
Assessment of Environmentally Safe Conditions of the Urban
Environment as a Means to Promote the Economic Development of
Urban Planning Systems
Oksana Anatolievna Rastyapina
a
, Viacheslav Valentinovich Prokopenko
b
and Olga Aleksandrovna Ganzha
c
Volgograd State Technical University, Lenin Avenue, 28, 400005 Volgograd, Russia
Keywords: Quality of the urban environment, threats to the favorable development of the urban environment, components
of the urban environment, effectiveness of the urban environment.
Abstract: The formation of favorable living conditions within the urban environment is one of the strategic objectives
of the development of the state. Favorable conditions of the urban environment determine the sustainable
development of not only a single territory but also the state as a whole. The creation of favorable and, therefore,
high-quality conditions for the life of the urban environment contributes to increasing its attractiveness and
further economic development. To create such conditions, it is necessary to analyze the components of the
urban environment. To assess the quality of the urban environment, based on the assessment of the criteria
that characterize the urban environment, taking into account their significance, it is necessary to calculate the
environmental quality indicator. The paper defines threats to environmental safety as criteria that characterize
the urban environment and have a negative impact on the development of the urban environment. Thus, the
influence of all the criteria that characterize the urban environment is determined as positive and negative,
based on the impact on the development of the urban environment. When analyzing all the criteria that
characterize the urban environment, taking into account their potential impact on the development of the urban
environment, it is possible to develop measures in certain areas to improve the quality of the urban
environment and, as a result, achieve sustainable development.
1 INTRODUCTION
The economic efficiency of the state is determined
not only by a number of economic indicators that
characterize the level of development of the state and
its economic activity but also by a number of
indicators that determine the quality of the standard
of living of the population, as well as the level of
technological development. The last two parameters
are determined by the level of development of the
urban environment, environmental parameters, and
the implementation of measures aimed at preserving
the environment. All this meets the requirements of
the modern concept of sustainable development.
Achieving the parameters of sustainable
development, defined on a global scale, inevitably
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6257-1413
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8161-9766
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8648-2535
contributes to the formation of the economic image of
the state, and, accordingly, economic efficiency. To
achieve this, activities at the global level should be
used to implement a common policy ensuring a safe
and favorable urban environment that contributes to
the achievement of sustainable development. In the
modern urban environment, a person is exposed to
influences that have a negative effect on him,
although the urban environment is created for a
person, and its improvement is aimed at improving
the quality of life in this environment (Marco de
Silva, 2017; Rastyapina, 2020). In various studies,
about 600 situations associated with risk and extreme
living conditions in an urban environment were noted
(Vladimirov, 2017; Cortinovis, 2021; Patinom,
2021). All unfavorable situations can be divided into
groups (according to Vladimirov): situations of
Rastyapina, O., Prokopenko, V. and Ganzha, O.
Assessment of Environmentally Safe Conditions of the Urban Environment as a Means to Promote the Economic Development of Urban Planning Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0010696100003169
In Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference "Ensuring the Stability and Security of Socio-Economic Systems: Overcoming the Threats of the Crisis Space" (SES 2021),
pages 179-183
ISBN: 978-989-758-546-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
179

technogenic nature, natural origin, and environmental
nature. The situations of technogenic nature should
include situations related to transport accidents, fires,
accidents with emissions of harmful substances
(radioactive and biologically dangerous substances),
collapse of buildings, accidents in the utility
infrastructure of the city (communications, electric
power facilities, sewage treatment plants), etc. In
total, about 45 situations are allocated. Situations of
natural origin include processes that occur as a result
of natural factors, such as geophysical, geological,
meteorological, agrometeorological, hydrological,
natural fires, and infectious diseases. Environmental
situations include: changes in the properties and
composition of the air, land (soil, subsurface,
landscape), and hydrosphere. As a rule, most of the
unfavorable natural processes in the urban area
develop under the influence of technogenic factors.
That is why the issue of not only reducing the
technogenic load on the environment but also
conducting an assessment of the environmental safety
of the surrounding urban environment becomes
relevant. Factors that affect the urban environment
should be considered threats to the security of the
urban environment
2 COMPONENTS OF THE
URBAN ENVIRONMENT
Urban planning, urbanized environment is quite
diverse and its safety is determined by many factors.
In this paper, environmental safety is considered from
the point of view of ecology and the degree of
favorability of the urban environment. It is not
enough to comply with the standards for a variety of
environmental parameters. It is necessary to analyze
the factors that contribute to the formation of a safe
(favorable) urban environment. Sustainable
development should not be determined by the stable
pace of space development, taking into account
modern requirements, but by the ability to restore the
natural environment, taking into account its urban
(anthropogenic) development (Benites, 2021).
Sustainable development of the urban environment
should be considered a balanced development of the
anthropogenic and natural environment. Factors that
have an adverse impact on the ecological state of the
city will be considered potential threats to the
development of this environment. Accordingly, to
achieve favorable conditions for the development of
the urban environment, it is necessary to analyze the
factors that affect this environment and are potential
threats (Han, 2021; Briones-Hidrovo, 2021).
Given the diversity and complexity of the urban
environment, the factors that affect it should be
grouped as follows: natural, architectural and
landscape, socio-economic, infrastructural, and
technogenic. The group of natural factors includes
criteria that characterize climatic conditions,
hydrogeological conditions of the territory,
hydrological, topographic conditions, probability of
occurrence of adverse natural processes, under
existing conditions (Table 1). These criteria
determine the degree of comfort of the urban
environment and may be favorable or unfavorable for
the development and formation of the urban
environment. In the case of unfavorable criteria for
development, it is necessary to develop measures
aimed at improving the level of improvement of the
urban area. Favorable natural and climatic conditions
create more attractive conditions for life, and not
favorable ones reduce the attractiveness of the
territory.
Table 1: Group of natural factors.
Factors/criteria Assessment
(impact)
Temperature range
Favorable
(+)/unfavorable (-)
Wind mode
Radiation mode
Groundwater quality
Available groundwater (depth
of occurrence)
Ground conditions
Available reservoirs
Terrain
Adverse natural processes
probability
(-)
The group of architectural and landscape factors
consists of criteria that characterize the natural and
anthropogenic landscape of the urban environment
and the architectural and planning composition
formed during the development of the city.
To assess the degree of security of the territory,
this group includes the following criteria:
architectural (historical, architectural, and cultural
values) and assessment of the landscape features of
the territory. When analyzing landscape criteria, it is
necessary to analyze the value of the landscape, its
suitability for the formation of favorable and safe
living conditions. The presence of such elements will
give a certain color and value to the territory, which
will affect the attractiveness of the territory. The
absence of such elements does not affect the overall
comprehensive assessment of the territory.
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
180
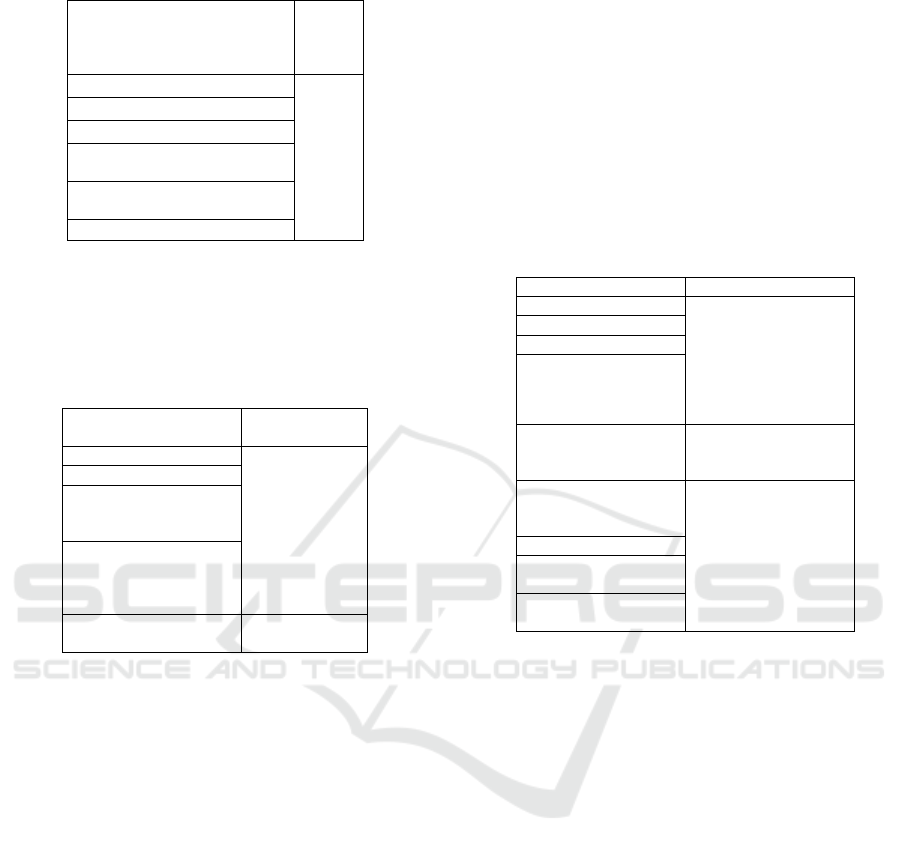
Table 2: Architectural and landscape factors.
Factors/criteria Assess
ment
(impac
t)
Architectural stylistics
presence (+)/absence
Valuable construction elements
Landscape value
Available elements to be
preserved
Historical and architectural
value
Cultural value
Socio-economic factors (Table 3) of the
environmental safety assessment determine the
possibility and efficiency of the implementation of
environmental measures.
Table 3: Socio-economic factors.
Factors/criteria Assessment
(impact)
Street lighting
Comparison with the
number (area of the
environment) with
regional averages of
presence (+)/absence (-)
Pavement quality
The structure of surface
elements of engineering
communications
Quality/availability of
pedestrian paths
Morbidity rate Increase (-
)/Decrease (+)
The criteria of this group are included in the
analysis of the current state of the urban environment
and are compared with previous indicators. It is based
on the calculation of the increase rate that it is
possible to judge the efficiency of the implemented
measures and assess the degree of favorability of the
urban environment. No less important is social
security, in terms of feeling and perceiving the
security of living conditions in the urbanized
environment. To assess social security, it is necessary
to analyze: street lighting, pavement quality (presence
of holes, defects in the pavement, etc.), safety
assessment of engineering communication elements
(closed sewer manholes), presence of pedestrian
paths, sidewalks. To analyze these indicators, it is
necessary to compare them with both the total area
and the number of inhabitants.
The group of infrastructure factors includes
criteria for the analysis of transport, utility, and
information infrastructure (Table 4). The analysis of
transport infrastructure (Ryriakopoulou, 2021)
involves considering the accessibility of transport for
the population, coverage of all points of the urban
environment, constancy of routes, variety of
transport, and level of motorization. To assess the
utility infrastructure, it is necessary to evaluate the
following criteria: reliability, safety, energy
efficiency, and durability of civil engineering
systems. The information infrastructure is evaluated
according to the degree of modernity of the
information provision to citizens, the speed and
accuracy of information provided, as well as the
extent and variety of information. The presence of
tourist infrastructure also contributes to the economic
development of the urban environment.
Table 4: Infrastructure factors.
Factors/criteria Assessment (impact)
Transport accessibility
Specific
indicator (per
person or area)
of comparison
with the
regional value,
above the level
(+)
Variety of transpor
t
Level of motorization
Number of parking
lots
Physical wear and tear
of municipal
structures
More than 50% with
negative impact
Compliance with
modern requirements
(update)
presence
(+)/absence(-)
Tourist attractions
Available information
about transpor
t
Available information
about events
When analyzing this criterion, it is necessary to
assess the degree of accessibility (transport and
information) of the main tourist attractions.
The factors that make up the technogenic urban
environment (Table 5) can be considered from the
point of view of evaluating all functional zones of the
urban environment for their safe placement and
appropriate mutual placement; the quality of
development. Construction quality parameters
include analysis of the construction material,
construction technology, number of floors of
buildings, and operating time. Landscaping of the
territory has protective functions and contributes to
the creation of a favorable visual appearance of the
urban environment (Zhu, 2021; Hian, 2021). The
analysis of the visual appearance of the buildings is
based on the assessment of the aggressiveness and
homogeneity of the fields.
Assessment of Environmentally Safe Conditions of the Urban Environment as a Means to Promote the Economic Development of Urban
Planning Systems
181
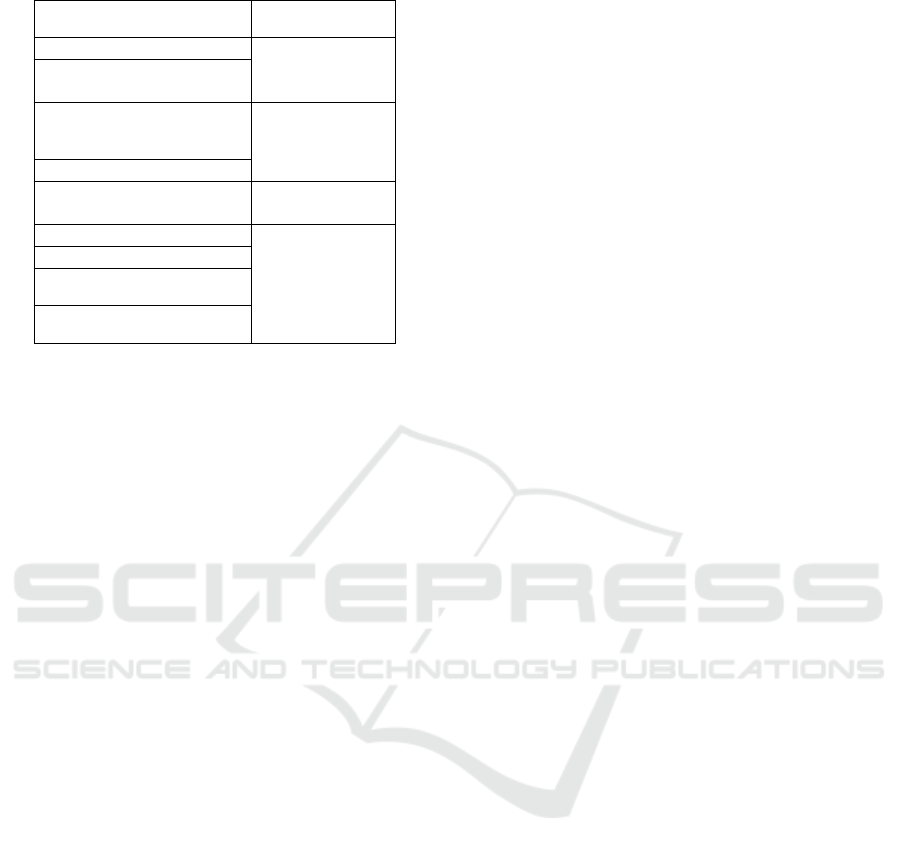
Table 5: Technogenic factors.
Factors/criteria Assessment
(impact)
Construction material safe (+)/dangerous
(-)
Tear-and-wear of buildings
(more than 50%)
Number of floors of buildings
(proportionality of
construction)
favorable (+)/(-)
Visual assessment
Species diversity of
landscaping
presence
(+)/absence (-)
Landscaping
Comparison
with
standards,
compliance
(+)/ non-
compliance (-)
Ambient air quality
Acoustic pollution of the
territory
Radiation pollution of the
territory
All factors of the technogenic environment can
have both positive and negative effects. Therefore, to
assess their impact, it is necessary to compare them
with the standard values, if exceeded, the impact
should be assessed as negative. This refers to the
criteria that can be measured (air pollution, water
pollution, soil pollution). The landscaping degree of
the territory is also compared with the standard
values. However, exceeding the standard values of
the landscaping parameters has a positive effect,
while an insufficient value of this parameter is
characterized as a negative effect. The system of
green areas should be diverse, which contributes to
the efficient protection and improvement of the
environment due to the negative impact of
anthropogenic impact.
The analysis of the presented criteria in different
groups, depending on the significance of the criteria,
allows us to determine the quality of the urban
environment. The integrated assessment indicator
will increase with a positive influence, and it will
decrease accordingly with a negative influence. The
higher the indicators of a comprehensive assessment
of the urban environment, the more favorable
conditions are formed for the development and
sustainable functioning of the environment.
The main principles of the formation of a modern
urbanized environment are as follows (Rastyapina,
O.A., Polyakov, V.G., Prokopenko, V.V., Ganzha,
O.A., Sabitova T.A., 2020): integrity, harmony,
environmental friendliness, and meaning-making.
The analysis of the marked directions and criteria will
allow determining the compliance of the urban
environment with these principles.
3 THREATS TO
ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY
THAT DETERMINE THE
ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY OF
THE URBAN ENVIRONMENT
The presented analysis of the factors influencing the
quality of the urban environment confirms the
complexity and versatility of the methodology.
Accordingly, economic efficiency cannot be
determined based on only economic indicators or
social indicators that characterize the quality of life of
citizens. It is necessary to conduct a multi-factor
analysis, based on the assessment of criteria that
allow determining the level of development of the
urban environment. The formation of favorable living
conditions following the modern requirements of the
population, introduction of technologies that
contribute to the development of a "smart" urban
environment, development of tourist infrastructure –
all this contributes to the economic development of
the urban environment, as well as sustainable
development.
All the factors presented can have both positive
and negative impacts on the degree of safety of the
urban environment. All the factors that shape the
urban environment and have a negative impact can be
divided into three groups: chemical, physical, and
mechanical. The values of the criteria for a group of
chemical factors are usually calculated based on a
comparison with the standard values. This group
includes: volume of pollution (total and summed,
reduced to a single measurement indicator), index of
atmospheric pollution, area of industrial enterprises
(located directly on the border with the residential
zone), density of the street and road network
(calculated as a specific indicator), area of sanitary
protection zones, area of landfills, area of the
cemetery, and total indicator of soil pollution. To
analyze and determine the favorability of these
indicators, it is necessary to determine the ratio of the
total area of the urban environment. This specific
indicator will be taken into account when determining
the overall assessment of the safe environment, given
the weight factors of the criteria. Physical factors are
included in the analysis of indicators of physical
origin. This group includes: proportion of streets with
a high acoustic background, area of power lines, and
area of heating mains. Certain criteria, such as
transport accessibility and level of motorization, do
not have standard values, but their presence creates
favorable conditions for the development of the urban
environment and forms a source of technogenic
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
182

impact on the environment. These indicators should
be defined as specific, based on the population and
the area of the urban environment. The group of
mechanical factors includes criteria for the formation
of the urban environment that characterize the
qualitative characteristics of the buildings. This group
includes: coefficient of high-rise buildings,
coefficient of visual aggressiveness of buildings,
compliance of the construction with the requirements
and perception of the urban appearance. Depending
on the obtained value determined experimentally, the
criteria can have a positive and negative impact.
The analysis of these indicators will allow us to
identify potential threats to the development of the
urban environment. Taking into account the detail of
the factors presented, to improve the efficiency of the
urban environment, it is necessary to develop
measures aimed at neutralizing the negative impact of
groups of factors on the urban environment and
achieving sustainable development.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The presented analysis of the components of the
urban environment allows us to determine the main
directions of assessing the quality of the urban
environment. When considering the directions, the
criteria for evaluating the urban environment are
identified. All the criteria presented can be considered
as having a positive or negative impact. The degree
of influence should be taken into account when
determining the overall/integrated assessment
indicator with the appropriate mathematical sign. If
the criterion has a positive impact, it increases the
integrated assessment indicator; if it is negative, it
reduces it. Taking into account the diversity of urban
areas and the peculiarities of development, it is
necessary to introduce the weight (significance) of
this parameter for each criterion. The weight factor
should be calculated based on the opinion of experts,
as a weighted average of the significance of the factor
for a specific urban environment. When assessing the
level of safety of the urban environment, taking into
account the analysis of the presented criteria, it is
possible to determine those criteria and parameters
that do not meet the requirements and require the
implementation of measures aimed at improving the
quality of the urban environment and increasing its
economic attractiveness in the future.
REFERENCES
Benites, A. J., Felipe, A., Simões, 2021. Assessing the
urban sustainable development strategy: Application of
a smart city services sustainability taxonomy. In
Ecological Indicators. 127.
Briones-Hidrovo, A., Uche, J., Martínez-Gracia, A., 2021.
Hydropower and environmental sustainability: Holistic
assessment using multiple biophysical indicators. In
Ecological Indicators. 127.
Cortinovis, С., Geneletti, В., Hedlun, К., 2021.
Synthesizing multiple ecosystem service assessments
for urban planning: Review of approaches and
recommendations. In Landscape and Urban Planning.
213.
Han, H., Guo, L., Zhang, J., Zhang, K., Cui, H., 2021.
Spatiotemporal analysis of the coordination of
economic development, resource utilization, and
environmental quality in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei
urban agglomeration. In Ecological Indicators. 127.
Hian, S., Chan, M., Qiu, L., Esposito, G., Mai, K., 2021.
Vertical greenery buffers against stress: Evidence from
psychophysiological responses in virtual reality. In
Landscape and Urban Planning. 213.
Marco de Silva, A., Bortoleto, A. L., Castelli, K. R.,
Argenton e Silva, R., Mendes, P. B., 2017. Prospecting
the potential of ecosystem restoration. A proposed
framework and a case study. In Ecological
Engineering. 108.
Patinom, J., Hong, A., Duque, J. S., Rahimi, K., Zapata S.,
Lopera V., 2021. Built environment and mortality risk
from cardiovascular disease and diabetes in Medellín.
In Landscape and Urban Planning. 213.
Rastyapina, O. A., Ganzha, O. A., Prokopenko, V. V.,
2020. Setting-up of ecological settlements to promote
sustainable development of urban areas. In IOP
Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering.
The conference proceedings ICCATS-2020.
Rastyapina, O. A., Polyakov, V. G., Prokopenko, V. V.,
Ganzha, O. A., Sabitova T. A., 2020. Analysis and
assessment of urban planning safety to achieve
sustainable development of urban planning
environment. In E3S Web of Conferences.
Ryriakopoulou, E., Pierre, M., 2021. On the design of
sustainable cities: Local traffic pollution and urban
structure. In J. of Environmental Economics and
Management.
Vladimirov, S. N., 2017. Impact of urbanized territories on
the quality of life. In Scientific Almanac. 5-3(31).
Zhu, W., Wang, J., Qin, B., 2021. Quantity or quality?
Exploring the association between public open space
and mental health in urban China. In Landscape and
Urban Planning. 213.
Assessment of Environmentally Safe Conditions of the Urban Environment as a Means to Promote the Economic Development of Urban
Planning Systems
183
