
Problems of the Russian Federation Food Security Ensuring in the
Context of the Crisis, the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Instability of
World Markets
Alexander Evgenievich Suglobov
1a
and Alexey Vladimirovich Rodionov
2b
1
Russian University of Cooperation, 12/30 Vera Voloshina str., Mytishchi, Moscow Region, Russian Federation
2
Academy of the Federal Penitentiary Service of Russia, 1 Sennaya str., Ryazan, Russian Federation
Keywords: Food security, international trade, crisis, state regulation of the economy, infrastructure development.
Abstract: The article outlines the problems of Russian Federation food security ensuring in the context of the crisis
caused by COVID-19 pandemic and world markets instability. The key challenges of our time in the field of
food security ensuring at the national and global levels are identified. The dynamics of international food
markets’ main indicators is analyzed. The possibilities of expanding the acreage in Russia are determined.
The ways of balancing export supplies and the needs of the Russian food market are justified. The features of
state price regulation as a factor of production volumes reducing are revealed. Promising directions for
improving the level of food security are presented. The information base of the study is presented by data of
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, the Ministry of Agriculture and the Federal State
Statistics Service of the Russian Federation.
1 INTRODUCTION
A significant increase in food prices in the Russian
Federation in late 2020 – early 2021 had a serious
impact on the processes of social stability ensuring
and required the adoption of appropriate measures by
the national political leadership. Elements of state
price regulation were introduced, as well as
restrictions on the export of certain food products.
Despite significant progress in the development of
Russian agriculture and the results achieved in food
import substitution, the high level of risks of threats’
materialization in the field of national food security
remains obvious.
The openness of the Russian economy and the
high degree of its integration into the global division
of labor objectively increases the dependence of the
domestic market on the dynamics of the main
indicators of foreign trading platforms. It should be
noted that food supply planning parameters of the
Russian Federation should be carried out taking into
account the medium and long-term trends in the
global production and distribution of food.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1860-6783
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9311-4896
The authors of this paper turned their attention to
the call of the President of the People's Republic of
China Xi Jinping to start saving food, which he
announced on 11.08.2020 during one of his public
speeches. The Chinese leader urged his compatriots
to refrain from wasteful eating and show restraint. At
the same time, the population was advised not to take
into account the success of Chinese farmers and the
positive dynamics in agricultural production. Special
attention should be paid to the fact that the head of the
People's Republic of China has set the task to develop
an appropriate legislative framework and supervisory
mechanisms to ensure that food savings and the
rejection of excesses are observed acquire a long-term
character.
It is obvious that the long-term nature of this
program is determined by the corresponding forecast
horizon and the level of threats to China's food
security. On 30.11.2021, the first law against food
waste has already been passed in the People's
Republic of China. This regulatory act provides for
fines to visitors of public catering establishments if
they leave a significant part of the purchased food
Suglobov, A. and Rodionov, A.
Problems of the Russian Federation Food Security Ensuring in the Context of the Crisis, the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Instability of World Markets.
DOI: 10.5220/0010679700003169
In Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference "Ensuring the Stability and Security of Socio-Economic Systems: Overcoming the Threats of the Crisis Space" (SES 2021),
pages 5-9
ISBN: 978-989-758-546-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
5
products not fully consumed. In addition, the law
provides for a number of non-fiscal measures to fight
for the rational use of food, including propaganda,
explanatory work, etc.
Starting from September 2020, almost
immediately after the above-mentioned statement of
Xi Jinping, world prices for a number of food
products showed a significant increase. In our
opinion, the Chinese analytical groups made the
correct forecast about the upcoming food shortage,
and the Chinese leadership voiced the call, taking into
account the fact that food savings in the near future
will become a long-term phenomenon.
In the context of global food shortages and rising
prices on international markets, Russian producers
have made an obvious choice in favor of export
supplies, and traders have increased domestic prices
in order to ensure the corresponding attractiveness of
trade in the domestic market. Thus, the growth of
domestic production and all the successes in the
development of the Russian agricultural sector are
significantly offset by the observed externalities in
the world markets. It is obvious that state regulation
of prices and export restrictions may have some
positive impact on the dynamics of domestic prices,
but this effect will be short-term. At the same time, in
the future, the accumulated losses will be recouped by
the market due to a longer, but progressive increase
in prices, when the effect of deferred consumption
will work.
In the context of the deepening economic crisis
associated with the COVID-19 pandemic, the
problem of food security ensuring is of particular
relevance. The decline in household incomes, the
increase in the debt burden of households,
corporations, regions and states multiply all the
negative phenomena in the international food
markets. The complex of issues related to the stable
growth of the production of high-quality and
affordable food products for the Russian population
entire demand requires the development of
appropriate mechanisms aimed at improving the level
of national food security. The development of such
mechanisms requires the identification of all
significant trends that determine the content of the
measures to be taken. The systematic implementation
of these measures will increase the level of Russia’s
population food supply stability and protect the
interests of domestic agricultural producers selling
their products on world markets.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The information base of the study is presented by the
data of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the
United Nations (FAO), the Ministry of Agriculture
and the Federal State Statistics Service of the Russian
Federation. The methodological basis of this study is
formed by the works of specialists in the field of food
security and the development of agro-industrial
production. The research material is based on the
ideas about the significant impact of climate change
on the processes of food security ensuring (Michalk
et al., 2019), as well as the importance of the
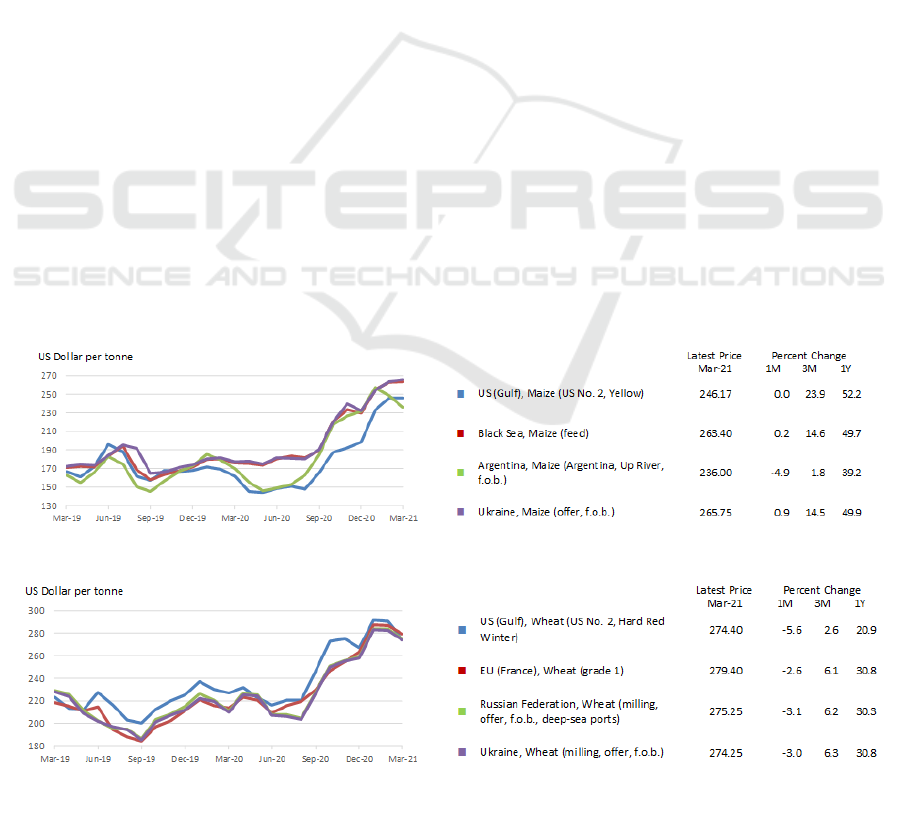
Figure 1: Dynamics of corn prices in the world's main producing regions (March 2019 – March 2021).
Figure 2: Dynamics of wheat prices in the world's main producing regions (March 2019 – March 2021
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
6
transition to sustainable development of the world
economy (Bindi et al., 2015). The paper also uses an
approach to the analysis of the mutual influence of the
world food market and the markets of individual large
food producing countries (Vasylieva, 2020), as well
as ideas about the global distribution of food (Kick et
al., 2017) and the specialization of individual
producing countries (Campi et al, 2021), as methods
of food security ensuring. The study also examined
and systematized the experience of food security
ensuring in Argentina (Feeney & MacClay, 2016) and
Egypt (Abdelaal & Thilmany, 2019), as well as
analyzed foreign views on the import substitution
policy of the Russian Federation (Wegren, 2014).
Special attention was paid to current research on the
impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on food security
processes (Eileen & Cosmas, 2021).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 International Food Markets
According to the FAO, starting from September 2020
to February 2021, corn prices increased by 40-55 %
(fig. 1) in various producing regions (USA,
Argentina, Black Sea region, Ukraine).
A similar situation was observed in the grain
market. The price of wheat produced in the United
States, the European Union, the Russian Federation
and Ukraine over the same period increased by 45-
50% (fig. 2). Despite a slight decline in prices in
March 2021, futures quotations on major commodity
exchanges indicate a high potential for further growth
in prices for basic agricultural commodities, which,
accordingly, will affect the growth of livestock
products prices worldwide.
Worth to be noted that a similar situation is
observed in the market of sugar, oilseeds and other
basic food products. It is noteworthy that the majority
of experts in their forecasts published in mid-2020
assumed that the level of prices for agricultural
products would remain stable and even slightly lower
in the context of a deepening crisis, a decline in the
global economy and other disincentive factors.
3.2 International Food Markets
It is obvious that in the context of the formation of
long-term trends for the growth of food prices, as well
as the increase in food shortages in the world's largest
markets (primarily in South-East Asia), the urgent
task is to increase the volume of agricultural
production. The Russian Federation is one of the few
countries with significant reserves for the growth of
used acreage. In most grain-producing countries, the
ploughing of agricultural land has reached peak
values or is limited by objective anthropogenic and
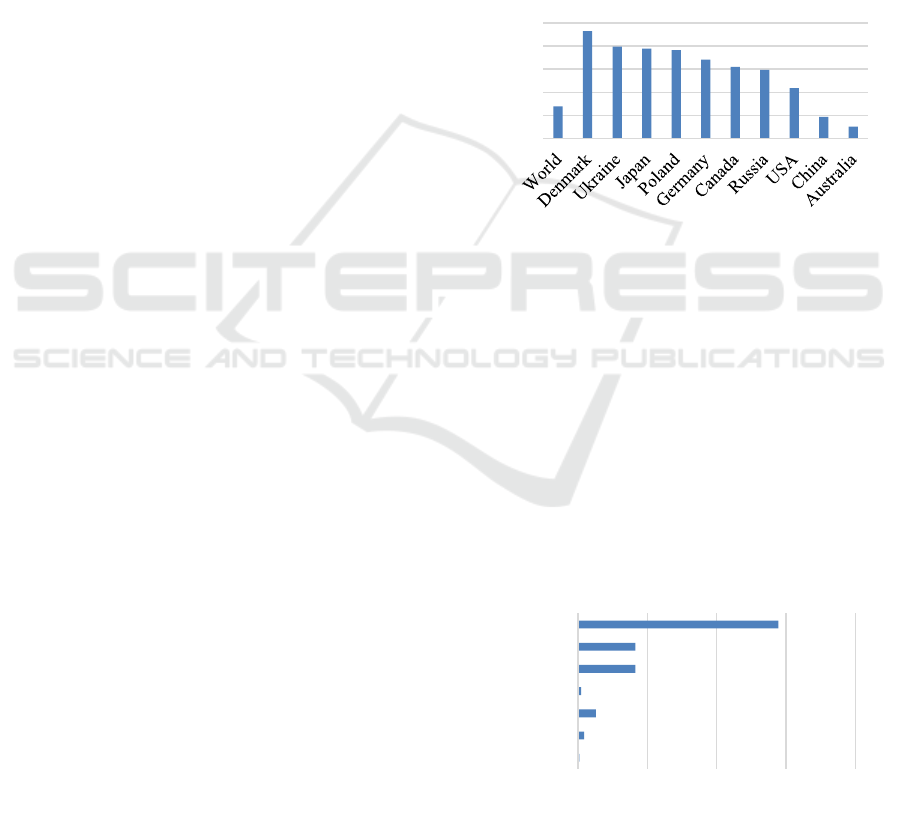
natural-climatic factors (fig. 3). The Russian
Federation has significant reserves of agricultural
land that can be further involved in agricultural
turnover to increase the production of cereals,
oilseeds and industrial crops, as well as vegetables. It
should also be noted that in most Russian agricultural
regions there is no shortage of water resources typical
for most countries of the world, which creates
additional conditions for increasing the growth of
agricultural production.
Figure 3: Ploughing of agricultural land in the countries of
the world in 2014.
Data on the area of the main agricultural crops in
the Russian Federation in 2020 (fig. 4-5) show that
cereals, in particular wheat, occupy the largest part of
the land bank used. In the conditions of further
growth of prices for cereals and oilseeds, it is almost
impossible to increase the area of land used for their
cultivation by reducing the area under other crops.
Thus, the introduction of new lands into circulation
(in reality, the return to agricultural circulation of
previously withdrawn ones) remains the most
promising direction for ensuring the rapid growth of
agricultural production.
Figure 4: Acreage of major agricultural crops in the Russian
Federation in 2020.
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
0,2
0,92
2,6
0,48
8,3
8,3
28,9
0 10203040
Rice
Sugar beet
Corn
Flax
Sunflower
Barley
Wheat
Problems of the Russian Federation Food Security Ensuring in the Context of the Crisis, the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Instability of
World Markets
7
The scarcity of agricultural land in Europe is
confirmed by the fact that the Republic of Belarus
plans to start measures to return to agricultural
circulation arable land that suffered from radioactive
contamination after the tragedy at the Chernobyl
nuclear power plant in 1986. It is planned to start
work on the restoration and processing of 265
thousand hectares of fertile agricultural land.
3.3 Export vs Import: Ways to Balance
the Russian Food Market
In 2020, Russian food exports exceeded the volume
of agricultural imports for the first time. Domestic
producers sold products worth 30.7 US dollars billion
on the world markets. Special attention should be paid
to the results in the export of meat products, as
commodities with a high degree of added value.
Meat exports increased by 53%, reaching 887
million US dollars. Pork producers doubled their
supplies to foreign partners (200 thousand tons worth
336 million US dollars).
The increase in domestic prices for cereals and
industrial crops, respectively, will lead to an increase
in the cost of feed, which will accordingly affect the
competitiveness of Russian meat products.
Restrictions on the export of grain and additional
duties will have a disincentive effect on business
activity in the grain market. In this case, we should
look for ways to balance the interests of grain
exporters and meat producers.
The relevance of this task is determined by the
fact that grain exports in the amount of 49 million tons
generated foreign exchange earnings of more than 10
billion US dollars, which had a positive impact on
macroeconomic stability in the face of falling prices
for the main export products of the Russian
Federation – hydrocarbons.
A similar situation is observed in the market of fat
and oil products. Revenue from the export of these
products amounted to more than 5 billion US dollars,
while the increase in prices on the domestic market
significantly affected the prices of most finished food
products. This situation had a negative impact on
social stability and the actual decline in the our
country citizens’ standard of living.
3.4 Export vs Import: Ways to Balance
the Russian Food Market
Government regulation of food prices and restrictions
on the export of products in the context of a positive
market situation on foreign trading platforms can
have a short-term effect, allowing to restrain the
growth of retail prices. However, further use of these
measures is futile and can only lead to the
abandonment of the previous volumes of agricultural
products production.
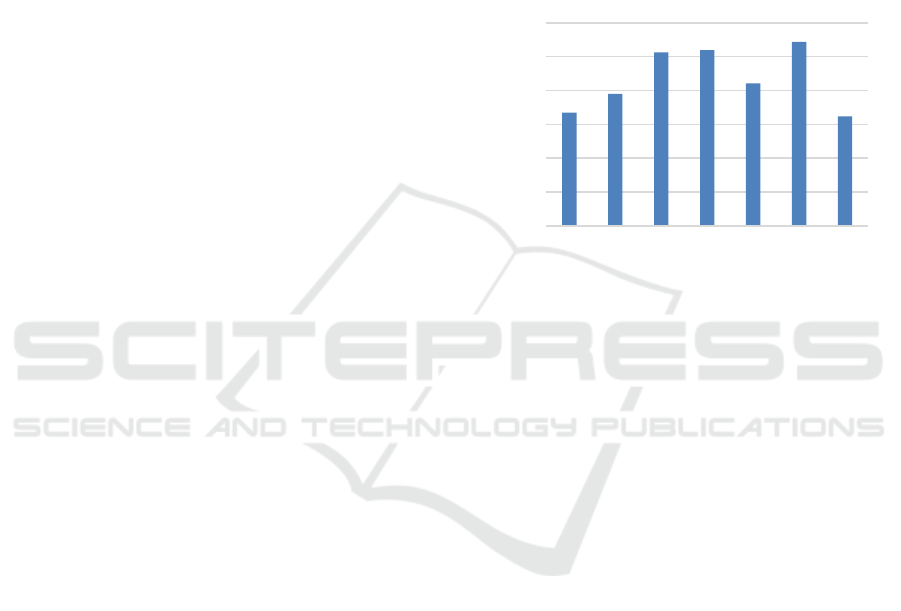
In this case, it is necessary to give as an example
the volume of the gross harvest of sugar beet in the
Russian Federation in 2014-2020 (fig. 6). In the
context of a crop failure in 2020, as well as a decrease
in interest in this crop due to state price regulation,
the sugar market may show their unacceptably high
growth with a parallel decrease in the volume of sugar
beet production.
Figure 5: Gross sugar beet harvest in the Russian Federation
in 2014-2020, thousand tons.
3.5 Promising Directions for
Improving the Level of Food
Security
In conditions of low efficiency of state price
regulation, the most promising direction of
development is a return to end-to-end planning of the
agricultural sector with the involvement of large
producers in the implementation of these plans. Small
and medium-sized agribusinesses should be provided
with information about the planned volumes of
acreage under individual crops and the forecast values
of the gross harvest of large producers.
An important task of the state is to ensure broad
access to the infrastructure for the transportation and
long-term storage of agricultural products. It should
be noted that the role of the state in this case is to
create conditions for ensuring transparency and
stability of prices for these types of infrastructure and
technical support.
Among the promising projects, it should be noted
the further spread of agricultural machinery based on
gas-engine fuel, which is a cheaper and more
environmentally friendly analogue of diesel fuel, the
prices of which are also under state regulation (in
order to prevent price shocks in the markets)
33475
38988
51325
51913
42066
54350
32395
0
10000
20000
30000
40000
50000
60000
2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
8

Expanding access to grain storage infrastructure,
as well as transportation and refueling with natural
gas engines will significantly increase the
competitiveness of producers, reduce their costs and
risks.
Separately, it should also be noted the relevance
of the interstate cooperation complex of issues.
Combining the production capabilities of the
Eurasian Economic Union countries with the
prospective involvement of Ukraine (as one of the
world's largest agricultural exporters) and Iran (as one
of the largest importers and prospective transiters of
agricultural products) will in the future create the
largest foreign trade association capable of regulating
world prices for critical imports of most countries.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Thus, ensuring the food security of the Russian
Federation in modern conditions requires the
systematic implementation of a number of programs
and projects aimed at increasing the volume of
agricultural production in order to saturate the
domestic market and simultaneously expand the
presence and market share on foreign trading
platforms. The return to state planning and the
rejection of state price regulation, while developing
programs to expand access to infrastructure and fuel
resources, in our opinion, will help to stabilize the
domestic market, increase the competitiveness of
domestic producers and increase the export supply of
Russian food products.
REFERENCES
Abdelaal, H. S. A., Thilmany, D., 2019. Grains Production
Prospects and Long Run Food Security in Egypt. In
Sustainability. 11(16).
Bindi, M., Palosuo, T., Trnka, M., Semenov, M., 2015.
Modelling climate change impacts on crop production
for food security. In Climate research. 65(31). pp. 3-5.
Campi, M., Duenas, M., Fagiolo, G., 2021. Specialization
in food production affects global food security and food
systems sustainability. In World development. 141.
Eileen, B. N., Cosmas, K. L., 2021. Regional impact of
COVID-19 on the production and food security of
common bean smallholder farmers in Sub-Saharan
Africa: Implication for SDG's. In Global Food Security.
29.
Feeney, R., MacClay, P., 2016. Food Security in Argentina:
A Production or Distribution Problem? International
food and agribusiness management review. 19(2). pp.
1-31.
Kick, E. L., Tiezzi, F. Pena, D. C., 2017. Food Production
or Food Distribution: The Key to Global Food
Security? In Perspectives on global development and
technology. 16(6). pp. 666-682.
Michalk, D. L., Kemp, D. R., Badgery, W. B., Wu, J. P.,
Zhang, Y. J., Thomassin, P. J., 2019. Sustainability and
future food security-A global perspective for livestock
production. In Land degradation & development. 30(5).
pp. 561-573.
Vasylieva, N., 2020. Ukrainian Cereals in Global Food
Security: Production and Export Components. In
Montenegrin journal of economics. 16(2). pp. 143-153.
Wegren, S. K., 2014. The Russian food embargo and food
security: can household production fill the void? In
Eurasian geography and economics. 55(5). pp. 491-
513.
Problems of the Russian Federation Food Security Ensuring in the Context of the Crisis, the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Instability of
World Markets
9
