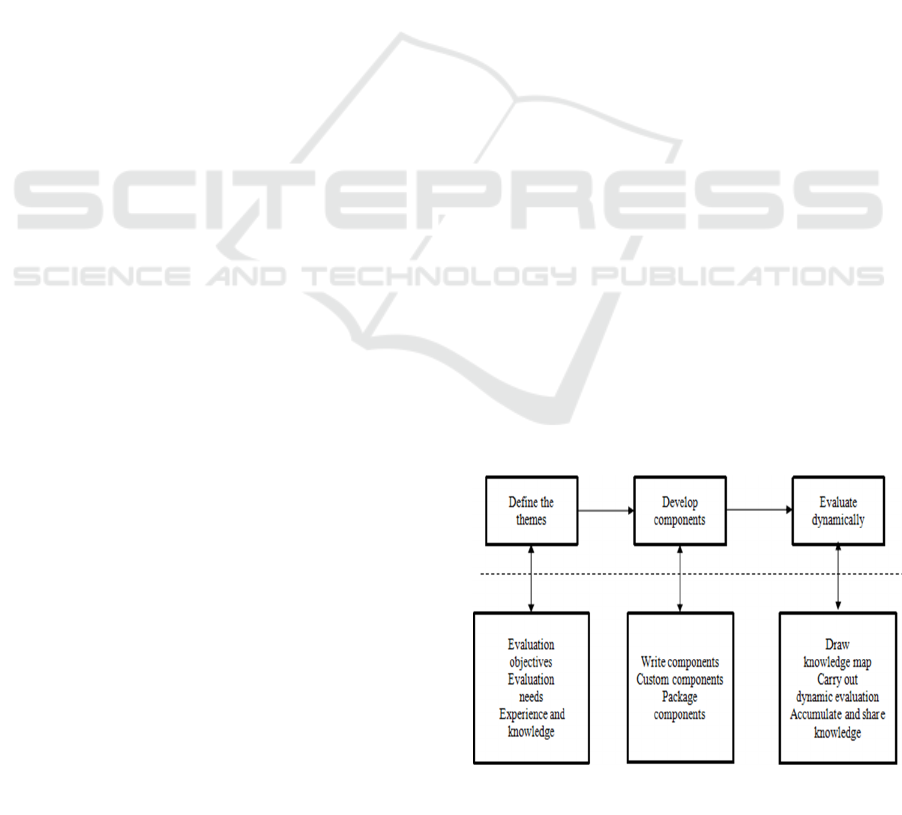
2.2 Process of Dynamic Evaluation
Theme Service
The theme service of dynamic evaluation should start
from defining the theme. Under the guidance of
evaluation objectives, evaluators refer to the
experience and knowledge of experts and themselves
and divide complex evaluation problems into
multiple core themes. Under the strong guidance of
theme driven, through qualitative discussion, with
professional theoretical knowledge as the master line,
clarify the relevant concepts and relationships, and
initially formulate the structure of evaluation
knowledge map. In the evaluation process, select the
evaluation indexes and method components related to
the theme, combine the pre-developed indexes and
method components with the knowledge map,
quickly build the evaluation model suitable for
different themes, and realize the dynamic evaluation
of visible and credible with online rapid response and
flexible correction of evaluation methods. The
process of dynamic evaluation of theme services is
shown in Figure 1. With the needs of management
and decision-making, the continuous changes of
evaluation objectives and the continuous
development of evaluation work, themes can be
constantly updated and accumulated to form a
comprehensive and rich evaluation theme database,
which can provide guidance for future evaluation and
make effective use of knowledge.
Figure 1: The basic process of dynamic evaluation
.
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
342

2.3 Construction of Evaluation Index
Database
Indexes usually do not exist independently, and there
are often related and inclusive relationships among
indexes. It is easy to generate disputes in the process
of description, production and use. The reliability of
index data itself and the processing process of data
are very important. Only on the open and
interoperable data-based platform, can indexes
realize their potential (Wilsdon et al., 2015). In this
paper, the definition and evaluation standard of the
index are given. According to the index calculation
method, the production process of the index is
component-based, and the index is processed in the
form of knowledge map, which can reduce
misunderstanding as much as possible and give full
play to the potential of the index. The index database
is a complete set of indexes that may be involved in
the evaluation of a certain field. It can be established
by consulting relevant experts, querying scientific
research literature and other ways. By
componentizing these indexes, an evaluation index
component database for this field is formed.
Evaluators can find valuable indexes from the index
database according to their needs.
2.4 Componentization of Evaluation
Method
The evaluation method is component-based, that is,
the evaluator develops and designs the weight
calculation method components and evaluation
method components according to the purpose of
decision and evaluation. After testing, they are
uploaded to the Web server, and finally the evaluation
method component library is built. The use of
component library is simple and low-cost. Evaluators
only need to know the service objects and computing
properties of all components in the component
library, obtain the corresponding components through
personalized customization and evaluation theme,
and add them to the corresponding nodes of the
knowledge map to calculate the weight of each
evaluation index and the evaluation results.
Weight calculation component library: There are
many methods to calculate the weight of each index
in evaluation. In addition to AHP, there are principal
component analysis, Delphi, mean square error,
membership frequency, entropy determination and so
on. Each method has its own advantages and
disadvantages and application. If these weight
calculation methods are packaged into components,
the evaluators can use them on demand, or use a
variety of weight determination methods for
comparative analysis.
Evaluation method component library: The
starting point, evaluation mechanism and applicable
objects of different comprehensive evaluation
methods are different, and each method has its
advantages and disadvantages. The evaluation
conclusions of different methods for the same object
may not be consistent. The evaluation method is
packaged as a component, and the evaluation method
component library is constructed. The advantages and
disadvantages of these methods and the applicable
objects are compared and summarized. The evaluator
can customize different methods components at any
time, dynamically get the evaluation results of
different methods and support decision-making. Due
to the limited space, the paper takes the compound
fuzzy matter element method as an example to
analyze how to make the evaluation method
component based.
Step 1. the calculation steps of compound fuzzy
matter element (Du et al., 2021):
(1) Using m eigenvalues of n things to construct
m-dimensional composite fuzzy matter elements 𝑄
of n things:
𝑄
=
𝑞
⋯𝑞
⋮⋮
𝑞
⋯
𝑞
(1
)
𝑞
is the corresponding index value.
(2) In fuzzy matter-element model, the fuzzy
value is usually the relative membership degree 𝑢(𝑞)
of each characteristic value. According to the
characteristics and functions of the index, it can be
divided into the larger the better type (Formula 2) and
the smaller the better type (Formula 3). The
calculation formulas are as follows:
𝑢
=
𝑞
𝑞
(2)
𝑢
=
𝑞
𝑞
(3)
Where 𝑢
is the normalized value of index 𝑞
;
𝑞
and 𝑞
is the maximum and minimum of
each index.
(3) The relative membership of each eigenvalue is
used to construct the fuzzy matter element with
superior membership 𝑄′
:
𝑄
=
𝑢
⋯𝑢
⋮⋮
𝑢
⋯𝑢
(4
)
Study on Dynamic Evaluation of River Health based on Theme Service
343
(4) Using the constructed standard fuzzy matter
element 𝑄
and 𝑄′
to calculate the difference
square fuzzy matter element 𝑄
:
𝑄
=
𝛥
⋯𝛥
⋮⋮
𝛥
⋯𝛥
(5)
Where 𝛥
=𝑢
𝑢
(
𝑖=1,2,∙∙∙, 𝑚;𝑗=1,2,∙
∙∙,𝑛
)
.
The u in standard fuzzy matter element takes the
maximum value of the superior membership degree
of each evaluation index, which is generally 1.
(5) Substitute the weight and difference squared
fuzzy matter element 𝑄
into the calculation to get
the Euclid nearness ρ
, the ρ
is used to represent
the comprehensive index of river health. According
to the closeness degree, the river health status is
classified, and the evaluation grade is given.
ρ
=1
𝓌
𝛥
(6)
𝓌
is the weight value.
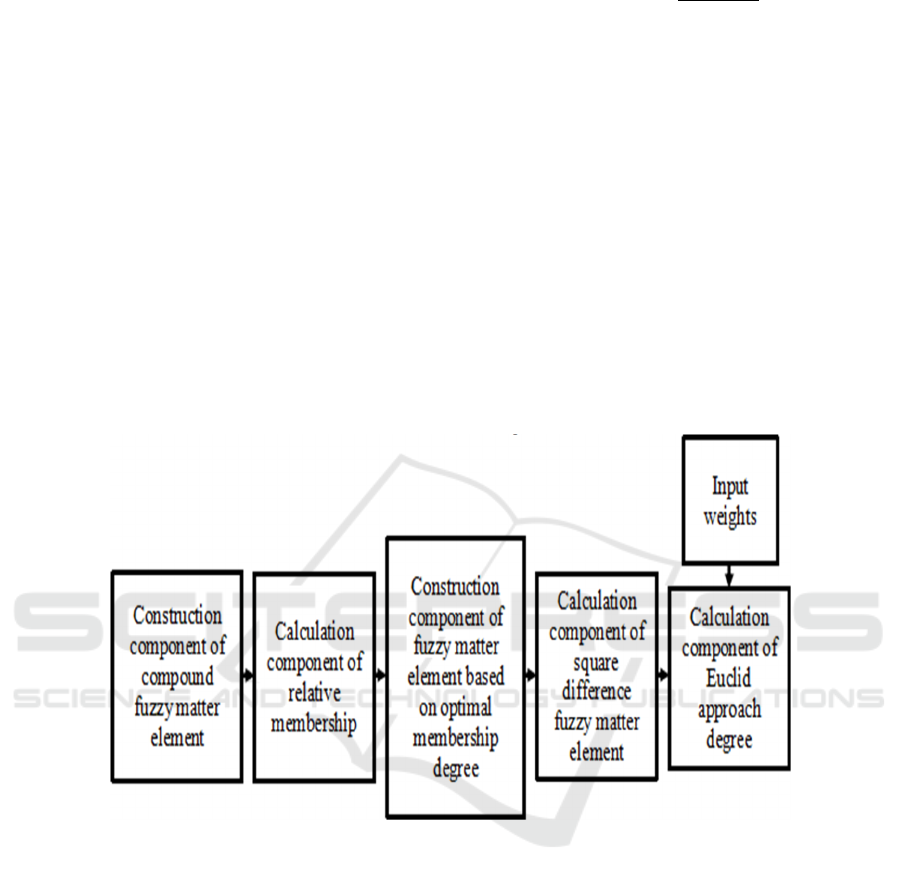
Step 2. According to the above steps, combined
with the component development process, the
compound fuzzy matter element method is divided
into five computing components: compound fuzzy
matter element construction component, relative
membership calculation component, fuzzy matter
element based on optimal membership degree
construction component, difference square fuzzy
matter element calculation component, Euclidean
approach degree calculation component. According
to the process in step 1, the logical relationship of the
five computing components is determined as shown
in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Composite fuzzy matter-element method calculation component module relationship map.
Step 3. Based on the synthesis integrated platform,
the component technology is used to develop the
computing components divided in step 2 and stored
in the method component library of the platform.
During the evaluation process, the relevant
components can be called from the method
component library for calculation.
2.5 Drawing of Evaluation Theme
Knowledge Map
After determining the evaluation theme, establishing
the relevant evaluation index database and
modularizing the evaluation method, draw the
knowledge map of the evaluation theme based on the
synthesis integrated platform. Firstly, open the
synthesis integrated platform, create a new
knowledge map, draw the knowledge map according
to the established evaluation process, retrieve the
components related to the required evaluation indexes
and methods from the component library, and add the
components to the corresponding nodes of the
knowledge map after customization; if the knowledge
package has been drawn and meets the requirements
of the evaluation theme, the existing knowledge map
results can be opened through the knowledge pack
management interface, and can be used directly or
after modification on the original knowledge map.
After the knowledge map is modified, it is packaged
and released to achieve the purpose of knowledge
accumulation and sharing. In the follow-up
evaluation or evaluation for other themes, we can
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
344

make full use of the existing relevant achievements of
the theme database as a reference for solving similar
complex decision-making problems. The main work
of theme knowledge map includes drawing nodes,
designing component interfaces, customizing
components, etc. There are some connections
between these works, such as the data requirements
of front-end components flowing to subsequent
components in the evaluation process, or the
relationship between front-end nodes and back-end
nodes in the knowledge map. Based on the drawn
theme evaluation knowledge map, select and
customize the method components suitable for the
evaluation theme from the component library, quickly
get the evaluation results of different methods, and
realize dynamic evaluation.
3 APPLICATION EXAMPLES
3.1 Support of Dynamic Evaluation
Theme Service
Weihe River is the largest tributary of the Yellow
River, with a total length of 818 km and main stream
of 502km in Shaanxi. It flows through Baoji,
Xianyang, Yang ling agricultural demonstration area,
Xi'an and Weinan and across Guanzhong Plain. In
Shaanxi, the upstream section is above Baoji, the
midstream section is from Baoji Gorge to Xianyang,
and the downstream section is after Xianyang. The
elevation difference between the upstream and
downstream is nearly 3000m.
In this study, the watershed controlled by
Xianyang hydrological station to Lintong
hydrological station of Weihe River is selected as the
study area. The Xianyang-Xi'an section of the main
stream of Weihe River is about 63.48km long and the
watershed area is about 11600km
2
.This area is
located in the downstream area of Weihe River,
belonging to the impact plain, with gentle terrain and
many tributaries. The total population of Xi'an and
Xianyang is large, and the industry is relatively
developed. Therefore, the main stream of Weihe
River in this area is the direct receiving water body of
industrial wastewater and domestic sewage on both
banks of Weihe River, and this area is a relatively
serious area of the whole main stream of Weihe
River.
The data used in this paper come from Shaanxi
water resources bulletin, Shaanxi Provincial monthly
report on water environment and so on.
3.2 Establish the Themes and Methods
of River Health Evaluation
According to the previous investigation on the
Xianyang-Xi'an section of the main stream of Weihe
River, considering the concerns of the management
department and the actual situation of the river, and
combined with the opinions of relevant experts, two
types of themes for river health evaluation are
determined. The themes determined in this paper
mainly consider the river ecosystem structure and
social service function, including the theme of river
ecological environment quality and the theme of river
social service function capacity. After determining
the evaluation theme, the evaluation method is
modularized according to Section 2.4. For the above
two themes, by reviewing literature and consulting
experts, this paper decides to use analytic hierarchy
process, principal component analysis, fuzzy
comprehensive evaluation, composite fuzzy matter-
element method, and comprehensive index method to
optimize and evaluate the indexes under different
themes. Above methods are detailed in the literatures
(Du et al., 2021; Zeng et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2007;
Liu et al., 2018; Shen, 2008) and are not repeated in
the paper due to space constraints.
3.3 Construction of Evaluation Index
System under Different Themes
Due to the complexity of river health status and the
differences of health problems in different rivers,
there is no fixed index system that can be applied to
the health evaluation of any river. It is necessary to
update the theme and modify the index system
according to the actual situation of the river. Through
the early investigation and analysis of the health
status of the Xianyang-Xi'an section of the main
stream of Weihe River, combined with expert
opinions, the evaluation indexes corresponding to
each theme are selected from the 42 evaluation
indexes (omitted) in the evaluation index database
constructed in Section 2.3, the initial evaluation index
system is established, and then the indexes are
optimized in combination with subjective experience
and expert opinions. The evaluation indexes are
optimized by fusing multi-source data (Yang et al.,
2015). The methods mainly include: using the
calculation results of analytic hierarchy process to
eliminate the indexes with small weight, using
common diagnosis and correlation analysis to
eliminate the indexes with high correlation degree,
using sensitivity analysis to eliminate the indexes
with low discrimination, and using principal
Study on Dynamic Evaluation of River Health based on Theme Service
345
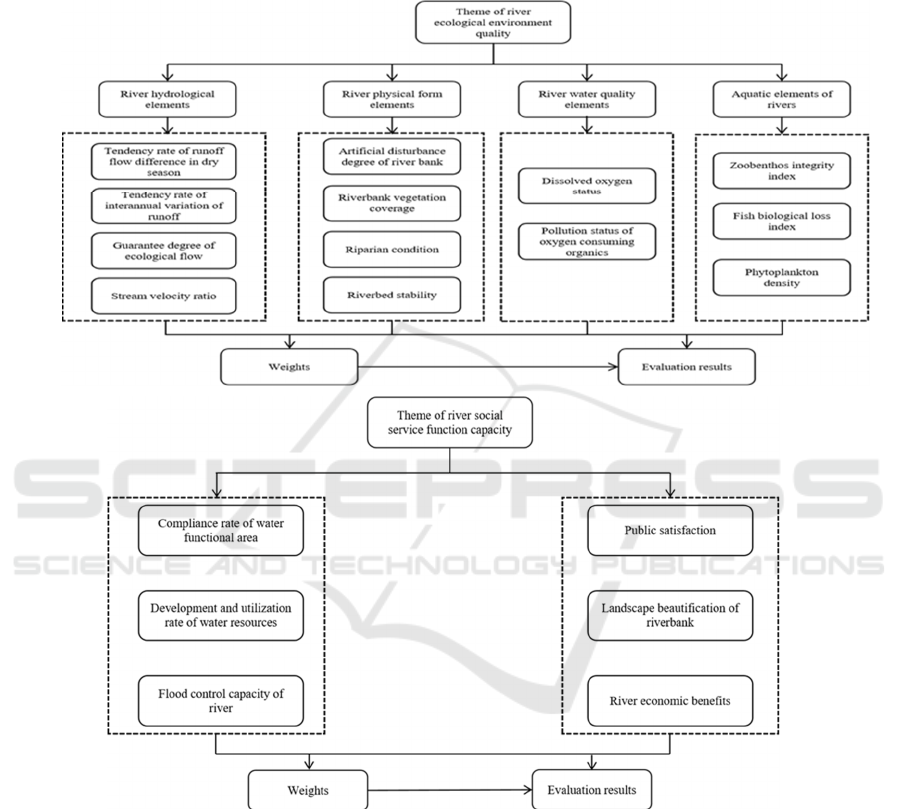
component analysis to calculate the load matrix of
each initial index. Extract the indexes with high load,
and finally construct the evaluation index system
suitable for each theme. Through the screening and
sensitivity analysis of the initial evaluation index
system. 19 evaluation indexes are finally determined
in Figure 3, including 13 indexes of river ecological
environment quality and 6 indexes of river social
service function capacity.
(a)
(b)
Figure 3: Evaluation index system of different themes of river health in the Xianyang-Xi'an section of the main stream of
Weihe River.
3.4 Dynamic Evaluation based on the
Synthesis Integrated Platform
Based on the synthesis integrated platform, the
evaluation index systems corresponding to different
themes constructed above are described and
visualized, and the evaluation knowledge maps
corresponding to different indexes are drawn, as
shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. According to the
knowledge map, call the weight calculation method
component developed in Section 2.4 to calculate the
weight of each theme of evaluation indexes. After
calculating the weight of each evaluation index,
obtain the statistical data of each evaluation index
from the database, and call the evaluation method
component developed in Section 2.4 to calculate the
evaluation results of the theme. Considering the
complexity and dynamism of the actual situation of
different rivers, when the river needs to increase the
evaluation theme or supplementary evaluation index
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
346
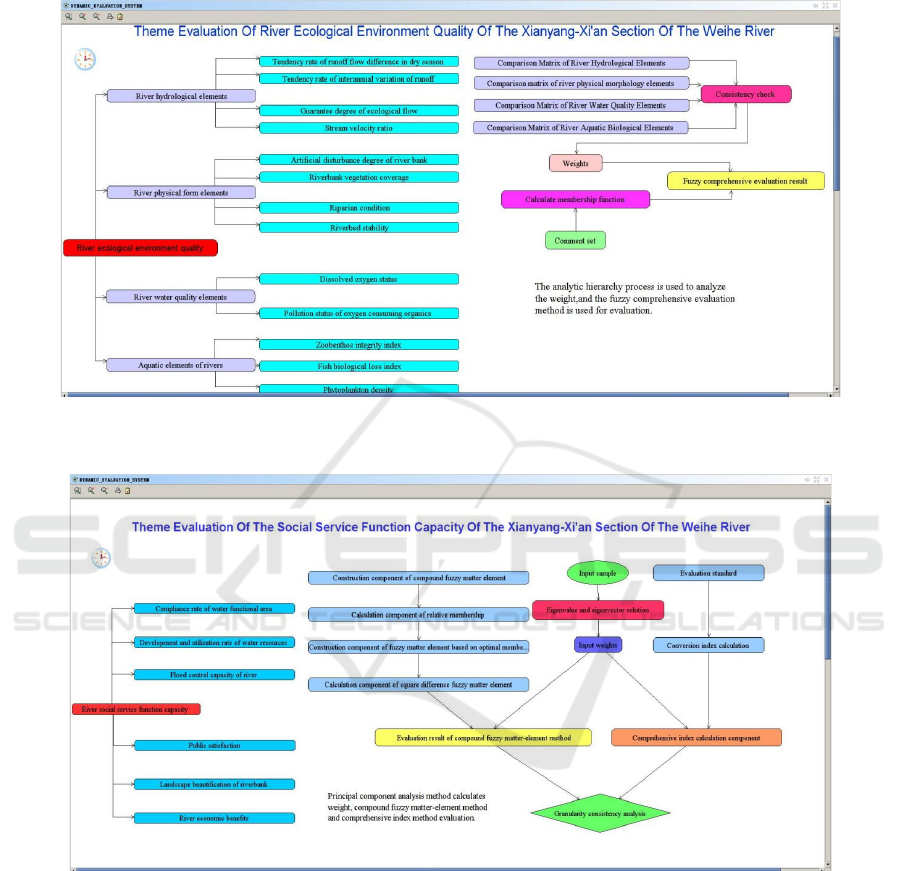
when the great change takes place, based on the
synthesis integrated platform, the knowledge map can
be modified rapidly, and the new evaluation index
weight and evaluation results can be calculated from
the component library, and the dynamic process of
evaluation is realized.
Figure 4: Theme evaluation knowledge map of river ecological environment quality in the Xianyang-Xi'an section of the
main stream of Weihe River.
Figure 5: Theme evaluation knowledge map of river social service function capacity in the Xianyang-Xi'an section of the
main stream of Weihe River.
3.5 Analysis and Discussion on
Evaluation Results of Different
Indexes
According to the relevant data collected, the river
health evaluation years of different themes are unified
to four years from 2015 to 2018. Due to the different
emphasis and evaluation indexes of different
evaluation themes, different evaluation methods are
used to evaluate different themes in this paper. Due to
the componentization of the corresponding evaluation
methods in Section 2.4, the corresponding evaluation
method components can be quickly called for
calculation based on the synthesis integrated platform.
When applied to the health evaluation of other rivers
in China, the evaluation model adopted in this paper is
also applicable.
Study on Dynamic Evaluation of River Health based on Theme Service
347
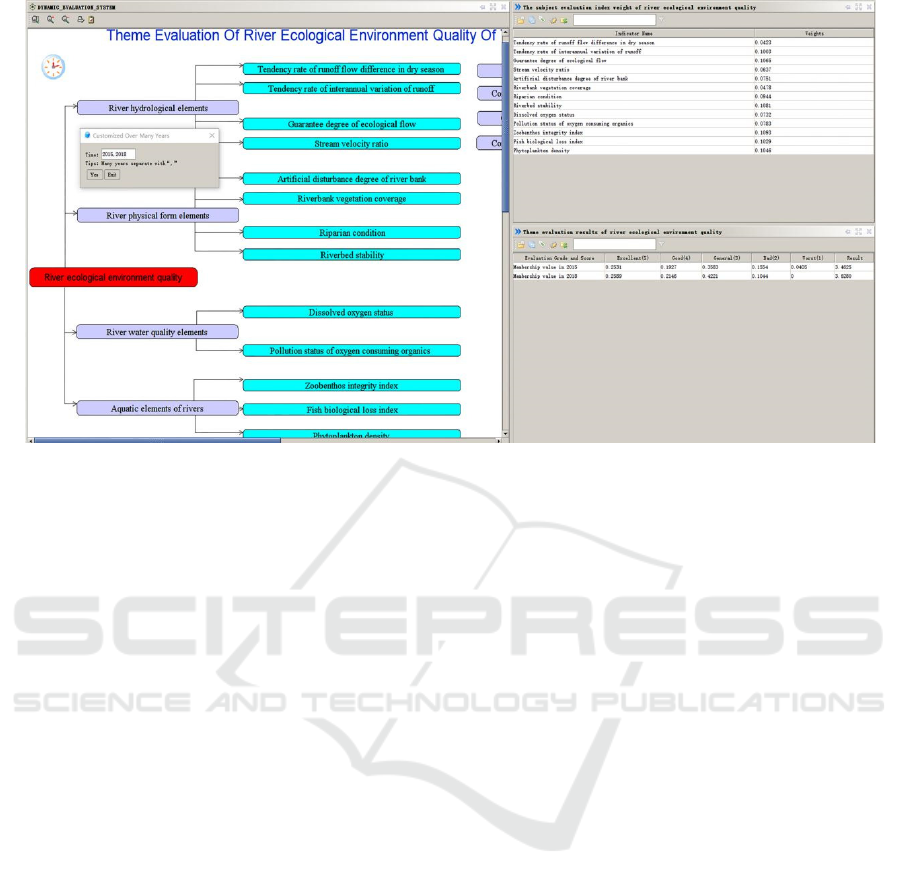
Figure 6: Theme evaluation results of river ecological environment quality in the Xianyang-Xi'an section of the main stream
of Weihe River.
3.5.1 Theme Evaluation Results and
Analysis of River Ecological
Environment Quality
AHP is used to determine the weight of the evaluation
index of the river ecological environment quality
theme in the Xianyang-Xi’an section of the main
stream of Weihe River. Fuzzy comprehensive
evaluation method is used to comprehensively
evaluate the river ecological environment quality
theme in 2015 and 2018. The results are shown in
Figure 6. According to the calculated membership
values, the results of the theme evaluation of river
ecological environment quality in 2015 and 2018
were 3.4625 and 3.6280 respectively by weighted
calculation with the score of the evaluation grade.
Among them, the membership of the corresponding
grade "general" was the largest, which was 0.3583
and 0.4221 respectively. The river ecological
environment quality in 2015 and 2018 was between
"good" and “general”, and the situation in 2018 was
improved compared with that in 2015. Through
statistical data analysis and practical investigation, it
is found that the evaluation results are basically in line
with the actual situation.
3.5.2 Theme Evaluation Results and
Analysis of River Social Service
Function Capacity
Principal component analysis was used to determine
the evaluation index weight of the theme of social
service functional capacity. Due to the deep-seated
interaction among the evaluation indexes of the theme
of social service functional capacity, such as the
substandard water functional area, the poor flood
control capacity of the river and the low degree of river
bank landscaping will reduce public satisfaction; The
low utilization of river water resources will also affect
the economic benefits of the river. Therefore, the
composite fuzzy matter-element method and the
comprehensive index method are used to conduct a
comprehensive evaluation on the four years of 2015,
2016, 2017 and 2018, and the granularity analysis is
used to judge the consistency of the evaluation results
of the two methods, and the results are shown in
Figure 7. It can be seen from the evaluation results that
the evaluation ranking of the two methods is
consistent. From 2015 to 2018, the social service
function capacity has improved year by year, and each
evaluation index has developed healthily year by year.
The evaluation results are consistent with the actual
situation that Xi'an and Xianyang have carried out
Weihe River control measures in recent years to
ensure the safety of river flood discharge, so that there
are beautiful green forest belts, landscape parks and
ecological wetlands on the bank side of Weihe River,
and the public satisfaction has been greatly improved.
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
348

Figure 7: Theme evaluation results of river social service function capacity in the Xianyang-Xi'an section of the main stream
of Weihe River.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This paper puts forward the dynamic evaluation mode
of river health based on theme service, builds the
dynamic evaluation system of river health based on
theme service through the synthesis integrated
platform, and draws different theme knowledge maps
to make the whole evaluation process visible and
credible. By developing components and drawing
theme knowledge map, complex evaluation problems
are simplified with the help of information
technology. The component technology is used to
establish the evaluation index weight calculation
component library and evaluation method component
library. For the same or different evaluation themes,
the method components can be quickly extracted, and
the evaluation system can be quickly built to obtain
the evaluation results of different index systems and
multiple evaluation methods. Based on the synthesis
integrated platform, the evaluation index system can
be updated quickly, the knowledge map can be
modified dynamically, and dynamic evaluation can
be realized.
The application example of the Xianyang-Xi'an
section of the main stream of Weihe River shows that:
Based on theme service mode can realize river health
evaluation quickly and from multiple angles, which
has more advantages than traditional evaluation
methods. The results show that: In 2015 and 2018, the
river ecological environment quality was between
"good" and "general", and the situation in 2018 was
improved compared with that in 2015. From 2015 to
2018, the social service function capacity and
evaluation indexes of rivers have been improved year
by year. The evaluation results of different themes are
consistent with the field research and previous
research results, which shows that the dynamic
evaluation results based on theme services proposed
in this paper are credible, practical and worth
popularizing.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Natural Science Basic
Research Program of Shaanxi Province (Grant No.
2019JLZ-16, 2019JLZ-15) and Science and
Technology Program of Shaanxi Province (Grant
No.2019slkj-13, 2020slkj-16, 2018slkj-4). The
authors thank the editor for their comments and
suggestions.
REFERENCES
Anthony, R. L., Lindsay, J. W., & Jane, A. D. (1999).
Development and testing of an Index of Stream
Condition for waterway management in Australia.
Freshwater Biology, 41(2), 453-468.
Chen, A., Sui, X., Wang, D. S., Liao, W. G, Wu, S. N., &
Tao, J. (2014). River ecosystem health assessment and
implications for Post-Project environmental appraisal
Study on Dynamic Evaluation of River Health based on Theme Service
349

in China. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 3636, 8-
12.
Chen, X., Jin, T. T., & Su, H. D. (2019). Construction and
application of health evaluation index system for Lhasa
River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(03), 799-809.
Du, X. Z., Yuan, Y. L., & Meng, Y. (2021). Comprehensive
health evaluation of Huaihe River mainstream based on
compound fuzzy matter element-entropy weight
combination model. Water Resources Protection,
37(03), 145-151.
Gu, X. Y., Xu, Z. X., Liu, L. F., Yin, X. W., & Wang, M.
(2018). Health evaluation of the stream ecosystem in
the North Canal River Basin, Beijing, China.
Environmental Science, 39(06), 2576-2587.
Li, Y. Y., Yu, L. J., & Lv, X. Y. (2016). Health evaluation
and repairing mode on river ecosystem of Huaihe River
basin (Henan section). Environmental Science &
Technology, 39(07), 185-192.
Lian, P. T., Pan, E. H., & Xie, J. C. (2019). Issues and
dynamic realization of water right confirmation. Water
Resources Informatization, 5, 20-25.
Liu, Y. (2018). Study of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
model for river health evaluation. GuangXi Water
Resources & Hydropower Engineering, 4(02), 95-99.
Petersen, R. C. (1992). The RCE: a riparian, channel, and
environmental inventory for small streams in the
agricultural landscape. Freshwater Biology, 27(2), 295-
306.
Pinto, U., & Maheshwari, B. (2014). A framework for
assessing river health in peri-urban landscapes.
Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 14(2), 121-131.
Raven, P. J., Holmes, N. T. H., & Dawson, F. H. (1998).
Quality evaluation using River Habitat Survey data.
Aquatic Conservation Marine & Freshwater
Ecosystems, 8(4), 477-499.
Shen, Y. P. (2008). Case study on evaluation of urban river
ecosystem health. Meteorological and Environmental
Sciences, 4(02), 13-16.
Wang, S., Zhang, Q., Yang, T., Zhang, L. Q., Li, X. P., &
Chen, J. (2019). River health assessment: Proposing a
comprehensive model based on physical habitat,
chemical condition and biotic structure. Ecological
Indicators, 103, 446-460.
Wilsdon, J., Allen, L., Belfiore, E., Campbell, P., Curry, S.,
Hill, S., Jones, R., Kain, R., Kerridge, S., Thelwall, M.,
Tinkler, J., Viney, I., Wouters, P., Hill, J., &Johnson,
B. (2015). The Metric Tide: Report of the Independent
Review of the Role of Metrics in Research evaluation
and Management. United Kingdom: Higher Education
Funding Council for England.
Xie, J. C., Chai, L., & Gao, Y. (2015). Theme-oriented
service for business application mode based on
platform. Water Resources Informatization, 6, 18-24.
Xie, J. C., & Luo, J. G. (2010). Integrated service platform
for the information explosion process in water
resources industry and its application pattern. Water
Resources Informatization, 5, 18-23.
Yang, L., Wang, N., & Xie, J. C. (2015). Index optimization
of eco-environment evaluation in irrigation district
based on multi-source information fusion decision.
Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural
Engineering, 31(14), 225-231.
Zeng. W. Y., Wang, L. Q., & Li, T. N. (2020). Health
evaluation analysis of the lower reaches of the main
stream of Wuken River based on Analytic Hierarchy
Process. Water Conservancy Science and Technology
and Economy, 26(08), 18-21+32.
Zhang, Y., Liu, L., & Yan, W. M. (2007). Study on water
environment secuirty of the Three Gorge reservoir
region. Sciencepaper Online, 4(09), 666-672.
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
350
