
Survey on Mobile Banking and e-Wallet Usage and Its Security
Concerns
Anubhav Bose
1
, Chetna Choudhary
1
, Sunil Kumar Chowdhary
1
and Manoj Kumar
2
1
Amity University Uttar Pradesh, Noida
2
School of computer science, University of Petroleum and energy Studies, Dehradun
Keywords: e-Wallet, Mobile Banking, Online Transactions, Security Issues.
Abstract:
The rapid development in Information Technology has led to the introduction of many new technologies in
every aspect of our life. It has significantly contributed to the field of online transactions. As mobile
technology continuously grows, it has resulted in a rapid increase in transactions through mobile devices. It
has revolutionized e-banking and virtual money transactions by providing ease of quick transfer of money
from any location. Demonetization in India has further facilitated the use of mobile wallets as it encourages
cashless transactions online. There has also been a significant rise in usage of mobile banking during
demonetization as it saves a lot of time and effort to transact. However, there are many security concerns for
consumers due to the unfamiliarity and complexity of mobile devices and their associated technologies. The
major concern for users is the protection of their personal identification information and stealing of sensitive
payment information. This paper intends to study the usage patterns of mobile banking and E wallets and
identify the concerns related to security and privacy issues among the masses in the Indian context.
1 INTRODUCTION
The total number of mobile phone users in our
country are expected to increase to 730.7 million by
2018, which means almost half of the total
population of the country uses mobile phones.[9]
With the ease of connectivity and always on
availability, mobile phones today not only offer
advantages in terms of instant communication,
entertainment and greater productivity but they have
become tools that consumers use for banking,
payments, and shopping. Being easy and convenient,
currently, more than 43.7 million mobile users have
used Mobile banking services in one form or the
other (Trak, 2021). Until last year, e wallets totalled
200 million and expected to grow to 650 million by
2020 (BusinessLine, 2021). As mobile banking and
E wallet usage continues to grow by leaps and
bounds, security vulnerability and threats to
sensitive information are increasing fast.
In the coming times, the security of transactions
is probably going to emerge as the greatest worry
among Mobile banking and E wallet users. The
quick development in online theft and extortion are
on the ascent. Online fraud is found to be third
amongst economic crimes prevailing in our country
according to a survey conducted by PwC in 2011
(iPleaders, 2021). The incidence of ATM, credit,
debit and web transaction-related fraud has gone up
by over thirty five percent between 2012-13 and
2015-16 in our country, as concluded by the Central
Bank (ZDNet, 2021).
2 RELATED WORK
As we have seen, in recent years, there has been an
explosion of internet based electronic banking
applications (Dixit and Datta, 2010). Harshad Patel
and Vijay Pithadia (2013), found that “Advancement
achieved in the Information Technology and
communication Technology in the last two decades
has resulted in the successful implementation of
Electronic Banking in India” (Sailaja and
Thamodaran, 2016 ).
R. Karuppusamy and Dr N. Venkatesa
Palanchamy (2011) state in their study that “Ravi
(2008) stated that with the advent of innovative
technology, banks were able to provide customized
Bose, A., Choudhary, C., Chowdhary, S. and Kumar, M.
Survey on Mobile Banking and e-Wallet Usage and its Security Concerns.
DOI: 10.5220/0010789600003167
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Innovation in Computer and Information Science (ICICIS 2021), pages 13-17
ISBN: 978-989-758-577-7
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
13
products and services like internet banking, mobile
banking, ATMs, Tele-Banking, to their customers.
Latest technology helped the banks to reduce their
transaction cost. But certain risks associated with
innovative technology and technology related frauds
were found to increase” (Karuppusamy and
Palanichamy, 2011).
In fact, in Aladwan's (2001) investigation of web
based banking, potential clients evaluated web security
and client's protection as the most significant future
difficulties that banks are confronting. Observed
efficiency of online banking has a direct impact on the
acceptance of web banking, too (Aladwani, 2001).
Customers stress that unapproved people can access their
online record and heavy monetary consequences will
take place. In India, slowly the Indian customer is
moving towards web banking. However, they are very
concerned regarding the security and privacy of web
banking (Malhotra and Singh, 2009). (Dixit and Datta,
2010) Infact, a majority of studies highlight the fact that
“security” is the biggest single concern for customers
when faced with the decision to use web banking.
Security has an issue perpetually, but its scope has been
modified from mere doubts regarding the privacy of
personal information to worries of monetary loss. (Sayar
and Wolfe, 2007).
A study done by Neha Dixit and Dr Saroj K.
shows that Security and protection, trust and
originality, have a positive impact on the
acknowledgment of web banking in India. Their
study aimed to find out the level of acceptance of
online banking among those customers who are over
thirty five years of age. (Dixit and Datta, 2010)
Jayaram. J and Dr P. N. Prasad (2013) deduce in
their examination that the greater part of the
investigations that have been done on issues
concerned with web banking in countries like
Australia (Sathye, 1999), Malaysia (Mukti, 2000;
Chung and Paynter, 2002; Sohail and Shanmugham
2004), Singapore (Gerrard and Cunningham, 2003a,
2006b), Turkey versus UK (Sayar and Wolfe, 2007)
and Saudi Arabia (Sohail and Shaikh, 2007).
(Jayaram and Prasad, 2013 ) A considerable measure
of work has not been done in India with importance
to e-banking concerns.
The current study intends to understand the
amount of level of usage of mobile banking and E
wallets and problems relating to the security and
privacy problems among the masses in the Indian
context.
3 RESEARCH MODEL
To investigate the E wallet and E banking Usage
patterns and related security concerns, we designed a
survey questionnaire. The questionnaire contains
three part: Demographics, E wallet and E banking
usage patterns and related Security Concerns.
We used Google forms to create, distribute the
survey and store the responses online. A total of 348
responses were received.
4 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
4.1 Demographics and Personal
Attributes
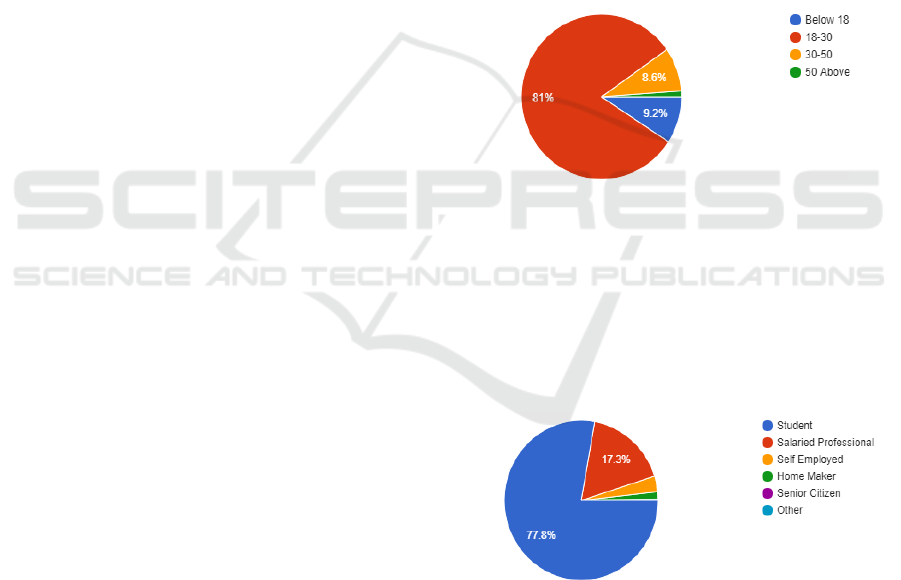
1.Age: 81% of participants were 18-30 years old.
9.2% were younger than 18 years old, and 8.6%
were between 30-50 years. Only 1.1% of the
participants were above 50 years of age.
Figure 1: Age distribution.
2.Profession: 77.8% of the participants were
students and 17.3% were salaried professionals.
While only 3.2% of the participants were self-
employed, 1.4% were home makers. The majority of
the participants were from Non-IT domain
accounting for 77.8%. The remaining 17.3% were
associated with the IT industry.
Figure 2: Profession.
4.2 Usage Patterns
1.E-wallet type: The majority of the participants
used Paytm as their E-wallet, accounting to 78.4%.
While 17.3% used Freecharge,11.4% used
Mobikwik, 7.5% used PayU money, and 3.2% used
M-pesa. The remaining 20.2% of participants didn’t
use any.
ICICIS 2021 - International Conference on Innovations in Computer and Information Science
14
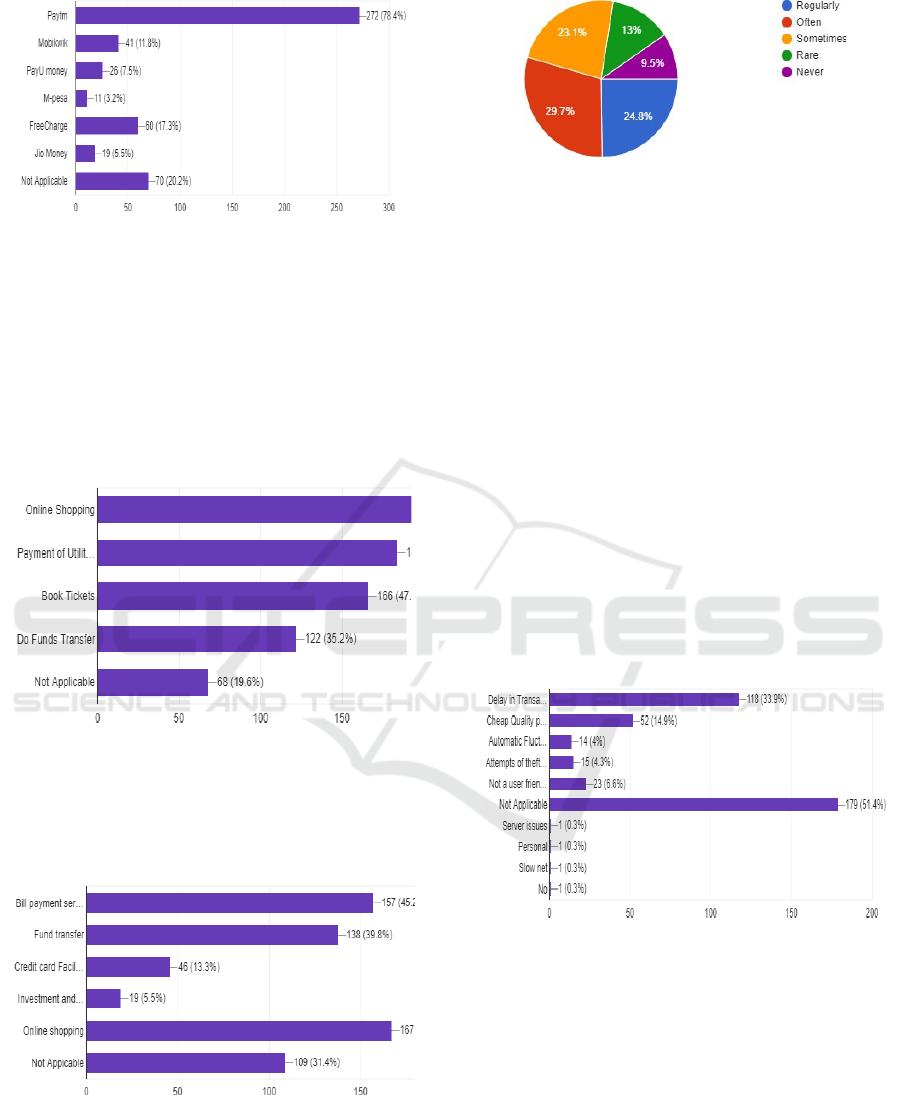
Figure 3: Types of E-wallets.
2.E-wallet usage: The majority of the participants,
59.4% used E wallets for online shopping while 53%
used it for payment of utility bills, and 47.8% used it
for booking tickets online. 35.2 used e wallets for
transferring funds.
3.E Banking Usage: 66% used E banking services,
while the rest 34% did not. Among those who use,
27.1% use State Bank of India’s services, which is
the highest number.
Figure 4: E-wallet usage purposes.
4.E banking Usage Pattern: As we had seen in E
wallets, In E-banking too, 48.1% used E banking
services for online shopping. 45.2% use it for bill
payment services and about 40% for funds transfer.
Figure 5: E-banking usage purpose.
5.Frequency: 24.8% of people have said that they
use E wallet and E banking services Regularly. The
highest, about 30%, use it. Often, and 23.1% use it
sometimes.
Figure 6: Frequency of usage.
6.Convenience: About 40% of the people find both e
wallets and e banking convenient to use, though
36% prefer only E wallets and almost 24% prefer
only E banking.
7.Effect of Demonetization: After demonetization in
the country in 2016, usage of e wallets and e
banking increased for almost 80% of all the people.
4.3 Security Concerns
1.Problems Faced: Almost 60% of the people have
not faced any problem while using E wallets and E
banking services, but about 40% of the people have
faced one.
2.Types of Problems faced: Among the users who
have faced a problem, the leading problem is Delay
in Transaction with about 34% suffering from it.
14.9% of respondents suffered from cheap quality
while shopping online and 6.6% from the problem of
not having a user-friendly interface.
Figure 7: Problems faced in online transaction.
A small number also suffered from Automatic
Fluctuation and Attempts of theft. However, almost
half of the respondents, 51.4%, did not experience a
single problem. Infact, the majority of the
population, 78.4% find online transactions safe to
use, which shows people’s immense level of trust.
21.6% have voted for a No.
3.An amount that people find safe to transact: The
majority of the people, 37.9%, find it safe to transact
less than 5000INR.
Survey on Mobile Banking and e-Wallet Usage and its Security Concerns
15
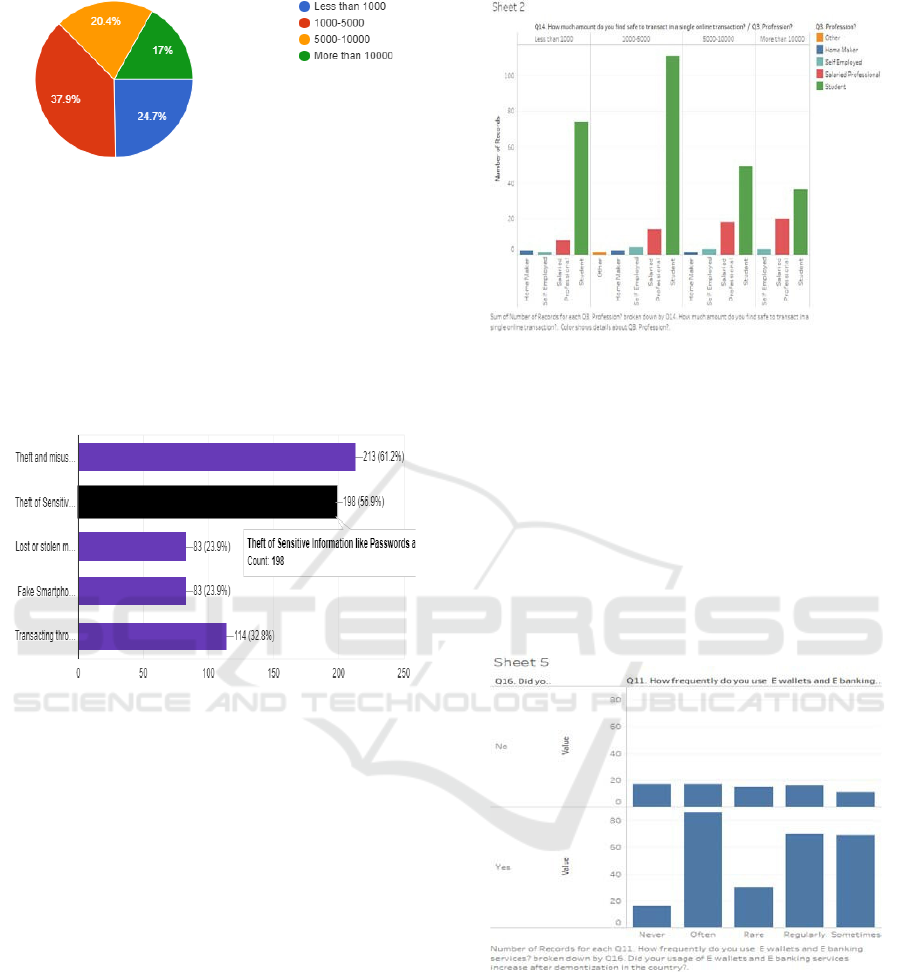
Figure 8: Online transaction amount.
4.Security related concerns: About 61.2 of the
people fear the theft and misuse of Personal
information while 56.9% fear Theft of Sensitive
Information like Passwords and Pin leading to
financial loss. 32.8% fear that they might be
transacting through mobile devices infected by
malware. 23.9% of respondents feared that their
mobile would be stolen, and they might be
downloading Fake smartphone apps.
Figure 9: Security concerns.
4.4 Cross Analysis
1.Cross Analysing the two parameters; Profession
and the amount people find safe to transact, we see
that:
• Among the students, a maximum online transaction
is between 1000-5000 INR.
• Among the Salaried Professionals, a maximum
online transaction is More than 10000 INR.
• Among the Self Employed, a maximum online
transaction is again between 1000-5000 INR.
Figure 10: Relationship between Profession and online
transaction amount.
2.Cross Analysing the two parameters; Usage levels
after Demonetization and Frequency of Usage, we
see that all the levels (Regularly, Often, Sometimes,
Rare and Never) of Frequency of Usage were high
for people who had voted that their Usage of E
banking and E wallets Services increased after
Demonetization. Also, we see that the levels of
Frequency of Usage were low for people who had
voted that their usage did not increase after
demonetization.
Figure 11: Relationship between Demonetization and
frequency of usage of mobile transactions.
3.Cross Analysing the two parameters; Age and
Convenience concerning usage of E wallets or E
banking or both, we see that
• Below Age 18, Respondents prefer E wallets.
• Between 18-30, though the Respondents prefer
Both, their second preference is for E wallets.
• For 30-50 Age group, though the Respondents
prefer Both, their second preference, in this case, is
E banking.
ICICIS 2021 - International Conference on Innovations in Computer and Information Science
16
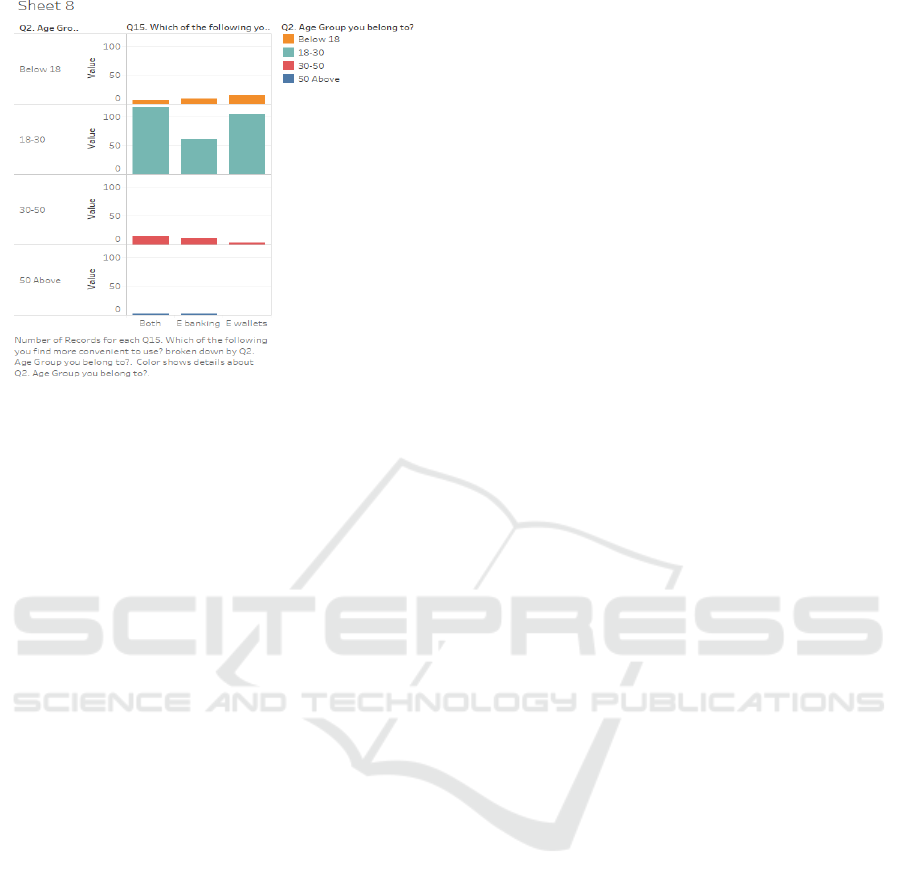
Figure 12: Relationship between Age and preference of e-
wallet or e-banking.
5 CONCLUSION
Our study found out that the usage of mobile
banking and E- wallets has significantly increased in
recent years. Demonetization has encouraged the
people of India to move towards a cashless economy
and has further facilitated the use of mobile banking.
The young people below 18 years prefer using e-
wallets and tend to transact not more than Rs 5000
while working professionals use both e-wallets and
mobile banking and tend to transact more than Rs
10000. Also, a lot of people are concerned about
performance and security issues of transacting
online via mobile devices. The major concerns are
theft and misuse of personal information and delay
in transactions. Many people who are more
proficient over the internet are also cautious about
installing fake smart phone applications via third
party stores. We conclude that in spite of the
security concerns, there is a major rise in the usage
of mobile banking and e-wallets in India.
Further, this paper will serve as a fundamental
advance in investigating clients' perspectives and
assumptions in regards to mobile banking and its
related security concerns. Additional research and
investigation are required to explore issues identified
with mobile banking in a more profound way and
what methodologies ought to be embraced by banks
by which they can upgrade the security provided to
their consumers.
REFERENCES
Karuppusamy, R. and Dr NV Palanichamy, (2011),
“Awareness and adoption of Value Added Services
offered by the banks in Coimbatore District”.
Dixit, N. and Dr SK, Datta. “Acceptance of E-banking
among Adult Customers: An Empirical Investigation
in India”.
Jayaram, J. and Dr P. N., Prasad (2013). “Review Of E-
Banking System And Exploring The Research Gap In
Indian Banking Context”.
Sailaja, P. and Dr.V., Thamodaran (2016). “Customers
Perception on Security System in Mobile banking”.
Kumar, K. and Mittal, M. (2013). “E-Banking Security
and Challenges: A survey”.
Patel, H. and Dr V., Pithadia (2013), “Emerging trends in
customer satisfaction of value added services in
selected banks at mehsana district of gujarat”.
Aladwani, A., “Online banking: a field study of drivers,
development challenges, and expectations”.
Nema, S. and Shukla, N., (2013), “Mobile Payment
Security issues: a Comprehensive Survey”.
https://www.statista.com/statistics/274658/forecast-of-
mobile-phone-users- in-india/
http://trak.in/tags/business/2009/10/08/mobile-banking-
users-india/
http://www.thehindubusinessline.com/economy/india-
skips-plastic- money-leapfrogs-into-mobile-wallet-
payments/article9407059.ece
https://blog.ipleaders.in/online-banking-frauds-in-india-
how-to-recover-lost-money/
http://www.zdnet.com/article/online-banking-and-plastic-
card-related- fraud-in-india-increases-35-percent/
Survey on Mobile Banking and e-Wallet Usage and its Security Concerns
17
