
Evolutions of Landscape Architecture in Jilin City of Northeastern
China
Yue Hu
1
, Hongli Zeng
1,*
and Chun Yan
2
1
Beijing Forestry University, Beijing 100083, China
2
China Fire and Rescue Institute, Beijing 102202, China
Keywords:
History of landscape architecture, Scenic spot, Green space layout, Garden types
Abstract:
According to the unique characteristics of natural geographical environment and important historical
development stages of Jilin City, and using of field research, literature research, and induction and
interpretation, this paper summarizes the development history of landscape architecture in Jilin City into five
development stages: germination stage, turning stage, generation stage, river crossing preliminary stage and
steady development stage. According to the principle of "scenery comes from the environment, borrowing
from the body", this paper analyzes the important reasons for the development and evolution of landscape
architecture in Jilin City from many factors, such as landscape, terrain, vegetation, climate, society, economy,
military, politics, culture and so on. This paper analyzes the reasons why the landscape architecture of
different periods in Jilin city is backward compared with that of other typical regions in the corresponding
period. Finally, it summarizes the significance of the research on the development history of local landscape
architecture for urban development and construction.
1 RESEARCH BACKGROUND
For a long time, the academic circle has been
relatively deficient in the study of the landscape
architecture of northeast China and has not yet
formed a systematic historical pedigree of the
landscape architecture of northeast China. With the
improvement of the quality of life of the citizens and
the continuous rise in the pursuit of spiritual
civilization, landscape architecture in the northeast is
generally expected in the future.
1.1 Compilation of History of Chinese
Landscape Architecture
As a key book in the 13th Five-Year Plan, “History of
Chinese landscape architecture”, this book from a
national perspective, excluding the general
description, is divided into five volumes. They are the
history of northern landscape architecture, the history
of Jiangnan landscape architecture, the history of
Lingnan landscape architecture, the history of
Northwest landscape architecture and the history of
Southwest landscape architecture. Influenced by the
compilation of the history of Chinese landscape
architecture, the research on the history of landscape
architecture in the regional scope has been rising
gradually. There have been some scholars started
studying the history of the landscape architecture of
Hebei Province. But the history of landscape
architecture in Northeast China is still blank,
therefore, the study of the landscape architecture
history in Jilin City can just enrich the contents of the
Northern Landscape Architecture History. As
academician Meng Zhaozhen said, “The
accumulation of thousands of years of Chinese
culture has rich connotation, and gardens are an
important part of traditional culture,” which shows
that the study of garden history is of great
significance to the inheritance of Chinese traditional
culture.
1.2 Blank in the Study of the History of
Landscape Architecture in Jilin
City
Northeast China is rich in natural, historical and
cultural landscape resources, and has a lot of famous
scenery, which has been a must for military strategists
since ancient times. Jilin city is located in the core of
Northeast Asia Grand Plan (Figure 1), and in the
12
Hu, Y., Zeng, H. and Yan, C.
Evolutions of Landscape Architecture in Jilin City of Northeastern China.
DOI: 10.5220/0011015000003354
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Water Resource and Environment (WRE 2021), pages 12-22
ISBN: 978-989-758-560-9; ISSN: 1755-1315
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
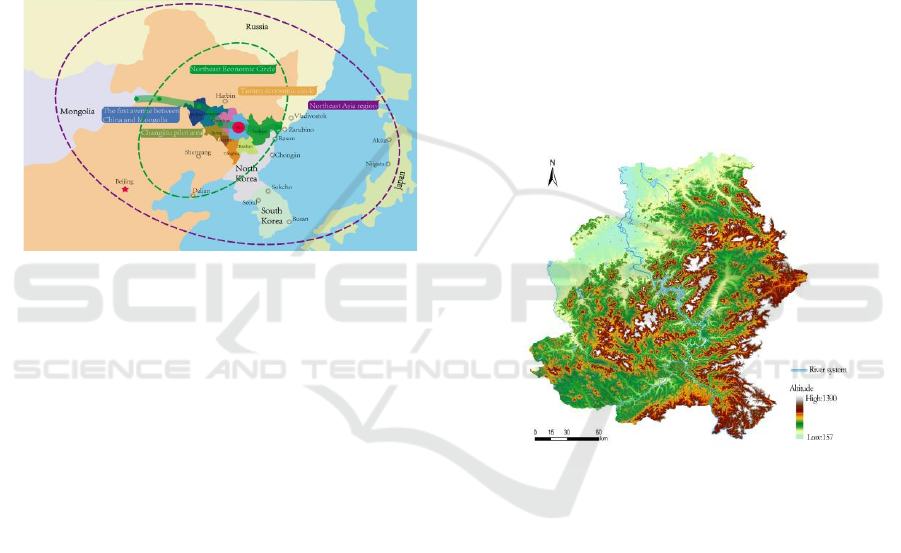
transition zone from mountain to plain in Jilin
Province (Figure 2). The landform is very rich and
changeable. It is one of the third batch of historical
and cultural cities selected by the state. Jilin's unique
natural landscape resources, historical landscape
resources and humanistic landscape resources are an
important part of landscape architecture in Northeast
China, but there has been no systematic study on the
historical development process. Under the
background of compiling the history of Chinese
landscape architecture, it is necessary to study the
history of landscape architecture in Jilin City, fill in
the blank, and summarize the development history of
landscape architecture in Jilin City for the first time.
Figure 1: Location map of Jilin City.
2 DIVISION OF HISTORICAL
STAGES OF LANDSCAPE
ARCHITECTURE
DEVELOPMENT IN JILIN CITY
Today's landscape architecture is a comprehensive
applied discipline that has broken through the
traditional landscape architecture. There is no mature
and standard system for the study of the history of
local landscape architecture, through collecting and
reading the typical domestic and foreign historical
works, the literature of Jilin City local chronicles, the
research on the construction of the whole and part of
the city, the author forms his own writing technique
line. According to the principle of "scenery comes
from the environment, depending on the local
scenery, the shape is moderate and appropriate",
starting from the landscape, terrain, vegetation,
climate, society, economy, military, politics, culture
and many other factors, combined with the important
historical development stages of Jilin City, the
development history of landscape architecture in Jilin
city can be summarized into five stages: germination
stage, turning stage, generation stage, cross the river
and initial exploration stage and steady development
stage.
2.1 Riverside Germination Period
From the stone age when there were human beings
living in Jilin City, prehistoric human beings formed
settlements along the Songhua River Basin in the
form of settlements, which became the initial and
most original base of the overall landscape of Jilin
City. In the bronze age, the "Xituan Mountain
Culture" named after the Xituan Mountain site in Jilin
City lasted for thousands of years. Farming tools such
as hoes and pickaxes gradually replaced stone axes
and adzes (Dong, 1992). With the improvement of
construction technology, human cave dwellings have
also changed from deep caves to shallow caves.
Houses veneered with birch bark have become
roasted yellow mud plastered surfaces, and
trench-style doorways have been set up (Figure 3).
Figure 2: Water system and topography of Jilin City.
In the Western Han Dynasty, depending on the
natural landscape base suitable for city construction,
Jilin city had its first county, Xuantu Shire
Shangyintai County (Dong, 2009). Driven by the
different cultures and political forces of different
nationalities, Shangyintai County has become a
gathering point of multi-ethnic cultural integration,
and at the same time has produced more advanced
agricultural and handicraft civilization. In
accordance with the land conditions of Jilin
Province, the landscape architecture culture of
people's production and lifestyle and its regional
value system began to sprout, and ‘garden’ and
social activity venues began to appear in villages.
Relying on the abundant natural water network
system of the second basin of Songhua River, the
rudiment of the landscape pattern of mountain, water
Evolutions of Landscape Architecture in Jilin City of Northeastern China
13

and city closely integrated in Jilin city gradually
emerged, and there are many settlements along the
river (Figure 4). By the end of the Western Han
Dynasty, the Beifuyu tribal regime was established
in the northeast (Dong, 2009), the regional center
status of Shangyintai County declined, and the
development of its landscape architecture also
stagnated.
(a) half cr
y
pts on slopin
g
lan
d
(b) half cr
y
pts
b
uilt on the platfor
m
(c) Restoration drawin
g
of half cr
y
pt buildin
g
Figure 3: Residential buildings in the period of Xituan
Mountain (drawn according to the information of Jilin
Museum).
(a) the settlement distribution
(b) the law of settlement location
Figure 4: Distribution of settlements in the riverside
germination period (drawn according to the information of
Jilin Museum).
As Professor Wang Xiangrong said: "the ancients
always regarded the natural and artificial landscape
environment as the basis of urban construction, and
the city formed its own unique landscape pattern and
urban personality in the process of adapting and
transforming the nature." The ancient human
settlements and ancient city landscape in the period of
Xituan Mountain culture and Fuyu kingdom are the
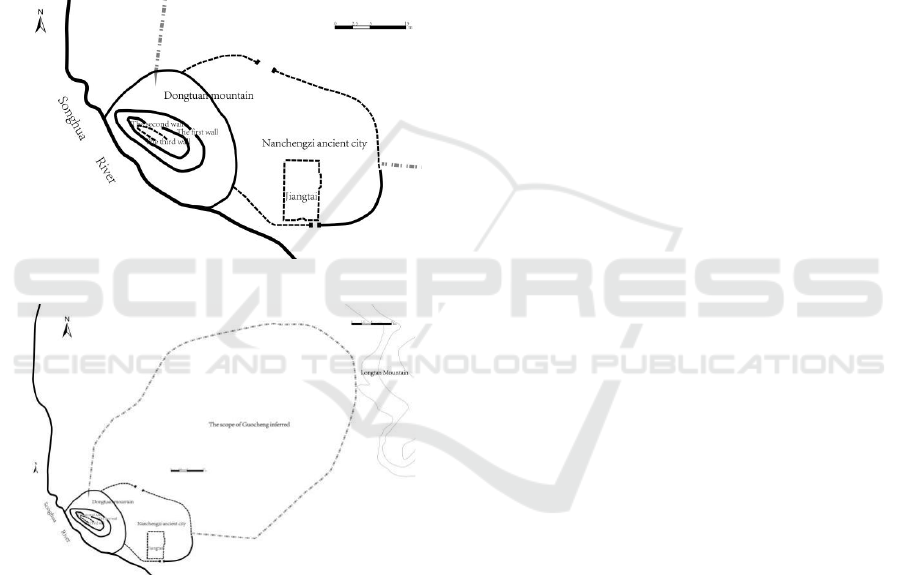
basis of Jilin city form. The ancient people choose the
location based on survival rationality, which has
become the most original power of Jilin city
formation. Today's Jilin city is gradually developed
and expanded based on Nanchengzi ancient city
(Figure 5) in Fuyu period.
2.2 The Turning Point along the River
The development of Chinese urban landscape
architecture is spiraling in the struggle between man
and nature, man and man. The decline of Shangyintai
County in the Western Han Dynasty made the
development of landscape architecture in Jilin City
temporarily stagnate. Until the early Western Jin
Dynasty, the Xianbei tribe grew stronger, and the
Fuyu people eventually disappeared. The Goguryeo
people occupied today’s Jilin City (the eastern part of
Fuyu), and built a military mountain city based on
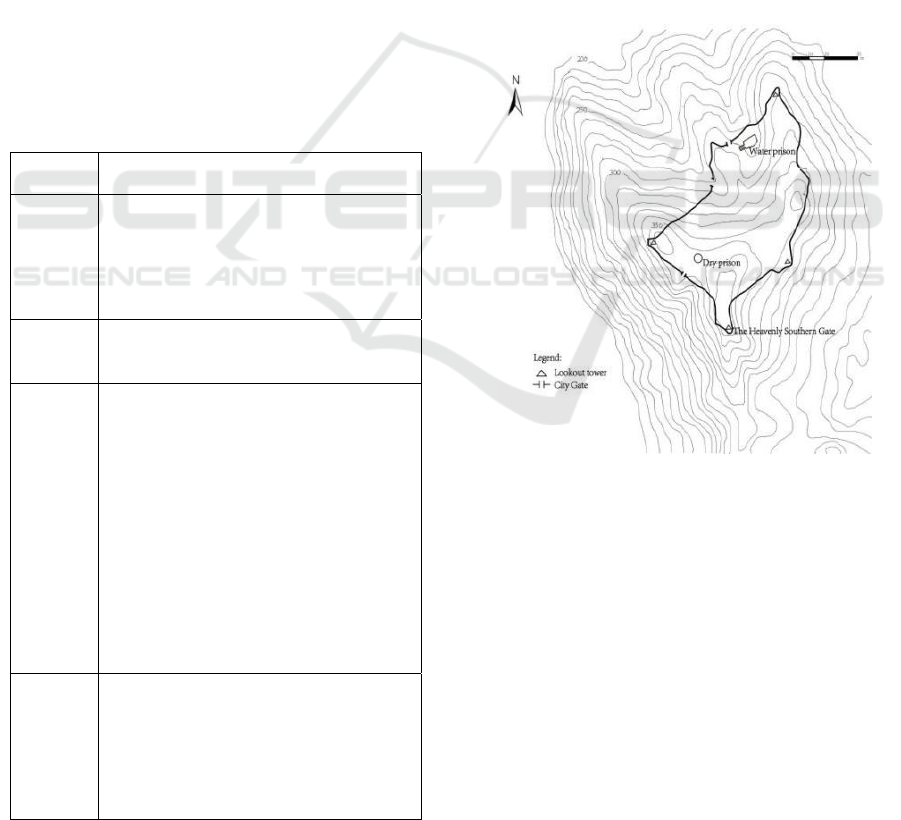
Longtan mountain on the Songhua River (Wang,
2017) (Figure 5). The Goguryeo regime has only
existed for more than 20 years, but thanks to its
tradition of "Passionate about building palaces"
(Dong, 1998), the development of landscape
architecture in Jilin City has begun to recover. In the
Tang Dynasty, in order to strengthen the rule of the
Northeast, the Bohai State was established, which
was both a local administrative institution and a
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
14
national power (Dong, 1986), Jilin became the state
governor of Suzhou, a solo prefecture in the south of
the Bohai State, and its military defense status was
important. Bohai's prosperous economy and the
improvement of productivity level promote the
planning of ancient cities in Jilin City (Yang, 2011).
Combined with the development of landscape
architecture, there are many ancient cities in Jilin
City, such as Longtanshan Mountain City, Dongguan
Mountain City, Sandaolingzi Mountain City, and the
hengdaozinanshan Mountain City of Jiaohe City,
Lafaxiaolizi Mountain City, etc (Han, 2015). Among
them, Longtan Mountain City (Figure 5) is the largest
and most representative.
(a) the plan of Nanchengzi ancient city (Dong,
2009) (redrawn)
(b) the sketch map of Guocheng of Nanchengzi
ancient cit
y
Figure 5: Map of the site selection of the Royal City in the
early period of Fuyu.
With the construction of the ancient city, the
princes and nobles have already developed more
advanced above-ground buildings, and the
mausoleum gardens have also begun to develop.
There are many types of tombs such as earth tombs,
brick tombs, and stone tombs. Noble tombs are
accompanied by frescoes, funeral objects,
inscriptions and ground buildings (Dong, 1986).
People of Bohai have a high level of ancient city
planning and landscape design. In Jilin City, the
improvement of landscape architecture consciousness
of people in Bohai is directly reflected in the planning
and construction of Sumi City (Hao, 2016) and
Suzhou City.
At the end of the Tang Dynasty, the political
situation in the Central Plains was unstable, and there
were frequent wars among the Khitan, Jurchen, and
Mongolians in the northeast. Until Yelu Abaoji
unified the Khitan tribes and established the Liao
regime, Suzhou City in Jilin City became a general
border city of Liao. The Liao people are good at
learning the production technology and Han culture
of Central Plains, imitating the Han system,
developing agriculture, building fortresses,
establishing cities, dealing with the Han people, so
that each has a spouse, and cultivates wasteland
(Zhang et al., 2016). And because the Khitan people
have a hunting tradition, the natural mountain and
woodland are respected by the Liao people (Chen,
1995). The Liao people formulated a series of laws
and policies concerning forest protection, wildlife
protection, and afforestation (Zhang, 2010). In the
Liao Dynasty, Jilin city was formed by the
interdependence of mountains, waters, forests, and
fields.
At the end of the Liao Dynasty, the Jurchen
nationality continued to grow, and eventually
destroyed the Liao Dynasty and built the Jin Dynasty.
On the territory of the Jin Dynasty, the border town of
Suzhou City (Jilin City in now) in the Liao Dynasty
became the golden "inland", and its strategic position
was lost. The Jin Dynasty adopted the military system
of Meng'anmuke for territorial expansion, developed
the smelting industry and ceramic industry by the old
system of the Song Dynasty, actively carried out a
foreign trade, and fundamentally borrowed and
absorbed the Han culture (Bi & Li, 2014). The
development of its landscape gardens should also be
progressive. There are very few relics preserved in
the Jin Dynasty in the Jilin area, but Wanyan Xiyin, a
famous politician, militarist and creator of Nuzhen
script, is his family cemetery (Zhao & Zhang, 2012)
are indeed well preserved. It began to develop into the
Chinese classical garden system, signifies that Jilin
City's landscape garden culture has breakthrough
development.
When Genghis Khan established the Yuan
Dynasty, the Yuan Dynasty established Liaoyang and
other provinces in the northeast, and Suzhou became
Jianzhou without an administrative system (Zhang,
2010), only a post station, and its political and
economic status declined for a while. At the same
time, the ancient city clusters along the Yangtze River
Evolutions of Landscape Architecture in Jilin City of Northeastern China
15
that existed from the Liao Dynasty to the Jin Dynasty
were also abandoned, and the development of
landscape architecture in the entire area of Jilin City
has stalled here.
2.3 Depend on the River Formation
Period
During the Ming Dynasty, Jilin Province is relatively
densely populated, and the Ming Dynasty established
Ulawei here. Ulawei established Wula Ancient City
(Table 1), which is the ancient city of Suzhou in the
Bohai period. In order to strengthen the ties between
the Liaodong Dusi and Nurgandos, especially to
strengthen the Ming Dynasty’s control of Nuergan,
Set up a shipyard on the hub of transportations
Songhua River (Gu, 2012), which consuming a large
amount of locally grown red pine, the forest resources
of Jilin Province were subjected to unprecedented,
large-scale and organized exploitation for the first
time.
Table 1: Construction history of the ancient city of "Wula
City".
Dynasty Historical changes
Bohai
State
Period
The Chengguo was built on the edge
of Sumo River, one kilometer
northwest of the old street to the
north of today's ancient city
It was destroyed by war in Liao
D
y
nast
y
Jin
Dynasty
Build a city in today’s Old Street on
the north side of the ancient city,
known as “ulahonil cit
y
”
Ming
Dynasty
"Ulahonil city" was seriously
damaged in the turmoil
The old city was rebuilt and renamed
"neiluo city"
Around neiluo city, wailuo city was
build in the north, East and south.
A slightly square palace city was
built in the center, known as the
"Forbidden City."
The high platform built in the
Forbidden City is called "White
Flower Point General Platform"
The ancient city was destroyed by
wa
r
Qing
Dynasty
Restoration of the ancient city
Sanxiao hall was built on the "White
Flower Point General Platform", and
later Lingguan pavilion was built
Then, because of the flooding of the
river, the new city was built
Built the “Wula City”
In addition, during the Ming Dynasty, Jilin
Province was the key outside the Great Wall in the
Northeast. In order to effectively control the
northeast, the Ming Dynasty regime set up Military
Bodies in the Jurchen tribe and the U Harian three
guards to carry out the political rule of “restricting
foreign by foreign” and appoint the heads of various
ministries as the officers of the Department of Health,
and pay regular tribute to the Ming Dynasty and trade
exchanges (Chen, 2006). The establishment of
"Selling Horses" in Jilin Province has a greater
impact on the landscape of Jilin City. Since the
Jurchen area of Jilin Province is rich in horses, it often
exchanges with the Central Plains Dynasty.
Large-scale horse breeding like this requires a large
area of land. So now, on the whole, the overall
landscape of Jilin City is characterized by low
mountains and hills. Pastoral landscape dominated by
river valley plains.
Figure 6: Plan of Longtan Mountain City.
In 1613, the Wula Acropolis was destroyed (Figure
6). The development of Jilin region turned into
depression (Ying, 2014). Since Jilin Province is the
holy land of Qing ancestors, the Qing emperors’
sentiments to this place directly affected the
landscape pattern of Jilin City. On the one hand, the
Qing Dynasty set up an observatory altar at Xiaobai
Mountain, and on the other hand, several Jiulong
Mountain were cut away to break the dragon veins of
Jilin City (Gu, 2012). At the same time, the Qing
Dynasty built a wall in the northeast and implemented
a ban policy, designate the Northeast as a Manchu
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
16

settlement to maintain the traditions and customs of
Manchu, riding and shooting, It is stipulated that the
Han nationality must not go beyond the boundary,
and the cultural blending between inside and outside
the boundary is slowed down, and the speed of the
spread of the landscape garden culture within the
boundary to the outside is also slowed down (Xu,
2005). It directly affected the development of Jilin
City's landscape gardens.
It was not until the first year of Qianlong (1736)
that the Yongzhou Confucian Temple (Zhao, 1991)
(now Jilin Confucian Temple) was built in Jilin City,
and the integration of Manchu and Han cultures
began to formally develop on the land of Jilin. The
free blending of culture has brought the architecture
and garden culture of the Central Plains to Jilin City.
There are many courtyards and quadrangle courtyards
in Jilin City, and the Fushen Residence Garden also
intends to decorate the gardens. Temple gardens,
private house gardens, and government office
gardens have seen unprecedented development
(Table 2).
Table 2: List of garden relics in the period of river
generation.
Types Representative Garden
Yamen Garden
Chief yamen of Dasheng Wula
Jilin general Mansion
Private house
garden
Kuifu Masion Garden
Hou fu Masion Garden
Sa fu Masion Garden
Wang Baichuan courtyard
Niu Zihou's old house garden
EN house courtyard
Temple garden
"Waiba Temple" in Wula
ancient cit
y
Zhenwu Temple of
Xuantianling
Yuhuang Pavilion of Beishan
Confucius Temple of Jilin
Academy Garden Chongwen Academy
Until the seventh year of Guangxu (1881), before
the Qing Dynasty organized the armory in Jilin City,
over the past two hundred years, Jilin City has
developed from the initial military garrison to the
handicraft industry and commercial regional trade
center (Wang, 2011), and the level of productivity
has reached the highest level ever. The relationship
between "city" and "market" has gradually merged,
and the urban landscape has also begun to change
from the shape of an ancient city to a modern city.
Until the construction of the Middle East Railway
in 1898, Tsarist Russian soldiers forced mining, road
repair, logging, and business operations here. The
overall style of Jilin gradually changed to an
industrial city landscape (Li, 2007). At the same time,
because the late Qing government collected logging
taxes and opened up the forest area, a large number of
Chinese and foreign timber merchants poured into the
forest area to cut indiscriminately. The great virgin
forest has been severely damaged and devastated. The
original harmony of mountains, water, forests and
fields is related to the destruction.
In general, the development of landscape
architecture in Jilin City during the Ming and Qing
Dynasties is a highlight in the history of landscape
architecture in Jilin City. The historical changes of
the ancient city of Wula and the establishment of the
shipyard and the new Jilin City laid the foundation for
the evolution of Jilin City into an industrial city. The
Fengshui pattern of "Four Mountains and One River"
in the New City of Jilin in the Qing Dynasty (Wu,
2005)
(Figures 7 and 8) established the basic urban
structure of the "One River and Three Districts" of
Jilin City in later generations (Wang, 2011). During
the Ming and Qing Dynasties, the major types of
landscape gardens achieved unprecedented
development (Xia & Cai, 2010). The overall urban
style, urban planning and layout, government offices
and industrial gardens, private home gardens, and
academies and temple gardens can all be verified
through literature or physical remains.
Figure 7: Schematic diagram of the site selection of Jilin
City.
Evolutions of Landscape Architecture in Jilin City of Northeastern China
17
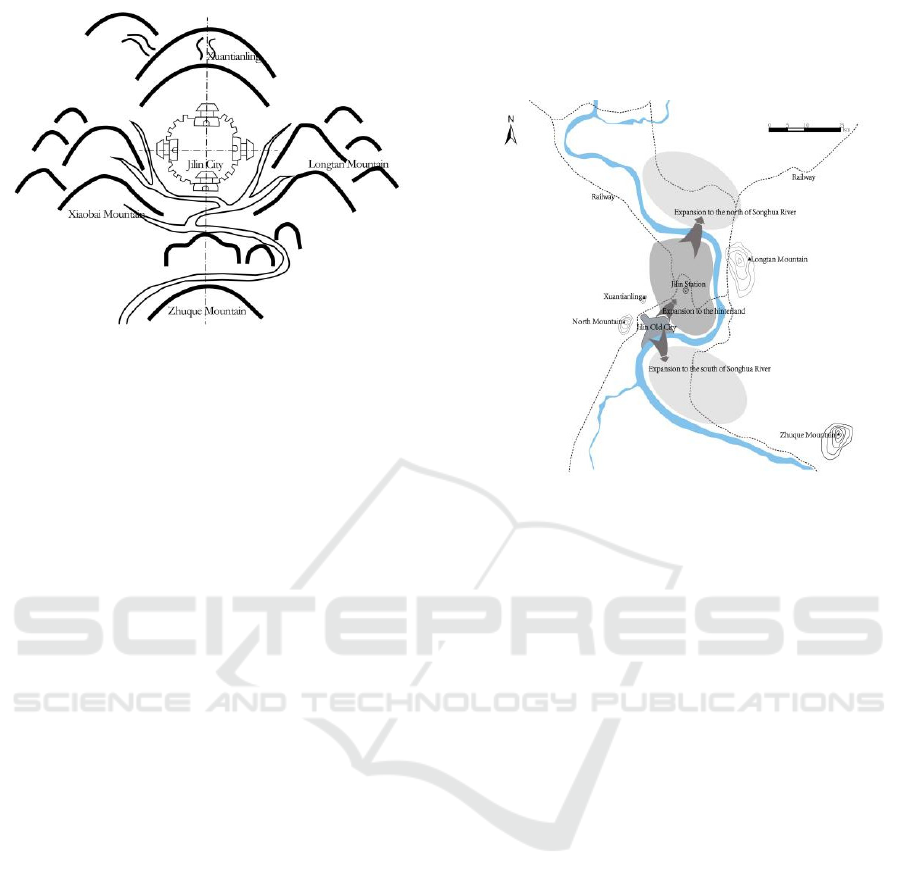
Figure 8: Fengshui sketch map of Jilin City in Qing
Dynasty (Lin et al., 1997) (repainted).
2.4 The Initial Exploration Period
across the River
After the turbulent development period from the
Republic of China to the Puppet Manchukuo in the
late Qing Dynasty, Jilin also continued to develop in
the process of fighting against foreign aggressive
forces (Yang, 2008). The city is constantly
transforming in the struggle, developing into an
industrial city with excellent revolutionary spirit, and
at the same time forming a city landscape with its
own characteristics.
While the military defense function is slowly
fading, the commercial function of the city is
gradually improving. The city wall of the ancient city
of Jilin was dismantled, and the limits restricting the
development of urban space disappeared. the
industrial and commercial landscape of Jilin City has
also been developed, but under the influence of the
"four mountains and one water" landscape pattern of
Jilin City, the development and change of urban
landscape is not very great.
In a turbulent social context, the development of
Jilin City's urban is slowly expanding (Figure 9). The
city contour line and street landscape texture are
gradually clear. The mature technology of railway
and bridge construction has led to the generation and
development of riverside green space (Chen, 2020a;
Qian & Chen, 2004) (mainly east mountain railway
bridge, full bridge and Jilin bridge). Monasteries and
academy gardens preserved by the Qing Dynasty
developed into urban parks during this period. The
difference of social class and the invasion of Japanese
puppet rulers made the urban and rural residential
buildings also present obvious class differentiation
and ethnic difference. Due to the needs of economic
development, although some relevant protection
policies were formulated during this period, the forest
resources were still destroyed to a certain extent in
essence.
Figure 9: Schematic diagram of urban expansion.
2.5 Steady Development Period
Since the liberation of Jilin in 1948, the production
and construction of Jilin City have been fully restored
from my country’s first five-year plan (Li, 1988).
After experiencing a short period of stagnation during
the Great Leap Forward and the Cultural Revolution,
the implementation of the reform and opening policy
in the 1980s began to resume development. In today’s
information age, the development of landscape
architecture in Jilin City has been steadily improved
amidst twists and turns, and the city’s landscape
architecture awareness has also been gradually
improved.
While Jilin City comprehensively promotes
economic construction, the demands of urban
development increasingly require innovation in the
old urban area. Jilin's cross-river development also
officially began at this time. In this way, the
comprehensive development trend of Jilin City's
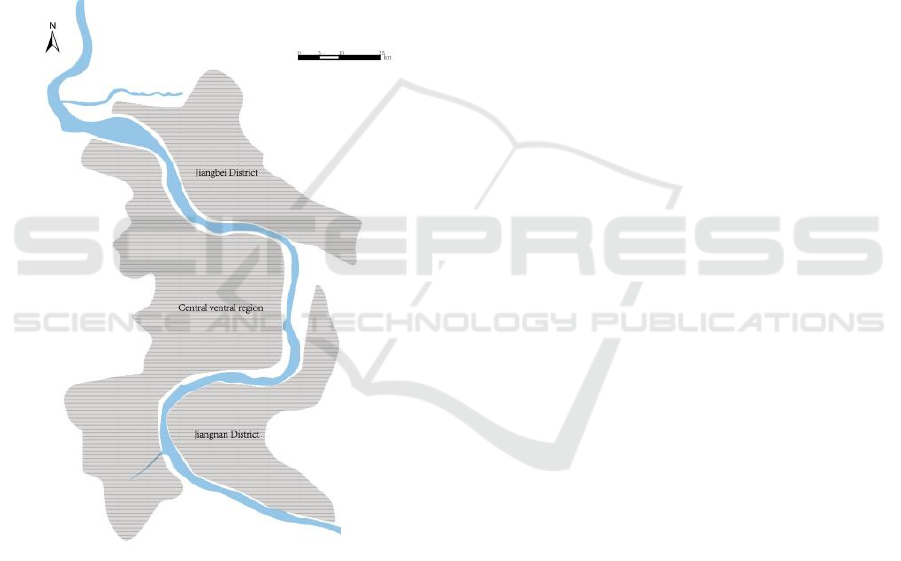
"One River and Three Districts" (Figure 10) has
formally taken shape.
In the process of development, on the one hand,
restricted by the landscape pattern of Jilin City, and
on the other hand, affected by the historical
limitations of the consciousness of landscape
architecture, the development of Jilin City’s
landscape architecture has undergone a triple
transformation:1) Many blocks with historical and
educational significance are in the founding of the
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
18
country. It was demolished and built during the early
period or during the "Cultural Revolution", which
made the street's landscape and architecture lose its
historicity. 2)Relying on the inherently excellent
natural ecological base, while carrying out economic
construction, the planning and construction of
supporting green space has been neglected, resulting
in that the green space system of Jilin City is still
incomplete.3)As the economic and cultural
construction of Jilin City has been steadily improved,
people's material living standards have gradually
improved, and people's demand for green ecological
space has gradually increased. Jilin City also began to
pay attention to the planning of green space system,
attention to the protection and utilization of historical
resources of urban landscape.
Figure 10: Schematic diagram of "one river and three
districts" mode.
In the period of steady development, although the
goal of building an international garden city with a
certain charm was proposed. However, due to the
determination of the nature of the city with "chemical
industry as the main part" and the weakness of the
"garden consciousness", the pace of the development
of urban garden and green space in the early days of
the People's Republic of China was still slow. After
the continuous baptism of the "First Five-Year Plan",
"Great Leap Forward", "Cultural Revolution" and
"Reform and Opening Up", Jilin City's landscape
architecture awareness has been continuously
improved, and a systematic green space planning and
construction pattern has gradually formed.
3 CONCLUSION
From a nationwide perspective, the study of the
history of the development of landscape architecture
in local cities can provide a more targeted reference
for the development and construction of cities in
landscape architecture, it provides the most direct
reference of landscape resources for the construction
of the city itself, so the research on the history of
landscape architecture in local cities is of great
significance to the development and construction of
the city. This paper systematically combs the history
of Jilin from the Xituanshan culture period to more
than 3,000 years, from which the development of Jilin
City landscape architecture can be summarized.
3.1 Status Quo of Protection and
Utilization of Landscape Resources
in Jilin City
In terms of natural scenery resources, relying on the
unique landscape framework of four mountains and
one river, Jilin City’s urban greening occupies an
inherent advantage, and most of the landscape
resources have been well utilized. Beishan Park,
Xuantianling Cultural Park, and Longtanshan Site
Parks and green belts along the river have been built
to greatly enrich the daily leisure life of citizens.
Zhuqueshan National Forest Park and Songhua Lake
Scenic Area in the suburbs are not only short-term
leisure places for residents of the city, but also a
famous tourist attraction that can reflect the cultural
characteristics of Jilin City.
In terms of historical buildings and gardens,
restricted by the historical limitations of economic
development and landscape gardening consciousness,
many historical and cultural heritages and historical
sites have suffered irreparable damage. For example,
the city wall of Jilin in the Qing Dynasty was built in
the 12th year of the reign of Kangxi, and is regarded
as a historical scar of the city. The scar was removed
after the Japanese invasion. In the history of Jilin,
there are many historical relics, such as the provincial
government and the military and government offices,
which have the characteristics of The Times, but now
there is no trace of them. There were six gatehouses in
Evolutions of Landscape Architecture in Jilin City of Northeastern China
19

the east, north and west parts of the old city, which
were also damaged due to historical factors. These
resources of landscape architecture, which can reflect
the historical features of the city, can only be found in
old photos. Compared with the protection of
historical buildings and historical gardens in cities
such as Shanghai and Nanjing, the historical relics of
Jilin City are well preserved.
In terms of the characteristics of the city, after Jilin
City was classified as a “chemical city”, most of the
industrial sites left over from history have not been
well protected due to development needs, and the
construction of subsidiary green spaces and
protective green spaces in the industrial zone has been
relatively weak. The characteristics of industrial
cities have not been fully landscaped.
3.2 Prospects and Suggestions for the
Development of Landscape
Architecture in Jilin
As a famous historical and cultural city, Jilin has
numerous high-rise buildings made of steel and
concrete, instead of traditional buildings and houses
that can reflect its culture, and many cultural relics
have been lost over time (Chen, 2020b; Yan, 2016).
The paper researches the history of landscape
architecture in Jilin, and the author believes that in its
future development, awareness of landscape
architecture should be enhanced, and the concept of
conservation established.
Firstly, we need to conserve scenic spots, cultural
heritage sites, cultural relics, and traditional
dwellings in a focused manner so as to develop
cultural features. Besides, we need to control the
spatial profile of the city, showing the natural
landscape of the city with its coexistence of
mountains and water.
Secondly, we need to protect the overall scene of
the “river city”. The name was given by Emperor
Kangxi who wrote a poem about Songhua River. In
the 12th Five-Year Cultural Industry Development
Plan issued by the Jilin Municipal Government, the
culture of the beautiful river city is clearly defined
and elaborated. The river is therefore an important
natural landscape resource that should be protected in
its future development. The height, form and color of
buildings along the river should be controlled, and the
maintenance and further design of green spaces along
the river should make full use of the historical theme
of the “shipyards”, thus making it more educational
and meaningful. Meanwhile, water pollution should
be prevented, water resources should be fully utilized,
and water and ice sports can also reflect the feature of
the “river city”.
Thirdly, it is necessary to regulate the landscape of
the “old city”. As an important commodity
distribution center, Jilin used to be well served by
both water and land transport. It was also the capital
city of Jilin province, and Shanying District used to
be home to numerous shops, all of which had elegant
storefronts well connected by roads and buildings,
thus making it an important area reflecting its
traditional scene and revealing cultural atmosphere.
Now these historic districts are no longer what they
used to be. In the future, Jilin should learn from the
experience and lessons of the past and put more
emphasis on combining the modernization of the city
with the preservation of its historical and cultural
features. Therefore, we should control the size of the
city, ensuring that the population of the central city
does not sabotage its historical landscape. Besides,
we are supposed to improve the dwelling quality for
local residents, paying more attention to their daily
life. On this basis, we can take measures to restore the
historic scene of the old city. We should make it clear
that the preservation of historical and cultural
resources should be through restoration instead of
reconstruction. In addition, stone monuments and
sculptures can be used to represent its history, and its
regional features can be elaborated to ensure that the
original architectural forms and colors can be
preserved. Local snacks and handicrafts should be
used to contribute to services and tourism by setting
up long-established shops, so that the local tradition
can last long.
Fourthly, landscape architecture can be used to
protect those cultural heritage protection units (Chen,
2021; Yang, 2018). As of 2019, Jilin is home to a
total of 24 national key cultural relics protection
units, as well as more than 40 provincial key cultural
relics protection units. These historical relics prove
that Jilin is an important cultural cradle in the
Songhua River basin, and also witness Jilin’s gradual
evolution from a cultural birthplace to a military area,
a political, economic and transportation hub.
Specifically, historical landscape conservation
areas can be established: Xituanshan Cultural
Landscape Conservation Area, Historical and
Cultural Landscape Conservation Area, Wula Street
Historical and Landscape Conservation Area,
Beishan Cultural Landscape Conservation Area and
Longtanshan Cultural Ancient City Landscape
Conservation Area. For example, Wula Street in
Longtan District is home to buildings and numerous
Manchu dwellings known as one of the four tribute
bases of the Qing Dynasty, and it is an area where
Manchu people live with a reputation of their
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
20

hometown. Therefore, the Wula Street Historical
Landscape Area can use Manchu folk buildings as the
main buildings. It can be used as a typica
l area of
historic landscape reserve together with tributary
culture temple architectures in Northeast China.
In addition, the “Songhua River Water Resources
Conservation Zone” can be established. A
combination of the nature of Songhua River and the
history of the Kangxi and Qianlong Emperors’ tour of
Jilin and their inspection of the Jilin Navy can be
reflected in the details of the landscape architecture
planning, thus highlighting the historical and cultural
connotations of Jilin as a “land of prosperity”.
Besides, infrastructure such as parks and green
spaces can also be installed, which means that the
protection of key historical heritage units should be in
line with Protection of Cultural Relics Act, and these
heritage units can contribute to the construction of
parks and green spaces. For instance, the
Longtanshan Mountain was built as a heritage park,
the former site of the Wang Baichuan Residence was
repaired and built as a city heritage museum with
local culture, and the Jilin Machine Bureau emerged
as Jilin City Arts Center after more than a century of
war, destruction, and restoration.
The city embraces rather scattered historical and
cultural monuments, and the ancient monuments and
buildings are protected in order, putting historical and
cultural landscapes and cultural routes into the
protection system. Besides, the cultural landscape of
Jilin is inherited, thus further accumulating historical
culture, creating a city cultural brand with regional
features and showcasing historical and cultural charm
to the outside world. The lives of the people are
enriched, so that Jilin can still develop as an ancient
historical and cultural city.
REFERENCES
Bi, J. H., & Li, L. (2014). Preliminary study on ecological
protection measures in Liao Jin Yuan period. Hebei
Forestry Science and Technology, 2, 46-49, 57.
Chen, X. G. (2006). Application of natural materials in
historical display of Ming and Qing shipyards in Jilin
Province. Museum research, 2, 68-70.
Chen, X. W. (1995). Summary of Liao Jin Archaeology in
Jilin Province. Northern Cultural Relics, 4, 40-47.
Chen, Y., Qian, H., & Hou, K. (2020a). The influence of
climatic conditions on the permeability and hydraulic
properties of the L5-S5 layers in the loess plateau,
north qinling mountains. Earth and Environmental
Science Transactions of the Royal Society of
Edinburgh, 11(4), 235 – 245.
Chen, Y., Qian, H., Hou, K., Zhang, Q., & Zhang, Y.
(2020b). Vertical distribution characteristics of soil
moisture with different strata in deep profile in
Guanzhong basin, China. Environmental Geology,
79(5), 103
Chen, Y., Qian, H., Hou, K., Zhang, Q. Y., & Zhang, Y. T.
(2021). Permeability and paleo environmental
implications of loess-paleo sol sequence from
Jingyang Loess Plateau. Environmental Earth Sciences,
80(1), 1-16.
Dong, X. Z. (1986). Investigation report on Gaogouli
mountain city and its nearby Acropolis in Longtan
mountain of Jilin City. Northern Cultural Relics, 4,
32-35.
Dong, X. Z. (1992). Study on the cultural site of xituan
mountain. Archaeology, 5, 52-60.
Dong, X. Z. (1998). Gaogouli mountain city, Longtan
mountain, Jilin City, the northern fortress of the
kingdom of Koguryo. World of Cultural Relics, 5,
18-20.
Dong, X. Z. (2009). Summary of sixty years' research
achievements of xituan mountain culture in Jilin
Province. Museum Research, 1, 28-37.
Gu, L. B. (2012). Research on Wanyan Xiyin family
cemetery. Jilin University, 2012.
Han, Y. N. (2015). Research on the city site of Bohai State.
Northeast Normal University.
Hao, J. J. (2016). Research on regional characteristics and
related issues of Jin Dynasty Tombs. Jilin University.
Li, D. W. (2007). Research on the evolution of modern
urban form of Jilin City. Harbin Institute of
technology.
Li, S. T. (1988). Local chronicles of Da Sheng Wula.
Changchun: Jilin Literature and History Publishing
House.
Lin, M. T. (1997). A brief history of Jilin. Changchun: Jilin
Literature and History Press.
Qian, Q. L. and Chen, Y. B. (2004). Study on urban green
space system planning of Jilin City. Journal of Beijing
Forestry University, 5, 61-65.
Wu, F. L. (2005). Forestry annals of Jilin City
(1988-2003). Forestry Bureau of Jilin City.
Wang, Z. S. (2011). The history and current situation of
Jilin Confucian temple. Jilin Provincial Museum
Association. Spring grass collection- Proceedings of
the first academic symposium of Jilin Provincial
Museum Association. Jilin Provincial Museum
Association. Changchun: Jilin Provincial Museum
Association, 611-614.
Wang, J. Z. (2017). Research on Fuyu Wangcheng in Han
Dynasty. Dalian University.
Xia, Z. X., & Cai, X. D. (2010). Research on urban space
development strategy of Jilin City. New Architecture, 5,
126-129.
Xu, L. Y. (2005). Historical changes of Wula ancient city.
Journal of Jilin Normal University, 5, 97-99.
Yan, X. F. (2016). Study on the conservation and
utilization of historical buildings in Jilin section of
Middle East Railway. Jilin University of Architecture.
Evolutions of Landscape Architecture in Jilin City of Northeastern China
21

Yang, C. (2008). Research on urban morphology of Jilin
City Based on traditional environmental concept.
Harbin Institute of Technology.
Yang, S. S. (2018). Research on ecological and livable city
construction in Jilin. Science and Technology and
Innovation, 22, 96-97.
Yang, Y. S. (2011). Jilin town in Bohai State and Liao Jin
period. Journal of Liaoning University of Technology,
13(5), 449-455.
Ying, X. (2014). Complete works of Dazheng Wula
chronicles. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Ancient Books
Publishing House.
Zhang, G. Q. (2010). Temple fields in Liao Dynasty and
related issues. Chinese Agricultural History, 29(04),
66-75.
Zhang, Z. et al. (2016). Archaeological excavation Bulletin
of South urn outside Sumi City, Huadian City, Jilin
Province. Frontier Archaeological Research, 1,
83-100.
Zhao, D. S., (1991). Research on Wulashiluohulun.
Changchun: Jilin literature and History Press
Zhao, Q., & Zhang, Q. (2012). Characteristics of
architectural decorative components in Liao and Jin
Dynasties- decorative forms and construction of
buildings in Jin and Liao in Jin Dynasties. Ancient
Architecture and Garden Technology, 1, 27-29+65.
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
22
