
Flow and Sediment Movement Characteristics on the Varisized Plain
of Compound Channel
Zuwen Ji
*
, Dangwei Wang, Qing Lu and Anjun Deng
State Key Laboratory of Simulation and Regulation of Water Cycle in River Basin, China Institute of Water Resources and
Hydropower Research (IWHR), 20 Chegongzhuang West Road, Beijing, 100048, China
Keywords:
Compound channel, Flow velocity, Sediment concentration, Main channel, Flood plain
Abstract: In this paper, river reaches are generalized into two types: the straight and lotus-root-shape compound
channels according to plane characters of the Lower Yellow River and the Songhuajiang River. It can be seen
from some experimental data of flow and sediment in two kinds of channels. The difference arises from the
fact that the momentum transfer is stronger in the louts-root-shape channel than in the straight channel. Thus,
the relative velocity of plain to channel type, still increases with increment of the relative depth, their
differences are large at the lower relative depth, but close at the higher one. The distributions of flow velocities
in two channels are similar with water depth, and the mean velocities are on the decline from main channel to
flood plain. At two sides of floodplain, the change ranges from maximal to minimal velocities. Transverse
velocity gradient in the interface area is bigger in the straight channel than in the lotus-root-shape channel.
This is largely because, relative sediment concentration in both compound channels go up with the increase
of the relative velocity and depth. The relationship of sediment concentration to depth, is such that, the
enlarging speed is more rapid in the straight channel than in the lotus-root-shape channel. The transverse
variation of the vertical average sediment concentration is smaller in the lotus-root-shape channel than in the
straight channel, and are bigger on the plain than in the channel.
1 INTRODUCTION
The average annual sediment load in the Lower
Yellow River was 1.6 billion tons before 1980s, and
ranked first in the world. The average sediment
concentration was 35 kg/m
3
and the highest sediment
concentration was recorded at 911 kg/m
3
. Large
quantities of sedimentation have resulted in
“suspended rivers” and frequent shift of the river
courses in the lower reaches. The average level of
riverbed is 4 to 6 m higher than that of normal ground
level, and the maximum has reached 13m in some
places. This explains why Throughout the history of
China, the Yellow River has been associated with
floods and famine. It has been a difficult problem to
harness the Yellow River because, the whole length
of the lower reach is about 878 kilometers. In its plane
form, it is involved in mainly meandering and
wandering, and their configurations of cross-section
include two parts: main channel and floodplain. The
area of floodplain is about 3,544 km
2
, accounting for
84 % in the total area of the river. Thus, it is very
important to study flow and sediment in the
compound channel in the Lower Yellow River.
Compound channels are universal forms of fluvial
river, and are often in areas that are densely populated
and economically developed. Compound channels
are different in form of expression from those in the
natural rivers. From the point of view of cross-
sectional shape, although all compound channels
have basic forms like main channel and flood plain,
other variants exist such as, one plain with one
channel, two plains with one channel, and even much
more channels and plains; For plane form, there are
equally many expressions, such as straight channel,
lotus-root-shape channel, meandering channel and so
on, increasing the complexity of the research. The
problems that overbank flooding of compound
channels causes necessitates water resource planning,
floodplain planning, flood level design, channel
improvement and so on. At present, the research on
the overbank flow in the compound channels mainly
focuses on the study of the flow structure and the
interaction mechanism of the plain channel. The bed
shear stress and resistance characteristics of the
Ji, Z., Wang, D., Lu, Q. and Deng, A.
Flow and Sediment Movement Characteristics on the Varisized Plain of Compound Channel.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Water Resource and Environment (WRE 2021), pages 171-178
ISBN: 978-989-758-560-9; ISSN: 1755-1315
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved
171
compound channel were also observed (Lyhess et al.,
2001; Knight, 1999). The relationship between flow
structure and flow distribution characteristics and bed
morphology were studied (Hu et al., 2010;
Wormleaton et al., 2004; Ji et al., 2016). The basic
exchange model and distribution characteristics of
flow and sediment were put forward (Armugha et al.,
2018; Chen & Zhang, 1996; Knight, 2005; Moron et
al., 2017). The influence of overland flow on bed
morphology, surface slope and sediment transport
were analysed (Tang & Knight, 2006; Ji et al., 2019;
Wu et al., 2020). The above results lay a good
foundation for related researches of compound
channel, as presented by the analysis of two
generalization physical model experiments.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
METHODOLOGY
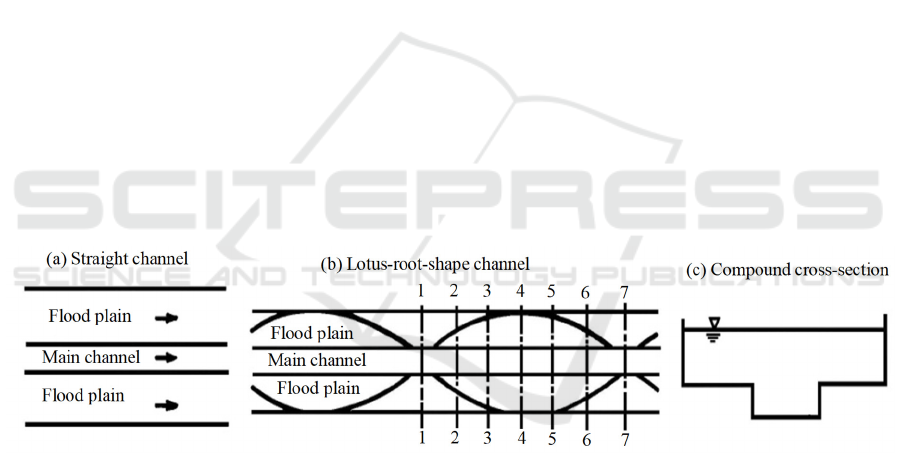
This experimental study conducted on a 30m long
circulating straight channel, with basic dimensions of
width of 0.3m, floodplain width of 0.7m and beach
channel bed height difference of 0.06m. The bed
surface and side wall of water channel are both
cement surfaces, and the water channel structure is
shown in Figure 1 (a) to (c). For lotus-root-shape
channels, the width of main channel was 0.3m and the
width of floodplain was 0-0.7m. The whole water
channel is composed of four lotus roots with each
having a length of 4m. The transition section with the
length of 1m exists between every two lotus roots.
The outer boundary of each lotus root is symmetrical
about the axis of the main channel circular arc and
curvature of 0.17m. The water channel structure is
indicated in Figure 1(b) and Figure 1 (c), and 7 cross
sections are arranged on experimental measurement
section.
In this experiment, cross-sections of straight
channel and lotus-root-shape channel are both
considered, rectangles with equal main channel width
and beach channel height difference. However, the
outer boundary of straight channel is unchanged
along the way, and that of lotus-root-shape channel is
curved with a great change along the way. In order to
facilitate comparison, the lotus-root-shape channels
adopt 4
#
cross section, and the size of this section is
exactly consistent with that of straight channel.
During the experiment, the experimental water depth
of straight compound channel is taken as 0.02 m~
0.13m, and the sediment concentration is 4 ~
83kg/m
3
; the experimental water depth of lotus-root-
shape compound channel is given by 0.07 ~ 0.12 m,
while the sediment concentration is 4 ~ 25kg/m
3
.
Both compound channels use the same experimental
sand with a median grain size of 0.014mm.
Figure 1: Sketches of the straight and the lotus-root-shape compound channels.
3 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS ON
FLOW MOVEMENT
CHARACTERISTICS OF TWO
TYPES OF COMPOUND
CHANNELS
3.1 Cross-section Flow Capability
According to the water level flow relationship
between straight channel and lotus-root-shape
channel, it can be known that under the same water
depth, whether for main channel or floodplain, the
flow capacity of lotus-root-shape channel is less than
that of straight channel. The greatest difference lies in
total flow capacity of cross section, closely followed
by the flow capacity of main channel, relative to the
smallest difference in the flow capacity of floodplain.
In case of small water depth of floodplain, the
difference in the flow capacity of the two channels is
small. As the water depth increases, that difference
becomes gradually greater.
Figure 2 shows the water level flow relationship
between three channels, i.e., single channel, straight
compound channel and lotus-root-shape compound
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
172
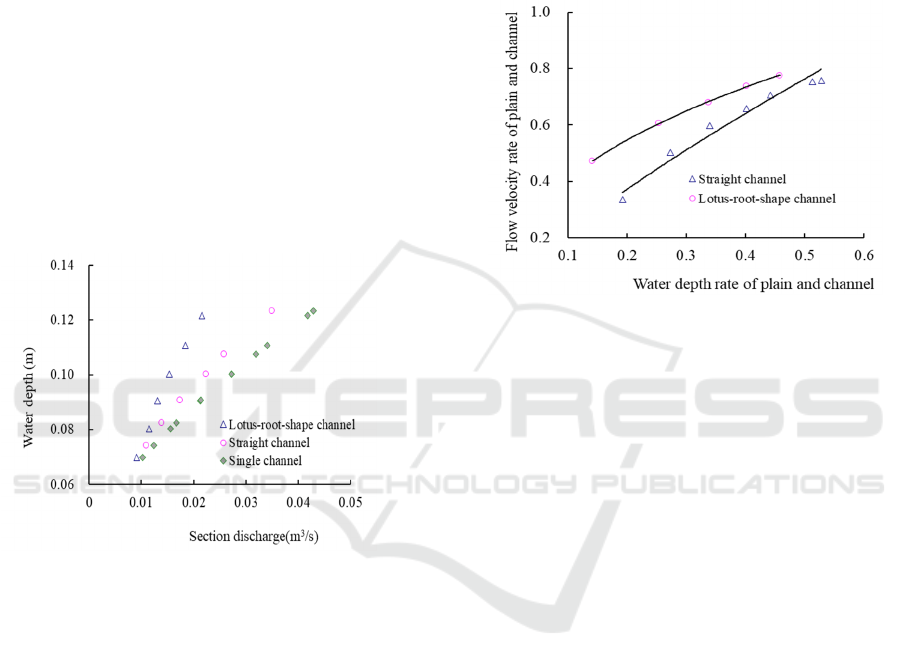
channel. Among them, the water level flow
relationship of straight channel and lotus-root-shape
channel are measured from data acquired by the
author, while that of single channel is the calculation
result obtained from the Manning formula assuming
the water depth to flow area is same as straight
channel to lotus-root-shape channel. It can be seen
from the figure that under the same water depth and
flow area, the single channel has the largest flow
capacity, followed by straight channel, and the least
is lotus-root-shape channel. Meanwhile, the
difference in the flow capacity of the three channels
becomes greater with water depth. In the case where
the relative water depth of floodplain is about 0.14 ~
0.51, the flow capacity of straight channel is reduced
by 7% - 21% compared with single channel; the flow
capacity of lotus-root-shape channel is reduced by
11% - 48% over single channel; the flow capacity of
lotus-root-shape channels is reduced by 4% - 34%
over straight channel.
Figure 2: Stage-discharge relations in single.
3.2 Average Flow Velocity of
Floodplain
The change in average flow velocity of lotus-root-
shape channel floodplain is basically like that of
straight channel. The flow velocity of main channel
and cross section increases first and then decreases
and then increases again with water depth. However,
the flow velocity of floodplain indicates monotonic
increases with water depth. The characteristics of this
change show that there is momentum exchange
between the floodplains of the two channels, but the
intensity is different, as shown in Figure 3. It can be
seen from the figure that regardless of water depth on
floodplain, the flow velocity of lotus-root-shape
channel is larger than that of straight channel. This
shows laterally, momentum exchange between the
lotus-root-shape channels is stronger than that of the
straight channel. Because the outer boundary of the
straight channel is straight, the longitudinal change of
floodplain flow is not large. In the lateral direction,
there is a certain difference in the flow velocity of
floodplain, which is small for lotus-root-shape
channels. This is because in the straight channel, the
floodplain current itself has a certain momentum. If
there is no floodplain momentum exchange, the
floodplain current cannot also flow.
Figure 3: Relations between relative velocity and straight
and lotus root - shape channels relative depth corresponding
to plain and channel.
This momentum is provided by the gravity
component of uniform water flow. The reason for the
momentum exchange between the floodplains is
mainly due to the certain difference in the flow
velocity of the two channels, and such difference
gradually decreases over water depth. However, in
the lotus-root-shape channels, the floodplain water
movement is different. Running in the transition
section, because of the single channel, the flow speed
is high. When the flow enters the diffusion section,
the current with higher momentum is transmitted to
floodplain. While before the momentum exchange of
floodplain current is very small. On the one hand, the
flow velocity of floodplain is very small; balanced on
the other hand, by the high velocity flow just before
entering the diffusion section. It is conceivable that
when they meet, due to the large difference in
velocity between the two channels, violent
momentum exchange will inevitably occur.
Therefore, the floodplain momentum exchange of
lotus-root-shape channels is stronger than that of
straight channels.
In addition, it can be seen from Figure 3 that when
the relative water depth of floodplain is relatively
small, the difference in the floodplain velocity of the
two channels is large. In case of larger water depth of
floodplain, the floodplain velocity ratio of the two
channels has a small effect.
Flow and Sediment Movement Characteristics on the Varisized Plain of Compound Channel
173

For a certain flowing cross-section, the momentum
of the water body on cross-section is constant. The
momentum of floodplain will increase, and the
momentum of main channel will be reduced. The
momentum exchange of lotus-root-shape channel
floodplain is more intense than that of the straight
channel. The momentum transferred from former
main channel to floodplain will be large inevitably, so
that the momentum of the main channel on lotus-root-
shape channels decreases more, and the increase in
amplitude of the momentum on floodplain is
relatively larger. Therefore, the floodplain velocity
ratio of lotus-root-shape channel is larger than that of
the straight channel. When the water depth of
floodplain is small, due to the larger floodplain
resistance, a considerable part of the reduced
momentum of the main channel is used to overcome
the floodplain resistance, and the actual momentum
obtained on the floodplain decreases. In the case of
basically equal water depths of the two channels, the
reduced momentum of main channel on lotus-root-
shape channel is larger than that of the straight
channel. It is shown that on the one hand, the main
channel of the lotus-root-shape channel reduces the
momentum more, and the floodplain indicates more
increased momentum; On the other hand, when the
momentum of the main channel of the straight
channel is reduced, the momentum of floodplain is
also less increased. Among the reduced momentum
of the main channel of the straight channel, the
momentum used to increase the velocity of floodplain
is less weighted relative to the remaining momentum
of the main channel. However, in the reduced
momentum of the main channel in the lotus-root-
shape channels, the momentum used to increase the
flow velocity of floodplain has a greater weight in the
remaining momentum of the main channel. When the
water depth of floodplain is relatively small, the
weight of the two channel types differs greatly, which
is expressed in the flow velocity ratio of floodplain,
i.e., the difference in floodplain velocity of lotus-root-
shape channels is greater than that of the straight
channel. With the increase of water depth on
floodplain, the difference in weight between the two
channels gradually decreases, and the difference in
floodplain velocity ratio also gradually decreases.
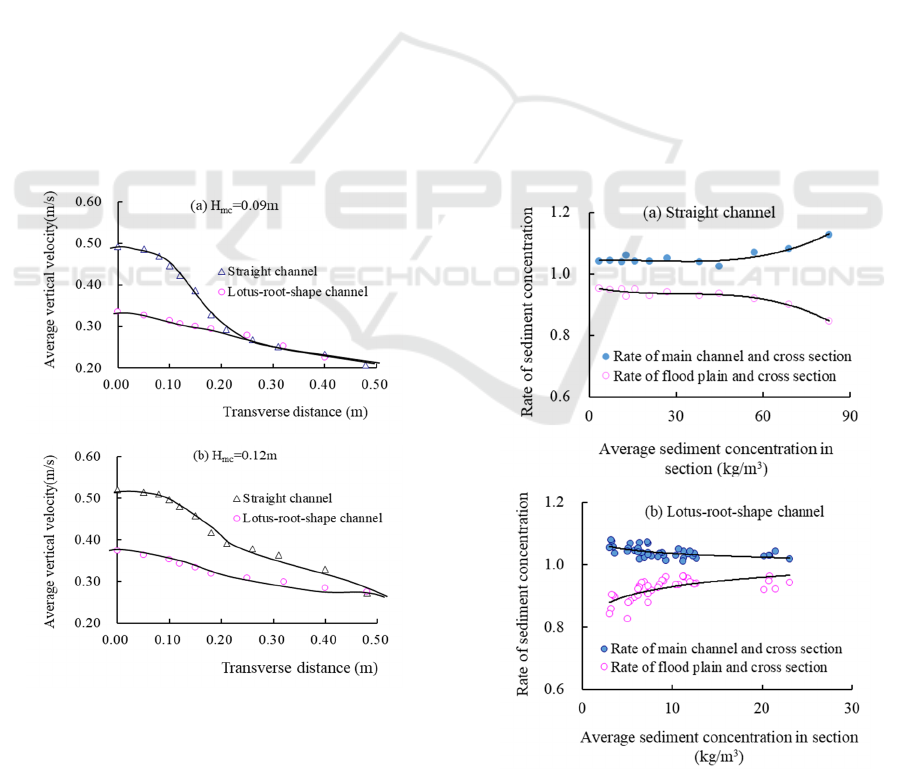
3.3 Vertical Velocity
There are some differences between the vertical
velocity distribution of lotus-root-shape compound
channel and the straight channel, which is mainly
manifested near the interface of floodplain. The
vertical velocity distribution of the straight channel is
large in the middle and small at two ends, while that
of lotus-root-shape channel basically shows the
characteristics of larger on the top while small at the
bottom, but the distribution is relatively uniform.
According to preliminary analysis, the momentum
exchange of floodplain in the straight channel is only
concentrated in a certain depth below the water
surface, which reaches the maximum at the water
surface and gradually weakens downward. This
exchange method determines that the vertical velocity
distribution is large in the middle, while small on
surface and bottom. However, in the lotus-root-shape
channels, almost the entire vertical line from water
surface to the bottom participates in the floodplain
momentum exchange, which is mainly due to the
strong momentum exchange of floodplain in lotus-
root-shape channels. The momentum exchange
process ensures that the main water body channel
with larger momentum entrains the floodplain water
body with less momentum into the main channel
water body. In addition, the main water body channel
with larger momentum in equivalent volume enters
the floodplain water body, which leads to the increase
of floodplain water body momentum. According to
the principle of conservation of momentum, it can be
shown that the momentum of main channel water
body will decrease. Due to the large difference in the
flow velocity of floodplain water body (especially
when it starts to diffuse), for the entrainment of main
water body channel on floodplain water body, almost
the entire vertical water body above the floodplain
bed surface participates in such exchange. It can be
seen from the rapid increase of floodplain flow
velocity that such exchange of massive water body
causes a sharp decrease in the momentum of the upper
water body of the main channel. The momentum
difference between the lower and upper water bodies
of the main channel becomes large sharply, so that the
upper and lower water bodies will inevitably generate
momentum exchange. This results in most of the
water bodies on the vertical line of the main channel
participating in the momentum exchange. The result
of this momentum exchange is the redistribution of
the momentum throughout the entire vertical line of
the main channel. In the vertical distribution, the
velocity is relatively uniform with small gradient, and
the distribution still shows the characteristics of larger
on the top and lower at the bottom, but the velocity
value of the entire vertical line decreases. It should be
noted that although there is also momentum exchange
in the vertical direction of water body of the straight
channel, the momentum exchange in the floodplain is
smaller than lotus-root-shape channel. Meanwhile,
momentum exchange is also gradual in the vertical
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
174
direction, i.e., gradually increasing from the
momentum exchange occurrence area to water
surface, and there is no sharp change between the
upper and lower water bodies in the area where the
momentum exchange occurs.
3.4 Average Velocity of Vertical Line
Distributed along the Lateral
Direction
The vertical average velocity of lotus-root-shape
compound channel is basically similar to that of the
straight channel in the lateral distribution. The
vertical average velocity gradually decreases from the
central area of the main channel to both sides of the
floodplain, as shown in Figure 4. However, there are
some differences between the two channels. First, the
difference between the maximum and minimum
velocity of the floodplain is different. The variation in
flow velocity of the lotus-root-shape channel is
smaller than that of the straight channel. Secondly,
the decreasing rate of vertical average velocity of
lotus-root-shape channel is smaller than that of the
straight channel. Lastly, the vertical average velocity
of the two kinds of compound channels differs greatly
in the main channel, while less in the floodplain.
Figure 4: Transverse distributions of the depth - averaged
velocity.
From the previous analysis, it can be known that
the movement status of floodplain flow of the lotus-
root-shape and straight channels before momentum
exchange of floodplain is different. For the main
channel, on the one hand, the difference in the flow
capacity of the two channels determines whether the
main channel of lotus-root-shape channel has less
momentum than the straight channel. On the other
hand, the momentum exchange of main channel flow
of the lotus-root-shape channel has larger weight than
the straight channel. Determined by the combined
effect of these two aspects, the vertical average
velocity of the main channel of the lotus-root-shape
channel is relatively smaller than that of the straight
channel. For the floodplain, on the one hand, the
momentum of the main channel water body in the
lotus-root-shape channel used for the momentum
exchange of floodplain has a larger weight. The unit
water body on the floodplain of the lotus-root-shape
channel gains more momentum than the straight
channel. On the other hand, before momentum
exchange, the floodplain water body of the straight
channel already has a certain momentum, while the
momentum of floodplain flow of the lotus-root-shape
channel is very small. Therefore, the combined effect
of these two aspects determines that the flow velocity
of the floodplain of the straight channel is larger than
the lotus-root-shape channel, but the difference
between the two channels is relatively smaller than
that of the main channel.
Figure 5: Relations among sediment concentration
corresponding to main channel, floodplain and cross section.
Flow and Sediment Movement Characteristics on the Varisized Plain of Compound Channel
175

4 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS ON
SEDIMENT CONCENTRATION
DISTRIBUTION
CHARACTERISTICS OF TWO
TYPES OF COMPOUND
CHANNELS
4.1 Average Sediment Concentration of
Floodplain
The distribution of the average sediment
concentration in the floodplain of the lotus-root-shape
compound channel has certain similarities to that of
the straight channel. In general, the average sediment
concentration of floodplain is less than that of the
main channel. However, the average sediment
concentration ratio of the floodplain cross section of
lotus-root-shape channels varies contrarily with the
change of the sediment inflow and the straightness of
the channel. As shown in Figure 5, the reason for this
difference may be due to the different boundary
characteristics of the two channels.
In the straight channel, the boundary is straight,
the flow of floodplain and main channel has a certain
capacity, and the momentum exchange occurs due to
the different velocity of the two channels. Because the
boundary is constant along the way, when the water
body runs a distance, the water body between
floodplain will reach a dynamic balance, the same is
true of the movement of sediment in the water body
of floodplain. In the straight channel, the water body
of floodplain has a certain ability to independently
carry sediment. Although the sediment in the water
body of main channel will enter floodplain partially
through the momentum exchange of floodplain, the
sediment of floodplain also enters the main channel
through the exchanges of water body. The average
sediment concentration of floodplain is less than that
of the main channel thus, the net transport of sediment
in the main channel to floodplain occurs. Before the
sediment concentration in the water body of
floodplain reaches saturation, the average sediment
concentration of floodplain is relatively small.
Therefore, the sediment transported to floodplain
from main channel is smaller compared to the
sediment carried by the floodplain itself, which is
negligible. In this case, since there is no obvious
siltation in the water body of floodplain, the average
sediment concentration of the floodplain changes
little. Therefore, the ratio of the average sediment
concentration of floodplain to the average sediment
concentration of cross section changes little with
sediment inflow. After the average sediment
concentration of floodplain reaches saturation, as
sediment inflow increases, the average sediment
concentration of the main channel also rises, but that
of floodplain cannot reach a significant increase due
to saturation. Therefore, the ratio of average sediment
concentration of floodplain to the average sediment
concentration of cross section (reflecting sediment
inflow) decreases as sediment inflow increases, and
the ratio of average sediment concentration of the
main channel to that of cross section increases as
sediment inflow increases. As the sediment inflow
increases, the siltation on floodplain increases, and
the net sediment transported to the floodplain from
the main channel increases. This also suppresses the
increase in the average sediment concentration of the
main channel and cross section to a certain extent. In
the lotus-root-shape channels, the channel boundary
is curved, and the flow cross-section of floodplain
varies greatly. The boundary characteristics of the
lotus-root-shape compound channel determine that
the momentum required for the movement of
floodplain is mainly provided by water body of main
channel. Similarly, the sediment carried by water
body of floodplain is also provided by the sediment
in the water body of the main channel. This means
that with the exchange of water body of floodplain
and the main channel will transport the net sediment
to the floodplain. Such net sediment transport volume
is the same order of magnitude as that in the water
body of floodplain. Meanwhile, with the increase of
sediment inflow, the net sediment transport from the
main channel to the floodplain gradually increases. It
can be seen that in the lotus-root-shape compound
channels, part of the sediment in water body of main
channel will be transported to the floodplain, and the
sediment concentration of the main channel itself will
also decrease, which is reflected in the ratio of
average sediment concentration of the floodplain to
that of the cross section, i.e., the ratio of the average
sediment concentration of the floodplain to that of the
cross section increases as the sediment inflow
increases. The ratio of the average sediment
concentration of the main channel to that of the cross
section decreases as the sediment inflow increases.
Before the sediment in the water body of floodplain
is saturated, the average sediment concentration of
the floodplain and that of the cross section vary
greatly. After the sediment in the water body of
floodplain reaches saturation, the sediment in the
water body of floodplain will become silted. As the
sediment inflow increases, the siltation on the
floodplain gradually increases, which further
suppresses the increase in the average sediment
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
176
concentration of the main channel and the cross
section, resulting in a decrease in the ratio of the
average sediment concentration of the floodplain to
that of cross section.
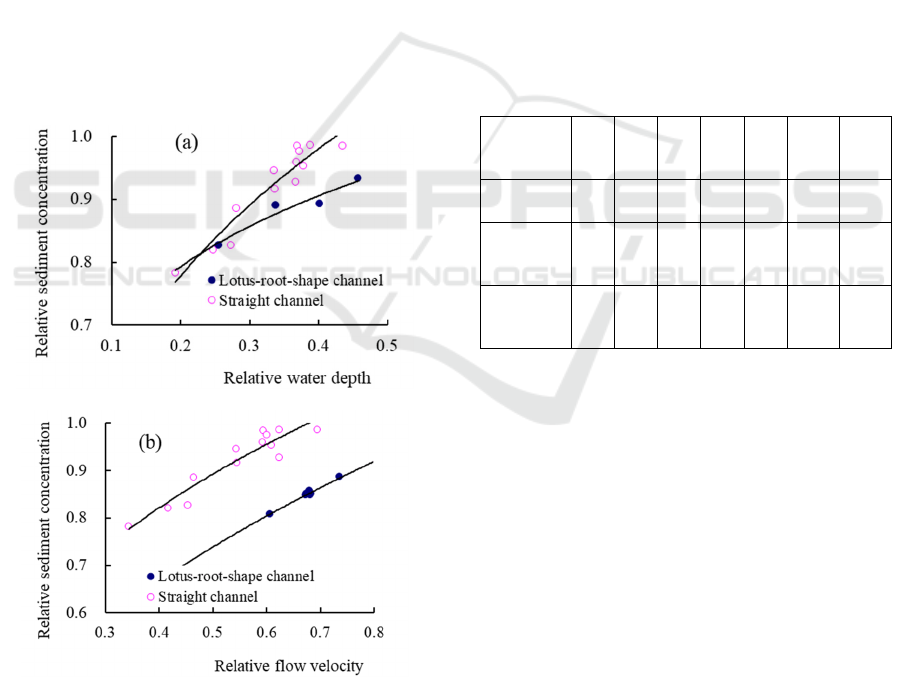
Figure 6 shows the relationship between the
relative sediment concentration of the straight
channel and the lotus-root-shape channel, the relative
water depth and the relative flow velocity of
floodplain. It can be seen from the figure that the
average sediment concentration ratios of the straight
channel and the lotus-root-shape channel both
increase with the increase in the relative water depth
of floodplain. However, the average sediment
concentration ratio of the floodplain along straight
channel increases faster with the relative water depth
of the floodplain, while the width of the lotus-root-
shape channel increases relatively slowly; the average
sediment concentration ratio of the floodplain of
straight channel and lotus-root-shape channel
increases with the rise in relative flow velocity of the
floodplain, while the amplitudes of the two channels
vary little with the relative flow velocity of the
floodplain.
Figure 6: Relations among relative velocity, sediment
concentration and depth for floodplain and main channel.
4.2 Distribution of Vertical Sediment
Concentration
It can be seen from Table 1 that the vertical gradient
of the sediment concentration of the lotus-root-shape
compound channels is smaller than that of the straight
compound channels. For the same river type,
regardless of the straight channels or lotus-root-shape
channels, the vertical average gradient of the average
sediment concentration of floodplain is always
significantly greater than that of the average sediment
concentration of the main channel, and that of
sediment concentration gradually increases from the
vicinity of floodplain interface to both sides of the
floodplain. It is shown that the vertical unevenness of
the sediment concentration of the floodplain is rather
larger than that of the main channel. Near the
interface of the floodplain, this unevenness reaches a
minimum value and gradually increases toward both
sides.
Table 1: Transverse gradient changes of vertical average
sediment concentration (kg/ m3.m).
Transverse
distance
(m)
0.00 0.08 0.12 0.15 0.25 0.35 0.45
Straight
channel
22.12 19.79 19.42 70.08 96.15 100.65 121.81
Louts-root-
shape
channel
16.47 15.86 15.62 64.13 77.34 80.51 99.21
Ddifference
b
etween the
two
5.66 3.93 3.80 5.95 18.82 20.14 22.61
5 CONCLUSION
By comparing the flow capacity of three types of
channels, i.e., single channel, straight compound
channel and lotus-root-shape compound channel, it is
known that the single channel has the largest flow
capacity, followed by the straight channel, and that of
the lotus-root-shape channel is the smallest.
The velocity ratio and discharge ratio of straight
channel and lotus-root-shape channel increase with
the increase of the relative water depth of plain and
channel, and the ratio of lotus-root-shape channel is
greater than that of straight channel.
The distribution of sediment concentration in the
floodplain of the lotus-root-shape compound channel
is similar to that of the straight compound channel.
However, the sediment concentration ratios of
Flow and Sediment Movement Characteristics on the Varisized Plain of Compound Channel
177

floodplain cross section of the two types show
contrary change laws with sediment inflow.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported was supported by
National Key Research and Development Program of
China (grant No. 2018YFC0407305) and the
National natural science foundation of China (grant
No. 51879282) and Technology Project of Power
China (grant No. DJ-PTZX-2019-05)).
REFERENCES
Armugha, K., Liaqat, A. K. R., Ali, P. Y., & Himanshu, G.
(2018). Characterization of channel planform features
and sinuosity indices in parts of Yamuna River flood
plain using remote sensing and GIS techniques.
Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 11(17), 1-11.
Chen, L., & Zhan, Y. Z. (1996). The form and function of
water and sediment exchange in overbank and high
sand - bearing stream. Journal of Sediment Research. 2,
45-9.
Hu, C. H., Ji, Z. W., & Guo, Q. C. (2010). Flow movement
and sediment transport in compound channels. Journal
of Hydraulic Research, 48(1), 23-32.
Ji, Z. W., Hu, C. H., & Ji, M. D. (2016). Distribution
characteristics of sediment grain size in compound
channel. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering,
24(4), 649-60.
Ji, Z. W., Hu, C. H., & Zhao, X. (2019). Characteristics of
water and sediment distribution in the lotus-root-shape
compound channels. Proceedings of the 38TH IAHR
World Congress-IAHR (pp. 307-314). Panama.
Knight, D. W. (1999). Flow mechanisms and sediment
transport in compound channel. Sino-US Workshop on
Sediment Transport and Disasters, 14(2), 217- 36.
Knight, D. (2005). Sediment transport in rivers with
overbank flow. Journal of Siehuan University
(Engineering Science Edition). 37, 16-29.
Lyhess, J. F., Myers, W. R. C., Cassells, J. B. C., &
Sullivan, J. J. (2001). Influence of planform on flow
resistance in mobile bed compound channels.
Proceedings of 11w Institution of Civil EngiBeers
(Water Maritime and Energy), 148(1), 5-14.
Moron, S., Edmonds, D. A., & Amos, K. (2017). The role
of floodplain width and alluvial bar growth as a
precursor for the formation of anabranching rivers.
Geomorphology, 278(1), 78-90.
Tang, X. N., & Knight, D. W. (2006). Sediment transport
in river models with overbank flows. Journal of
Hydraulic Engineedng, 132(1), 77-86.
Wormleaton, P. R., Sellitl, R. H. J., Bryant, T., Loveless, J.
H., Hey, R. D., & Calmur, S. E. (2004). Flow structures
in a two-stage channel with a mobile bed. Journal of
Hydraulic Research, 42(2), 145-62.
Wu, W. M., Wang, L., Ma, X. D., Nie, R. H., & Liu, X. N.
(2020). Flow Characteristics and Bed Morphology in a
Compound Channel between Two Single Channels.
Water, 12(12), 3544-3544.
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
178
