
Theoretical and Methodological Foundations of Balanced Regional
Innovation Development
Oksana V. Takhumova
a
Kuban State Agrarian University named after I. T. Trubilin, Krasnodar, Russia
Keywords: Sustainable Development, Balance, Innovation Development, Harmony, Proportionality, Region.
Abstract: At the current stage of the development of scientific thought, the concept of the regional sustainable
development is considered as one of the strategic directions of scientific discussions. The economic content
of the term is based on the principle of harmony, balance, and stability. In this context, the work provides the
scientific substantiation of the sustainable development concept as a stable process independent of
fluctuations in the external and internal environment with the constant development of the social, economic,
technical, institutional environment, taking into account the resource potential. The paper considers the
theoretical aspects of the regional system management, based on the methods of the unity of logical and
historical approaches to research, formalization, and generalization: the terminological apparatus was clarified
and supplemented, including the author's interpretation of the concept of “balanced innovative regional
development”, “sustainable development”. The paper proves that in order to achieve a balanced regional
system development, it is necessary to maintain sustainable growth trends in terms of the main social,
economic and environmental indicators. The study reveals the nature of the emergence of the theory of
sustainable innovative development origin on the basis of G. F. Hegel categorical system, systematizes the
list of the main conditions and factors influencing the process of balanced development of the region, within
which it is determined that the specificity of the regional development is determined by the external and intra-
environment conditions formed by a set of key parameters. The stages of the origin of theories of balance and
the determinants of development are revealed. The results formulated in the study make it possible, on a
scientific basis, to improve the understanding of the regional sustainable development and to develop
instruments of influence to increase the efficiency of agricultural production and accelerate the innovation
process within the study area.
1 INTRODUCTION
At the current stage of the development of scientific
thought, the concept of sustainable development is
considered as one of the strategic directions of
scientific discussions. The economic content of the
term is based on the principle of harmony, balance,
and stability. In our opinion, the above-mentioned
scientific substantiation of the sustainable
development concept identifies a stable process that
does not depend on fluctuations in the external and
internal environment with the constant development
of the social, economic, technical, institutional
environment, taking into account the resource
potential. In the plane of scientific discussions of the
theory and practice of sustainable development, the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7002-7100
emphasis is placed on identifying the factors for
achieving this process. And in relation to the
formation of ideas about balanced development, the
term “sustainability” is not advisable to be regarded
as a synonym. The term “sustainable development”
by itself consists of two concepts. Sustainability is
understood as the property of a system to maintain its
state regardless of external conditions (Azrilian et al.,
2008); in the technical translator's reference book -
the stable state of the system and its ability to return
to its original state (Takhumova, 2020); according to
A.N. Folomev sustainability is a type of state of a
certain economic system in a market environment
(Folomev, 2009); K.S. Tikhonkov applies the ability
to maintain the same behavior of a system (structure)
when exposed to environmental factors to the concept
Takhumova, O.
Theoretical and Methodological Foundations of Balanced Regional Innovation Development.
DOI: 10.5220/0010592504670474
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 467-474
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
467

of stability (Gladilin, 2013). Following the
development of the theory of sustainability, it can be
assumed that this is an unchanging, equilibrium state
of a certain system, which has the properties to return
to its original state under various fluctuations of the
external environment. “Development” is a
movement, a transition from one state to a new,
higher quality level. Modern trends in the
development of modern society are taking place in the
context of an intensification of the globalization
process, and for further scientific substantiation of the
subject of study, it seems most interesting to study the
innovation balance as a condition to achieve
harmony, consistency, and proportionality of the
development of structural elements of the economic
system. Nowadays, the technological order calls for
compliance requirements along with social and
economic stability and increased economic growth in
the innovation sphere, which can serve as a faster way
out of the current crisis situation in the regions of the
country. In the current trend of global production
development, more and more attention is paid to the
concept of compatible and continuous development
of the economy of territories, the environment, and
society, which cannot be achieved without the
implementation of innovations.
The era of globalization generates not only the
dependence of one country on another, but also
necessitates the intensive use of elements of scientific
and technological progress. In this regard, it is
obvious that there is a need for research to promote
innovative products in various industries, towards
building a “green economy”, observing the principle
of maximizing economic growth, without affecting
the quantity and quality of natural assets and using the
resources of the basic and accumulated potential. The
problem of increasing the innovation activity of the
region resulted from the need to transfer the
production processes of the regions to a new stage,
which would increase profitability and provide
society with quality goods and services in the
required quantity.
Innovation balanced development is understood
as the ratio of interdependent elements of the system
on the basis of coordinated actions that ensure its
normal, stable functioning with the continuity of
innovation and financial processes. Innovation is a
promising area of scientific discussion and an integral
part of fundamental research.
Fundamental foundations and basic concepts are
reflected in scientific works of: G.A. Bezdudnyi,
O.D. Smirnova, O.D. Nechaeva (1998), JI.H.
Borisoglebskaya (2010), P.V. Akinin (2015)
conditions (Azrilian et al., 2008), (Smirnova, 1985)
and (Takhumova, 2020).
In modern scientific literature, considerable
attention is paid to the assessment of innovative
activity, N. E. Egorovetal (2015) propose to use an
econometric method to quantify the innovation
activity of economic entities of the region at different
levels on the basis of an innovative spatial-spatial
model, making it possible to assess the role of each
participant in the regional innovation development as
a whole, as well as broken down by specific
municipalities, sectors of the real economy, territorial
innovation clusters, etc. Aspects of forecasting the
dynamics of innovative activity in industries based on
data on changes in the structure and intensity of
competition were considered in the article by R.
Akhmetzianov, V. I. Kosachev (2016), in trade A. N.
Mayorova, et al. (2018). The issues of innovation
activity at the enterprise level are considered in the
work, the authors analyze the impact of cross-border
mergers and acquisitions (M & A) on the innovation
of European firms.
A large number of works are devoted to the study
of various aspects of the development of cluster
initiatives of territorial economic systems and the
state. The study (Falck, O. Heblich, S. Kipar 2010)
assesses the cluster-oriented policy introduced in
Bavaria, Germany, in 1999.
It is believed that the founder of the formation of
this theory is Schumpeter, who at the beginning of the
twentieth century introduced a system of knowledge
about new combinations that are manifested in the
process of transformation and development. The
formation of scientific thought about the innovation
activity development can be traced at all stages of the
evolution of the economy. Back in the 17-18th
century, the famous historian, culturologist A.
Toynbee put forward the idea that the single logic of
development is progress. The origin of the
fundamental foundations of justifying basic
innovations marked the beginning of the first stage,
the outstanding representatives of which were J.
Schumpeter (1930), N. D. Kondratyev (1920), J. Van
Gelderen (1913), S. De Wolf (1924) et al. (Smirnova,
1985) (Mirokhina et al., 2019) (Figure 1).
The second period is devoted to the development
of the functional foundations of innovation
management, an important role in the formation of
scientific thought was played by the ideas of K.
Friedman (1955), R. Nelson (1945), G. N. Sorvin and
Yu. V. Yakovets (1968).
The third stage is associated with the formation of
concepts of innovation systems (G. Mensh, V.
Jevons, A. Gelfand, E. Hansen) (Gladilin, 2013).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
468
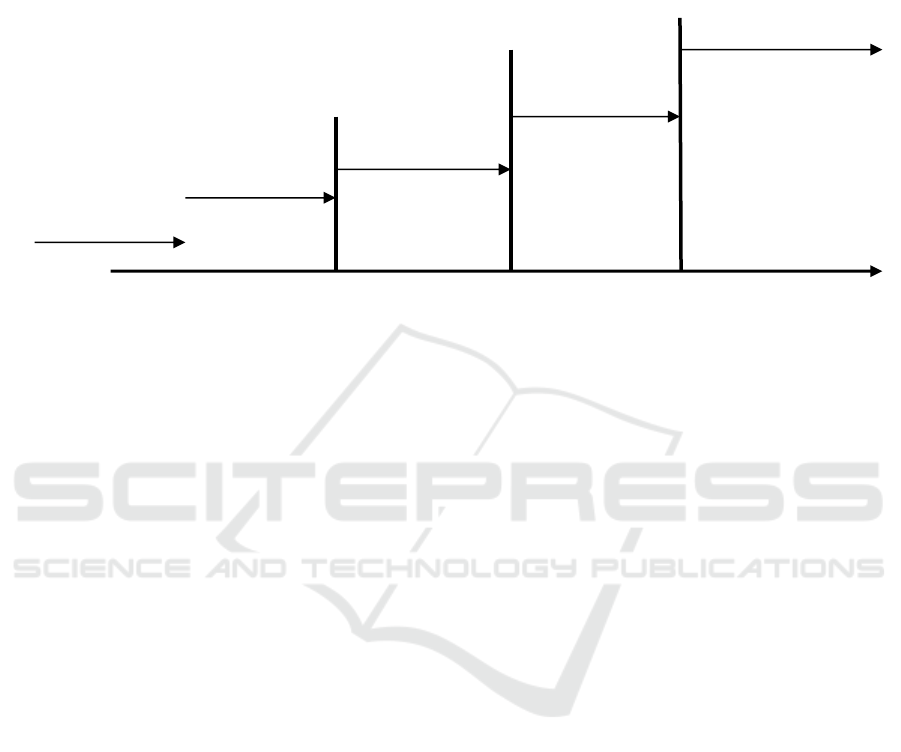
The fourth period in the development of
innovation theories begins in 1980. Thus, K.
Freeman (1982) introduced the concept of a system
of institutions aimed at creating, changing, and
integrating new technologies (Nelson, 2002). B. O.
Lundvall believes that the innovation system is within
the state, based on the principle of interactivity with
the use of new economically reasonable knowledge
(Smirnova, 1985).
Figure 1: Stages of the formation of the innovation sustainable development theory.
An increase in the population, the role of urban
agglomerations, and culture are raising the issue of
providing high-quality and in the required amount of
food products. The ongoing processes have become
an imperative to intensify production through
improved technology. The evolution of economic
development shows that this has made it possible to
increase the population density and improve its well-
being. The origins of the development of agriculture
took place in Egypt and in a number of Asian
countries. In the 6th millennium BC, farmers began
to grow legumes and wheat in India, later in northern
Africa and Europe. The innovation processes of this
period were accompanied by the selection of plant
varieties, the search for ways to increase the
productivity of livestock, and soil reclamation.
Significant progress in agriculture was manifested
during the agrarian revolutions. About 10 thousand
years ago, at the first stage of the Neolithic
transformations, there was an improvement in tools,
soil irrigation, and the appearance of primeval barns
for storing crops. During the Golden Age of Islam
from the 7th - 13th centuries AD, there has been
significant progress in the earth sciences, ending
cycles of food shortages. This period is characterized
by the improvement of agricultural cultivation
technologies, the acquired skills began to actively
spread beyond the borders of the Arab Caliphate. A
massive increase in productivity and the development
of new varieties that bring greater yields occurred
during the British Agrarian Revolution of the 15th
and late 19th centuries. Most scientists call this period
evolutionary in the agriculture development,
associating it not only with the emergence of new
technology, fertilizers, but also with the emergence of
new market segments for the sale of food products.
During the period of Scottish agrarian
transformations, there is a departure from the rune
control system, 1739 is associated with the
appearance of the potato. Among the innovations - the
appearance of the first working header, the
development of a new method of plowing the root-
inhabited layer of soil without top layer deformation.
During the Green Revolution, there was a massive
increase in agricultural products, which has improved
global food security and living standards. The
emergence of aquaculture, according to scientists of
that period, made it possible to bring the growth rate
of agricultural production closer to the growth rate of
the population. However, such a breakthrough in
technology, in methods of soil cultivation, the
emergence of new types of fertilizers, pesticides have
become a threat to the environment. In this regard,
fundamental research began to be based on the search
for ways to increase the well-being of the population
while reducing the load on the ecosystem using the
achievements of the digital economy. It can be
achieved by balancing the economic system elements.
1900 1940 1970
1980
Pre-scientific
stage
1st stage
2nd stage
3rd stage
4th stage
K. Frimen
Yu. Moiseev
L. Tarasova
I. Sandu
J. Schumpeter
N. Kondratyev
J. Gelderen
S. Wolf
K. Friedman
R. Nelson
G. Sorvin
Y. Yakovets
G Menshem
V. Jevons
A. Gelfand
E. Hansen
Theoretical and Methodological Foundations of Balanced Regional Innovation Development
469
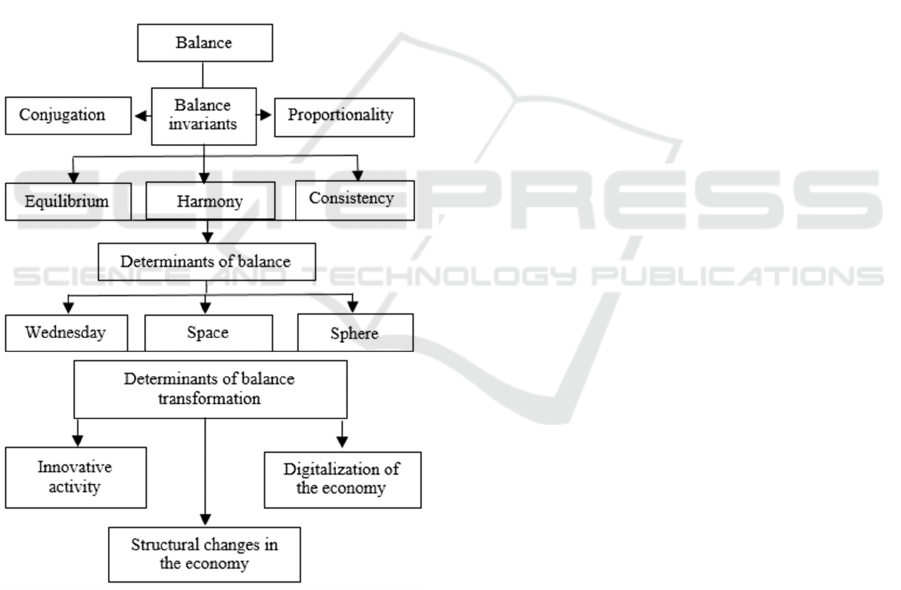
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Summarizing judgments about the content side of the
concept of "balance", we can highlight the nature of
its formation (Figure 2).
Balance is the property of a system to maintain a
set of certain invariants with respect to changes
caused by the determinants of transformations.
Balance has several contexts and areas of study.
Modern trends in the development of modern
society are taking place in the context of an
intensification of the globalization process, and for
further scientific substantiation of the subject of
study, it seems most interesting to study the
innovation balance as a condition to achieve
harmony, consistency, and proportionality of the
development of structural elements of the economic
system.
Figure 2: The nature of the origins of theories of balance.
Innovative balanced development is understood
as the ratio of interdependent elements of the system
on the basis of coordinated actions that ensure its
normal, stable functioning with the continuity of
innovation and financial processes.
It is possible to explicate the concept and nature
of the origin of innovations from the point of the
scientific views of G.F. Hegel. Despite the denial of
the evolutionary approach to development, his
judgment that the development process is determined
by the sequence and connection with the previous
cycles seems to be interesting. The interrelation of
opposites provides the basis for functioning, and the
world is organized in an orderly, natural, and rational
way (Hegel, 2002). The epistemology of Hegel's
teachings is revealed through the constituent parts of
the philosophical system, which includes logic,
philosophy of nature, and philosophy of spirit (Figure
3).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
470
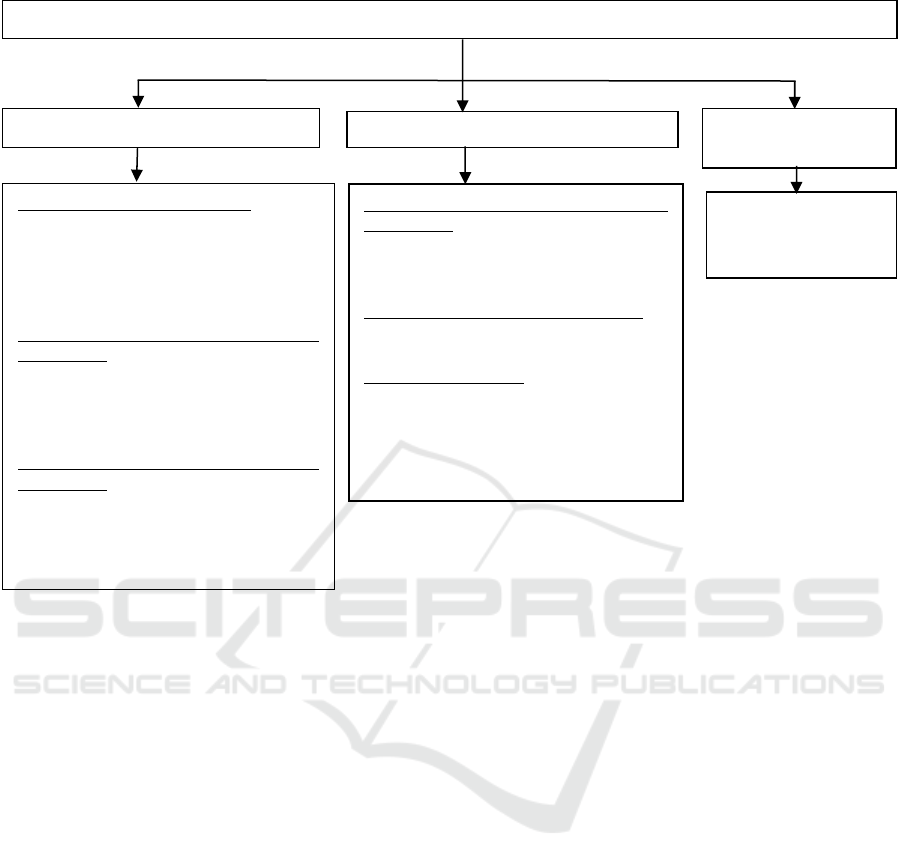
Figure 3: The origin of the theory of sustainable innovation development based on the system of F. Hegel.
The development of social and economic,
technological, international processes is based on the
acceleration of scientific and technological progress.
In agricultural production, this is achieved through
constant renewal based on the achievements of
modern science and technology.
In the world scientific practice, there are enough
approaches to the study of the level of sustainable
development of regions. However, from the point of
a balanced approach, scientific judgments go through
a stage of gradual formation with an emphasis in
research on harmony and proportionality of
development.
Thus, the developed classification of innovations
implementation indicators by the Commission of the
European Community, on the basis of which a system
of indicators was proposed, seems interesting. The
assessment methodology in comparison with the
indicators of competitiveness deserves attention. This
can be achieved on the basis of an innovation policy
in terms of increasing the competitiveness of a market
entity. On the basis of a balanced system of
indicators, including indicators of development,
promotion, the efficiency of innovation, it became
possible to develop an innovative activity index of
regions.
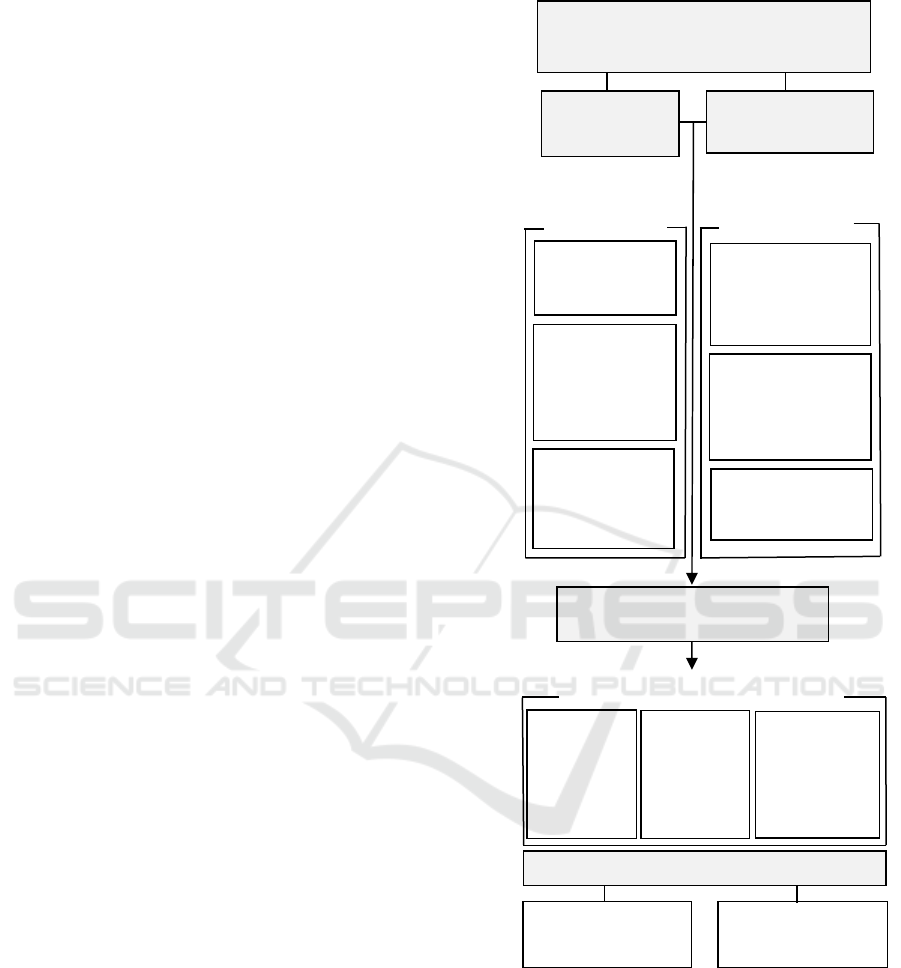
3 RESULTS OF RESEARCH
Based on the generalization of theoretical, practical
scientific ideas on the issues of balanced innovative
regional development, it seems possible to identify
the key factors and conditions, affecting the
harmonious development process in the external and
internal environment key of the forms of agrarians
formation in the region (Figure 4).
To summarize, one can make a judgment about
the multifaceted nature, complexity, inexhaustibility
of scientific judgments, and ideas about the balanced
development of economic systems.
It is believed that a significant contribution to the
formation of the theory of sustainable development of
the modern scientific school was made by WCED
representatives, who, as the main conclusion in “Our
Common Future”, a report put forward a hypothesis
about the need to achieve sustainable social and
economic development with the obligatory
consideration of the environmental factor. In their
Philosophy of the innovation formation syste
m
Source and origin of innovation:
unexpected event;
new knowledge;
changes in value attitudes;
structural market changes;
structural industry changes;
The regularity of the development of
innovations:
changes in technology and production
technology;
social crisis of society;
depression of agricultural production.
The origins of the development of
innovations:
development of society;
formation of laws in nature;
diffusion of innovations;
product differentiation.
The entity
The nature of the entit
y
The source of the
nature of the entity
Spatial characteristics of the diffusion of
innovations:
national level;
regional level;
industry level.
Time characteristic of the main cycles:
innovative activity;
innovation crisis.
Development Feature:
Variability of achievement of the set
goals;
high risks;
satisfaction of a fundamentally new
need.
Individual;
Society;
Religion, art.
Theoretical and Methodological Foundations of Balanced Regional Innovation Development
471
opinion, sustainable development implies meeting the
basic needs of individuals and only in a prosperous
society, there will be no poverty and economic crises.
All consumed goods should be spent in such
quantities that they will be enough for the future
generation.
The formation of theories of balance has been
actively developing in the last few decades.
Representatives of the modern scientific school such
as: Abdeev R. F. Gladilin A. V., Selkov A. V. etc.
identify the concepts of “Balanced Development” and
“Sustainable Development”. However, in our
opinion, each interpretation has its own lexical
meaning and sustainable development is possible
only if a number of conditions are met, including the
obvious fact of the need to achieve a balanced
development of the studied conditions, phenomena in
economic systems (Gladilin, 2013) (Schumpeter,
2007) (Lundvall, 1992).
Balance is the property of a system to maintain a
set of certain invariants with respect to changes
caused by the determinants of transformations.
Figure 4: Systematization of conditions and factors
affecting the balanced innovation development of regions
(compiled by the author).
Based on the analysis of the factors of the
balanced development of the region, the classification
of the main areas of the balanced innovative
development of the agricultural production of the
territories was determined (Figure 5).
Key features
Essence of
occurrence
The nature
of the
essence of
emergence
The origin
of the nature
of the
essence of
arising
S
y
stemic influence of factors and
Promoting
economic growth
Hindering
economic growth
Balanced innovative regional
development
External
conditions
Intra-environment
conditions
Key parameters
The balance of
opportunities
a
n
d
t
hr
eats
The ratio
between the
consumption
accumulation
fun
d
Correlation of
the influence
of STEP
factors
The ability for
self-development
and self-
organization
Availability of
reserves and
innovative
potential
Striving for
improvement
Factors in the formation
of innovative
p
otential
Key parameters
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
472
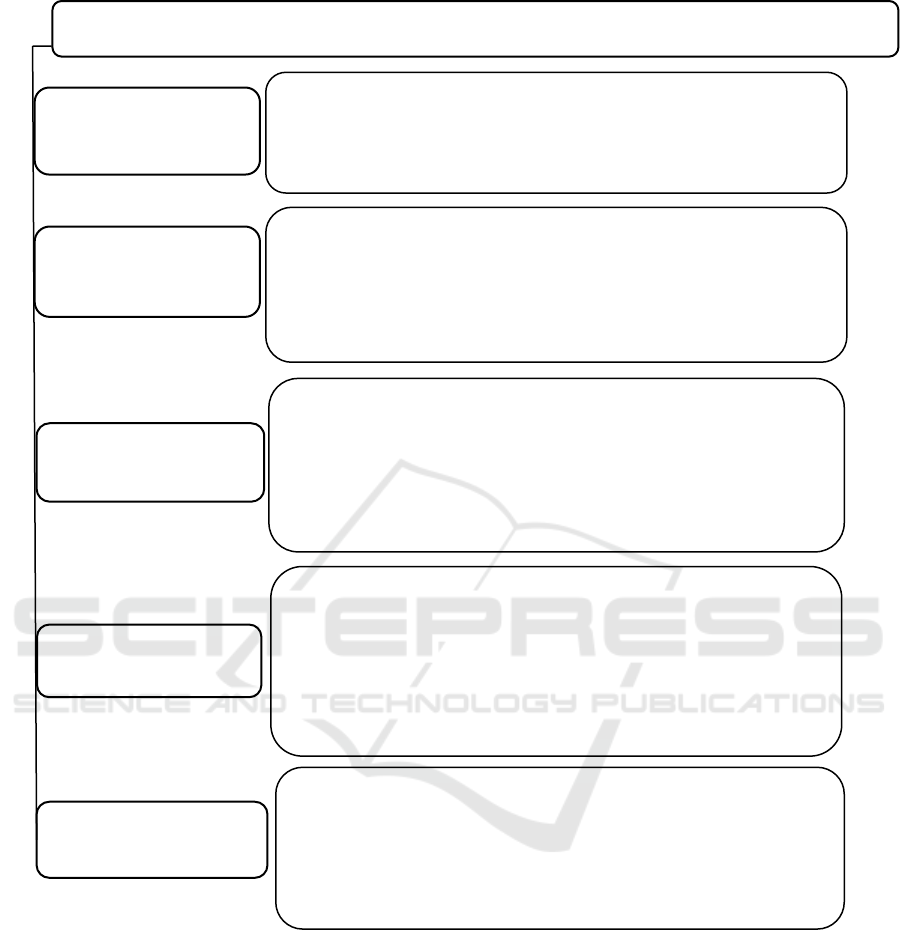
Figure 5: Areas of consideration of balanced innovative development and directions of implementation in the agrarian region
(compiled by the author).
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Thus, the results will help to substantively determine
the need for innovations, depending on the goals of
implementing an innovation policy that contributes to
the effective functioning of agricultural production
and the creation of conditions for sustainable
development of the region. To summarize, one can
make a judgment about the multifaceted nature,
complexity, inexhaustibility of scientific judgments,
and ideas about the balanced development of
economic systems. Balance is understood as the
spatial and coordinated relationship of many elements
of the system that ensure the effective functioning of
the whole in order to create conditions for advanced
growth. Balanced innovative regional development is
the ratio of interdependent elements of the system
based on coordinated actions that ensure its normal,
Areas of consideration of the balanced innovative development of agricultural production in the region
Technical and
technological
Improvement of product processing technologies; production of
innovative high-tech products; the transition of agricultural
producers to new markets, the use of new technologies and related
business models for conducting production activities.
Economic and
environmental
Integration of resource-saving technologies in the production
process; improving the environmental friendliness of products; use
of waste-free technologies for product processing; improving the
energy efficiency of the production process; development of
integration processes in the agro-industrial complex.
Industry
Organization of management of structural elements of the agro-
industrial complex; increasing the efficiency of interregional
cooperation; development, modernization and implementation of
project-oriented programs in production activities based on the
integration and consolidation of scientific resources of production
capabilities and resource base of organizations.
Functional
Improvement of logistics services for the storage and promotion
of agricultural products to the domestic foreign markets;
shortening the period between the investment process and profit
from production; an increase in the share of processing
organizations; providing access to the world information
resources of regional producers in order to gain and exchange
experience.
Aesthetic
Improving the quality of products and
p
ackaging; ensuring a
harmonious relationship between humanity and the surrounding
nature; increasing the functionality of products in accordance with
the needs of society; creation of optimal conditions for increasing
labor productivity; increasing functional orderliness in the
p
roduction activities of a
g
ricultural enter
p
rises.
SPHERES OF INNOVATIVE DEVELOPMENT
DIRECTIONS OF IMPLEMENTATION OF INNOVATIONS
Theoretical and Methodological Foundations of Balanced Regional Innovation Development
473

stable functioning with the continuity of innovation
and financial processes.
5 CONCLUSION
The paper developed the theoretical aspects of the
formation of sustainable development of the regional
system based on the methods of the unity of the
logical and historical approaches to research,
formalization, and generalization: the terminological
apparatus was refined and supplemented, including
the author's interpretation of the concept “balanced
innovative regional development”, which means the
ratio of interdependent elements of the system on the
basis of coordinated actions that ensure its
harmonious, stable functioning with the continuity of
innovation and financial processes. The results can be
used in the development of the main directions of the
national cluster policy and the choice of tools for their
implementation. The results formulated in the study
make it possible, on a scientific basis, to improve the
understanding of the regional sustainable
development and to develop instruments of influence
to increase the efficiency of agricultural production
and accelerate the innovation process within the study
area.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work was performed within the framework of the
RFBR grant No. 20-010-00089 “Formation of an
organizational and economic mechanism for a
balanced innovative development of agricultural
production”
REFERENCES
Azrilian, A.N., Azrielyan O.M., Kalashnikova E.V.,
Kvardakova O. (2008). Big economic dictionary, 1472
p.
Cooke, Ia., Mayers, P. (1996). Introduction to Innovation
and Technology Transfer, 235 p.
Folomev, A. N. (2009). Economic potential of Russia: its
development and effective use, 332 p.
Freeman, C. (1982). Technological infrastructure and
international competitiveness. Draft paper submitted to
the OECD ad hoc group on science, technology and
competitiveness.
Gladilin, A. V. (2013). Balanced development of regions in
a single economic space of Russia, 168 p.
Hansen, E. (1951). Economic cycles and national income,
1: p. 221.
Hegel G.V. (2002). Science of logic.
Lundvall, B.A. (1992). National Innovation Systems:
Towards a Theory of Innovation and Interactive
Learning.
Mirokhina, G., Narozhnaya, O., Takhumova, O. (2019).
Methodical approach to assessing the effectiveness of
business development in the system of market relations.
IAJPS, 06(03): 5747-575.
Nelson, R.R., Winter S.J. (2002). Evolutionary theory of
economic change, 536 p.
Smirnova, N.B. (1985). Methodological foundations for
ensuring the balance of plans for the main production
facilities of the textile industry, p. 133.
Smith, A. (2007). Research on the nature and causes of the
wealth of peoples, 960 p.
Schumpeter, J.A. (2007). Economic development theory,
862 p.
Schumpeter, J.A. (1942) Capitalism, Socialism and
Democracy, George Allen & Unwin, London.
Takhumova, О. (2020) Business Mechanism for
Agricultural Production Sustainable Development
Management. E3S Web of Conferences, 208:7.
https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202020803043
Tool, M. (1993). Institutional Economics: Theory, Method,
Policy.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
474
