
Assessment of Efforts for Content Creation for the Common Digital
Space of Scientific Knowledge
N. Kalenov
a
, G. Savin
b
, I. Sobolevskaya
c
and A. Sotnikov
d
Joint Supercomputer Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences - Branch of Federal State Institution “Scientific Research
Institute for System Analysis of the Russian Academy of Sciences” (JSCC RAS - Branch of SRISA),
119334, Moscow, Leninsky av., 32a, Russia
Keywords: Digital Knowledge Space, Information Space, Digital Library "Scientific Heritage of Russia",
Russian Scientists, Information System, Network Technologies, Virtual Exhibitions, Museum Objects,
Digitization, Scientific Digital Library, Digitalization, Digital Books, 3D-models, Technology,
Labour Contribution, Span Time.
Abstract: The article presents a labor cost calculation methodology for creating integrated digital content for the
Common Digital Space of Scientific Knowledge (CDSSK). This methodology is demonstrated by the example
of the content creation technology for the Digital Library "Scientific Heritage of Russia" (DL SHR) content.
The content of the CDSSK contains rare (out of print, hard-to find) books and archival documents, which
make digital copies of these materials very labour intensive. This needs to be assessed when planning the
content filling for CDSSK. The developed technique includes the decomposition of the entire technological
process into a number of operations performed by specialists of a certain profile (archivists, librarians, editors,
scanners, etc.). Each phase is divided into several operations, and for every operation the time spent on this
type of work is estimated. A unit of CDSSK content can be an archival document, a page of a book, a whole
book, a biography of a scientist, etc. The assessment of the time period is carried out either according to
published standards, or, in their absence, based on analysis of the experience of performing the operation
when forming the content of the DL SHR. The article provides data on the calculation of time costs for
individual operations of the formation of digital objects and their collections in relation to DL SHR, taking
into account Russian standards and 15 years of experience.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Common Digital Space of Scientific Knowledge
(CDSSK) is one of the most important objects of the
modern information society. The space in its
mathematical (formalized) conception is the set of
some objects with certain rules for manipulation with
them and the sets of axioms that these rules must
follow. I.e., it is a set with the structure introduced on
it (Antopol'skij et al., 2019). The global information
space contains all the information accumulated by
mankind in the process of its evolution, that was made
available on physical media. It includes various kinds
of documents available in printed, handwritten or
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5269-0988
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4189-1244
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9461-3750
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0137-1255
electronic forms (publications, archival materials,
scientific and technical documentation, etc.),
photographs, film, video, audio materials, multimedia
and 3D models of real-world objects (Abdelali et al.,
2019).
The digital information space (DIS) is a part of the
global information space. The digital space of
scientific knowledge (DSSK) is a part of the DIS
containing reliable fundamental scientific,
educational and popular science information in
various fields of science, presented in various forms.
The Common digital space of scientific knowledge
(CDSSK) is a computer environment containing the
information represented in the DSSK. This
information is well organized and provided to users
Kalenov, N., Savin, G., Sobolevskaya, I. and Sotnikov, A.
Assessment of Efforts for Content Creation for the Common Digital Space of Scientific Knowledge.
DOI: 10.5220/0010641900003060
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications (CHIRA 2021), pages 131-138
ISBN: 978-989-758-538-8; ISSN: 2184-3244
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
131

according to uniform rules for all sciences. In other
words, the CDSSK consists of a set of subspaces
related to individual areas of science interconnected
on the basis of an unified ontology to the whole space
(Antopol'skij et al., 2019
). This unified ontology
includes a number of subject ontologies that describe
individual scientific areas with the help of thesauruses
and classification systems.
Each subspace of the CDSSK includes axioms
and fundamental results that form the basis of each
specific research area, as well as a dynamic part
containing information on cutting edge science in this
field.
For each separate field of science, specific
scientific knowledge is defined for each individual
field of science. There are two classes of knowledge
in almost all areas of knowledge: a priori knowledge
and experimental knowledge (Antopol'skij et al.,
2019).
The DIS resources are a source of the CDSSK
content. These resources should be analyzed for
reliability, importance and relevance.
Scientific social networks provide numerous
services for share information, posting research
results, reviews and comments, search for vacancies,
etc. (Kalenov et al., 2012).
The formation of the CDSSK involves the
development of special approaches and algorithms
that are based on new principles.
2 STRUCTURE OF THE
COMMON DIGITAL SPACE OF
SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE
The space of scientific knowledge should include two
components - static and dynamic. The static
component is the fundamental theoretical and
experimental data tested by time and practice. The
dynamic component is a part of the CDSSK which
includes new data and knowledge.
These components can be considered as two parts
of the knowledge space. One of which - basis -
contains fixed scientific knowledge, and the other -
suspension - new scientific information. At the same
time, after passing through an expert filter, the second
part goes into the first (Sobolevskaya and Sotnikov,
2019).
The connections between the basis and the
suspension can be managed at the level of an
interdisciplinary scientific ontology. At the same
time, the basis and the suspension are a class of
subspaces (facets) in various scientific fields.
3 CONTENT OF THE COMMON
DIGITAL SPACE OF
SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE
Information resources are the sources of scientific
knowledge. They contain postulates, theories,
experiments description, experimental results and are
presented on physical storage media (Kalenov, 2014).
As a rule, the information contained in these
resources is reliable and verified (Chen and Lu,
2015). However, an expert examination is required to
decide what is to be loaded to the CDSSK. Experts
should be qualified representatives of the scientific
community in the relevant subspace area.
The basis and superstructure of the CDSSK
consist of a kernel and a convex shell (Kalenov,
Sobolevskaya, Sotnikov, 2019).
Digitized publications, archival materials, images
of museum exhibits, multimedia materials, and
thematic databases supported by scientific
organizations form the convex shell of the CDSSK.
4 SHAPING CONTENT OF THE
COMMON DIGITAL SPACE OF
SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE
The CDSSK is based on the principle of distributed
data with centralized editorial processing, content
downloading and technology support.
The digital library "Scientific Heritage of Russia"
(DL SHR) (http://e-heritage.1gb.ru/Catalog/IndexL)
has been operating since 2010. The DL SHR is based
on the principle of distributed data with centralized
editorial processing, content downloading and
technology support (Sotnikov et al., 2017). More than
20 libraries, institutes and museums prepare
information for DL SHR according to uniform rules.
Object-oriented design, data distributed
technology, various digital scientific objects as well
as the long-standing positive experience in the
operating of the DL SHR allow us to consider as a
prototype of the Common Digital Space of Scientific
Knowledge (CDSSK) (Antopol'skij et al., 2019.).
In accordance with the DL SHR metadata
standards bibliographical data related to scientists,
their scientific interests in terms of classification, and
a bibliography of their main works are entered into
the library.
Librarians perform this work. It includes 3 stages:
- the search for sources of scientist biographical
data and the compilation of a detailed biography;
CHIRA 2021 - 5th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
132
- the selection of bibliography;
- the input of data into the DL SHR technological
block.
Lets denote the average time spent on the
implementation of each stage, respectively, through
𝑡
, 𝑡
, 𝑡
.
Generating information on the scientist that is
reflected in the DL SHR includes three times
intervals.
The first stage (time interval 𝑡
).
Analysis of the data of the DL SHR shows that on
average, when compiling a biography of a scientist,
the time spent on compiling a biography of a scientist
from 2 to 3 sources is 15 minutes.
The time spent on library technical operations,
related to the issuance and acceptance of items from
the library stock, is normalized per item and total 13
minutes. Let us estimate that operations last about 30
minutes (considering that 2 items are to be loaned).
To estimate the time spent on compiling a
biography of a scientist, we will use the rule “writing
an abstract: studying and analyzing the document for
which the abstract is being prepared; writing a text ",
equating conditionally compiling a biography to
compiling an abstract of selected publications). This
rate per one author's sheet (40,000 characters) is 5920
minutes. An analysis of the data reflected in the DL
SHR shows that the volume of the text of a scientist's
biography ranges from 1000 to 31000 characters and
is, on average, about 6000 characters, or 15% of the
printed sheet. Thus, the standard time for compiling a
biography of a scientist and entering it into the system
is 888 minutes, the total time for completing the first
stage of forming data about a scientist is 𝑡
=15+
30 + 888 = 933 minutes.
The span time on the implementation of the
second stage (the formation of a bibliographic list of
the scientist's publications) can be estimated on the
time allotted for compiling a bibliographic index,
which is 13500 minutes per author's sheet. Analysis
of the data entered in the DL SHR shows that the
bibliographic list of one scientist, on average, is 2200
characters, or 5.5% of the author's sheet. According
to the norms, it takes 742 minutes to compose it.
The total time spent on creating digital library
information about one scientist (𝑇
=𝑡
+𝑡
+𝑡
)
is 1681 minutes or (rounded up) 28 hours of work for
a librarian.
5 PREPARING IMAGES OF
SCANNED ARCHIVAL
RECORDS
Suppose the personal data is entered into the system.
Then the technological processes that is carried out in
order to prepare the publication for inclusion in the
DL SHR are presented in Table 1. We understand an
archival document as a paper document. Digitizing a
photo and video archive requires much more labor
than digitizing paper documents.
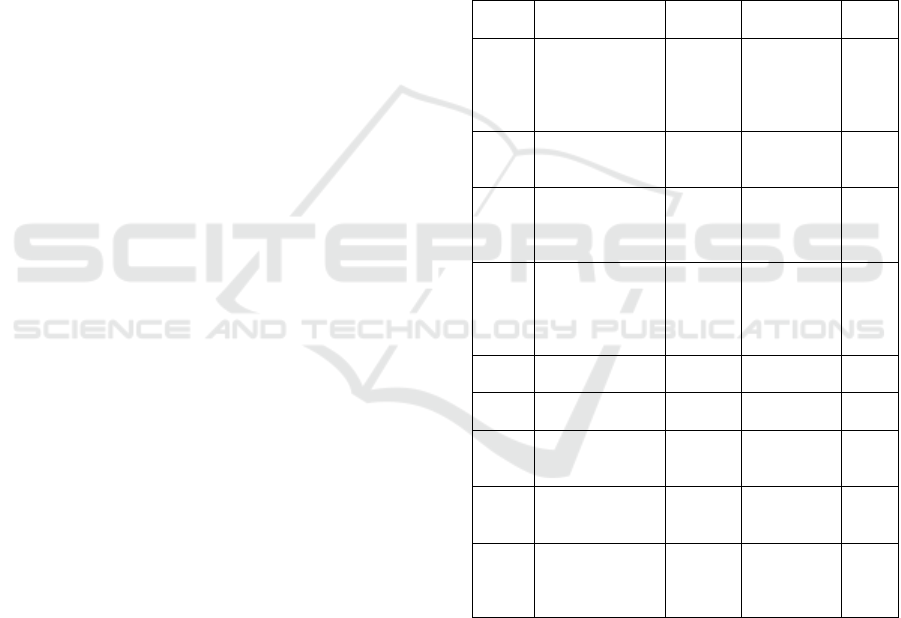
Table 1: Technological processes carried out in the
preparation of the archival record for inclusion in the DL
SHR.
Stage
numbe
r
Project scope By whom
Accounting
uni
t
Time
1
Selection and
input the archival
record proposed
for inclusion in
the digital library;
registrar
archival
record
𝑡
2
Application
consideration
Editorial
team
membe
r
archival
record
𝑡
3
Getting and
introduction the
archival record
from the Archive;
registrar
archival
record
𝑡
4
Sending for
scanning,
preparing archival
record for
scanning
registrar
archival
record
𝑡
5
archival record
Scanning
Scanner-
Operato
r
archival
record page
𝑡
6 Image processing
Technical
Specialis
t
archival
record page
𝑡
7
Archival record
metadata quality
control
Editor
archival
record
𝑡
8
page metadata and
navigation system
quality control
Editor
archival
record page
𝑡
9
Downloading the
digital archival
record into the DL
SHR
Technical
Specialist
archival
record
𝑡
Thus, if an archival record of 𝑁 pages is entered
into the DL SHR then total span time 𝑇
for its
inclusion in the Library will be:
𝑇
=𝑡
+𝑁∙𝑡
(1)
When assessing the labor costs of registrars 𝑡
, 𝑡
and 𝑡
, we will use considered norms for archival
documents digitization (42 minutes per document),
“indexing (meaningful cataloging)” (7 minutes per
Assessment of Efforts for Content Creation for the Common Digital Space of Scientific Knowledge
133

document) and “entering computer basic information
about the document (author, title, etc.) in a specialized
program” (6 minutes). The results are as follows:
𝑡
+𝑡
+𝑡
=55 min.
We will take the experience in provisioning as a basis
for DL SHR database provisioning and the norms for
scanning documents in a non-contact method (this is
the technology used in the DL SHR), presented in
(Burrows, 2018; Bilgaiyan et al., 2019).
The rate for one employee is 45 archival records
per shift. Based on this, we get
𝑡
=10 min
The rate per operator for page scanning (step 5) is 200
pages per shift. It means that
𝑡
=0.15 min
The main task of the 6th stage (image processing) is
to check and edit the graphic images of the digital
pages.
The rate per operator during this stage is 200
pages per shift. Thus
𝑡
=0.15 min
Stage 7 (archival record metadata quality control).
The day's work for one specialist is 10 archival
records per shift, it therefore follows:
𝑡
= 32 min.
At stage 8 (page with metadata and navigation system
quality control), the issuing editor checks the layout
of the archival record on the production server.
When certain defects are identified, the
corresponding information is transmitted to the
operator of the 6th stage. The norm for these works is
800 pages per shift, based on this, we get
𝑡
=0.3 min.
At the final stage, the issuing editor publishes the
archival record and metadata on the e-library portal
and checks the availability of the downloaded
information. The production rate for one specialist is
100 archival records per shift,
𝑡
=19.2 min.
Substituting the obtained values into formula (1), we
find that the average time spent on digitizing and
including one archival record of N pages in the digital
library will be (in minutes)
𝑇
= 116.2 + 0.6 ∙ 𝑁
Registrar workers from this time spend
𝑇
=55 min
Editors
𝑇
=57+0.3∙𝑁
Technical specialists
𝑇
= 87.5 + 0.15 ∙ 𝑁
Scanning operators
𝑇
=0.15∙𝑁
To prepare and enter into Digital Library (DL) the
archival record of a scientist that was not previously
presented in the DL, 100 archival in volume will take
about 27 hours, including ~ 20.5 hours of work of
registrar specialists, ~ 2 hours of work of an editor, ~
1.5 hours of work of an operator- scanner, ~ 3 hours
of work of a technical specialist. By introducing
another archival record by the same person, the
processing time will be reduced the work needs of
registrars will be reduced to one hour, and the total
preparation time for a archival record will be about 7
hours.
6 PREPARING IMAGES OF
SCANNED BOOKS
If a book of 𝑀 pages is entered into the DL SHR then
total span time 𝑇
for its inclusion in the Library will
be:
𝑇
=𝑡
+𝑀∙𝑡
(2)
When assessing the labor costs of librarians 𝑡
, 𝑡
and 𝑡
, we will use, together with the already
considered norms for the selection of literature, the
norms for "forming a bibliographic record for
documents in a language (descriptive cataloging)" (18
minutes per document), "indexing (meaningful
cataloging)” (18) and “entering computer basic
information about the document (author, title) in a
specialized program” (5 minutes), “preparing
documents for microfilming and scanning
documents” (5 minutes), “transferring documents for
microfilming and scanning” (16 min.). The results are
as follows:
𝑡
+𝑡
+𝑡
=75 min.
Consider the processes (indicated as stages in Table
1) performed by the staff of the editorial team,
scanners and technicians. As a basis. We will take the
experience in provisioning as a basis for scanning
documents in a non-contact method (this is the
technology used in the DL SHR), presented in (Ali
and Gravino, 2019; YUmasheva YU.YU., 2012).
CHIRA 2021 - 5th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
134

The rate for one employee is 30 books per shift.
Based on this, we get
𝑡
=16 min
The rate per operator for page scanning (step 5) is 800
pages per shift. It means that
𝑡
=0.6 min
The main task of the 6th stage (image processing) is
to check and edit the graphic images of the digital
pages.
The rate per operator during this stage is 800
pages per shift. Thus
𝑡
=0.6 min
The main tasks of the 7th stage are:
- formation of the table of contents of the book
(recognition and editing of text or its manual input);
- layout of an e-book in a special program based
on prepared high-quality graphic formed pages and a
generated table of contents;
- creation of the most accurate navigation system
of the digital book.
In the process of creating a navigation system, the
technician must ensure:
- the correctness of typing, titles, notes and other
parts of the navigation system;
- the correctness of the electronic links and the
navigation system;
- completeness of the e-book: sequential number
of pages, order of sections.
The day's work for one specialist is 5 e-books per
shift.
𝑡
=96 min
Stage 8 (book metadata quality control) includes:
- checking the correspondence of the author name,
the title, the output data to those on the cove page;
- checking the formatting of records - spelling,
punctuation, accepted word abbreviations in
bibliographic data;
- checking the compliance of the information
entered in the fields "type of publication",
"language", "pages", the original. The "pages" field is
verified strictly according to the electronic version of
the book and includes the total number of files in the
digital version, prepared for uploading to the site,
checking for the presence of appropriate indexes;
- checking the formatting of the bibliographic
description (according to standards).
The day's work for one specialist is 10 e-books per
shift, from which follows:
𝑡
= 48 min.
At stage 9 (page metadata and navigation system
quality control), the issuing editor checks the layout
of the e-book on the production server. The work of
the editor includes the analysis of graphic images of
the pages and checking the navigation system. It
includes:
- checking the sequential display of pages;
- checking the quality of scanning (the degree of
readability of the text, at least 99% of the information
presented on the page must be readable);
- checking the quality of processing of scanned
pages (correct page cropping, geometric text
correction, absence of text bends and other
distortions, absence of "extraneous elements" -
stripes, shadows, operator fingerprints, etc.);
- checking links for their opening;
- checking links for compliance with the chapters
and contents of the book.
When certain defects are identified, the
corresponding information is transmitted to the
operator of the 6th stage. The norm for these works is
1200 pages per shift, based on this, we get
𝑡
=0.4 min.
At the final stage, the issuing editor publishes the
book and metadata on the e-library portal and checks
the availability of the downloaded information
(Kozlova et al., 2019). The production rate for one
specialist is 50 e-books per shift,
𝑡
=9.6 min.
Substituting the obtained values into formula (2), we
find that the average time spent on digitizing and
including one book of N pages in the digital library
will be (in minutes)
𝑇
= 244.6 + 1.6 ∙ 𝑁 (4)
Library workers from this time spend
𝑇
=75 min
Editors
𝑇
=64+0.4∙𝑁
Technical specialists
𝑇
= 105.6 + 0.6 ∙ 𝑁
Scanning operators
𝑇
=0.6∙𝑁
To prepare and enter into DL the first book of a
scientist that was not previously presented in the DL,
200 pages in volume will take about 38 hours,
including ~ 29.5 hours of work of library specialists,
~ 2.5 hours of work of an editor, ~ 2 hours of work of
an operator- scanner, ~ 4 hours of work of a technical
specialist (Kirillov S.A., 2009). By introducing a
Assessment of Efforts for Content Creation for the Common Digital Space of Scientific Knowledge
135
book by the same author the processing time will be
reduced to one and a half hours, and the total
preparation time for a book will be about 10 hours.
7 PREPARATION OF 3D DIGITAL
MODELS OF MUSEUM
OBJECTS
Along with digital publications DL SHR contains
multimedia content and, in particular, 3D-models of
museum objects. These objects can be associated with
a specific person (or several persons) or they can be
combined into an independent collection dedicated,
among other things, to a certain research area or
event. Estimated staff time required to create a 3D
model and digital collections that include several
objects will be discussed below.
Various methods are used to visualize a three-
dimensional object (Kalenovet al., 2020). These
methods can be based on SfM-technologies (Sotnikov
et al., 2017; Wróżyński et al., 2017; Scopigno, 2017;
Garstki, 2017), software and technological solutions
used, in particular, in laser and optical 3D-scanning,
photogrammetry methods (Guidi et al., 2020; Hosni
and Idri, 2018).
For the formation of digital 3D-models in the DL
SHR there was a model of interactive animation
technology (Sobolevskaya and Sotnikov, 2019). This
technology does not imply the construction of a full-
fledged 3D-model based on a programmatic change
(scrolling) of a fixed view of an object (frames) using
standard interactive display programs that simulate a
change in the point of view of the original object. To
create such an interactive cartoon, you need a set of
pre-prepared scenes that will separate exposition
frames.
Before proceeding with the formation of digital
3D-models of museum objects in order to include
them in the electronic library, it is necessary to carry
out certain preparatory work performed by the staff
of the museum, which owns the modeled object.
The standard time
𝑇
, desired for preparatory
work is, on average, 130 minutes per object.
After these preparatory works is completed, the
main cycle of work begins on the creation of a digital
3D-model of the museum object.
This cycle of work includes the following main
stages:
1. Preparation for digitization. It means setting up an
object at the shooting location, adjusting lighting,
etc.
2. Digitization of the object. The end result of this
stage is an array of data, files with photographs of
the object taken from 120 angles;
3. Processing of the data set obtained at the first
stage. At this stage, the background on which the
image was taken is removed from each photo.
This is done using a software module specially
designed for this stage;
4. Layout and quality control of the digital resource
image. The result of this phase is digital 3D-
images of museum items.
5. Description of the museum item, the digital 3D-
model of which is included in the digital
library.
The museum staff does this work.
6. Loading the generated model into the DL SHR.
Lets 𝑇
,𝑇
,𝑇
,𝑇
,𝑇
,𝑇
- time intervals required for
processing one museum object at stages 1-6,
respectively.
Table 2 shows the technological processes carried
out in the creation of museum 3D-objects for
inclusion in the DL SHR.
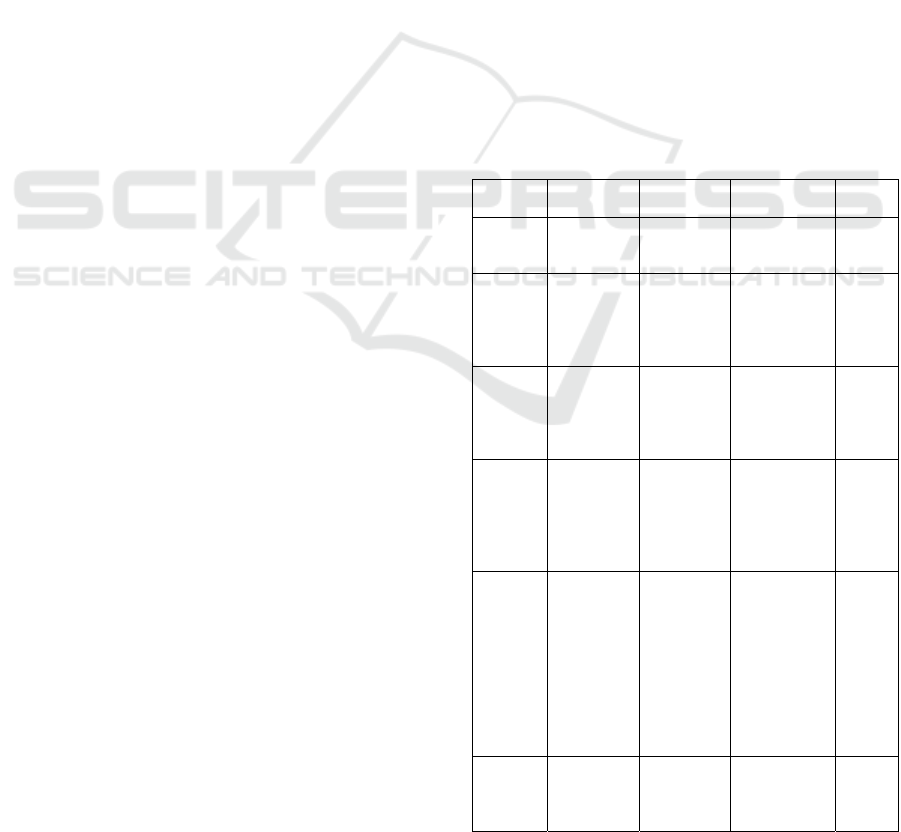
Table 2: The technological processes carried out in the
creation of museum 3D-objects for inclusion in the DL
SHR.
Stage
numbe
r
Project
scope
By whom
Accounting
uni
t
Time
1
Preparing
for
digitizing
Museum
employee
Museum
object
𝑇
2
Digitization
of the object
Technical
Specialist
Folder
containing
120 jpg files
for each object
photographe
d
𝑇
3
Processing
of the data
set obtained
at the first
stage
Technical
Specialist
obtained files
𝑇
4
Layout and
quality
control of
the digital
resource
image
Technical
Specialist
Digital 3D-
object
𝑇
5
Description
of the
museum
item, the
digital 3D-
model of
which is
included in
the digital
library
Museum
employee
Digital 3D-
object
𝑇
6
Loading the
generated
model into
the DL SHR
Technical
Specialist
Digital 3D-
object
𝑇
CHIRA 2021 - 5th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
136

Thus, if there are 𝑀 digital museum 3D-objects
are introduced into the DL SHR then the average time
𝑇
for the inclusion of this volume of digital
resources in the DL SHR is:
𝑇
=𝑀∙𝑇
After several objects have been digitized, they can be
combined into one or more collections. Let 𝑇
be the
average time required to form and describe a
collection. Then the total time 𝑇 is the total for the
formation of a digital collection of museum 3D
objects is:
𝑇=𝑇
+𝑇
The following are the numerical values of the average
time spent on the formation of digital 3D-models of
museum items based on the experience of creating
content in the DL SHR. In the process of replenishing
the digital library content, more than 100 3D-models
of museum items were prepared, combined into
several collections. Among them is a digital 3D-
collection of models of fruits by I.V. Michurin, stored
in the State Biological Museum named after K. A.
Timiryazev (GBMT), digital 3D-collection of
anthropological reconstructions by M.M. Gerasimov,
stored in the GBMT and the State Darwin Museums
(http://acadlib.ru/; http://vim.benran.ru/).
The average time values 𝑇
,𝑇
,𝑇
,𝑇
,𝑇
,𝑇
are
given below, based on the experience of formation,
including these collections.
To implement the first stage (preparation of an
object for digitization, interval 𝑇
), an average of 45
minutes is required.
To implement the second stage (digitization of the
selected content, interval 𝑇
), on average, 20 minutes
per object.
To implement the third stage (processing the files
obtained as a result of digitization, time interval 𝑇
),
an average of 290 minutes per object is required.
To implement the fourth stage (layout and quality
control of the image of a digital resource, time
interval 𝑇
), on average, 25 minutes per object is
required.
To implement the fifth stage (description of a
digital 3D-object, time interval 𝑇
), an average of 15
minutes is required per object.
To implement the sixth stage (loading a 3D-object
into the DL SHR, time interval 𝑇
), on average, 35
minutes are required per object.
Thus, the total time spent on presenting one digital
3D-model of a museum object in the DL SHR is:
𝑇 = 45 + 20 + 290 + 25 + 15 + 35 + 130 =
= 560 min.
To generate at least 40 digital 3D-models of museum
objects (time 𝑇
), an average of 180 minutes is
required.
When forming a digital 3D-collection of
anthropological reconstructions, M.M. Gerasimov
was created and uploaded to the site http://acadlib.ru/,
integrated with the DL SHR, 50 works by M.M.
Gerasimov. The total time taken to create this
collection was:
𝑇
= 415 ∙ 50 + 180 = 28 180 min.
That is approximately 470 hour
.
8 CONCLUSIONS
Using the results obtained, it is possible to solve the
problem of optimizing the time spent on creating
digital copies of printed materials and museum
objects by paralleling "technological processes
performed by library or museum specialists
(preparation of object metadata) and technical
specialists (digitization of materials and quality
control).
The estimates can be further extended for the
digital copies creations of the other types of objects
and to be used for work planning on the formation of
the Single Digital Space of Scientific Knowledge.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research is carried out by Joint SuperComputer
Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences – Branch
of Federal State Institution “Scientific Research
Institute for System Analysis of the Russian Academy
of Sciences” within the framework of a state
assignment 0580-2021-0014.
REFERENCES
Abdelali Z, Mustapha H., Abdelwahed N. 2019.
Investigating the use of random forest in software effort
estimation. In Second international conference on
intelligent computing in data sciences (ICDS2018).
Vol. 148 . pages: 352-343 .
Ali A., Gravino C. 2019. A systematic literature review of
software effort prediction using machine learning
methods. In Journal of software-evolution and process.
Vol. 31 (10). Article Number: e2211.
Assessment of Efforts for Content Creation for the Common Digital Space of Scientific Knowledge
137

Antopol'skij A.B., Kalenov N.E., Serebryakov V.A.,
Sotnikov A.N. 2019. O edinom cifrovom prostranstve
nauchnyh znanij. In Vestnik Rossijskoj akademii, Vol.
89 (7). pages 728-735.
Bilgaiyan S., Mishra S., Das M. 2019. Effort estimation in
agile software development using experimental
validation of neural network models. In International
Journal of Information Technology. Vol. 11(3). pages:
569-73.
Burrows T. 2018. Connecting Medieval and Renaissance
Manuscript Collections. In Open library of humanities.
Vol. 4 (2). Article Number: 32.
Chen J., Lu Q. 2015. A method for automatic analysis
Table of Contents in Chinese books. In Library hi tech.
Vol. 33 (3). pages 424-438.
Garstki K. 2017. Virtual representation: the production of
3D digital artifacts. In Archaeol. Method Theory. Vol.
24. pages 726–750.
Guidi G., Malik, US., Micoli, LL. 2020. Optimal Lateral
Displacement in Automatic Close-Range
Photogrammetry. In Sensors. Vol. 20 (21). № 6280.
Hosni M., Idri A. 2018. Software Development Effort
Estimation Using Feature Selection Techniques. In 17th
International Conference on New Trends in Intelligent
Software Methodology Tools, and Techniques
(SoMeT). Vol 103. pages: 439-452.
http://acadlib.ru/ (last access 24.01.2021 (24.01.2021).
http://heritage1.jscc.ru/ (last access 24.01.2021).
http://vim.benran.ru/ (last access 24.01.2021 (24.01.2021).
Kalenov N.E. 2014. Upravlenie tekhnologiej napolneniya
elektronnoj biblioteki "Nauchnoe nasledie Rossii". In
Elektronnye biblioteki: perspektivnye metody i
tekhnologii, elektronnye kollekcii: trudy XVI
Vserossijskaya nauchnaya konferenciya RCDL. pages
357-361.
Kalenov N.E., Kirillov S.A., Sobolevskaya I.N., Sotnikov
A.N. 2020. Vizualizaciya cifrovyh 3d- ob"ektov pri
formirovanii virtual'nyh vystavok. In Elektronnye
biblioteki. Vol. 23 (4). pages 418-432.
Kalenov N.E., Savin G.I., Serebryakov V.A., Sotnikov
A.N. 2012. Principy postroeniya i formirovaniya
elektronnoj biblioteki "Nauchnoe nasledie Rossii". In
Programmnye produkty i sistemy, 2012. Vol. 4 (100).
pages 30-40.
Kirillov S.A. Malinin A.I. 2009. Metodika obrabotki
otskanirovannyh izobrazhenij v proekte elektronnoj
biblioteki "Nauchnoe nasledie Rossii". In
Informacionnoe obespechenie nauki: novye
tekhnologii. pages 99-107.
Kozlova T., Zambrzhitskaia E., Simakov D., Balbarin Y.
2019. Algorithms for calculating the cost in the
conditions of digitalization of industrial production. In
International scientific conference digital
transformation on manufacturing, infrastructure and
service. Vol. 497. № 012078.
Scopigno R. 2017. Digital fabrication techniques for
cultural heritage: a survey. In Comput. Graph. Forum.
Vol. 36. pages 6–21.
Sobolevskaya I. N., Sotnikov A. N. 2019. Principles of 3D
Web-collections Visualization. In Proceedings of the
3rd International Conference on Computer-Human
Interaction Research and Applications. pages 145-151.
Sotnikov A.N., Kirillov S.A., Kondrat'eva E.A. Pruglo
O.A., Zabrovskaya I.E., A.N. 2017. Voprosy
formirovaniya fondov elektronnoj biblioteki
"Nauchnoe nasledie Rossii". In Informacionnoe
obespechenie nauki: novye tekhnologii. pages 184-191.
Wróżyński R., Pyszny K., Sojka M., Przybyła C., Murat-
Błażejewska S. 2017. Ground volume assessment using
'Structure from Motion' photogrammetry with a
smartphone and a compact camera. In Open
Geosciences. Vol. 9. pages 281-294.
YUmasheva YU.YU. 2012. Metodicheskie rekomendacii
po elektronnomu kopirovaniyu arhivnyh dokumentov i
upravleniyu poluchennym informacionnym massivom.
VNIIDAD. pages 125.
CHIRA 2021 - 5th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
138
