
The Fundamental Goals and Principles of Sustainable Development
of a Commercial Bank
Nadezhda N. Semenova
a
and Anastasia A. Vasilkina
b
Department of economics, National Research Mordovia State University, Bolshevistskay Street, Saransk, Russia
Keywords: Sustainable Development, Bank, Principles, Goals of Sustainable Development.
Abstract: Globalization, increased international competition, digital transformation have a significant impact on the
functioning of commercial banks. At the same time, the stability of banks is the most important parameter for
the development of the country's banking system. Under the influence of various endogenous and exogenous
factors on the activities of banks, the time lag in which a credit institution can be in a relatively static, stable
state is reduced. In this regard, the issues of ensuring the stability of the bank acquire particular relevance,
which requires the development of appropriate theoretical and methodological provisions. The authors
substantiated the fundamental principles of sustainable development of a commercial bank, taking into
account the components of the concept of sustainable development: economic, social, environmental and
institutional. Also, in accordance with the main goals within the framework of the four components of goal-
setting, theoretical and methodological principles of sustainable development of a commercial bank are
proposed.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the modern world, banks perform many different
functions: accumulating temporarily free funds of
legal entities and individuals and their placement,
mediation in payments, transactions in the stock and
foreign exchange markets, settlement and cash
services, acquiring, virtual pooling, etc. Banks do not
just accumulate financial resources, carrying out
internal accumulation of funds, they ensure their
continuous movement in order to ensure sustainable
development of the economy, address environmental
and social problems (Bespalov et al., 2019; Cosma et
al., 2020; Zhixia, 2018). Banks can reduce the
negative impact of environmental and climatic factors
on sustainable development by reallocating financial
resources in favor of green sectors of the economy
(Miah et al., 2020).
At the same time, the bank is influenced by many
factors of the external and internal environment,
which can lead to bankruptcy, loss of stability of the
organization (Bitkina, 2018; Semenova et al., 2019).
In this regard, the issues of developing fundamental
goals, principles and criteria for sustainable
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2270-256X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1469-6075
development of commercial banks are highly
relevant.
2 METHODOLOGY
The study is based on an integrated approach that
considers the sustainable development of a bank as a
combination of four components: economic,
environmental, social and institutional. At the same
time, sustainable development is seen as a value
setting and the main goal of any bank.
The study is also based on the historical-genetic
approach, the essence of which is the analysis of
historical trends, the reproduction of the historical
and social logic of the development of economic
systems.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The analysis of modern literature on the sustainable
development of commercial banks allows us to single
Semenova, N. and Vasilkina, A.
The Fundamental Goals and Principles of Sustainable Development of a Commercial Bank.
DOI: 10.5220/0010590403450350
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 345-350
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
345

out two main approaches to disclosing the content of
this definition: broad and narrow.
According to the first approach (foreign scientists
and various organizations), the sustainable
development of a commercial bank is considered
from the standpoint of the main provisions of the
general theory of sustainable development. It
provides an assessment of four main components
(economic, social, environmental and institutional) of
sustainable development of a commercial bank.
Note that the first reference to sustainable
development in banking was used in the World
Bank's report ". Sustainable Banking with the Poor:
A Worldwide Inventory of Microfinance
Institutions." It examined the sustainability of
microfinance institutions as a new, socially oriented
business model for financial activities (World Bank,
1997). However, this report does not provide a
definition of the definition in question, but only
describes the social services that financial institutions
provided to people with low income. The monograph
Sustainable Banking: The Greening of Finance
(2001) by J. Bouma, M. Jeucken and L. Klinkers
argues that banks have a role to play in ensuring
environmental sustainability.
Within the framework of a narrow approach
(Bulanov, 2015; Fetisov, 2003), the sustainable
development of the bank is considered from the
position of ensuring its equilibrium state, and further
prospects under the conditions of the action of
external and internal environmental factors (mainly
of an economic and social nature), without paying due
attention to the changes taking place in the ecological
and institutional environment.
Commercial banks are complex dynamic systems,
the functioning of which obeys the laws of dynamic
equilibrium. They, as adaptive systems, are able to
change their behavior and ensure sustainable
development through managerial influences
(decisions). In our opinion, operating in market
conditions, a commercial bank has boundaries of a
zone of stability, at each point of which the bank
remains stable. These boundaries change depending
on the influence of multidirectional factors: the
political situation in the country and in the world;
changes in the commodity, consumer and labor and
capital markets; changes in legislation in the field of
regulation of financial and credit relations; the policy
of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and
international financial and credit institutions and
others. In the long term, a bank will be sustainable if
its development proceeds along the tube of the
stability zone along the trajectory of sustainable
development. If the vector of the bank's functioning
is stagnant, then at some point the bank may fall out
of the stability zone, which will lead to its
disappearance. Consequently, stability in the short
term does not ensure sustainable development of a
commercial bank in the future. Stability characterizes
the state of the bank in the short term, and sustainable
development - in the long term.
In our opinion, stability is a static state of an
object, characterized by a certain number of stable
values of the parameters of this object. This category
is identified with invariance, i.e. maintaining any
properties, parameters constant for any changes in the
external and internal environment. Sustainable
development is a process aimed at a qualitative and
quantitative change of an object, its characteristics
(parameters). Therefore, the category “sustainable
development” should be viewed from the perspective
of a dynamic approach. In this regard, we understand
the sustainable development of a commercial bank as
its ability to maintain a dynamic balance for a long
time, effectively using its internal potential, adapting
in a timely manner to changes in external and internal
environmental factors in order to achieve its goals.
Thus, according to this approach, it is necessary to
ensure the successful development of the bank in the
long term. In this regard, the sustainable development
of a commercial bank will be considered by us as a
general goal.
Within the framework of this general goal, several
subgoals should be distinguished, i.e. fundamental
goals. In accordance with the concept of sustainable
development, four sub-goals can be distinguished:
economic, social, environmental, and institutional.
Since commercial banks are important actors in
the financial system, which in turn is a component of
the national economy based on market relations, the
dominant goals of banks will be the goals of the
economic component of goal setting, namely: capital
growth and business value growth.
Achievement of this goal is ensured by setting and
achieving a number of derived goals or goals of the
next level. These include:
increasing the client base and increasing the
level of customer loyalty;
establishing long-term partnerships with
influence groups (employees, shareholders,
government bodies, and others);
improving the competitive position of the bank
in the banking and financial services market;
formation of a modern infrastructure of a
commercial bank and the introduction of
modern technologies in order to increase labor
productivity and efficient use of resources;
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
346

increasing the economic efficiency of activities
and management of the bank and its structural
divisions.
The fundamental goals of banks are: formation,
expansion and development of the client base,
increasing the level of customer loyalty. The
activities of a commercial bank should be aimed at
solving the problems of customers (legal entities and
individuals). This determines their loyalty, that is,
their commitment to the bank, their willingness to use
its services for a long time. The higher the level of
customer loyalty, the greater the profit and
profitability of banking.
Achievement by a commercial bank of the goal of
increasing its client base is complicated by the
conflicting interests of primarily two main categories
of clients: depositors and borrowers. Bank depositors
are individuals and legal entities. Entering into a
relationship with the bank, they are interested in high
interest rates on deposits with minimal terms for
placing their funds. At the same time, the bank's
borrowers consider the availability of credit, the
speed and simplified procedure for processing
documents, understated requirements (up to their
complete absence) to collateral, low interest rates and
long borrowing periods as the most important features
of a loan product. The bank also has its own interests.
For him, the quality of the loan is primarily
determined by guaranteed repayment, which, as a
rule, excludes quick procedures for considering
applications and issuing loans, as well as their
complete or partial lack of security. Consequently, the
bank must carry out its financial and credit activities
taking into account the economic interests of all
interested parties. Its regulatory role should be
reflected in the development of a reasonable
economic policy and adequate mechanisms to ensure
a balance of interests of partners not only in the
current period of time, but also in the long term. The
bank must not allow the interests of some partners and
counterparties to dominate over others, therefore one
of the fundamental goals of a commercial bank is to
establish long-term partnerships with influence
groups (stakeholders).
The owners (shareholders) of the bank are
interested in the growth of profits, market value and
sustainable development of the bank. It is important
for managers to ensure the sustainable development
of the bank in a dynamic market environment. The
bank's personnel are interested in confidence in
keeping their jobs, decent wages, and career
opportunities. Clients are interested in the fulfillment
of their obligations by commercial banks on time and
in full. Business partners are interested in the
reliability of the bank, in the clear and timely
fulfillment of its obligations, and trusting relations
with the bank. The authorities are called upon, in
cooperation with the bank, to protect the interests of
society and investors. The society is interested in the
bank's participation in solving national and regional
problems. Thus, the establishment of long-term
partnerships with influence groups based on mutually
beneficial interests is the key to the successful
development of not only the bank, but also its
stakeholders.
Achieving the goal of increasing the economic
efficiency of the bank's activities and management
affects all aspects of the bank's activities and directly
affects its financial condition of the credit institution
(the size and quality of capital and assets, profitability
and liquidity, costs, profitability and profitability), its
compliance with mandatory standards and limits
established The Bank of Russia, it also provides for
improving the quality of management of the bank, its
operations and risks.
Effective management of the bank's divisions is
also of great importance for the efficient operation of
a commercial bank. The bank's organizational
structure directly depends on the chosen business
model. But regardless of the chosen organizational
structure, it must meet the following requirements:
prompt decision-making, no duplication of functions,
quick solution of the assigned tasks.
The second component in the system of
sustainable development of a commercial bank is the
social one. In recent decades, attention has increased
to the problems of social responsibility of business
and its role in the socio-economic development of
society. The problem of socially responsible business
behavior is reflected in the studies of many scientists,
such as G. Bowen (1953), M. Schwartz (2003), J.
Stiglitz (2020), A. Carroll (2017). The concept of
corporate social responsibility provides for the
observance of norms and rules implicitly defined or
undefined by legislation (in the field of ethics,
ecology, mercy, philanthropy, compassion, etc.) that
affect the quality of life of individual social groups
and society as a whole.
The fundamental social goal of a commercial
bank in the system of its sustainable development is
to increase its social responsibility. Its content is
covered by the following sub-objectives:
сompliance with ethical standards of doing
business;
creation of favorable conditions for the life of
bank employees;
The Fundamental Goals and Principles of Sustainable Development of a Commercial Bank
347

joint solution of social problems with partners
and authorities.
Compliance with ethical business conduct is
referred to as "fairplay". Forming the parameters of
the banking product (term, interest, commission), the
bank sets the conditions for working with the client or
the “rules of the game”. A bank focused on
sustainable development must refrain from
misleading customers by including hidden fees and
paid services without notifying the client. Unfair
behavior of credit institutions leads not only to a
deterioration in the economic condition of the client,
but also in the future may lead to a decrease in the
performance of the bank itself, a threat to its
economic stability due to the loss of confidence in it.
Ensuring the harmonious development of the
individual is one of the basic provisions of the
Concept of sustainable development. In this regard,
one of the sub-goals of the social component of the
goal-setting of sustainable development of a
commercial bank is to ensure favorable living
conditions for the bank's employees, which implies
proper working conditions, decent wages,
opportunities for professional and career growth, and
the company's care for its employees. These measures
allow a commercial bank to reduce staff turnover,
build employee loyalty to the company, and increase
the competitiveness of a credit institution by retaining
qualified personnel.
An important goal in the social component of the
goal-setting of a commercial bank is also the joint
solution of social problems with partners and
authorities. This also applies to issues of charity.
Credit organizations can not only make donations, but
also act as a conduit between their clients and
charitable foundations.
The main goal of the environmental component of
goal setting is to increase the bank's environmental
responsibility. Its achievement can be carried out by
setting the following subgoals:
rational use of natural resources, including
energy resources, as well as resources used by
the bank itself (diesel fuel, gasoline, electricity,
natural gas, etc.). This goal can be achieved
through the use of energy-saving technologies,
optimization of the bank's logistics system,
including through cashing and outsourcing.
assistance by the bank in the implementation of
projects related to environmental protection,
rational use of resources, i.e. the so-called
"green" financing of the economy.
The main goal in the institutional component of
goal-setting is the development of the banking
institutional environment. Its implementation
requires the achievement of the following subgoals:
transition to a partnership model of interaction
between a commercial bank, the Central Bank
and authorities. Through participation in
associative structures such as the Association
of Russian Banks and the Association of
Regional Banks, commercial banks have the
opportunity to lobby their interests in
government bodies and contribute to changes
in the legislative and regulatory framework.
development of new forms of interaction
between the bank and partners, assistance in the
development of banking infrastructure. The
digitalization of the economy, IT innovations in
the financial sector, marketing technologies are
changing the environment for the functioning
of commercial banks, in which new
institutional elements appear, such as financial
and technical organizations using technologies
and innovations in the field of financial
services. The integration of a commercial bank
with leased organizations allows us to
significantly expand the boundaries of classical
banking by combining banking and non-
banking products, which contributes to an
increase in the level of customer service and the
profitability of banks.
To achieve the considered fundamental goals, the
bank must be guided by the relevant principles. In
accordance with the main goals within the framework
of the four components of the goal-setting of
sustainable development of a commercial bank, we
have proposed the basic principles of sustainable
development of a commercial bank (Table 1).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
348
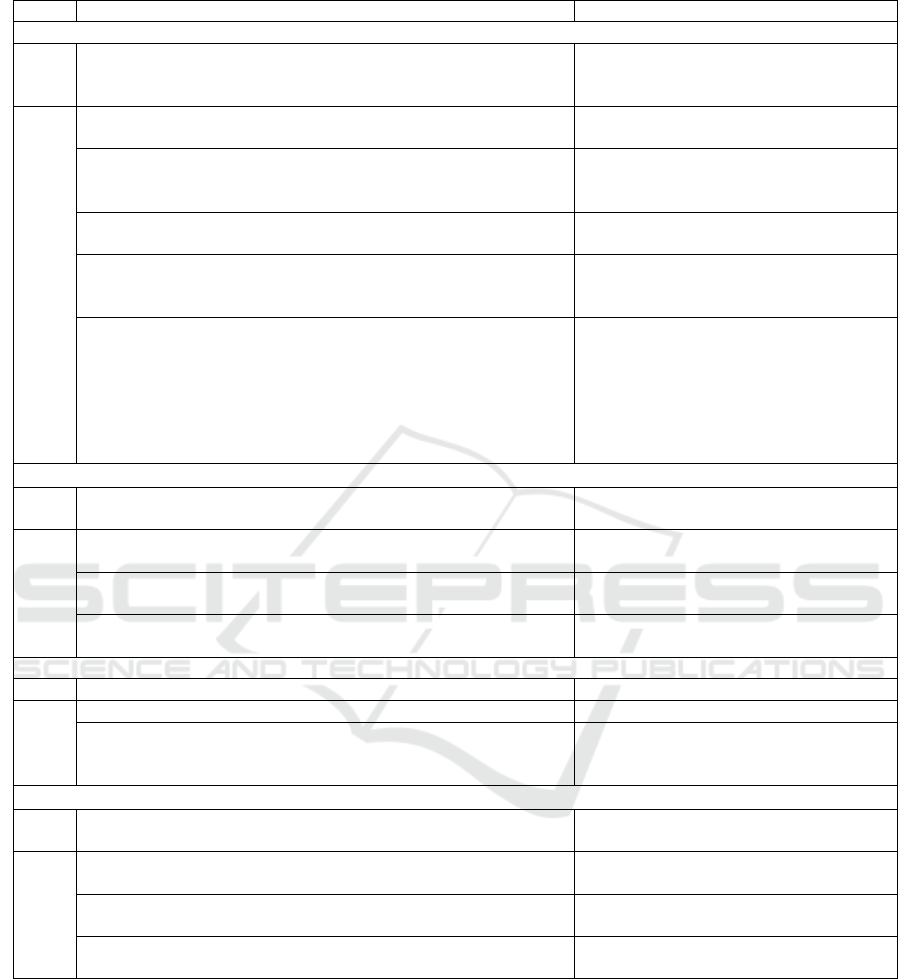
Table 1: Fundamental goals and principles of sustainable development of the bank.
Level Goals Princi
p
les
The economic com
p
onent of
g
oal settin
g
1 1.1. Building up capital
1.2. Business value growth
Capitalization of own income
Capitalization of assets
Business diversification
2 2.1. Increasing the customer base and increasing customer loyalty Customer focus
Customer lo
y
alt
y
2.2. Establishing long-term trust relationships between the bank
and influence groups
Partnerships
Reliability of relationship
Trust
2.3 Improving the competitive position of the bank in the banking
and financial services market
Competitiveness
Com
p
etitive advanta
g
es
2.4. Formation of modern infrastructure of the bank and
introduction of new technologies
Information and technical security
Innovativeness
Securit
y
2.5. Improving the efficiency of activities and management of the
bank and its structural divisions
Effectiveness
Profitability and profitability
Resource saving
Motivation and stimulation of staff and
business partners
Minimizing risks
Trans
p
arenc
y
, o
p
enness of mana
g
ement
The social component of
g
oal settin
g
1 1.1. Increasing social responsibility in relation to shareholders,
em
p
lo
y
ees, customers of the bank and societ
y
as a whole
Social responsibility
2 2.1. Compliance with ethical business conduct Transparency
Fairness
2.2. Creation of favorable conditions for the life of bank
employees
Equity remuneration
Social securit
y
2.3. Joint solution of social problems with partners and
authorities
Social engagement
The ecolo
g
ical com
p
onent of
g
oal settin
g
1 1.1. Increasing the bank's environmental responsibilit
y
Environmental responsibilit
y
2 2.1. Rational use of natural resources Saving natural resources
2.2. Participation in financing and development of projects
related to environmental protection, rational use of natural
resources
Green financing
The institutional component of
g
oal-settin
g
1 Development of the banking institutional environment Participation in the development of the
b
anking institutional environment
2 2.1. Transition to a partnership model of interaction between the
b
ank and authorities
Partnership
2.2. Development of new forms of interaction between the bank
and
p
artners
Cooperation
Inte
g
ration
2.3. Development of modern banking infrastructure Involvement in the development of the
institutional environment
4 CONCLUSIONS
We regard sustainable development as the general
strategic goal of a commercial bank. This goal is
multifaceted, therefore, to achieve it in real practice,
it was structured into sub-goals, which made it
possible to identify the fundamental goals in
accordance with the requirements of the concept of
sustainable development in the following areas
(economic, social, environmental, institutional):
capital accumulation, business value growth;
increasing social responsibility; increasing
environmental responsibility; development of the
banking institutional environment. To achieve them,
it is necessary to implement the goals of the second
level, which reflect the bank's values at this stage of
The Fundamental Goals and Principles of Sustainable Development of a Commercial Bank
349

development. In accordance with the fundamental
goals, the principles of sustainable development
adequate to them have been substantiated.
REFERENCES
Bespalov, R.A. and Antonenko, S.V. (2019). Creation of a
"green" bank in the context of "digitalization" of the
economy. Bulletin of the Bryansk State University, 2:
143-151.
Bitkina, I.K. (2018). The influence of macroeconomic
factors on the deposit operations of commercial banks.
Bulletin of the Moscow Humanitarian and Economic
Institute, 1: 33-39
Bouma, J., Jeucken, M. and Klinkers, L. (2001).
Sustainable Banking: The Greening of Finance,
Sheffield, UK: Greening Publishing, 480.
Bowen, H. R. (1953). Social Responsibilities of the
Businessman. New York: Harper & Row, 248.
Bulanov, Ju.N. (2015). Stability of a commercial bank:
methodological aspects and methods of practical
implementation. Finance, credit, and banks, 3: 58-61.
Carroll, A. B., Buchholtz, A.K. and Shabana, K.M.
(2017). The Institutionalization of Corporate Social
Responsibility. Business and Society, 56 (8):1107-
1135.
Cosma, S., Venturelli, A., Schwizer, P. and Boscia, V.
(2020). Sustainable development and European banks:
Anon-financial disclosure analysis. Sustainability,
12(15): 61-46.
Fetisov, G.G. (2003). Stability of the banking system and
methodology for its assessment. Moskva: Finansy i
statistika, 425.
Miah, M.D., Rahman, S.M. and Mamoon, М. (2020). Green
banking: the case of commercial banking sector in
Oman. Environ Dev Sustain., 23: 2681–2697.
Schwartz M. and Carroll A. (2003). Corporate Social
Responsibility: A Three-Domain Approach. Business
Ethics Quarterly,13(4): 503–530.
Semenova, N.N., Ivanova, I.A. and Gribanov, A.V. (2019).
Assessment of external factors influence on
commercial bank deposit policy formation based on
dynamic modeling. Espacios. 40(13).
Stiglitz J. (2020). Key challenges facing modern finance:
Making the financial sector serve society. Finance:
theory and hractice, 24(2): 6–21.
World Bank (1997). Sustainable Banking with the Poor: A
Worldwide Inventory of Microfinance Institutions.
Washington, DC.
Zhixia, C., Hossen, Md. M. Muzafary, S. S. and Begum, M.
(2018). Green Banking for Environmental
Sustainability-Present Status and Future Agenda:
Experience from Bangladesh. Asian Economic and
Financial Review, 8(5): 571-585.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
350
