
Corporate Property Tax as One of the Factors of Sustainable
Development
Larisa A. Aguzarova
1
and Fatima S. Aguzarova
2
North-Ossetian State University named after K.L. Khetagurov, Vladikavkaz, Russia
Keywords: Tax on the Property of Organizations, The Value of Property, Fixed Assets of the Company, Budget.
Abstract: The corporate property tax is recognized as a regional direct payment that goes to the budgets of the
constituent entities of the Russian Federation. As the authors of the article rightly note, the sustainable
development of the country's regions depends on the performance of this tax. Conducted in the study, the
analysis allowed to conclude that the proportion of minor tax revenues in the budgets of the Russian
Federation, despite the fact that taxes on the property he occupies a significant share. When studying the
chosen topic, the most relevant problems are revealed, including: problems related to unstable tax legislation
in the part of Chapter 30 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; problems of corporate property tax
evasion, and others. The authors suggest ways to solve the identified problems: ensuring stable tax legislation;
strengthening the procedure for conducting tax administration and control.
1 INTRODUCTION
The corporate property tax is one of the regional
taxes. This means that the organizational and legal
basis for its construction is established by the federal
authorities, with the exception of such elements as tax
rates, payment deadlines and tax benefits. These
elements may be established by the authorities of the
subjects of the federation within the permissible norm
of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The sustainable development of the regions is
directly affected by the performance indicators of the
corporate property tax in the budgets of the budget
system of the Russian Federation.
Since the object of taxation of this tax is
recognized as property, it is included in the group
"Property taxes". In addition to the tax under
consideration, this group includes: transport tax;
gambling tax; land tax; and personal property tax.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The value of the corporate property tax in the Russian
tax system is not as high as, for example, the mineral
1
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2607-3932
2
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2699-8561
extraction tax or the value added tax. However, the
number of property taxes under consideration, the
payment is ranked first in terms of revenue (Figure 1).
482
Aguzarova, L. and Aguzarova, F.
Corporate Property Tax as One of the Factors of Sustainable Development.
DOI: 10.5220/0010592704820488
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 482-488
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
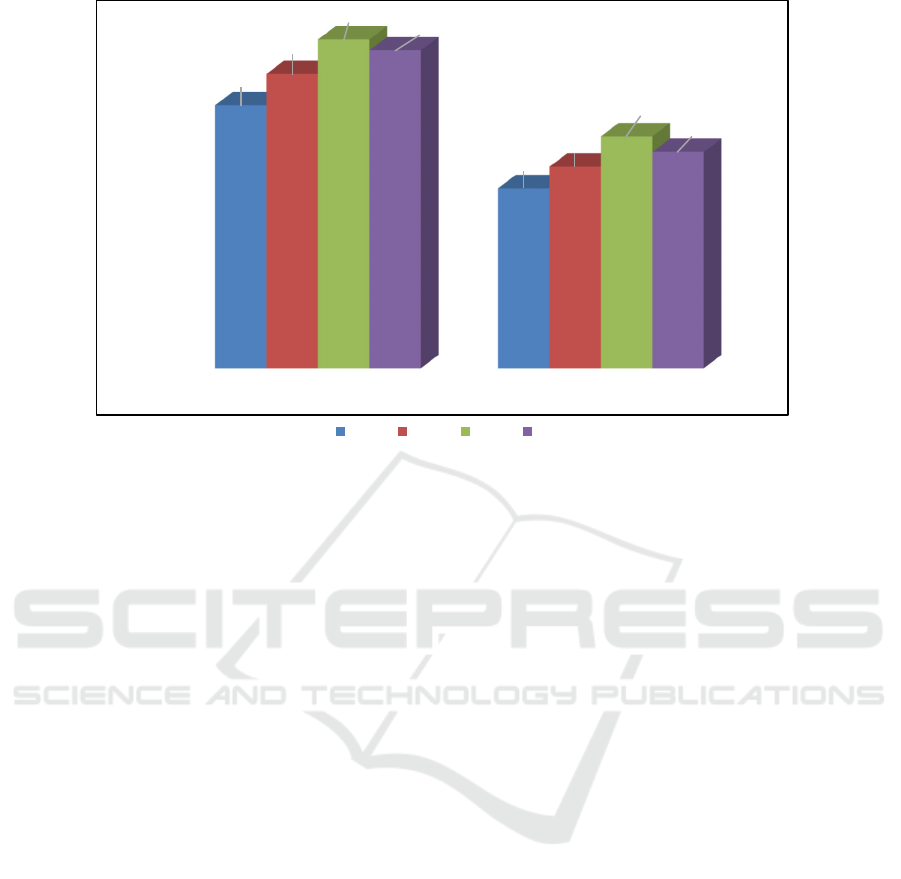
Figure 1: Dynamics of corporate property tax in the general system of property taxes of the budgets of the Russian Federation
for 2016-2019 (billion rubles).
The data in Figure 1 confirm the fact that the
corporate property tax dominates the property tax
system of the consolidated budget of the Russian
Federation for 2016-2019. For example, if in 2016 the
amount of property taxes amounted to 1117.1 billion
rubles, then 764.7 billion rubles of them are the
component of the property tax of organizations, the
amount of income from other property taxes is 352.4
billion rubles (Batashev, 2020).
The nature of the tax is that its payment is made
regardless of whether there is the positive results of
financial-economic activity of subjects or not, i.e.
whether the owner of the property has the income
from the use of the objec or not, the removal of taxes
is necessaryly carried out (even with unprofitable
activities of the organization). In this regard, the tax
refers to direct real payments. In this case, there are
advantages and disadvantages. The advantages
include the fact that the payment of corporate
property tax to the budget is inevitable, so this
payment is characterized by the stability of revenues,
it is not subject to various economic fluctuations and
cataclysms. At the same time, the owner of the
organization's property may suffer financial
insolvency in different periods and then have to resort
to loans, credits and other leverage to stay in the
market (Aguzarova, 2018). Note that the already
insolvent owner of the property additionally burdens
himself by taking out a loan, which we consider a
serious disadvantage.
3 RESULTS OF THE STUDY
In modern realities, the largest number of regional
budgets are not self-sufficient, they need additional
financial sources. Although the corporate property tax
is recognized as a stable source, its component in the
budget system of the subjects is insignificant. (Table
1).
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
Property taxes Tax on property of organizations
1117,1
764,7
1250,5
856,3
1397
985,4
1350,9
918,8
2016 2017 2018 2019
Corporate Property Tax as One of the Factors of Sustainable Development
483
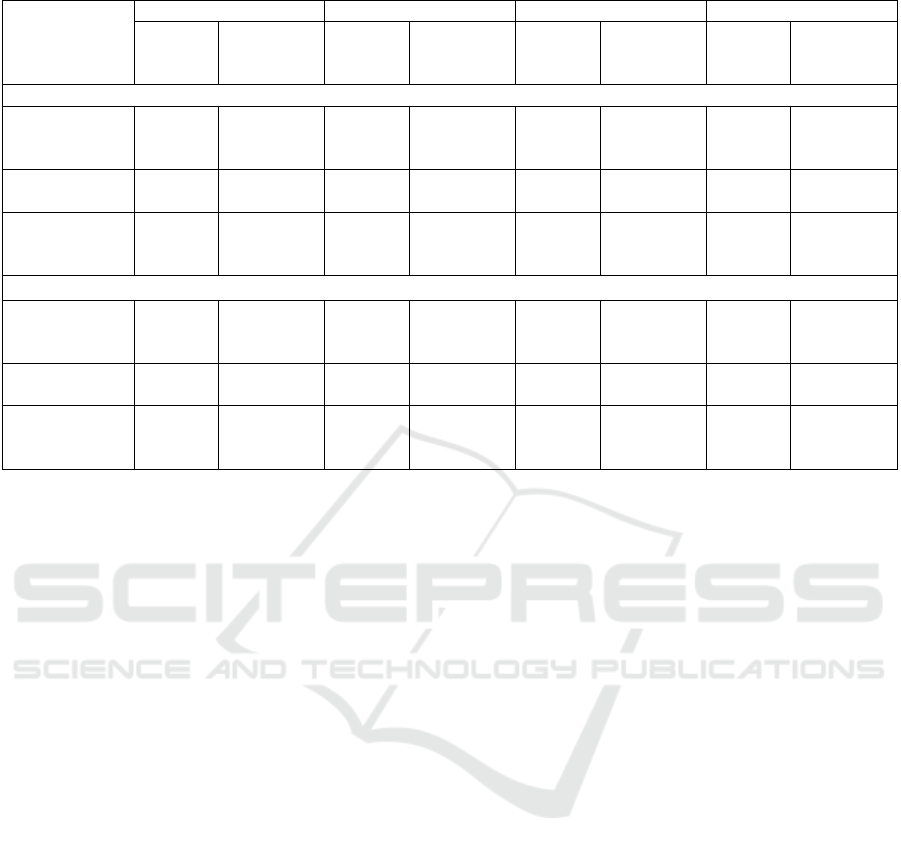
Table 1: The share of corporate property tax in the budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation for 2016-2019.
Name of
indicator
2016 2017 2018 2019
Fact.,
Billion
rubles.
Specific
gravity., %
Fact.,
Billion
rubles.
Specific
gravity., %
Fact.,
Billion
rubles.
Specific
gravity., %
Fact.,
Billion
rubles.
Specific
gravity., %
Bud
g
ets Of The Bud
g
et S
y
stem Of The Russian Federation
Budget
revenues
including:
28181,5 100,0 31046,7 100,0 37320,3 100,0 39497,6 100,0
Property taxes
From them:
1117,1 4,0 1250,5 4,0 1397,0 3,7 1351,1 3,4
Tax on
property of
organizations
764,7 2,7 856,3 2,8 985,4 2,6 918,8 2,3
Budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation
Budgetr
evenues
including:
9923,8 100,0 10758,1 100,0 12392,5 100,0 13572,3 100,0
Property taxes
fromthem:
1117,1 11,3 1250,5 11,6 1397,0 11,3 1350,9 10,0
Tax on
property of
organizations
764,7 7,7 856,3 8,0 985,4 8,0 918,8 6,8
Source: official website of the Federal Treasury of the Russian Federation // http: // roskazna.gov.ru, calculations of the
authors.
The analysis carried out in Table 1 showed that
for 2016-2019, the budget revenues of the budget
system of the Russian Federation, including the
revenues of the budgets of the subjects, are steadily
increasing. As for the tax on the property of
organizations, among them, it should be noted that
there is an unstable income, since until 2018 there is
a dynamic growth, in 2019, tax revenues decreased.
In general, for the entire period, corporate property
tax receipts increased by 154.1 billion rubles
(performance 2019«-» performance 2017).
The decrease in tax revenues is due to the
introduction of amendments to the Tax Code of the
Russian Federation, concerning the taxation
procedure. In accordance with Federal Law No. 302-
FL of 03.08.2018 "On Amendments to Parts One and
Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation",
movable property is excluded from taxation starting
from the tax period of 2019 (Korshunova, 2020). As
a result, the tax revenue decreased.
Despite the fact that the share of the tax in the
budgets of the country's budget system increased in
2018, there is a decrease over the entire period: 2,7%;
2,8%; 2,6%; 2,3% accordingly. A similar indicator in
the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian
Federation was: 7,7%; 8,0%; 8,0%; 6,8%
accordingly.
It is important to note that until 2019, all property
taxes, including the tax under consideration, were
fully credited to the budgets of the constituent entities
of the Russian Federation. However, since January 1,
2019, another payment has been added to the property
tax system - the "Single Tax payment of an
individual", which is distributed between the two
levels of the budget system. Part of the proceeds from
the payment of the new payment goes to the federal
budget, the other part - to the budgets of the subjects
of the Russian Federation. So, in 2019. the total
amount of the single tax payment for individuals was
183230,4 thousand rubles, from them to the Federal
budget allocated 183204,3 thousand RUB, the
remaining 26.1 thousand RUB credited to the budget
of the RF subject.
A single tax payment of an individual is
recognized as money voluntarily transferred to the
budget system of the Russian Federation to the
corresponding account of the Federal Treasury by a
taxpayer-an individual in order to fulfill the
obligation to pay personal income tax, transport tax,
land tax, and property tax (Isaev, 2019).
Figure 2 shows the dynamics of corporate
property tax revenues in the budget revenues of the
budget system of the Russian Federation for 2016-
2019, in order to identify its role (Figure 2).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
484
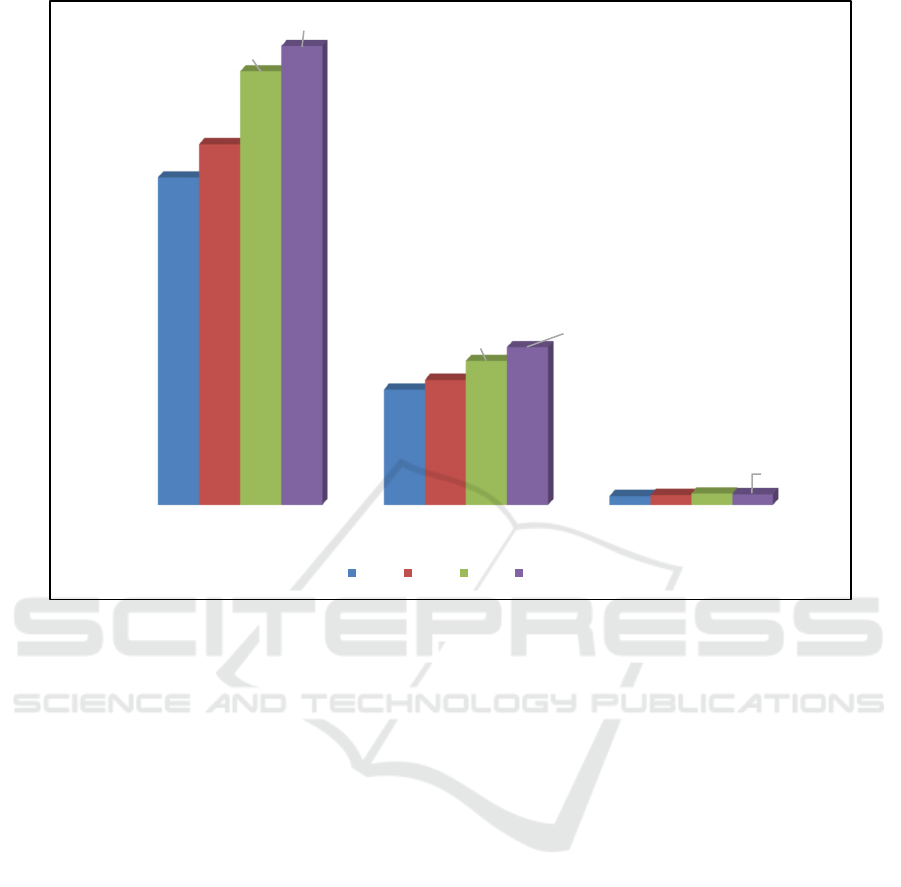
Figure 2: Dynamics of corporate property tax revenues in the budget revenues of the budget system of the Russian Federation
for 2016-2019 (billion rubles).
Figure 2 shows that for 2016-2019, the corporate
property tax does not play a significant role in the
budgets of the budget system of the Russian
Federation, including in the budgets of the constituent
entities of the Russian Federation, and the proceeds
from its payment are insignificant.
4 DISCUSSION OF THE RESULTS
Despite the fact that the tax on the property of
organizations has a long-term practice of levying,
problems with it remain to this day.
In Russia, the system of property payments paid
by organizations due to the specifics of the historical
development of the country is in the process of
formation. In countries with developed market
economies, a system of property taxes has already
developed, taking into account both national
characteristics and the uniqueness of individual
territorial entities. First of all, this is due to the fact
that property taxes are a significant source of income
for the budgets of territories and affect their
sustainable development (Kozin, 2020). Despite the
fact that each country has its own methods and
mechanisms for taxing the property of organizations,
it is possible to distinguish a number of general
principles for implementing the property tax
mechanism: a single tax regime prevails; the object is
land, buildings (industrial, residential) and other
types of real estate.
It should be noted that problems still remain in the
Russian system of property taxation in organizations.
One of these problems is the mechanism for
determining the tax base. In most countries, the
calculation of the taxable base usually takes into
account the market value of the property subject to
taxation. In some countries, there are cadastre
systems that are predefined for accounting for
information about property objects, property.
Benefits are mainly provided taking into account the
specifics of the object, the type of real estate, and not
taxpayers. Tax payments on property taxes of
organizations are mainly received by local budgets.
In Russian tax practice, the procedure for
determining the tax base is still undergoing a stage of
reform (Alieva, 2021). Only since 2015, the tax base
of some objects of property of organizations has been
determined based on the cadastral value (shopping
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
30000
35000
40000
Budget revenues of the Budget System of
the RF
Budget revenues of the constituent
entities of the RF
Tax on property of organizations
28181,5
9923,8
764,7
31046,7
10758,1
856,3
37320,3
12392,5
985,4
39497,6
13572,3
918,8
2016 2017 2018 2019
Corporate Property Tax as One of the Factors of Sustainable Development
485

centers, administrative and business centers, premises
not housing). The other part of the objects of property
of organizations is still determined based on the
average annual cost of fixed assets of the enterprise.
In our opinion, certain measures should be taken
to solve the problem in this direction (Ilyasov, 2019).
In particular, we completely eliminate the definition
of the tax base of the property's facilities
organizations on the basis of the cadastral value (so
that when determining the taxable base, only the
cadastral value of the organization’s property is taken
into account).
There are problems concerning the definition of
objects of property of organizations. As you know,
the objects of taxation include real estate owned by
the owners and on the balance sheet of the enterprise
(buildings, garages, etc.). When implementing
control measures, tax authorities often identify
incorrectly recorded or completely unaccounted
objects of property of organizations, despite the fact
that they are difficult to hide (Ivanov, 2021). This
means that if an object of property is not taken into
account, is not registered with the tax authorities and
does not appear on the balance sheet as fixed assets,
property tax property tax is not paid, becausethere is
no information about this objec. In the documentation
of organizations, information on the object of taxation
is incorrectly reflected, for example, the cadastral
value is incorrectly indicated (either overstated or
understated), the useful life, etc.
It is important to take into account one more point
when determining the objects of real estate. The Civil
Code of the Russian Federation refers to immovable
objects of vessels subject to state registration: air, sea,
inland navigation. In addition to the tax on the
property of organizations, these objects are subject to
transport tax (Vishnevsky, 2018). According to the
tax legislation one and the same object may be the
subject of tax payment only once during a single tax
or accounting period. Here there is a fact of double
taxation and this problem should be solved. It is
advisable to pay attention to the fact that the Tax Code
of the Russian Federation does not clearly define the
concept of real estate. It is the absence of the concept
that leads to double taxation.
As a recommendation to taxpayers, we note that
you should carefully evaluate all the objects of
property of organizations that are registered as real
estate. It is important to take into account how
autonomous each registered object is, how strongly it
is involved in the technological processes of the
enterprise, and other factors.
In order to avoid mistakes in the qualification of
property as immovable, production companies may
be recommended, based on a full-scale analysis of
judicial practice, to develop methodological
recommendations for their employees on such
qualifications. It is necessary to describe in detail the
rules and guidelines that should be used by staff when
qualifying a newly acquired objects of fixed assets
and registering them for accounting.
Such measures will help to level out some of the
claims of the tax authorities in respect of fixed assets,
for which the tax on the property of organizations is
not planned to be calculated and paid.
An equally important problem of corporate
property taxation is the instability of Russian tax
legislation. In recent years, a large number of
amendments have been made to Chapter 30
"Corporate Property Tax" of the Tax Code of the
Russian Federation, which highlights the
imperfection of legislative norms. For example, the
list of real estate taxed at the rate of 0% has been
changed. This innovation, on the one hand, only
improved the financial situation of some payers (that
is, the change occurred in favor of tax payers).
However, on the other hand, as a result of changes in
the list of immovable property taxed at the rate of 0%,
tax revenues to the budget decreased (Federal Law
No. 242-FL of 03.07.2016). The procedure for
reflecting the property of organizations in the Unified
State Register of Taxpayers in case of errors has also
changed. Now the cadastral value should be taken
into account from the tax period when this value was
applied incorrectly.
The situation when there is an incorrectly
specified information in the Unified State Register of
Real Estate (hereinafter-USRT) (overstatement or
understatement of the cadastral value) creates
considerable problems with the payment of tax. For
example, when the cadastral value is overstated, there
is a special challenge mechanism that allows you to
make certain adjustments to the calculation method
and ultimately achieve a fairer tax assessment.
However, this definition is unique to others. For
clarity, we will give the opposite situation. The
taxpayer owns a real estate object that was estimated
at 50 million rubles in the Unified State Register of
Legal Entities. At first glance, it may seem that the
amount is not small, however, since we are talking
about the property tax of objects under the
jurisdiction of the organization, the above amount is
sufficient and acceptable. But at the same time, in this
particular example, the amount of 50 million rubles.
it turned out to be extremely low (due to a technical
error in the USRT, relatively speaking, "one zero was
lost").
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
486

Further, in the course of the planned regular
revaluation, it was found that the object was already
valued at 500 million rubles. It is obvious that real
estate could not rise in price by 10 times, even though
real estate prices in dynamics tend to increase (taking
into account their physical wear and tear). The newly
established cadastral value indicates that the previous
estimate was incorrect in terms of the possibility of a
technical error.
Note that Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the
Russian Federation states that the taxpayer in the case
of revaluation (increase in cadastral value) must take
into account the new cadastral value only from the
next year. Both the tax authorities and the Supreme
Court in the ruling of 19.07.2019 No. 305-KG18-
17303 "If the taxpayer realizes that the cadastral
valuation is initially greatly underestimated, he can
not expect that after its revision, the new value will
be applied from the next tax period (Abakarova,
2020). In taxation, the fair market value, determined
by the court in disputed cases, should be applied,
including in respect of past tax periods" concluded
that this applies exclusively to bona fide taxpayers.
Relatively speaking, another taxpayer who decided
not to draw attention to his undervalued 10 times (due
to the smaller amount of tax payment) was in a
hopeless situation for his bad faith.
At first, all the courts, including the Supreme
Court of the Russian Federation, considered that an
unscrupulous taxpayer could not expect to apply the
increased cadastral value only from the next tax
period, because he had to be aware of the fact of
underestimating his estimate. And there is a situation
in which the taxpayer needs to pay additional tax on
the property of organizations for all previous years,
taking into account the fact that it is necessary to
evaluate the market value at their own expense at the
beginning of each tax period and pay extra taking into
account this point.
Thus, in addition to numerous inaccuracies and
shortcomings, including in the tax legislation itself in
the field of property taxation of organizations, which,
as the above example has shown, can often turn
against the taxpayer himself, he must also keep in
mind the aspect of good faith and abuse of law,
because a completely different level of control is
formed by the tax authorities, with an eye on the
behavior of the taxpayer (Lermontov, 2021).
It is no secret that every payer-legal entity tries to
reduce the tax burden as much as possible, saving on
tax payments. Since the initial value of the property
is taken as the basis for calculating the tax on the
property of organizations, there is a deliberate
underestimation of it (the value of real estate is
underestimated when buying). For example, an
organization has acquired real estate on the market for
a certain period of time. The official documents
clearly indicate an undervalued price, by prior
agreement of the parties to the transaction. This
means that when determining the amount of corporate
property tax, the amount of payment will be lower
than the potential possible amount (Bryzgalin, 2020).
The result of such an example is a tax savings for the
payer, and a loss of additional financial resources for
the budget.
In accounting, there is such a concept as "physical
wear and tear" (it is also called material or technical),
which is understood as the loss over time (partial or
complete) of the original characteristics of the
property object as a result of the impact of various
factors (natural, climatic, human, etc.factors). In other
words, physical wear is understood as a deterioration
in the operational properties of the property and a
decrease in its value. The indicators of physical wear
and tear are affected by the chronological age of the
property object, the quality of materials.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Thus, we have identified the actual problems of
taxation of the property of organizations. These
include: the problem of determining the tax base (the
part of the property is determined on the basis of the
cadastral value, the other part is based on the average
annual value); the problem of determining the
properties of the entities (objects of property
considered incorrect or is breached, also is the place
to be double taxation); problems associated with the
unstable tax legislation in the part of Chapter 30 "the
property Tax of the organizations" of the tax code;
problems of corporate property tax evasion; problems
of property exploitation, the useful life of which has
been exhausted.
To solve the identified problems, we propose: to
completely reduce the definition of the taxable base
of the objects of property of organizations based on
the cadastral value; to clarify the objects of real estate
(to evaluate the objects of property of organizations
registered as real estate); to ensure stable tax
legislation (so that the norms of tax legislation are
permanent and accurate); to strengthen the procedure
for tax administration and control (so that there is no
fact of tax evasion); to eliminate worn-out objects of
property from life.
Corporate Property Tax as One of the Factors of Sustainable Development
487

REFERENCES
Abakarova, R. (2020). The reform of the property tax of
organizations. Development of regional economies,
1(42): 107-111.
Aguzarova L. and Aguzarova F. (2018). Planning of tax
payments as a factor of economic growth. European
Research Studies Journal, 21(S2): 195-206.
Alieva, P. (2021). Analysis of the company's financial
performance. Academic journalism, 1: 63-87.
Batashev, R., Kurbanov, S. and Ayubova, J. (2020).
Research on the state of property taxation as a source of
income for regional budgets. Bulletin of the Academy of
Knowledge, 4 (39): 402-406.
Bryzgalin, A. (2020). Accounting policy of an enterprise
for tax purposes. Taxes and Financial Law, 3: 8-106.
Ilyasov, B., Makarova, E., Zakieva, E. and Gizatullina, E.
(2019). Estimation of data on the income of the
population in the regional context by the method of the
main components. Economy of the Region, 15 (2): 601-
617.
Isaev, A. (2019). The effects of inter-regional redistribution
of financial resources: the general equilibrium
approach. Economy of the Region, 15(2): 618-630.
Ivanov, P. and Shitov, A. (2021). Subdivisions for
combating tax crimes (history of origin and
development). Questions of history, 1: 232-239.
Korshunova, L. and Shmalko, M. (2020). Calculation of
property tax taking into account changes in legislation
since January 1, 2020. Accounting in construction
organizations, 3: 26-31.
Kozin, A. (2020). Concessionary agreement: features of
taxation at the concessionaire. Tax policy and Practice,
4 (208): 46-51.
Lermontov, Yu. (2021). Changes in tax legislation since
January 1, 2021. Financial Bulletin: Finance, Taxes,
Insurance, Accounting, 1: 22-31.
Vishnevsky, V., Chekina, V. and Robot V. (2018). Tax
inspector or how it can be used: a review of the
problems and solutions. Journal of tax reform, 4(1): 6-
26.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
488
