
Peculiarities of German World Economic Development Policy
Mikhail Savelyev
1a
, Andrey Savchenko
1b
,Valery Ivanov
2c
and Yury Polyakov
2d
1
Association for Methodological Support of Business Activity and Social Development "Mitra", Pushkinskaya 241, Izhevsk,
Russia
2
Udmurt State University, Universitetskaya, 1, Izhevsk, Russia
Keywords: Economic development policy, Germany, German world, culture, institutions.
Abstract: The growth rates and sustainability of the economic development of German-speaking countries in the years
1850-2020 have been investigated. The comparison is made for 18 economic cycles, which are grouped into
4 historical periods: imperial, republican-fascist, division and unity. The proposed method for economic
development policies to be studied makes it possible to quantify the proximity of economic development
strategies based on the changes in economic growth and risk. The features of progressive, regressive,
conservative and aggressive policies of economic development are described. The formula for evaluating the
index of similarity of economic development policy is proposed. In accordance with this indicator, a
comparison of the economic policy of Germany with more than 30 European countries showed that the
similarity of policies depends on the influence of the cultures and institutions of the compared countries on
the strategy of their economic development. In the current historical period, 3 cultural and geographical groups
of countries have been identified with a policy of economic development that coincides with Germany, with
an independent and opposite policy. The results of the research show the area of the German world as a sub-
civilizational community.
1 INTRODUCTION
The work examines the development of the
economies of the German world countries. The
hypothesis about the dependence of the economic
development policy of the studied countries is tested:
if the cultural and institutional proximity of these
countries, the similarity of their economic
development strategies affects the coincidence of
their economic development trends.
Such studies include the work (Baltserovich L. &
Zhontsy, 2012) where the trajectories of economic
growth of Australia and New Zealand are compared
on the basis of the similarity of their cultures. In the
work (Helantera A. & Ollus), based on a comparative
analysis of Finland and Russia, it is shown that the
differences in the economic and technological
development of these countries are determined by the
activities of the government.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4145-4098
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4452-5071
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8470-0869
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9328-218X
Some works are devoted to the German economy
(Ridley, 1968; Evans, 1986; Tsedilin, 2005; Uebele.
& Sarferaz, 2009; Streb & Waidlein, 2013; Olczyk,
2019; Boldyrev et al., 2020; Savelyev et al., 2020a).
However a comparative study of cultural and
institutional phenomena has not been identified.
Especially little is paid to research on the GDR
economic performance. The history of the post-war
economic recovery in eastern Germany is described
by Kulbakin (Kulbakin, 1979). Yablokov B.V.
explores peculiarities of practical implementation in
1963-1973 of the “new economic system” of the
GDR, which actually imitated market-based
mechanism within the centralized planned economy
(Yablokov, 2018). Having studied the GDR economy
from 1961 to 1976, P. Ludz, came to the conclusion
that the leadership of the GDR did not manage to
adapt the East German economy to a new type of
industrial society, which combines advantages in the
382
Savelyev, M., Savchenko, A., Ivanov, V. and Polyakov, Y.
Peculiarities of German World Economic Development Policy.
DOI: 10.5220/0010707200003169
In Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference "Ensuring the Stability and Security of Socio-Economic Systems: Overcoming the Threats of the Crisis Space" (SES 2021),
pages 382-387
ISBN: 978-989-758-546-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved

social sphere with the efficiency of a market economy
(Ludz, 1977).
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study is focused on the economic development
of the countries of the German world which
comprises German-speaking countries and countries
are exposed to the German institutions and culture.
The study does not include the American countries of
German migration, in which the influence of the
culture and institutions of their former metropolises is
more significant, and the former German colonies,
which practically did not inherit the institutions of the
German Empire and gained independence from other
countries, and data for the colonial period of their
relations with Germany have not been found.
The features of the policy of economic
development and their results in the historical
retrospective of 1850-2020 are under study.
A feature of the research methodology is the use
for assessing economic development, besides the
usual indicators of economic growth (growth rates of
real GDP), also indicators of stability (risks) of this
development - the standard deviations (here and after
SD) of the growth rates of real GDP. The risk
assessment period is defined as the economic cycle
from the first year of the start (or acceleration) of
economic growth to the last year of the recession (or
slowdown) in Germany. This approach allows us to
assess the quality of economic decisions and their
implementation within the specific culture of the
German world.
For the purposes of analysis, economic cycles are
combined into four historical periods:
imperial period - 7 cycles - until 1919;
period of the Weimar Republic and the Third
Reich - 3 cycles - until 1946;
the period of division into two states (FRG and
GDR) - 5 cycles - until 1990;
the period of united Germany - 3 cycles - until
2020.
Within this approach, the policy of economic
development is considered to be as progressive when
the subsequent period, in comparison with the
previous one, has a higher rate of growth of
macroeconomic indicators and a lower rate of risk
(SD). On the contrary, decreasing in growth and
increasing in risks are associated with the regressive
policy of economic development. A mutual decline in
growth rates and risks is the indicator of the
conservative policy of economic development, and in
the case of growth, it is aggressive.
The index of coincidence of the development
policies of Germany with the countries of the German
world is calculated by the formula (1).
IC M O N 100
⁄
%,
(1)
where:
IC is an index of coincidence of development
policies, for convenience on the percentage,
N is the total number of studied periods (economic
cycles),
M is the number of coincidences of development
policies,
O is the number of opposite development policies.
This approach is theoretically substantiated in
earlier studies by the authors, which shows the
correlation between culture and institutional models,
which is confirmed by econometric studies of
economic development (Savelyev, 2015; Savelyev,
2020; Savelyev et al., 2020a, 2020b; Savelyev et al.,
2021a, 2021b, 2021c, 2021d). Data sources were
works (Maddison, 2008; Bolt, van Zanden, 2014;
World Bank, 2019; TED, 2020).
Information base for the analysis of data on the
Russian Empire – Nominal GDP historical series
(Dincecco, 2013). This source contains data on
nominal GDP. For correct comparison for the period
1900-1913 according to (Maddison, 2008), the
average annual inflation index was evaluated and the
values of nominal GDP reduced by this index were
obtained. This indicator can be considered the closest
analogue of real GDP. Actual inflation by years may
differ significantly, but for the purposes of this work,
longer periods than a year are studied, and deviations
of real GDP from the calculated one due to the
deviation of the actual annual inflation index from the
average annual level are leveled, which allows us to
calculate growth data reduced by the average annual
inflation nominal GDP comparable to real growth.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The evaluation of the development policy during the
periods of certain economic cycles in the studied
countries is presented in Table 1. Analysis of the
evaluation of the coincidences of policies and
opposite policies in these periods is made in Table 2.
Peculiarities of German World Economic Development Policy
383
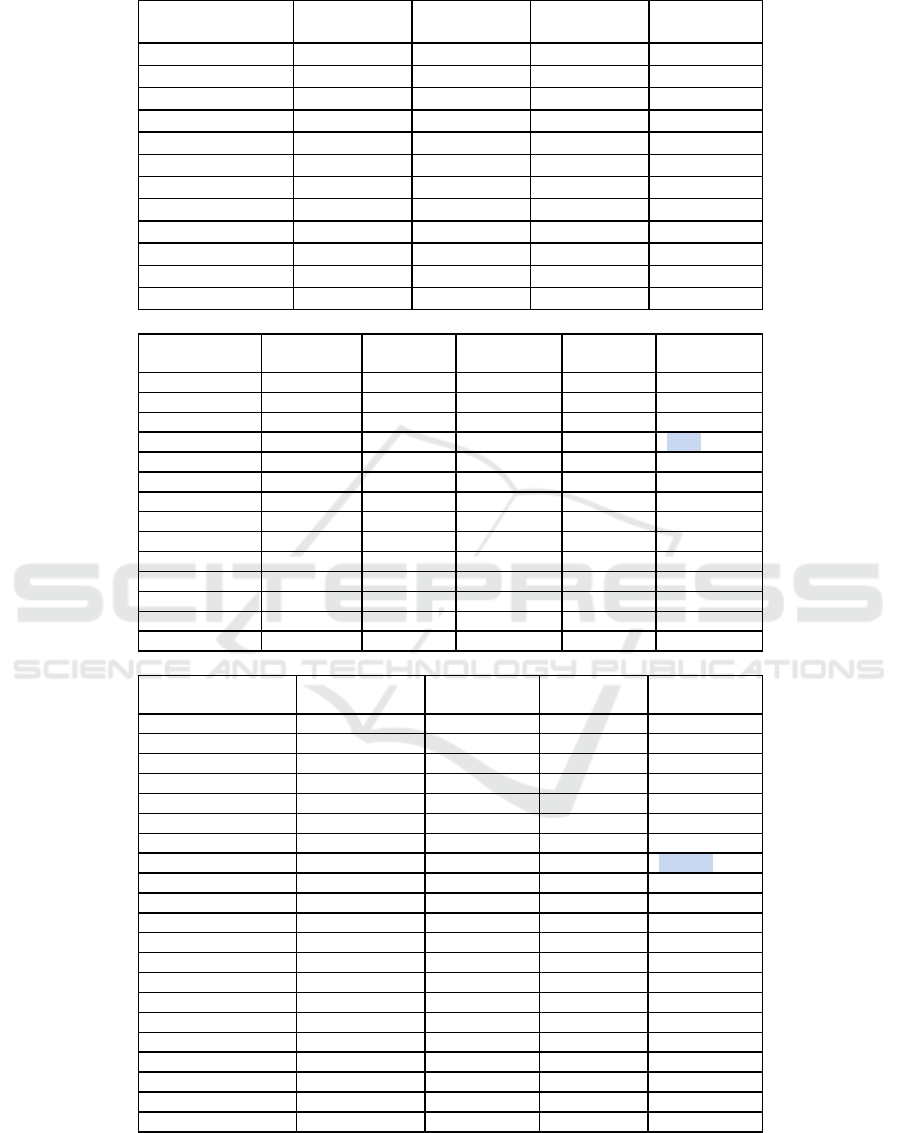
Table 1. Economic development policy of the countries of the German world
Country \
C
y
cle 1862-1871 1872-1880 1881-1891 1892-1901
German
y
Pro
g
. Re
g
ress. Pro
g
.A
g
ress.
Austria
─
─
A
g
ress. Conser.
Switzerlan
d
Conse
r
. Conser. Pro
g
.Pro
g
.
Great Britain A
g
ress. Conser. A
g
ress. A
g
ress.
Bel
g
iu
m
Conser. A
g
ress. Conser. Conser.
Netherlands Pro
g
. A
g
ress. Conser. A
g
ress.
France Re
g
ress. A
g
ress. Conser. A
g
ress.
Ital
y
─
Pro
g
.Re
g
ress. A
g
ress.
Denmar
k
Pro
g
. Conser. Pro
g
.Pro
g
.
Sweden Agress. Conser. Prog. Prog.
Finlan
d
ia Conser. Conser. Agress. Agress.
Russian empire -
─
─
Prog.
Country \
Cycle 1902-1908 1909-1915 1916-1919 1920-1923 1924-1932
Germany Prog.
R
egress. Regress. Agress. Prog.
Austria Agres. Regress. Cons. Prog. Regress.
Switzerland Regress. Cons. Regress. Prog. Cons.
Grea
t
Britain Cons. Prog. Regress. Agres. Prog.
Belgium Agres. Regress. Regress. Prog. Cons.
Netherlands Prog. Agres. Agres. Prog. Regress.
France Cons. Regress. Regress. Prog. Regress.
Italy Prog. Agres. Regress. Prog. Prog.
Denmark Regress. Regress. Regress. Prog. Cons.
Sweden Agres. Prog. Regress. Agres. Cons.
Finlandia Cons. Regress. Regress. Prog. Regress.
Russian empire Regress. Prog.
─
─
─
Czechoslovakia
─
─
─
─
Regress.
Yugoslavia
─
─
─
─
Regress.
Country \
Cycle 1933-1946 1947-1958 1959-1967 1968-1975
Germany Regress. Prog. Conser. Conser.
Austria Regress. Prog. Conser. Agress.
Switzerland Agress. Prog. Prog. Regress.
Luxembourg.
─
─
Prog. Agress.
Grea
t
Britain Agress. Conser. Prog. Regress.
Belgium Regress. Prog. Prog. Regress.
Niederl. Regress. Prog. Conser. Conser.
France Regress. Prog. Conser. Regress.
Italy Regress. Prog. Conser. Regress.
Denmark Regress. Prog. Prog. Conser.
Sweden Agress. Conser. Prog. Regress.
Finlan Agress. Prog. Prog. Agress.
Turkey Regress. Prog. Conser. Prog.
Czechoslovakia Regress. Prog. Conser. Conser.
Yugoslavia Prog. Agress. Prog. Agress.
USSR Agress. Prog. Regress. Conser.
Polan
d
─
Conser. Regress. Agress.
Hungary
─
Prog. Conser. Regress.
Romania
─
Agress. Conser. Regress.
Bulgaria
─
Prog. Prog. Regress.
R S F SR
─
─
Prog. Conser.
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
384
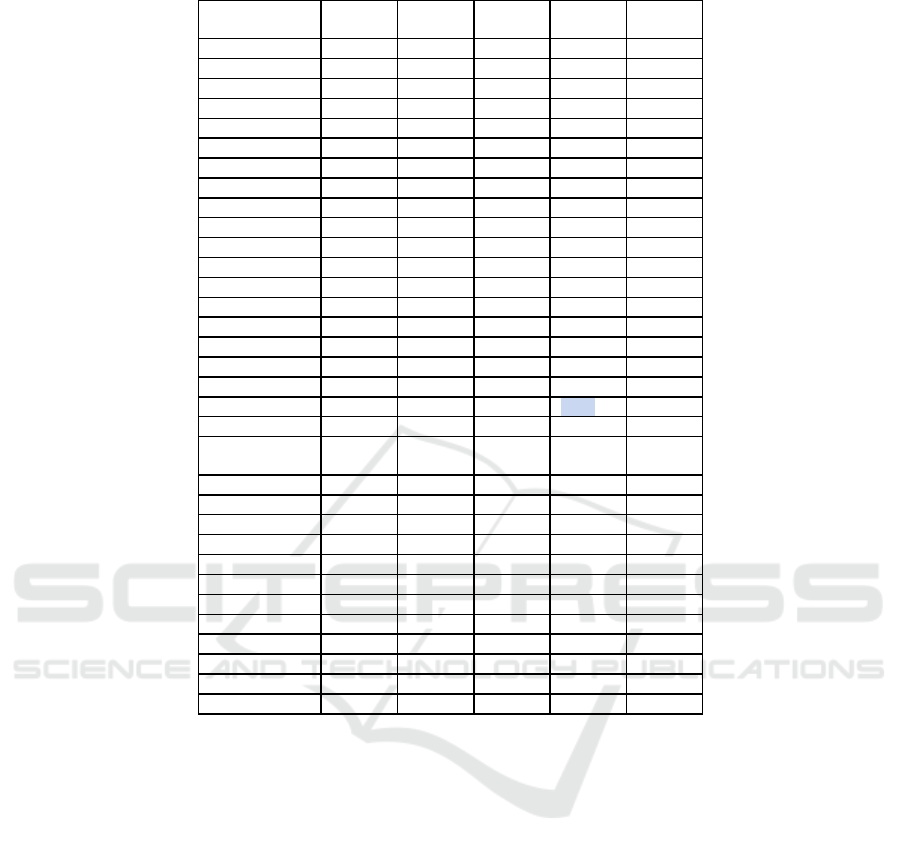
Table 1. Economic development policy of the countries of the German world (cont.).
Country \
Cycle
1976-
1982
1983-
1990
1991-
2003
2004-
2009
2010-
2020
Germany Conser. Conser. Conser. Regress. Prog.
Austria Regress. Agress. Conser. Regress. Regress.
Switzerland Conser. Prog. Conser. Agress. Conser.
Luxembourg Conser. Agress. Conser. Regress. Prog.
Grea
t
Britain Conser. Prog. Regress. Regress. Regress.
Belgium Conser. Prog. Conser. Regress. Regress.
Netherlands Conser. Prog. Regress. Regress. Conser.
France Conser. Regress. Regress. Regress. Regress.
Italy Conser. Conser. Regress. Regress. Regress.
Denmark Conser. Prog. Conser. Regress. Prog.
Sweden Regress. Prog. Regress. Regress. Regress.
Finlan
d
Conser. Prog. Regress. Regress. Conser.
Turkey Regress. Regress. Regress. Agress. Prog.
Czechoslovakia Regress. Regress. Agress. Prog.
─
Yugoslavia Conser. Regress. Regress. Prog.
─
the USSR Conser. Regress. Regress. Prog.
─
Polan
d
Regress. Agress. Prog. Prog. Regress.
Hungary Regress. Regress. Agress. Conser. Prog.
Romania Conser. Regress. Agress. Prog. Conser.
Bulgaria Regress. Regress. Agress. Prog. Conser.
Czech
Republic Regress. Prog. Regress. Prog. Conser.
Slovakia Agress. Conser. Agress. Prog. Conser.
Croatia Conser. Regress. Agress. Prog. Conser.
Slovenia Conser. Regress. Agress. Agress. Conser.
Russia Conser. Regress. Regress. Prog. Conser.
Kazakhstan Conser. Prog. Regress. Prog. Conser.
Lithuania Prog. Regress. Regress. Prog. Conser.
Latvia Prog. Prog. Regress. Agress. Conser.
Estonia Prog. Agress. Regress. Agress. Prog.
Kyrgyzstan Prog. Prog. Regress. Prog. Regress.
Serbia Conser. Regress. Regress. Prog. Conser.
Ukraine Prog. Prog. Regress. Prog. Regress.
Belarus Prog. Prog. Regress. Prog. Regress.
Analysis of the data in Table 2 confirms that the
policy matching index does not show the closeness of
the cultures of the German world. The policy
matching index of the German-speaking is not higher
than other Western European countries. This
indicator fails to reflect the institutional closeness of
the countries: for the CMEA countries and the EU
during the period of their simultaneous existence, this
indicator is approximately equal.
Most likely, this indicator characterizes the
closeness of development strategies in general and
innovation activity in particular, which, in turn, are
dependent on culture and institutions: in the period of
fragmentation, the similarity of policies is higher with
the EU countries than with the CMEA countries.
institutions in most of Germany coincided with those
of the EU. And the most consistently high rates of
similarity of policies are shown by countries
culturally close to Germany: Denmark, Luxembourg,
the Netherlands, Belgium.
Another phenomenon identified with the policy
similarity indicator for the last analyzed historical
period after the unification of Germany is an impact
on a group of countries by the German institution and
culture. These are mainly Protestant, German-
speaking, which have a similar economic structure
with Germany, an almost indistinguishable
institutional model, integrated geographically,
technologically and infrastructurally.
It is obvious that Italy, France, Great Britain and
Sweden have development strategies independent of
Germany and zero index values. They are culturally
and institutionally more distant from the German
World. The countries of Eastern Europe are currently
developing in relation to Germany, mainly with
negative indicators of the index, because they in a
relationship of semi-colonial dependence on
Germany as suppliers of resources and sales markets.
In fact, these three groups of European countries
outline the contours of Europe's future if the EU
continues to disintegrate.
Peculiarities of German World Economic Development Policy
385

Table 2. Index of coincidence of economic development policies of Germany with the countries of the German world
Country
Historical period Total for the
entire study
period
1862-1919 1920-1946 1947-1990 1991-2020
Austria 0 0 0 33,3 6,25
Switzerland 14,3 0 40 33,3 22,2
Luxembourg - - -25 100 28,6
Belgium 14,3 33,3 40 33,3 27,8
Netherlands 42,9 0 80 33,3 27,8
France 28,6 0 60 0 33,3
Italy 16,7 66,7 80 0 41,2
Grea
t
Britain 14,3 66,7 20 0 22,2
Denmark 42,9 33,3 60 100 55,6
Sweden 14,3 33,3 0 0 11,1
Finlandia 42,9 -33,3 20 33,3 22,2
Turkey - 100 40 0 33,3
Russian Empire , USSR, RF -66,7 0 60 -33,3 0
Kazakhstan - - 50 -33,3 0
Lithuania - - 0 -33,3 -20
Latvia - - 0 0 0
Estonia - - -50 33,3 0
Kyrgyzstan - - 0 -66,7 -40
Ukraine - - 0 -66,7 -40
Belarus - - 0 -66,7 -40
Czechoslovakia - 0 60 -100 11,1
Czech Republic - - 0 -33,3 -20
Slovakia - - 0 -66,7 -40
Yugoslavia - -100 0 -50 -33,3
Croatia - - 50 -66,7 -20
Slovenia - - 50 -66,7 -20
Serbia - - 50 -33,3 0
Polan
d
- - -60 -66,7 -62,5
Hungary - - 40 0 25
Romania - - 40 -66,7 0
Bulgaria - - 20 -66,7 -12,5
4 CONCLUSIONS
The index of coincidence of economic development
policies characterizes the proximity of economic
development strategies, which, in turn, depends on
culture and institutions. To differentiate the influence
of culture and institutions, a more sophisticated
research methodology is required.
The predictive application of the methodology
lies in the ability to identify groups of countries with
similar economic development policies, institutional
and cultural proximity for the formation of future
economic unions.
The result of the study is also the identification of
the boundaries of the German world, as a sub-
civilizational community
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The reported study was funded by RFBR, project
number 20-010-00869.
REFERENCES
Baltserovich, L., Zhontsy, A., 2012. Mysteries of economic
growth: forces and crises, MYSL Publ. Moscow.
Between East and West, Political Analysis (1961-1976),
1977. Munich.
Boldyrev, R. Y., Boldyreva, S. Y., Vakhabova, A. A.,
Tychina, O. L., 2020. Science and Technic
Revolution’s Impact on the Economic Development of
Germany in 16th – 19th Centuries. ISC 2019. In Lecture
Notes in Networks and Systems. 129.
Bolt, J., van Zanden, J. L., 2014. The Maddison Project:
Collaborative research on historical national accounts.
In Economic History Review. 67(3). pp. 627-651
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
386

Dincecco, M., Mauricio, P., 2013. “Nominal GDP Series,
1870-2000”. Global Prices and Incomes Database,
http://gpih.ucdavis.edu.
Evans, R., 1986. The German Empire 1871-1918. In
German History. 3. pp. 89-92.
Helantera, A., Ollus, S. E., Why Russia is not Finland? A
comparative analysis of the competitiveness,
https://iq.hse.ru.
Kulbakin, V. D., 1979. History of German Democratic
Republic (1949—1979), Nauka Publ. Moscow.
Maddison A., Historical Statistics, http://www.ggdc.net.
Olczyk, G., (2019). Elements of economic culture as
informal institutions in the economic development of
Germany. In Economics and Law. 18. p. 233.
Ridley, F., 1968. The Economic Causes of the German
Empire. In Business History. 10. pp. 121-125.
Savelyev, M., 2015. Multicultural institutionalism: General
economic theory of civilizations. The political economy
of traditionalism. In Network Society. 488.
Savelyev, M., 2020. Methods for researching the
sustainability of economic development of territories.
In Problems of regional economy. 3(4). pp. 54-62.
Savelyev, M., Gruzdeva, T., Savchenko, A., Koretsky, V.,
Pushina, N., 2021b. Assessment of the Competitiveness
and economic development policies of the countries of
the Former French Empire. In SHS Web Conf. 101
02005.
Savelyev, M., Ivanov, V., Polyakov, Yu., 2020a. The effect
of institutional differences on the economic
development of German-speaking countries. In E3S
Web of Conf. 222 05009.
Savelyev, M., Kutyashova, E., Savchenko, A., Koretsky,
V., Polyakov, Yu., 2021a. Diversity of economic
development in Portuguese-speaking countries. In SHS
Web Conf. 101 02004.
Savelyev, M., Pushina, N., Bryndin, A., 2021d. Search for
Effective Governments in Post-Soviet Russia While
Excluding the Factor of World Oil Prices from the
Results of the Country's Economic Development. In
IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ Sci.666062092.
Savelyev, M., Pushina, N., Savchenkо, A., 2020b.
Assessment of the sustainability of economic
development under the governments of Russia. In E3S
Web Conf. 208 03052.
Savelyev, M., Sokolova, N., Polyakov, Yu., 2021c. Newly
Industrialized Countries: Is There an Alternative to the
Golden Billion? In IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ Sci.
666062093.
Streb, J., Waidlein, N., 2013. Knowledge and Space in
Economic History: Innovations in the German Empire,
1877–1918. 5.
The conference board, https://conference-board.org.
Tsedilin, L. 2005. The EU Enlargement and the Prospects
of Eastern Germany Lands. In Economic issues. 4. pp.
23-42.
Uebele, M., Sarferaz, S., 2009. Tracking down the business
cycle: A dynamic factor model for Germany 1820-
1913. In Explorations in Economic History. 46. pp.
368-387.
World Bank, "World Development Indicators",
https://databank.worldbank.org.
Yablokov, B.V., 2018. Foreign economic policy of GDR in
the "New economic system" (1963- 1973).
Peculiarities of German World Economic Development Policy
387
