
Analysis of Financial Stability of the Insurance Market in
Novosibirsk Region
Mikhail K. Chernyakov
a
, Olesya V. Usacheva
b
and Natalia I. Aksenova
c
Novosibirsk State Technical University, Novosibirsk, Russia
Keywords: Insurance, Financial Stability, Analysis, Risks.
Abstract: The current state of the insurance market is characterized by a high degree of instability. The financial stability
of insurance companies is influenced by a large number of factors, such as the number of contracts, payout
ratio, capital structure, profitability and underwriting risk. The insurance industry acts as a protective barrier
for the country's economy from the effects of various risks, at the same time, the financial stability of insurance
companies is also subject to the influence of risks. The volume of scientific publications indicates the presence
of a steady interest in this problem. However, there is no methodology to establish the relationship between
financial stability and multiple factors influencing it. Our research is aimed at identifying links and
determining the influence of factors on the financial stability of insurance companies. We assumed that the
factors that change the financial stability of the insurance market can be identified and assessed using a
forward-looking analysis of the paradoxical theory of regulation. Based on this analysis, a regression model
was formed for the insurance market of the Novosibirsk region, which can form the basis for predicting the
financial stability of insurance companies.
1 INTRODUCTION
Insurance is a significant part of the country's
financial and credit mechanism, and sustainable
development of this segment contributes to the
development of the economy as a whole and allows
to raise the level of financial activity of the population
and the level of its social protection. The most
important strategic task is to comprehensively
promote the development of the insurance industry
and make it a strategically important Russian
economy sector. Regional insurance markets
represent integral elements of the national insurance
market. Even in the Strategy of development of
insurance activity in the Russian Federation until
2020, the expansion of regional programs for the
development of certain types of insurance was
specified as a measure to ensure sustainable
development of the voluntary insurance sphere.
Ensuring sustainable development of regional
insurance markets is a primary task in ensuring the
development of the insurance industry as a whole.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9837-4849
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2625-8988
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7487-9722
The insurance market's financial stability is its
main fundamental value since the insurer's ability to
timely and fully fulfill its obligations is significant for
all market participants, from the insurer to the
insurance supervisory authorities. As noted by
Konstantinova E. A., Trezorova O. Yu. as a factor
creating the relationship between economic entities
and insurance companies, scientists consider the
maintenance of financial stability of the insurance
organization within the given limits (Konstantinova
and Trezorova, 2016). Problems of estimation of
insurance organizations financial stability cause
steady both scientific and practical interest. In doing
so, scholars reveal different relationships between
industry regulation and insurers' financial stability
(Gavira-Durón et al., 2020), between capital structure
and financial stability (Rubio-Misas, 2020), between
financial stability and risk (Moreno et al.,2020),
between risk and digitalization (Bryzgalov et al.,
2020), between capital and risk (Dacorogna, 2018),
etc.
Chernyakov, M., Usacheva, O. and Aksenova, N.
Analysis of Financial Stability of the Insurance Market in Novosibirsk Region.
DOI: 10.5220/0010588802410250
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 241-250
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
241

Thus, Rubio-Misas, M. investigated the effect of
ownership concentration on risk taking by insurance
companies using Z-score as a validity criterion and
applying a two-step GMM framework. His study
results showed that insurers with a more concentrated
ownership structure tend to have lower levels of
financial stability (Rubio-Misas, 2020).
A study of the performance of Spanish insurance
companies during the economic crisis, based on a
dynamic panel data model, made it possible to
establish a direct relationship between actual
solvency margins and profitability, underwriting risk
and an inverse relationship with size, use of
reinsurance, long-term business and life insurance
specialization. Lower insurance market concentration
also leads to lower solvency margins (Moreno et al.,
2020).
The link between profitability and financial
stability of insurance companies is also discussed in
the article by scientists from Kazakhstan. They
investigated the profitability of insurance companies
by constructing an econometric linear multivariate
regression model and proved that it is influenced by
three indicators, firm size (its assets), fixed
production assets, and financial leverage and
substantiated the possibility of using these indicators
further to predict the profitability and financial
stability of insurance companies. Debt-to-asset ratio
characterizes the extent to which the company fulfills
its current obligations, so the paper focuses on the
need for adequate reflection of liabilities in the
financial statements as the main source of information
for interested users (Kulustayeva et al., 2020).
Insurance companies are the primary means of
protecting the country's economy from various risks
while being affected by risks that reduce their
financial sustainability. Financial globalization has
led to an accelerated growth of financial flows, which
has influenced the state and further the development
of the insurance sector of the economy. The security
of the insurance sector depends on the economic
security of the country as a whole. Palestinian
researchers see the need to study insurance
companies' financial conditions and identify the key
factors affecting their solvency and establish a close
relationship between them (Abdel and Ayyash,
2019).
The global trend shows an increase in systemic
risk due to insurance companies' sensitivity to
changes in interest rates (increasing aggregate risk)
and increased cyber threats (Gómez et al., 2018). The
digitalization of the insurance market creates new
opportunities for market participants, but on the other
hand, it also creates additional risks, such as
cyberattacks. The insurance market's financial
stability is also affected by high competition from the
banking sector, which offers insurance services along
with purely banking products. In doing so, banks
adapt their products to the trends and dynamics that
characterize the global insurance industry (Marzai,
2018). Another factor affecting the insurance industry
and carrying risk is the decline in purchasing power,
as most insurance products are designed for the mass
consumer. Nesterenko E.V. talks about the
interrelation of risks and financial stability of an
insurance company. In particular, it points to the
existence of two types of risks in the insurance
sphere: risks arising directly from the activities of the
insurance organization as an object of economic
activity, as well as risks transferred from the insured
(Nesterenko, 2018). Some authors consider the
presence of losses as a factor affecting insurance
companies' financial stability, which represents an
integral element of economic security in the insurance
sector (Pavlova et al., 2017). They consider the
necessity of risk assessment when accepting a facility
for insurance as an unconditional priority.
Eling, M. et al investigate the possibility of using
artificial intelligence by insurance companies to
improve the quality of loss probability prediction and
reduce asymmetric information. Researchers note
that artificial intelligence can significantly change the
risk landscape by transforming risks, requiring
insurance companies to rethink traditional insurance
coverage and develop adequate insurance products
(Eling et al., 2021).
Russian scientist D.V. Bryzgalov and his
colleagues devoted their research to the consideration
of transformational processes taking place in the
insurance market under conditions of digitalization of
the economy in the context of insurance theory. The
authors identified two indicators to assess the
insurance market's digitalization (the coefficient of
use of new digital technologies and the level of
penetration (digitalization)). They found
heterogeneity in the use of digital technologies across
different insurer business processes: from the
maximum in the organization of sales of insurance
services to the minimum in the risk management of
insurance companies themselves (Bryzgalov et al.,
2020).
The problems of efficiency evaluation of
insurance organizations are studied by the Swiss
scientist Michel Dacorogna. In particular, he points to
the inadequacy of existing performance indicators to
current trends in global insurance development and
notes a gradual shift towards introducing such
indicators as risk-adjusted return on equity, which
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
242
allows assessing the proportionality of profits earned
on a particular insurance contract to the risks
incurred. Central to this is the concept of risk capital
and the need to manage it in maintaining the solvency
of insurance operations (Dacorogna, 2018).
The current state of the Russian insurance market
is characterized as unstable, as evidenced by low
demand for insurance services: the share of insurance
premiums in domestic GDP is 1.4%, which is more
than 4 times lower than the global average. The ratio
of claims paid to premiums paid in 2019 was 41.4%,
i.e., for every ruble paid, the consumer receives 41
kopecks. The slowdown in the insurance market's
development is due to the lack of in-demand
insurance products and their low attractiveness for
consumers (Sukhorukova et al., 2016).
Thus, we can state the undoubted interest of
researchers from different countries to assess
financial stability in the insurance sector. We will try
to identify the parameters affecting financial
sustainability and establish the presence or absence of
relationships between them. As we see it, the research
results will be interesting both for insurance market
regulators and its main subjects: policyholders and
insurers, as well as scientists researching this and
related scientific fields.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
The research is performed using the prospective
analysis of the paradoxical theory of regulation
proposed by M.M. Chernyakova and tested on the
dairy industry's example (Chernyakova, 2019).
3 RESULTS OF RESEARCH
As a regional insurance market, the insurance market
of Novosibirsk region (NSR) was investigated in the
context of factors influencing its financial
sustainability. The peculiarities of the insurance
market infrastructure in the NSR have been
identified, which consists of the prevalence of
branches of federal-level insurance companies in the
market. While only three regional insurers (registered
in NSR) are active, providing a share of 6.15% of the
total premiums collected in NSR in 2019. One insurer
specializes in compulsory health insurance. The other
two, one of which is a mutual insurance company,
specialize in insuring means of land transport (except
for railway transport).
The Novosibirsk Region ranks 8th among Russian
regions (Table 1) and 1st in the Siberian Federal
District (Figure 1).
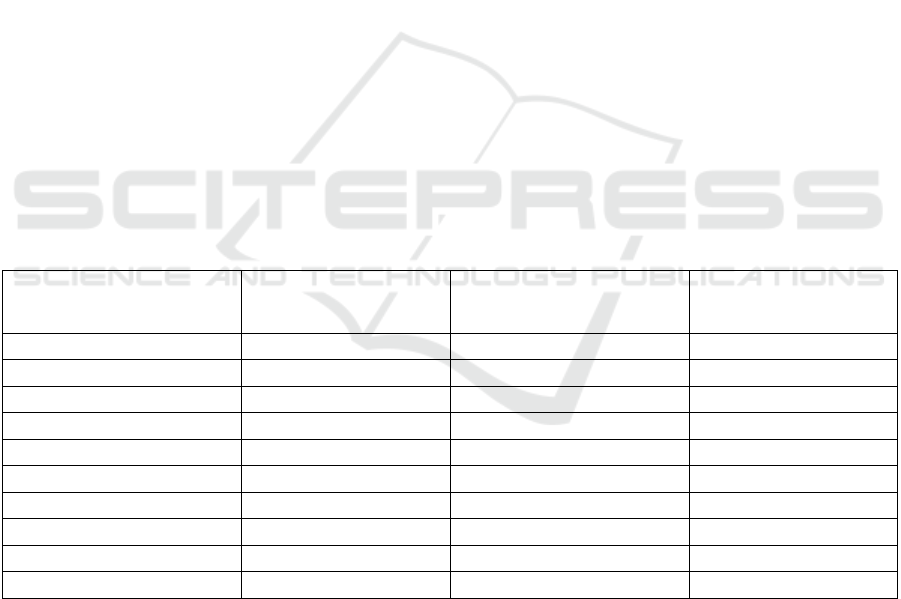
Table 1: Top 10 constituent entities of the Russian Federation in terms of premiums collected in 2019.
Region
Volume of insurance
premiums,
RUB bln
Number of contracts,
million
Volume of
premiums/contract,
thousand roubles
Moscow
727.6 100.4 7.2
St. Petersburg
123.8 8.6 14.4
Moscow region
58.9 6.2 9.5
Re
p
ublic of Tatarstan
27.9 3.6 7.8
Krasnodar Territor
y
26.9 3.9 6.9
Sverdlovsk re
g
ion
26.8 4.2 6.4
Samara region
25.1 2.8 9.0
Republic of Bashkortostan
18.9 2.5 7.6
Chelyabinsk region
18.3 3.2 5.7
Novosibirsk re
g
ion
17.9 2.8 6.4
Analysis of Financial Stability of the Insurance Market in Novosibirsk Region
243
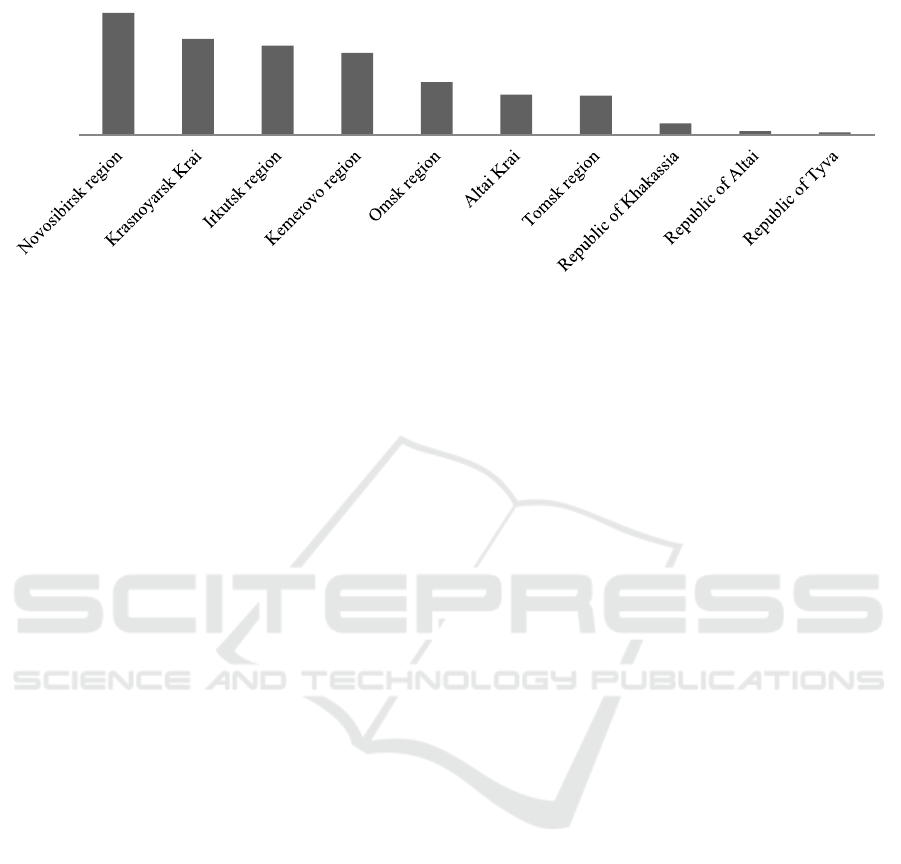
Figure 1: Insurance payments in 2019 by regions of the Siberian Federal District (as % of total).
Nearly 50% of the NSR insurance market in terms
of premiums collected in 2019 is held by 3 financial
groups:
1. 20% - SOGAZ Group - RUB 3.6 billion
(SOGAZ, SOGAZ-Life, VTB Insurance, VTB Life
Insurance)
2. 14% - "Sberbank insurance" - RUB 2,6 billion
("Sberbank Insurance", "Sberbank Life Insurance")
3. 13% - Alfastrakhovanie Group - RUB 2.4
billion ("Alfastrakhovanie", "Alfastrakhovanie -
life".
In 2019, 82 companies were active in the
insurance market of the Novosibirsk region (3
companies more than in 2018). In 2019, 9 new
insurance companies entered the regional market and
6 left the market. The new companies' main product
directions in the market are life insurance, travel
insurance, voluntary medical insurance, and property
insurance of enterprises and individuals.
The Novosibirsk Region's voluntary and
compulsory insurance market, excluding OMI,
amounted to RUB 17.8 billion (+13.3%) in 2019. The
voluntary insurance segment (life insurance, personal
insurance, property insurance) accounted for RUB
13.5 billion or 76%, and the compulsory insurance
segment (MTPL, hazardous facility liability
insurance, carrier liability insurance) accounted for
24%. As the key drivers of 2019 in the Novosibirsk
region market participants note - growth of premiums
in OSAGO, CASCO - insurance of legal entities, in
personal insurance high dynamics in accident and
illness insurance, in particular in bank insurance;
insurance of property of legal entities - cargoes,
means of air transport, insurance of business and
financial risks.
In the voluntary insurance market in the
Novosibirsk region in 2019, life insurance and
pension insurance amounted to RUB 6.03 billion,
which corresponds to 44.6% of the market (+8.2%
compared to 2018). Life insurance (99%) makes the
main contribution to the formation of insurance
premiums in this segment of the insurance market.
Property insurance segment in the voluntary
insurance market in Novosibirsk region increased by
26.4% compared to 2018 and took 31% (RUB 4.2
billion) by the end of 2019. 85% of the property
insurance segment accounts for property insurance
(of which RUB 1.4 billion are premiums under hull
insurance contracts) and 15% for voluntary civil
liability insurance.
Personal insurance reached 24.3% (RUB 3.2
billion) of the voluntary insurance market in the
Novosibirsk region in 2019 (+18.7% vs. 2018).
Accident insurance accounts for 71% (+33.4% vs.
2018 or RUB 2.3 billion). The remaining share is
accounted for by AMI (-6.6% vs. 2018).
In the compulsory insurance market in the
Novosibirsk region, OSAGO is the leader - 98.4%
(+6% vs. 2018) out of 4.4 billion rubles.
The payout rate in Novosibirsk region in terms of
insurance premiums in 2019 was 44% (+5%) or RUB
7.8 billion in absolute values (+25%). In life
insurance, the level of payments from the collected
insurance premiums amounted to 39% or 2.3 billion
rubles (+74%). The level of payments under CASCO
is 57%. Accident insurance - 12%. The level of
OSAGO insurance payouts in 2019 was 80%.
The Novosibirsk Region ranks 10th after federal
cities and 7 regions in terms of premiums collected in
2019 (Table 1). A total of 2.8 million insurance
contracts were concluded; each contract amounted to
an average of 6.5 thousand rubles. For comparison,
among the top 15 regions of the country in terms of
premiums collected, the highest indicator of
premiums collected to the number of contracts is in
22,6%
17,8%
16,5%
15,2%
9,8%
7,5%
7,3%
2,1%
0,7%
0,5%
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
244
St. Petersburg - 14.4 thousand rubles, the lowest one
- in the Rostov region.
The market of insurance services is dominated by
organizations registered in other regions and only 3
organizations and two branches - in NSO
(Gorshkova, 2020). The insurance companies of the
Novosibirsk region almost completely provide
services of voluntary insurance only (Tab. 2). The
insurance fund financial strength ratio was calculated
using the formula:
X19=(X2+X8+X12+X17)/(X3+X18) (1)
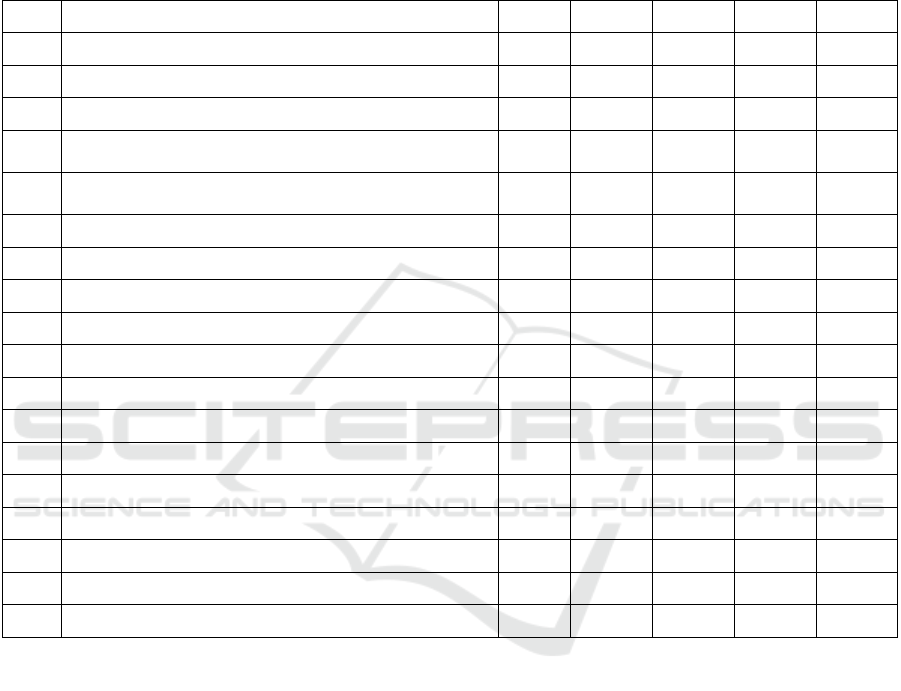
Table 2: Activities of insurers - legal entities registered in the Novosibirsk Region in 2015-2019.
X1 Time period, year 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
X2 Insurance premiums by insurance types, RUB bln 0.885 0.509 0.691 0.772 0.917
X3 Insurance payments by types of insurance, RUB bln 0.303 0.088 0.044 0.036 0.030
X4 Insurance proceeds, RUB bln 0.582 0.421 0647 0.736 0.887
X5
Number of contracts concluded by type of insurance, mln.
units
0.306 0.179 0.229 0.209 0.437
X6
Sum insured under the concluded contracts by types of
insurance, RUB bln
93.724 70.255 67.485 56.362 93.426
X7 Payout ratio by insurance types, % 36.300 18.000 6.500 4.700 3.300
X8 Investment income, RUB bln 1.285 0.048 0.427 1.306 0.339
X9 Share capital, RUB bln 0.969 0.638 0.657 0.657 0.657
X10 Net profit (loss "-"), RUB bln 0,137 0.023 0.064 0.0002 0.158
X11 Equity capital, RUB bln 1.107 0.661 0.720 0.657 0.814
X12 Insurance reserves, RUB bln 1.625 0.271 0.708 0.796 0.916
X13 Leverage 1.468 0.410 0.983 1.212 1.125
X14 Accounts receivable (end of period), RUB bln 0.948 0.769 0.810 0.840 0.901
X15 Accounts payable (end of period), RUB bln 0.242 0.045 0.753 0.847 0.888
X16 Ratio of AR to AP 3.920 17.012 1.076 0.992 1.014
X17 Other income from insurance activities, RUB bln 3.502 0.00317 0.00592 0.00034 0.000
X18 Case Management Costs (CMC), RUB bln 5.693 5.693 0.562 0.659 0.744
X19 Insurance fund financial strength ratio 1.214 0.144 3020 4.137 2.804
According to the data presented in the table,
insurance payouts and business expenses of insurers
tended to decrease during the period under review,
which was reflected in an increase in the insurance
fund financial sustainability ratio. One of the factors
affecting insurers' financial stability is the payout
ratio (X7), the decrease of which in the specified
period was also contributed by the decrease in the
amounts of insurance payouts by insurance types.
Since 2017, there has been a significant decrease in
the accounts receivable (AR) to accounts payable
(AP) ratio. Based on the fact that the value of the
insurance company's AR should roughly correspond
to the value of its AP, we regard this trend as positive.
An excess of AR over AP, as was the case in 2017,
may have as negative consequences the insurance
company's failure to meet regulatory requirements for
the placement of its insurance reserves, which will
result, accordingly, in a lower investment income and
reduced financial stability. This dependence is
confirmed by the data in Table 2 (X8 and X19). There
is also a trend of rapid growth in the profitability of
NSO insurance organizations, due to an increase in
insurance premiums (on average 10% annually) and
a 10-fold decrease in insurance payouts in 2019
relative to 2015. These results were achieved by
changing the proportions of personal and property
insurance - growth of personal and reduction of
property insurance (Fig. 2). It is worth noting that the
growth in insurance premiums occurred against the
backdrop of a decline in the number of insurers from
five to three in 2016.
Analysis of Financial Stability of the Insurance Market in Novosibirsk Region
245
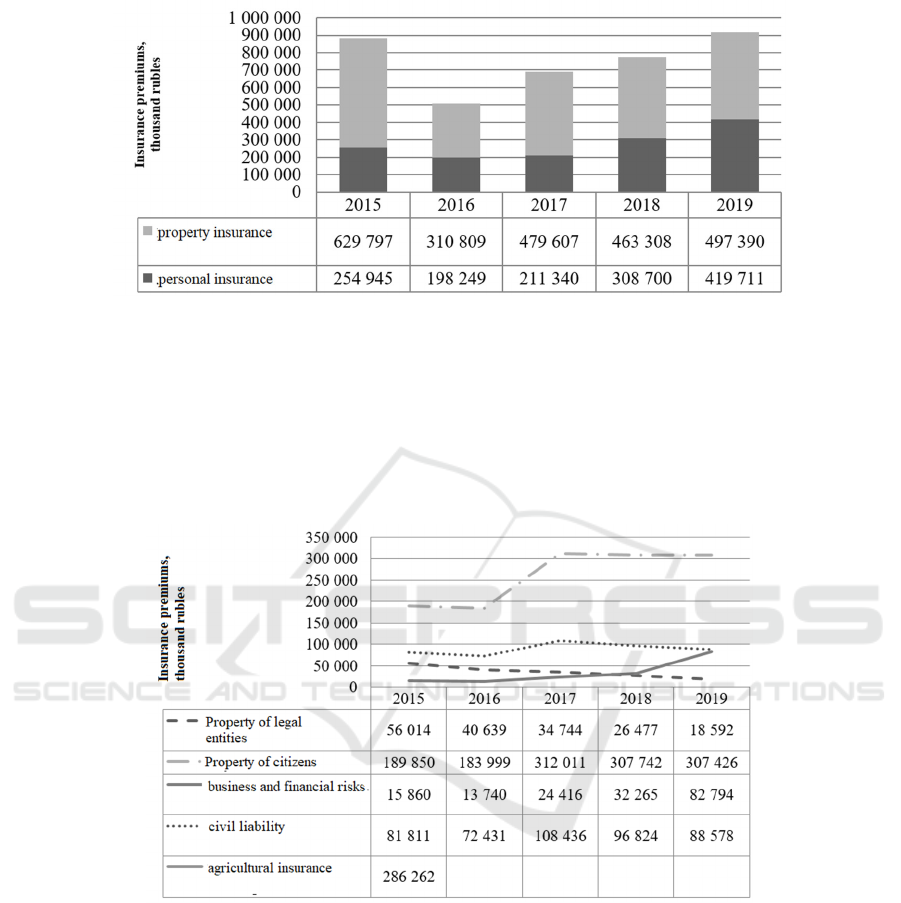
Figure 2: Changes in the structure of voluntary insurance.
The sharp decline in property insurance in 2016
(fig. 2) is associated with the exclusion of high-risk
agricultural insurance from the list of services of
insurers - legal entities registered in the Novosibirsk
Oblast (fig. 3) (Gorshkova, 2020). This was a
consequence of an erroneous management decision to
include state support for agricultural insurance in the
"single subsidy". The resulting management risk led
to an increase in psychological risk, which led to the
mass abandonment of insurance by economic entities
of the agricultural sector (Chernyakov and
Chernyakova, 2021), (Chernyakov and Chernyakova,
2019).
Figure 3: Change in the structure of voluntary insurance by individual types of insurance.
The correlation analysis of the table 2 shows the
possible direct close to linear relationship (R>0,7) of
time period (X1) with 8 of 18 insurance market
parameters (table 3): insurance payments (X3),
earnings (X4), payout ratio (X7), authorized capital
(X9), accounts payable (X15), other income from
insurance activities (X17), costs of doing business
(X18) and insurance fund financial stability
coefficient (X19). According to the paradoxical
theory of regulation (Chernyakova, 2019), other
parameters can be related to the time period only
indirectly, through parameters of direct influence.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
246
Table 3: Correlation analysis of insurers - legal entities registered in the Novosibirsk region in 2015-2019.
X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 X10 X11 X12 X13 X14 X15 X16 X17 X18 X19
X1 1.0 0.3 -0.8 0.8 0.4 -0.1 -0.9 -0.2 -0.7 0.0 -0.5 -0.3 0.0 -0.1 0.9 -0.5 -0.7 -0.9 0.7
X2 0.3 1.0 0.3 0.8 0.8 0.6 0.1 0.5 0.5 0.7 0.6 0.8 0.9 0.9 0.5 -0.8 0.4 -0.3 0.4
X3 -0.8 0.3 1.0 -0.4 0.1 0.5 1.0 0.5 1.0 0.4 0.9 0.8 0.4 0.6 -0.6 0.1 1.0 0.8 -0.5
X4 0.8 0.8 -0.4 1.0 0.7 0.2 -0.6 0.2 -0.2 0.4 0.0 0.3 0.5 0.5 0.9 -0.8 -0.2 -0.8 0.8
X5 0.4 0.8 0.1 0.7 1.0 0.8 -0.1 0.0 0.2 0.9 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.7 0.4 -0.5 0.2 -0.2 0.2
X6 -0.1 0.6 0.5 0.2 0.8 1.0 0.5 0.0 0.6 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.8 -0.2 -0.1 0.6 0.3 -0.4
X7 -0.9 0.1 1.0 -0.6 -0.1 0.5 1.0 0.3 0.9 0.3 0.8 0.6 0.2 0.4 -0.8 0.3 0.9 0.9 -0.7
X8 -0.2 0.5 0.5 0.2 0.0 0.0 0.3 1.0 0.6 0.0 0.5 0.7 0.8 0.6 0.2 -0.5 0.6 0.0 0.4
X9 -0.7 0.5 1.0 -0.2 0.2 0.6 0.9 0.6 1.0 0.5 0.9 0.9 0.7 0.8 -0.4 -0.1 1.0 0.6 -0.3
X10 0.0 0.7 0.4 0.4 0.9 1.0 0.3 0.0 0.5 1.0 0.8 0.7 0.5 0.8 0.1 -0.4 0.5 0.1 -0.1
X11 -0.5 0.6 0.9 0.0 0.5 0.8 0.8 0.5 0.9 0.8 1.0 0.9 0.7 0.9 -0.3 -0.2 0.9 0.5 -0.3
X12 -0.3 0.8 0.8 0.3 0.5 0.6 0.6 0.7 0.9 0.7 0.9 1.0 0.9 0.9 0.0 -0.5 0.9 0.2 0.1
X13 0.0 0.9 0.4 0.5 0.5 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.7 0.5 0.7 0.9 1.0 0.9 0.4 -0.8 0.6 -0.2 0.5
X14 -0.1 0.9 0.6 0.5 0.7 0.8 0.4 0.6 0.8 0.8 0.9 0.9 0.9 1.0 0.2 -0.5 0.7 0.1 0.1
X15 0.9 0.5 -0.6 0.9 0.4 -0.2 -0.8 0.2 -0.4 0.1 -0.3 0.0 0.4 0.2 1.0 -0.8 -0.5 -1.0 0.9
X16 -0.5 -0.8 0.1 -0.8 -0.5 -0.1 0.3 -0.5 -0.1 -0.4 -0.2 -0.5 -0.8 -0.5 -0,8 1.0 -0.1 0.7 -0.8
X17 -0.7 0.4 1.0 -0.2 0.2 0.6 0.9 0.6 1.0 0.5 0.9 0.9 0.6 0.7 -0.5 -0.1 1.0 0.6 -0.4
X18 -0.9 -0.3 0.8 -0.8 -0.2 0.3 0.9 0.0 0.6 0.1 0.5 0.2 -0.2 0.1 -1.0 0.7 0.6 1.0 -0.9
X19 0.7 0.4 -0.5 0.8 0.2 -0.4 -0.7 0.4 -0.3 -0.1 -0.3 0.1 0.5 0.1 0.9 -0.8 -0.4 -0.9 1.0
Table 2 shows that income (X4) has a direct
relationship (R>0.7) with insurance premiums (X2)
and the number of concluded contracts (X5), while
the latter is directly related (R>0.8) to the sum insured
on concluded contracts (X6) and net profit (X10).
Table 2 also shows that statutory capital (X9) has
a direct relationship (R>0.7) with equity (X11),
insurance reserves (X12), leverage (X13), and
accounts receivable (X14), while the penultimate is
directly related (R>0.8) to investment income (X8).
Given the existing system of relationships
according to the paradoxical theory of regulation
(Chernyakova, 2019), a regression model can be
built. The algorithm of such a three-level model is
shown in Figure 4.
Analysis of Financial Stability of the Insurance Market in Novosibirsk Region
247
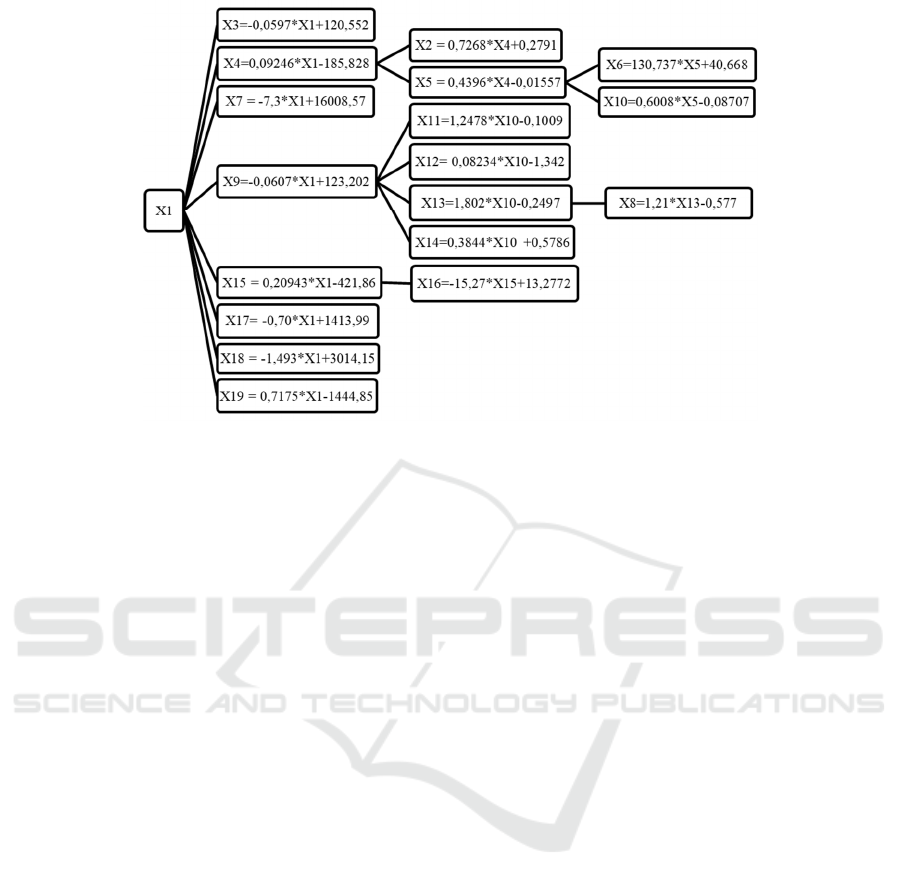
Figure 4: Algorithm of the mathematical model of the insurance market in the Novosibirsk Region.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The correlation analysis showed that the closest
directly proportional relationship, which is close to
functional, exists between the financial stability
coefficient of the insurance fund and the amount of
accounts payable (X15, correlation coefficient R =
0.9) as well as the amount of income from insurance
(X4, correlation coefficient R = 0.8). Close inverse
correlation was revealed between the insurance fund
financial stability coefficient and the cost of doing
business (X18, R = - 0.9), and the RS/CA ratio (X16,
R = - 0.8). Also, an inversely proportional
dependence was revealed between financial stability
and payout ratio by types of insurance (X7, R = - 0.7).
This means that a decrease in the share of insurance
claims has a positive impact on financial stability.
This finding is consistent with the results of the study
(Komen, 2012), but contrary to the research (Abdel
Jawad, 2019). The value of the correlation coefficient
below 0.7 suggests that there is no close relationship
between the performance indicator and the
parameters. We found that there is no explicit
relationship between insurance fund financial
strength and leverage (X13, R = 0.5) and return on
investment (X8, R = 0.4). At the same time, we allow
for the possibility of indirect influence of these
factors on financial stability.
Second-order factors were identified, through
which it is possible to influence the financial stability
of the insurance fund with the help of the first-order
factors we established earlier. The highest correlation
is established between the coefficient of payments by
insurance types and other income from insurance
activities (X17, R = 0.9), as well as costs of insurers'
case management (X18, R = 0.9). A linear functional
relationship is established between the size of
accounts payable and the cost of doing business (R =
-1.0), a relationship that is close to a functional one
between the size of accounts payable and insurance
income (X4, R = 0.9).
The analysis also revealed that there is a close
correlation between the time period and the amount
of insurance payments, the amount of income and the
payout ratio, which is close to a functional
relationship (correlation coefficient R >0.7).
Moreover, between the period of time and the amount
of insurance payments (R = - 0.82), as well as the
payout ratio (R = - 0.90) the dependence is inversely
proportional, i.e. with growth of the period of time the
values of these indicators will decrease. There is no
linear dependence between the period of time and
such factors as: insurance premiums, number of
concluded contracts by insurance types and sum
insured (the relation is weak, R is less than 0.5). We
assume that we cannot abstract from the influence of
the last named factors, as they affect the time period
indirectly through those parameters with which a high
correlation is established. We also found a high
relationship between the income indicator and
premiums (R = 0.77) and the number of contracts
signed (R = 0.74) and between the number of
contracts signed and the sum insured (R = 0.81). The
established relationships made it possible to form a
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
248

regression model for insurance companies of the
Novosibirsk region.
The obtained results confirm our hypothesis and
allow us to speak about the existing dependence
between the financial indicators characterizing the
activities of insurance companies and affecting their
financial stability.
5 CONCLUSION
The article reveals a comprehensive systematic
approach to assessing the impact of factors on
insurance companies' financial stability on the
example of economic entities of the Novosibirsk
region.
The research results indicate the presence of
common patterns and correlations between the
indicators characterizing the activities of insurance
companies and the financial stability of insurers. The
conducted analysis allows us to state that there are
direct and inverse proportional relationships between
certain financial indicators. Simultaneously, the lack
of correlation does not reject the fact of influence on
the financial stability of insurance organizations. We
concede that this influence is manifested indirectly
through other parameters.
This, in turn, indicates the possibility of managing
financial stability for given parameters based on a
mathematical model in the form of a system of
regression equations.
The research contributes to the development of
theoretical approaches to assessing insurance
companies' financial stability based on paradoxical
regulatory theory. The research's practical value lies
in the possibility of using the proposed approach to
assess and forecast financial stability taking into
account various parameters.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Novosibirsk State
Technical University (project TP-AUF-3-21).
REFERENCES
Abdel Jawad, Y. A. L. and Ayyash, I. (2019). Determinants
of the Solvency of Insurance Companies in Palestine.
International Journal of Financial Research, 10(6):
188. https://doi.org/10.5430/ijfr.v10n6p188
Bryzgalov, D. V., Gryzenkova, Y. V. and Tsyganov, A. A.
(2020). Prospects for Digitalization of the Insurance
Business in Russia. Financial Journal, 12(3): 76–90.
https://doi.org/10.31107/2075-1990-2020-3-76-90
Chernyakov, M. K., Chernyakova, M. M. (2021). A system-
inno-diversified approach to the development of
technologies for the effective transformation of
organizations of the agro-industrial complex into a
digital economy. IOP Conference Series: Materials
Science and Engineering, 1019: 11 p. DOI:
10.1088/1757-899X/1019/1/012026.
Chernyakov, M. K., Chernyakova, M. M. (2019)
Innodiversification model of the digital economy of the
agricultural sector. Advances in Social Science,
Education and Humanities Research, 240: 562-567.
DOI: 10.2991/sicni-18.2019.114.
Chernyakova, M.M. (2019). Paradoksal'naya teoriya
regulirovaniya: monografiya, 160 p.
Dacorogna, M. (2018). A change of paradigm for the
insurance industry. Annals of Actuarial Science, 12(2),
211–232. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1748499518000040
Eling, M., Nuessle, D. and Staubli, J. (2021). The impact of
artificial intelligence along the insurance value chain
and on the insurability of risks. The Geneva Papers on
Risk and Insurance, Issues and Practice.
https://doi.org/10.1057/s41288-020-00201-7
Gavira-Durón, N., Mayorga-Serna, D. and Bagatella-
Osorio, A. (2020). The financial impact of the
implementation of Solvency II on the Mexican
insurance sector. The Geneva Papers on Risk and
Insurance, Issues and Practice.
https://doi.org/10.1057/s41288-020-00196-1
Gómez, F. and Ponce, J. (2018). Systemic Risk and
Insurance Regulation. Risks, 6(3): 74.
https://doi.org/10.3390/risks6030074
Gorshkova, S.O. (2020). Strakhovoy rynok Novosibirskoy
oblasti v 2015-2019 godakh. Statisticheskiy sbornik, 28
p.
Konstantinova, Ye.A., Trezorova, O.YU. (2016). Problemy
i perspektivy razvitiya strakhovaniya v Rossii, Vestnik
Instituta ekonomiki i upravleniya Novgorodskogo
gosudarstvennogo universiteta im. Yaroslava
Mudrogo, 2(21):47-54.
Kulustayeva, A., Jondelbayeva, A., Nurmagambetova, A.,
Dossayeva, A. and Bikteubayeva, A. (2020). Financial
data reporting analysis of the factors influencing on
profitability for insurance companies.
Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues, 7(3):
2394–2406. https://doi.org/10.9770/jesi.2020.7.3(62)
Marzai, E. (2018). Bancassurance in a digital era.
Proceedings of the International Conference on
Business Excellence, 12(1): 601–611.
https://doi.org/10.2478/picbe-2018-0054
Moreno, I., Parrado-Martinez, P. and Trujillo-Ponce, A.
(2020). Economic crisis and determinants of solvency
in the insurance sector: new evidence from Spain.
Accounting and finance, 60(3):2965–2994.
https://doi.org/10.1111/acfi.12422
Nesterenko, Ye.V. (2018). Issledovaniye protsessov
ekonomicheskoy kontsentratsii na rossiyskom
strakhovom rynke. Korporativnaya ekonomika,
3(15):24-31.
Analysis of Financial Stability of the Insurance Market in Novosibirsk Region
249

Pavlova, T.A., Kosyakova, M.V., Shalimov, YA.O. (2017).
Protsedura anderraytinga i yeye rol' v ekonomicheskoy
bezopasnosti strakhovykh kompaniy. Aktual'nyye
problemy sotsial'no-gumanitarnykh nauk. Sbornik
nauchnykh trudov po materialam Mezhdunarodnoy
nauchno-prakticheskoy konferentsii, pp.92-99.
Reyting strakhovykh kompaniy Novosibirska (2021).
NSK.DK.RU URL: https://nsk.dk.ru/wiki/reyting-
strakhovykh-kompaniy
Rubio-Misas, M. (2020). Ownership structure and financial
stability: Evidence from Takaful and conventional
insurance firms. Pacific-Basin Finance Journal, 62,
101355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacfin.2020.101355
Sukhorukova, N., Ivashchenko, T., Tsvyrko, A. (2016).
Current state of the insurance market in Russia. Central
Russian Journal of Social Sciences, 11(1): 138–144.
https://doi.org/10.12737/18240
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
250
