
The Concept of Happiness in Elementary School Children
Nurfitriany Fakhri
1a
, Nurauliah Safitri Muchlis
1
, Ahmad Yasser Mansyur
1
and Sahril Buchori
2b
1
Psychology Faculty, Universitas Negeri Makassar, Jl. AP Pettarani, Makassar, Indonesia
2
Guidance and Counseling Department, Universitas Negeri Makassar, Jl. Tamalate 1, Makassar, Indonesia
Keywords: Happiness, Positive Emotion, Children.
Abstract: The problem of unhappiness can arise due to differences in perception and cognitive processes in each age
range. Measuring children's happiness by the standards of adults' happiness can create intergenerational
gaps. This study aims to describe the concept of happiness in elementary school children in Makassar City.
This study uses a qualitative method with the principle of constructive realism involving 461 respondents.
The data collection technique is in the form of a questionnaire using open questions. Based on the results of
the study, it was found that: (1) the definition of happiness based on children's perceptions, specifically
conditions related to positive emotions; (2) as for the source of children's happiness with the ten highest
percentages, videlicet, having harmonious relationships with the closest people, doing favourite activities,
doing "outing" activities (activities outside the home), getting rewards, doing sports, gaining achievements,
consuming favourite foods and drinks, celebrating special days, wishes fulfilled, and gratitude; and (3) The
reason for the importance of happiness in children is because happiness can make children feel positive and
prevent children from negative feelings. Based on this explanation, parents and educators must strive to
create and improve positive relationships in families and schools, provide opportunities for children to do
fun activities, provide opportunities for children to socialize with friends, try to meet children's needs, and
seek strategies to improve happiness and well-being in children at home and at school.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5323-8125
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7184-8576
1 INTRODUCTION
Strengthening character education is a priority
program for the Indonesian government in improving
the national education system (Fanhas & Mukhlis,
2017). Little is known about what shapes and causes
student well-being and happiness in primary
schools. Meanwhile, Seligman et al. (2009) suggest
that as educators, it is necessary to learn more about
what constitutes happiness in childhood and
consider ways and means to increase it. Happiness is
often defined as a state of well-being that consists of
positive emotions and feelings of satisfaction with
life in individuals (Carter & Seifert, 2012). To
achieve this, every person must increase pleasure
and reduce pain (Kahneman, 1999). Feelings of
pleasure and satisfaction are defined as affective and
cognitive components, and the two things are
interdependent (Carr, 2011). The mental part
becomes vital for a person, especially in feeling the
stimuli that lead to satisfaction, ultimately leading to
happiness (Argyle, 2001). Happiness can have
different meanings depending on the individual
exploring the meaning objectively or subjectively
(Veenhoven, 2000).
One concept that plays a role in determining
indicators of happiness is age (Butt & Beiser, 1987).
At different ages, some indicators of happiness also
differ. At each age range, the way individuals feel
happiness is different because of various cognitive
processes. This also shows that children think
happiness differently when compared to adults.
Children do not articulate a vision of the good life,
and school has a significant role in building
children's happiness (Seligman & Csikszentmihalyi,
2000). Happiness in young children may differ from
that in adolescents and adults because children do
not have cognitive maturity and have not
experienced some life circumstances that affect
people's happiness (Holder & Coleman, 2008).
Therefore, a deeper appreciation of the factors
Fakhri, N., Muchlis, N., Mansyur, A. and Buchori, S.
The Concept of Happiness in Elementary School Children.
DOI: 10.5220/0010811200003347
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Psychological Studies (ICPsyche 2021), pages 263-273
ISBN: 978-989-758-580-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
263
associated with childhood happiness and knowledge
is needed.
Age affects differences between the concepts of
happiness (Ryff & Keyes, 1995). Differences in
ages and developmental stages can cause gaps or
distances between children and adults, especially
parents, and it can lead to parental
misunderstandings about children's attitudes and
vice versa. There are significant differences in the
indicators of happiness in the perspectives of
children, parents, and teachers (Ben-Arieh, 2008).
This problem is seen as part of the gap between
generations. It can lead to different standards or
expectations of happiness (Trommsdorf, 2006).
Parents believe that they have an important
influence in shaping children's happiness according
to parental standards (Casas, 2011). Nevertheless,
parents and children often measure happiness
according to their self-interest so that children may
have different standards of happiness than their
parents. Furthermore, this condition can lead to
parent-child conflict, which then causes feelings of
unhappiness on both sides (Suldo & Fefer, 2015).
The problem that may arise is whether the
paradigm of children's happiness can be captured
and interpreted relatively by their parents who meet
their children every day and want their children to
be happy? This research will try to find the
paradigm of happiness in children. When parents
and children use the same paradigm, the probability
of problems arising is minimal. Still, if the
paradigms are different, it is likely to cause
problems because of their distinct demands.
Expressing the happiness paradigm between
parents and children will allow parents to anticipate
creating a conducive environment for children's
growth, especially considering that childhood
happiness is essential in optimizing children's
development (Batcho, 2012).
Research on children's happiness is generally
associated with children's external factors
(Stallings, et.al., 1997). A study on children aged
9-10 years, who grew up in Yogyakarta, found that
children's happiness is shown through temporal
indicators, called hedonic happiness (Ryan & Deci,
2001). Another research found that the material is
the only important factor that affects the
development and happiness of children (Anand &
Roope, 2016). Also, money and other materials can
become indicators to determine children's
happiness (Rees, Main & Bradshaw, 2015). At this
age, Piaget suggested that children's cognitive
development is in the final stage of concrete
operations leading to formal operations so that
concrete steps still affect them. To anticipate
Piaget's paradigm of cognitive development, the
indicators used for research on children aged
between 10-14 years must be in the form of
abstract indicators (Santrock, 2011). This fact
raises the question: what is the paradigm or
indicator of happiness in children aged 7-11 years
who are in the pre-operational cognitive
development stage to the concrete operational
stage?
Most positive psychology research concerns
subjective well-being in adults, but not many
studies have examined the characteristics of
happiness in children (Vinichuk & Dolgova, 2016).
Adults can only interpret the concept of happiness
in adults but not by children. It is undeniable that
happiness or unhappiness in childhood affects
personal well-being in adulthood. Individual
happiness depends on how the individual has felt in
the past (Tamir, et.al., 2015). Older adults who
remember that they were not happy in childhood
then feel unhappy and dissatisfied in adulthood.
Therefore, it is crucial to know the concept of
happiness from the child's perspective.
There is very little research on children's
happiness, especially in Indonesia. At the same
time, the benefits of happiness in children are
significant for children's lives, especially in the
next period of life, one of which is to make
children able to make the experience of failure as a
whip to find better ways to achieve goals. Based on
the previous explanation, everyone's perspective on
happiness can be different, including for children.
If measuring the concept of children's happiness is
based on indicators of adult happiness, this can
lead to intergenerational gaps. This research aims
to find out about the concept of happiness in
elementary school children in Makassar. The
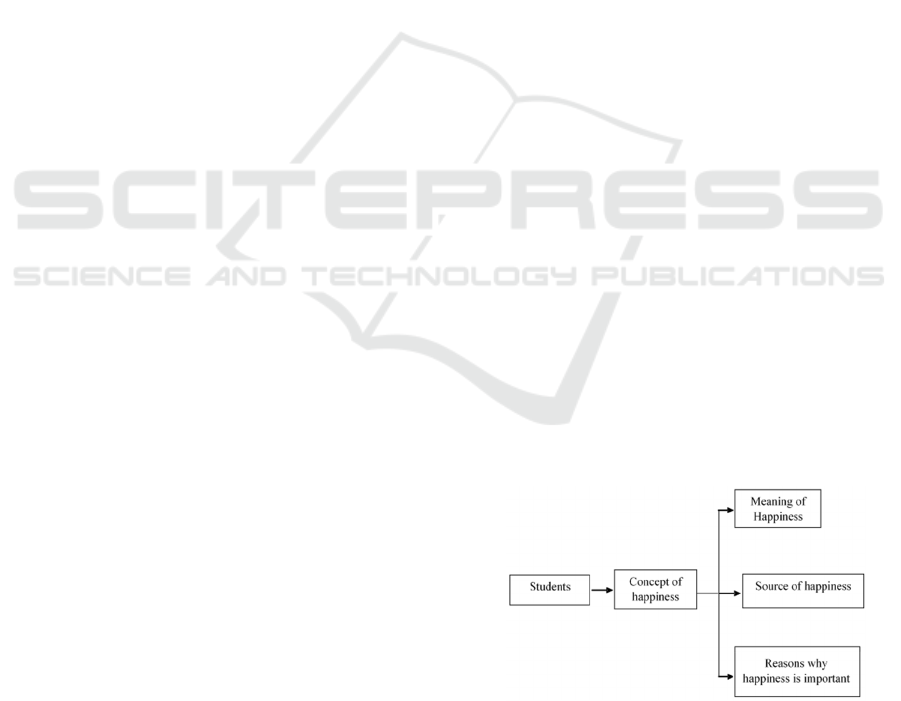
framework of thought in this research is as follows:
Figure 1: Research framework.
ICPsyche 2021 - International Conference on Psychological Studies
264
2 METHOD
This study uses a qualitative approach with the
principle of constructive realism to determine the
concept of happiness in elementary school children
in Makassar City, Indonesia. The number of subjects
in the study was 461 students grade 1 to grade 6 of 4
types of elementary schools in Makassar City. The
four elementary schools are public schools, nature-
based private schools, elementary schools that
combine Islam as their primary curriculum, and
elementary schools that integrate Christianity as
their primary curriculum.
The data collection technique in this study was to
use a questionnaire in the form of a diary book
design through the Quizizz application, making it
easier for respondents and interested in filling out
the questionnaire. The questionnaire consists of
three questions that the researcher prepared. The
first question is an open question about the meaning
of happiness according to the child himself. The
second question is also an open-ended question
about events that make the subject happy. The third
question is a question about the importance or not of
being happy according to the subject.
The entire data collection process took three
weeks. The next stage is the researcher performs the
process of copying the respondents' answers in the
form of verbatim data analysis. The data were then
analyzed using preliminary coding, categorization,
axial coding, and cross-tabulation techniques
according to the grounded theory research design
framework (Chun Tie, Birks, & Francis, 2019)
3 RESULT
3.1
Respondent Description
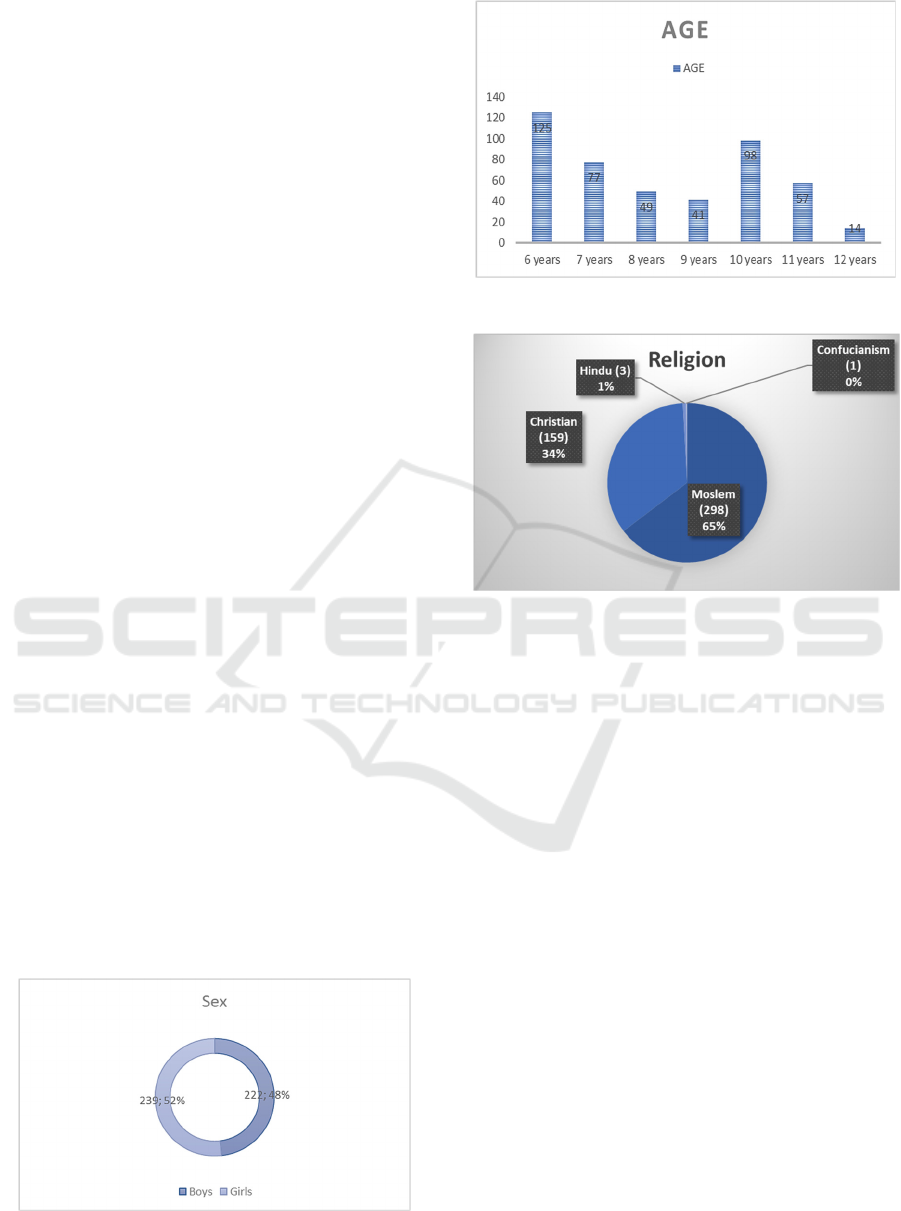
To provide an easier description, the researcher
presents the demographic data as follows:
Figure 2: Demographics of respondents by gender.
Figure 3: Demographics of respondents by age.
Figure 4: Demographics of respondents by religion.
3.2
Definition of Happiness
The results show that most respondents interpret
happiness as a positive emotion, feeling happy,
calm, peaceful, peaceful, happy, without
pressure/burden, not feeling sad, love, and
gratitude. The definition of happiness by students is
presented explicitly in the following table.
Based on table 1, the respondents' answers to the
question "What do you think is happiness?" There
are many different definitions of happiness. Table 1
presents the categories of the meaning of happiness
from students' answers. Most respondents (49.67%)
define happiness as a condition associated with
positive emotions (such as happy, joyful, cheerful,
peaceful, calm feeling).
The Concept of Happiness in Elementary School Children
265

Table 1: Coding of happiness definition by students.
# Basic Category Categories of respondents' Sum %
1.
Harmonious relationship with the
answers
Friends only
82
17,78
2.
closest people
Life satisfaction
Family only
Friends and family
Hope fulfilled
29
6,29
3.
Expression of Feelings
Wish fulfilled
Hopes and wishes
Laugh and smiling
29
6,29
4. Affection Affection 13 2,81
5. Religious Religious 4 0,86
6. Positive emotions
Positive emotions: happy, joy,
cheerful, not sad
229 49,67
7. Gratitude Gratitude 16 3,47
8. Value of Simplicity Simple 8 1,73
9. Doing activities that students like Doing favorable activities 21 4,55
10.
Peace
Playing
Peace
3
0,65
11. Body condition Healthy 2 0,43
12. Intrapersonal relationship Intrapersonal relationship 3 0,65
13. Life value Life value 4 0,86
14. Confidence Confidence 3 0,65
15. Feeling unhappiness Feeling unhappiness 2 0,43
16. Being rewarded Being rewarded 1 0,21
17. Not relevant All of the respondent's answers
not relevant
12 2,6
Total
461 100
3.3 Events That Make Children Happy
The researcher presents the results of the coding on
question number 2, namely what events make
students happy in the form of the following table:
ICPsyche 2021 - International Conference on Psychological Studies
266

Table 2: Coding of events that make children happy.
# Category Categories of respondents' answers Sum %
1 Harmonious relationship with Friends/closest one 334 23,94
the closest people
Family
2 Achievemen
t
Winning a contes
t
72 5,16
Having a good mark
Passing test
Get Ranked
Able to finish a tas
k
3 Study
Study 19 1,36
4 Outin
g
experience
Visitin
g
afamil
y
house 202 14,48
Travel and vacation
Going to the mall
Riding a vehicle
5 Doing a good deed
Doing a good deed 23 1,64
6 Doing a favorable activity
Playing 213 15,26
Shopping
Watching
Using handphone
Reading
7 Sport
Sport 75 5,37
8 Special day
Special day 41 2,93
9 Consuming favorite food or Consuming favourite food or drinks 52 3,72
drinks
10 Intrapersonal relationship
Intrapersonal relationship 3 0,21
11 Interpersonal relationship
Interpersonal relationship 18 1,29
12 Art activity
Art activity 17 1,21
13 Hope and Wish fulfilled Hope fulfilled 37 2,65
Wish fulfille
d
14 Sense of humor
Sense of humor 6 0,43
15 Religiosity
Religiosity 26 1,86
16 Reward
Reward 115 8,24
17 Affection
Affection 26 1,86
18 Gratitude
Gratitude 35 2,5
19 School
School 33 2,36
20 Pet
Pet 7 0,5
21 Daily activity
Doing daily activity 20 1,43
22 Body condition
Healthy 6 0,43
Good physical appearance
23 Expression
Expression 3 0,21
24 Getting good treatment Getting good treatment 6 0,43
25 Not answer Not answer 1 0,07
26 Not relevant
Not relevant 5 0,35
Total
1395 100
The Concept of Happiness in Elementary School Children
267

3.4 Why It Is Important to Feel Happy
The researcher presents the coding results for
question number 3, to be specific, the reasons for the
importance of being happy, in the following table:
Table 3: Coding of reasons for the importance of being happy for students.
#
1
2
Basic Category
Closest person
Ge
t
p
ositive feelin
g
s an
d
avoid
Kategori dari jawaban responden
Family
Friends
Laugh
Sum
6
202
%
1,3
43,81
negative feelings.
N
o
t
sa
d
Comfortable
Happy
Not angry
Solemn
Not crying
Joy
Not silent
Smile
Cheers
Peace
3 Needs and imperatives
Needs 13 2,81
Must
4 Avoidin
g
stress
Avoi
d
stress 16 3,47
5 As a meaning of life
Meaning of life 10 2,16
6 Giving encouragement
Encouragement 12 2,6
7 Affects body condition
Physically Healthy 29 5,29
Mental Health
Helping children's growth
Good
p
h
y
sical appearance and attractive
8 More
g
rateful
More
g
rateful 11 2,38
9 As a right
As a right 12 2,6
10 Memorable moment
Memorable moment 3 0,65
11 Improving the quality of life A better life 19 4,12
An easie
r
life
12 Lon
g
life
Lon
g
life 3 0,65
13 Life value Purpose of life
Life guide
Importan
t
thin
g
s in life
20 4,33
14 Positive meaning
Positive meaning
6 1,3
15 Value of simplicity
Value of simplicity
2 0,43
16 Interpersonal relationship
Interpersonal relationship
19 4,12
17 Reward
Reward
7 1,51
18 Prosperous
Prosperous
1 0,21
19 Irrelevant
Irrelevant
70 15,18
Total
461 100
ICPsyche 2021 - International Conference on Psychological Studies
268

4 DISCUSSION
4.1
Definition of Happiness
Based on the explanation in Table 1 shows that
children define happiness in various ways. The
definition of happiness with the highest percentage
among other definitions expressed by children is a
positive emotion. According to the child's
perception, happiness is a positive emotion
characterized by feelings of pleasure, joy,
cheerfulness, calm, not sadness, and a sense of not
having a burden. In line with the definition that
feelings of pleasure and peace characterize
happiness (Hefferon & Boniwell, 2011). So that
positive emotions as a definition of happiness are
things that adults and children feel.
Children also express other definitions of
happiness, but the essence of this definition is the
emergence of positive emotions in children. For
example, harmonious relationships with the closest
people in this category include children gathering
with family and friends accompanied by fun
activities such as joking. Likewise, with affection,
this category will also lead to the emergence of a
sense of pleasure.
The category of relationship with the closest
person and the category of affection can be related. If
the relationship with the family is warm and loving
despite occasional conflicts and punishment for
wrong behavior, children will feel that the family
loves and treats them fairly. However, happiness
will increase if the atmosphere at home is calm and
happy (Oishi, Graham, Kesebir & Galinha, 2013).
Furthermore, life satisfaction, this category also
raises positive emotions when children feel satisfied.
Happiness is a state of well-being and life
satisfaction, namely the pleasant satisfaction that
arises when needs and expectations are met
(Franklin, 2010). The basis of feeling happy is
positive emotions that are in line with satisfaction
and feelings of pleasure (Seligman, 2002).
Doing religious activities such as worship also
raises positive emotions. Expressing feelings is also
related to positive emotions; for example, when
children feel happy, happy, then express feelings by
laughing and smiling. Likewise with gratitude is
related to feelings of calm, peace, which lead to
positive emotions. Confidence is also one of the
definitions of happiness according to the child's
perception, but this category also leads to the
emergence of positive emotions in children.
There are still definitions related to happiness
expressed by children, such as the value of life,
intrapersonal relationships, good body condition,
and getting rewards such as praise or gifts; if
examined further, these definitions will also bring
positive emotions. Therefore, it can conclude that
happiness based on the child's perception as a
positive emotion felt by the individual. In line with
this explanation, happiness described as a positive
emotion felt by individuals and positive activities
liked by individuals. Happiness seen as an
achievement and a hope, which is generally
achieved by fulfilling goals and rewarding specific
efforts (Mínguez, 2020). Happiness naturally
produces positive and subjective emotions.
However, there is something quite interesting in the
results of this study, and it found that there were two
children who did not feel happy. After the
researchers studied further, respondents who
answered that they did not feel happiness told that
the event that made them happy was gathering with
their family.
4.2 Source of Happiness
As with the definition of happiness, children also
give perceptions about the sources of happiness in
various ways. A harmonious relationship with the
closest person is the dominant source of happiness,
which the child answers. This relationship with the
nearest person includes doing fun activities and
joking with family and friends to create a pleasant
happy atmosphere. The home atmosphere and
relationships with various family members are two
significant factors in happiness (Lu, 2001). Another
research results also suggested that a sense of
friendship is one of the essential indicators of
happiness (O’Rourke, & Cooper, 2010).
Achievement, study, and school also appear as a
source of happiness in children. Feelings towards
school can be a source of happiness or unhappiness
for children. Children who have good school grades
adjust well to teachers and classmates, and those
who like to learn new things make children happier.
Several studies emphasize the education system in
schools, including all the people involved in the
design, such as teachers and students. It is the most
influential part in making school a pleasant or
unpleasant place (Lee & Lee, 2014).
Outing activities are one of the sources of
happiness that arise in children. Outing activities are
activities carried out outside the home, including
visiting relatives' homes, sightseeing, vacations,
recreation, going to the mall, and taking
transportation. In adolescents, it also found that
recreation or leisure time looked quite happy but
The Concept of Happiness in Elementary School Children
269

with a frequency that was not high enough (Hartati,
2017). While for children outing activities have a
high presentation as a source of happiness after a
harmonious relationship with the closest person and
doing things they like.
Doing good is a source of happiness in children.
Doing good includes helping parents, helping
siblings, helping friends, sharing with others,
forgiving someone, and being kind to others.
Another one, doing what students love, is the second
dominant source of happiness in children. Activities
that children like include playing, playing games,
watching tv/cinema, reading books, and other fun
activities for children. Researchers found that
children would be happier if they did activities with
family and friends. However, in this category, it is
only for specific activities, such as playing,
shopping, watching movies, playing on mobile
phones, and reading.
In addition to the biological fact that exercise
triggers the release of the hormone dopamine, a
compound that makes individuals feel happy (Basso
& Suzuki, 2017). Psychologically, sports activities
are also a source of happiness for children. In this
study, children answered that sports activities such
as swimming, cycling, playing ball, running,
badminton, and other sports activities made
children happy. This is in line with research that
found that one of the five things that make children
happy is exercise (Chaplin, 2009).
Special days are one of the sources of happiness
in teenagers, which also found in children. Special
days include birthdays, Eid al-Fitr, and Christmas.
Based on the research results by Harmani and
Yulianti (2014) suggest that one of the events that
make teenagers happy is a birthday celebration
included in the category of personal affective events.
Meanwhile, consuming favorite foods and drinks is
one of the events that makes children happy, like
eating ice cream, chicken, Milo, Indomie, and other
favorite foods. Kaur and Van (2017) suggest that
certain types of food help generate positive
emotions. Getting a reward is also one of the events
that make children happy. Rewards include getting
gifts, buying toys, buying something children want,
buying storybooks, buying bicycles, being
surprised, getting chocolates, and others.
Another category, intrapersonal and
interpersonal relationships in children, is a source of
happiness. Having friends is an important source of
happiness (Demir, Özdemir & Weitekamp, 2007).
The friendship features of best friends and first
friends emerged as the strongest predictors of
happiness. Doing artistic activities is also a source of
happiness for children. This in line with a research
result, a meaningful life is a gateway to happiness,
and one of the sources of happiness is art. Art
activities include singing, painting, drawing,
dancing, and other art activities (Walshe, Lee &
Smith, 2020).
Another event that makes children happy is when
the child's hopes and desires are fulfilled. As for
some of the wishes and hopes mentioned by
children, namely seeing their parents happy, always
making others smile, and making both parents
happy. Sense of humor is one source of happiness in
children. Events related to a sense of humor are
events that make children feel positive emotions and
laugh, including having funny friends, seeing funny
events, and telling stories about funny topics.
Semrud-Clikeman & Glass (2010) suggest that
everyone has a sense of humor, both adults and
children. A sense of humor is needed to enjoy
humor in a relaxed and cheerful manner so that
children's development, incredibly emotional
development, can be optimal.
The next happy event is a religious activity.
Religious activities in children include covering
their private parts of the body, reciting or reading the
Qur'an, worshiping with family, praying on time,
praying in congregation at the mosque, and carrying
out religious orders. The results of this study are
contrary to the results of research from Holder,
Coleman, and Wallace (2010), which found that
children's spirituality, but not their religious
practices (e.g., attending church, praying, and
meditating), was strongly linked to their happiness.
Another event is gratitude. Gratitude, according to
children, includes being grateful for being able to
breathe fresh air, having parents and family, having
many kind-hearted friends, going to school, getting
sustenance, and all needs can be met. One form of
good moral quality is gratitude, which can foster
happiness for individuals (2005b).
Affection is an event that also makes children
happy. Affection, according to children, includes
getting love from both parents, siblings, family,
friends, and other closest people. One form of
affection that makes children happy is being kissed
by their parents. It suggests that if the relationship
with the family is warm and loving, the child will
feel that the family loves and treats him fairly. One
factor that influences happiness in children is the
home atmosphere (Badri, Al Nuaimi & Guang,
2018).
Pets also become a source of happiness for
children. Events related to this category include
playing with pets such as rabbits, cats, and other
ICPsyche 2021 - International Conference on Psychological Studies
270

pets. The next event that the researchers did not
expect that makes children happy is doing daily
activities. This category includes eating, drinking
and sleeping. The condition of the body is the next
source of happiness. Body condition includes having
a healthy physical and mental condition. The next
source of happiness is expression. Expression
includes expressing positive feelings in children in
the form of laughing and smiling faces. The last one
is, getting good treatment. These events involve
reading storybooks when they want to sleep,
cooking their mother's favorite foods, and helped
with homework.
4.3 Reasons for the Importance of
Happiness
This study found various reasons for happiness in
children. The reason for the importance of happiness
in children is because it makes individuals get
positive feelings and avoids individuals from
negative feelings, affects body conditions as a
value of life, improves the quality of life, has a
positive effect on interpersonal relationships, avoids
stress, needs, and obligations, gives encouragement,
is a right. Everyone becomes more grateful, as the
meaning of life, makes a long life, gets rewards, gets
memorable moments, is the value of simplicity, and
gets much sustenance. The dominant respondents
answered that happiness is essential because it
prevents individuals from negative feelings and
makes them experience positive emotions. This
aligns with previous research conducted by Patnani
and Juniar (2014) on children aged 9-12 years in
Central Jakarta. Most children reasoned that
happiness is important because happiness can make
children experience positive feelings and avoid
negative feelings.
5 CONCLUSION
This research shows that based on the child's
perception, happiness is considered as a condition
associated with positive emotions (such as happy,
joyful, cheerful, peaceful, calm feeling). The
dominant source of happiness for children is a
harmonious relationship with the closest people,
including gathering with family or friends, playing
with friends or relatives, traveling with family, and
spending time with family and friends. Therefore, to
increase happiness in children, it is best to focus on
efforts to create and improve positive relationships
in children's relationships with family and friends.
The reason for the importance of happiness in
children is because happiness can make children feel
positive feelings and prevent children from negative
emotions. Based on the results of the research
conducted, the researchers suggest, for further
researchers, it can be considered to conduct research
and development on similar topics, such as using
data collection methods in the form of interviews to
explore deeper meanings from respondents' answers.
REFERENCES
Anand, P. & Roope L. (2016). The development and
happiness of very young children. Social Choice and
Welfare. 47(4):825-51.
Argyle, M. (2001). The psychology of happiness (2
nd
ed.).
Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315812212.
Badri, M., Al Nuaimi, A., Guang, Y., Al Sheryani, Y., &
Al Rashedi, A. (2018). The effects of home and school
on children’s happiness: a structural equation model.
International Journal of Child Care and Education
Policy, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40723-018-
0056-z
Basso, J. C., & Suzuki, W. A. (2017). The effects of acute
exercise on mood, cognition, neurophysiology, and
neurochemical pathways: a review. Brain plasticity
(Amsterdam, Netherlands), 2(2), 127–152.
https://doi.org/10.3233/BPL-160040
Batcho, K. I. (2012). Childhood happiness: More than just
child’s play. Psychology Today.
Ben-Arieh, A. (2008). Indicator and Indices of children’s
Well-being: towards a more policy-oriented
perspective. European Journal of Education, 43(1):37-
50.
Butt, D. S. & Beiser, M. (1987). Successful aging:
international theme psychology. Psychology of Aging,
2:87-94.
Carr, A. (2011). Positive psychology: The science of
happiness and human strengths (2nd ed.).
Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group.
Carter, K. E., & Seifert, C. M. (2012). Learn psychology.
Jones & Bartlett Publishers.
Casas, F. (2011). Subjective social indicators and child
and adolescent well-being. Child Indicators Research
2011; 4(4): 555-75.
Chaplin, L. (2009). Please may I have a bike? Better yet,
may I have a hug? An examination of children’s and
adolescents’ happiness. Journal of Happiness Studies,
10, 541-562. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10902-008-
9108-3 Chun Tie, Y., Birks, M., & Francis, K.
(2019). Grounded theory research: A design framework
for novice researchers. SAGE Open Medicine, 7,
2050312118822927. https://doi.org/10.1177/20503121
18822927
Demir, M., Özdemir, M. & Weitekamp, L.A. (2007).
Looking to happy tomorrows with friends: Best and
The Concept of Happiness in Elementary School Children
271

close friendships as they predict happiness. J
Happiness Stud 8, 243–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/
s10902-006-9025-2
Fanhas, E. & Mukhlis, G. N. (2017). Pendidikan
karakter untuk anak usia dini menurut Q.S Lukman:
13-19. Jurnal Anak Usia Dini dan Pendidikan Anak
Usia Dini, 3(3a), 42-51. P-ISSN: 2599-0438; E-ISSN:
2599-042X.
Franklin, S. S. (2010). The psychology of happiness: a
good human life. Philosophy in Review, (5).
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Harmani & Yulianti, A. (2014). Peristiwa-peristiwa yang
membuat bahagia, Psympathic, Jurnal Ilmiah
Psikologi, 1(2): 109-119.
Hartati, N. (2017). Makna dan sumber kebahagiaan remaja
suku minangkabau. Jurnal Konseling dan Pendidikan,
5(2). ISSN: 2337-6740
Hefferon, K., & Boniwell, I. (2011) Positive psychology:
theory, research, and applications. Open University
Press: United States.
Holder, M. & Coleman, B. (2008). The contribution of
temperament, popularity, and physical appearance to
children’s happiness. Journal of Happiness Studies,
9(2), 279-302.
Holder, M. D., Coleman, B., & Wallace, J. M.
(2010). Spirituality, religiousness, and happiness in
children aged 8–12 years. Journal of Happiness
Studies: An Interdisciplinary Forum on Subjective
Well-Being, 11(2), 131–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/
s10902-008-9126-1 Kahneman, D. (1999). Objective
happiness. In D.
Kahneman, E. Diener, & N. Schwarz (Eds.), Well-being:
Foundations of hedonic psychology (pp. 3–25). New
York, NY: Sage.
Kaur, S. & Van, A. (2017). Do the types of food you eat
influence your happiness?. UC Merced Undergraduate
Research Journal, 9(2).
Lee, H., & Lee, J. (2014). Effects of teacher’s attachment
perceived children to school happiness of children:
The mediated effects of learning flow and peer
competence. Youth Facility and Environment, 12, 81–
91.
Lu, L. (2001). Understanding happiness: a look into the
Chinese folk psychology. Journal of Happiness Study,
407-32.
Lyubomirsky, S., Sheldon, K. M., & Schkade, D. (2005b).
Pursuing happiness: The architecture of sustainable
change. Review of General Psychology, 9(2), 111–131.
Mínguez, A.M. (2020). Children’s relationships and
happiness: the role of family, friends and the school in
four european countries. J Happiness Stud 21, 1859–
1878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-019-00160-4.
O’Rourke, J., & Cooper, M. (2010). Lucky to be
happy: a study of happiness in Australian primary
students. Australian Journal of Educational &
Developmental Psychology, 10, 94-107. ISSN 1446-
5442.
Oishi, S., Graham, J., Kesebir, S., & Galinha, I. C. (2013).
Concepts of happiness across time and cultures.
Personality & social psychology bulletin, 39(5), 559–
577. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167213480042
Patnani, M. & Juniar, D. (2014). Definitions and sources
of happiness: description of happiness in children age
9-12 years in central Jakarta. Jurnal Psikologi
Indonesia, 11( 1), 1-13. ISSN. 0853-3098.
Rees, G., Main, G., & Bradshaw, J. (2015). Children's
Worlds National Report England. York: University of
York.
Ryan, R.M. & Deci, E.L. (2001). On happiness and human
potentials: A review of research on hedonic and
eudaimonic well-being. Annu Rev Psychol 2001;
52(1):141-66.
Ryff, C.D. & Keyes, L.M. (1995). The structure of
psychological well-being revisited. Journal of
Personality and Social Psychology, 69(4).
Santrock, J.W. (2011). Life-Span Development: Masa
Perkembangan Anak ed.11. Penerjemah: Verawaty
Pakpahan dan Wahyu Anughraheni. Jakarta: Salemba
Humanika.
Seligman, M. & Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2000). Positive
psychology: An introduction. American Psychologist,
55(1), 5-14.
Seligman, M. E. P. (2002). Authentic happiness: Using the
new positive psychology to realize your potential for
lasting fulfillment. Free Press.
Seligman, M.E.P., Ernst, R.E., Gillham, J., Reivich, K., &
Linkins, M. (2009): Positive education: positive
psychology and classroom interventions, Oxford
Review of Education, 35:3, 293-311.
Semrud-Clikeman, M. & Glass, K. (2010). The relation of
humor and child development: social, adaptive, and
emotional aspects. Journal of child neurology. 25.
1248-60. 10.1177/0883073810373144.
Stallings, M. C., Dunham, C. C., Gatz, M., Baker, L. A.,
& Bengtson, V. L. (1997). Relationships among life
events and psychological well-being: More evidence
for a two-factor theory of well-being. Journal of
Applied Gerontology, 16(1), 104-119.
Suldo, S. & Fefer, S. (2015). Parent-child relationships
and well-being. Research, Applications, and
Interventions for Children and Adolescents: A Positive
Psychology Perspective, 131-47.
Tamir, M., Oishi, S., Schwartz, S. H., & Kim, M. Y.
(2017). The secret to happiness: feeling good or
feeling right? Journal of Experimental Psychology,
146(10), 1448-1459. doi:10.1037/xge0000303.
Trommsdorf, G. (2006). Parent-child relations over the
lifespan. A cross-cultural perspective. Parenting
beliefs, behaviors, and parent-child relations. A cross-
cultural perspective. New York: Psychology Press, pp.
143-183.
Veenhoven, R. (2010). Greater happiness for a greater
number: is that possible and desirable? Journal of
Happiness Studies, 11:605-629. Springer publications
online
Veenhoven, R. (2000). Freedom and happiness: A
comparative study in forty-four nations in the early
1990s. In E. Diener & E. M. Suh (Eds.), Culture and
subjective well-being (pp. 257–288). The MIT Press.
ICPsyche 2021 - International Conference on Psychological Studies
272

Vinichuk, N & Dolgova, M. (2016). The Image of
Happiness among Children with Different Levels of
Creativity. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences.
233. 481-485. 10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.10.198.
Walshe, N., Lee, E., & Smith, M. J. (2020). Supporting
children’s well-being with art in nature: artist
pedagogue perceptions. Journal of Education for
Sustainable Development, 14(1), 98–112.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0973408220930708
The Concept of Happiness in Elementary School Children
273
