
An Open Platform for Smart Production: IT/OT Integration
in a Smart Factory
Dan Palade
a
, Charles Moller
b
, Chen Li
c
and Soujanya Mantravadi
d
Department of Materials and Production, Aalborg University, Denmark
Keywords: Industry 4.0, Smart Production, Smart Factories, Enterprise Information Systems, ERP, MES, IoT, IT/OT
Integration, Vertical Integration.
Abstract: As industries are becoming increasingly digitalized, new manufacturing concepts require redesigning the
information systems architecture. The Smart Production Laboratory is used as a learning factory aimed at
exploring new industry 4.0 technologies and for demonstrating Smart Production solutions. The initial Smart
Production Laboratory was built on a proprietary software stack. Experimenting with the information systems
architecture using proprietary systems has shown to be difficult, which is why we built a complete modular
open-source software stack for the Smart Production Laboratory intended to enable high-speed and low-cost
development of demonstrators for research, teaching, and innovation. Therefore, the purpose of this research
is to capture the development of the software stack and identify the required target architecture for the
platform. This is further used for discussing potential future challenges in demonstrating new and innovative
Smart Production concepts.
1 INTRODUCTION
The industry 4.0 movement has seen a vast interest
from the manufacturing world as well as academia
[Xu, Xu & Li]. It entails a complex transformation of
the industrial environment focused on digitalization
and connectedness that leads to enterprise
transparency and holism. As production is being
increasingly digitalized, everything inside and
outside a factory is becoming instrumented,
interconnected and intelligent.(Martin et al., 2010)
The new technologies driven forward by the
Industry 4.0 movement have challenged the
manufacturing industry to transform and to develop
new and innovative solutions (Kagermann, 2015).
Those new solutions often require substantial changes
in the information systems and the architecture of the
enterprises (De Jong, Lalla-Sewgoolam and
Vainberg, 2019). Planning and managing changes in
the enterprise architecture is a complex and long-term
endeavor, and consequently, the architecture is not
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6595-7215
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0251-3419
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6249-8957
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9382-8314
designed but emerges as a consequence of legacy
systems and past IT-projects (Ross and Weill, 2006).
Smart Production is a research capturing the
industry 4.0 challenges from an industrial point of
view, and one of the elements, smart factories, have
been in the center of a number of research projects
over the last few years at Aalborg University (Madsen
and Møller, 2017). We have established and built a
Smart Production Laboratory environment, further
called Smart Lab, where we can emulate end-to-end
industrial manufacturing in a scaled-down version,
but with real industrial-grade technologies and
systems (Nardello, Madsen and Møller, 2017).
During the research and innovation projects, a
larger number of industrial demonstrators have been
developed. A demonstrator uses Smart Lab as a
platform to demonstrate a particular solution in a
scaled-down but realistic context. A central aspect of
these demonstrators is the underlying information
architecture and the platform they are built on.
The objective of this paper is to build and capture
the development of a modular open platform for
Palade, D., Moller, C., Li, C. and Mantravadi, S.
An Open Platform for Smart Production: IT/OT Integration in a Smart Factory.
DOI: 10.5220/0010436807070714
In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2021) - Volume 2, pages 707-714
ISBN: 978-989-758-509-8
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
707
smart production (OP4SP). The OP4SP is a
simplified enterprise software stack built on open-
source components and designed to be easily
integrated with any production system. The
foundation of the paper is a state-of-the-practice
analysis of the enterprise systems architecture with
the outset in (Li, Mantravadi and Møller, 2020),
leading to formulating the high-level platform
requirements. The next chanpter presents and
discusses the background of the research and the
concrete challenge leading to developing OP4SP,
while chapter 3 present the methodology for this
research. In chapter 4 we scrutinize the need for such
experimental platform through the analysis of four
research engagements where part of the solution was
applied. This led to formulating the target architecture
for the platform, where the selected components are
outlined. In the last chapter, we identify the gaps and
recommend further use and development of the
platform.
2 BACKGROUND
In this section, we provide the background for the
research and conceptualize the enterprise software
stack in regard to smart production. An analysis of
state-of-the-practice is presented, which drives the
research objective.
2.1 The Smart Production Laboratory
In order to make sense of this complex
transformation, a smart production concept covering
horizontal and vertical integration, end-to-end
engineering integrations, as well as customer and user
interactions was created that provides a lens of clarity
towards the impact of Industry 4.0 on a
manufacturing company.
The Smart Factory is the concepts within the that
framework. A common understanding of the term
refers to a highly digitized shop floor with connected
machines and devices that collect and share data
through information systems. It shares features and
goals with related areas such as smart home and smart
city.
At our institution Smart Lab was developed in
order to drive the research related to smart factories.
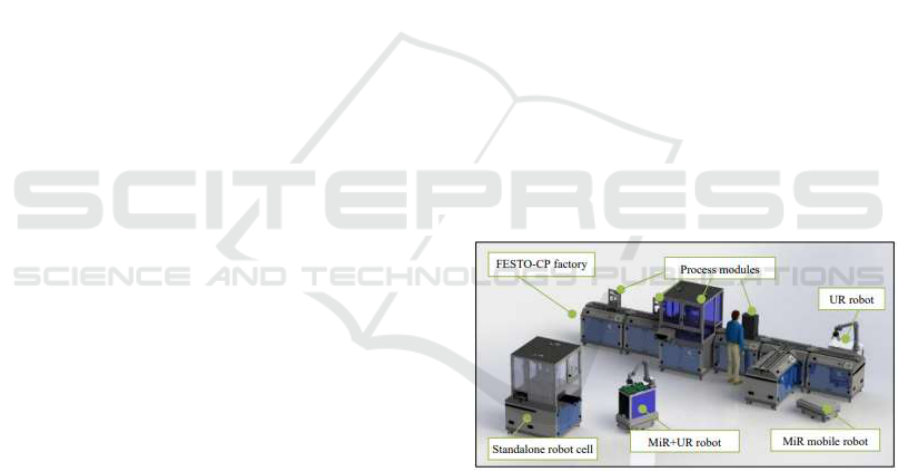
The Smart Lab (see overview in figure 1) acts as a
learning factory to enable collaborative projects
between researchers, students and enterprises. It is a
fully automated small production line integrating and
demonstrating various Industry 4.0 concepts and
technologies.
The Smart Lab is composed of several standard
FESTO-CP factory transportation modules (conveyor
belts), process modules like parts dispenser, drilling
module, and assembly module, as well as dedicated
integrated robots and mobile robot platforms. From a
data perspective, everything is IP enabled. All
modules have at least one PC controlling the sensors
and actuators. It is integrated using an MES system,
which acts as a unified system for controlling the
production line. It is a proprietary solution that came
from FESTO (MES4) with the procurement of the
line, and incorporates a couple of ERP specific
jurisdictions, like order creation and bill of materials.
In the last couple of years, several projects with the
scope of bringing transparency and connectedness to
the Smart Lab took place, which culminated with
demonstrators being presented to the industry.
Through these projects, we observed that a common
obstacle was to integrate the information systems and
allow for shared data and interoperability within the
system. To bypass this issue, we strive to create a
platform that encompasses minimal required software
applications to ensure streamlined order management
and monitoring. For this, we will use open-source
tools paired with standard protocols. The rest of the
chapter will present the hierarchical model of relevant
information systems and the argument for using open-
source software.
Figure 1: The representation of AAU Smart Production
Laboratory (Nardello, Madsen and Møller, 2017).
2.2 Enterprise Systems
Enterprise systems are information systems directed
at helping enterprises to collect, store, and distribute
relevant information with the aim to support
operations, decision-making, and general
management. There are multiple tools characterized
as enterprise systems: ERP (Enterprise Resource
Planning), MES (Manufacturing Execution System),
CRM (Customer Relations Management), PLM
(Product Lifecycle Management), CPM (Corporate
Performance Management), BA (Business
ICEIS 2021 - 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
708

Analytics), and other (Møller, 2005). However, in a
manufacturing context, the information systems do
not have the same weight (in terms of importance),
and there is a form of hierarchy backed by the
standard protocol and architecture (ISA-95) in order
to map them according to their scope.
ISA-95 firstly distinguishes between two
domains: Enterprise Domain and Control Domain.
Enterprise Domain refers to the strategic management
of the enterprise and correlates with the ERP system.
It encompasses Level 4 Business Planning &
Logistics from PERA model. The Control Domain
refers to actions within a factory wall, and
encompasses Level 3 Manufacturing Operations and
Control, which is popularly called the MES
(Manufacturing Execution System) or MOM
(Manufacturing Operations Management when
reffering to extended functionalities) layer, and Level
2,1,0, which are also known as OT (Operations
Technology).
Although ISA-95 clearly dictates boundaries
between ERP and MES functionality, this view is
being challenged by technology providers that extend
the functionalities of their tools to incorporate the
other ones. For example, the ERP is extended to
include order tracking, and MES includes resource
management and planning/scheduling (Franzosa,
2019). Moreover, the shift to the Cloud has the
potential to disrupt the whole hierarchy. De Jong,
Lalla-Sewgoolam and Vainberg (2019), outline the
challenges of the transformation from presented
decoupled information systems architecture towards
the future of the integrated modular components. This
transformation is central to most of the demonstrators
in the Smart Lab, which is the reason why we didn’t
develop the enterprise software stack as one entity,
but rather as a collection of modular systems with
clear integration protocols in place which are easy to
replace, extend, and deploy according to our needs.
The integration of the components found in the
PERA hierarchy model is called Vertical Integration
in Industry 4.0 ontology (on account of them being
presented in a vertical hierarchy) and is also
commonly known as IT/OT integration. In a nutshell,
IT/OT integration deals with connecting the data and
the processes from the manufacturing floor to the
strategic level. Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the
technologies enabling this integration.
2.3 Open Source
At the time of this writing, there are no less than 50
proprietary IIoT platforms; however, the proprietary
solutions often rely on an ecosystem of partnership,
thus making system integration difficult. However,
given the heterogeneous nature of data within IoT, it
is no surprise that open-source technologies,
standards, and protocols may be chosen as an
alternative and even preferred to proprietary IoT
solutions. The drivers for choosing open-source
technologies for IoT over proprietary solution are
summarized here from (Kim, Lee and Jeong,
2019): (1) The cost of implementing open source IoT
frameworks is low; (2) open-source code leads to
open innovation, thus making operability across
operating systems more probable; (3) the use of Open
APIs (Application Programming Interface) is
preferred, thus leading to the common gateway
(backed by standard protocols) for connecting
software and hardware; (4) the open-source
framework usually offers a wide range of working
libraries; (5) solves the problem of interoperability;
(6) open-source software is more secure than
proprietary software.
2.4 Research Objective
We strive to use the gained experience from building
Smart Lab demonstrators to construct a generalized
enterprise software stack incorporating minimal ERP,
MES, and IoT functionalities, for vertically
connecting information sources, to be able to explore
new concepts and easily make new demonstrators for
research and innovation purposes.
3 METHOD
This research is structured as a DSR (Design Science
Research) approach, with the creation and evaluation
of an artifact (OP4SP) at the center. The OP4SP
represents a concrete technological instantiation of a
full factory software stack that includes an ERP, an
MES, and an IoT solution. It is created and refined in
4 design cycles, which are presented in figure 2.
The knowledge base is provided by standards,
specifically ISA-95, and guides the architecture and
functionalities of each level of the artifact, which
ensures the rigor of the research. A study (Mantravadi
et al., 2020) deduced that ISA 95 structure is indeed
helpful in securing IIoT interconnections in a factory.
Furthermore, an open-source enterprise solution was
beneficial in the implementation of virtual intelligent-
assistant systems on the shop floor for operator
assistance (Mantravadi, Jansson and Møller, 2020).
Moreover, the identified principles related to
Industry 4.0 technology creation, also called Industry
4.0
An Open Platform for Smart Production: IT/OT Integration in a Smart Factory
709
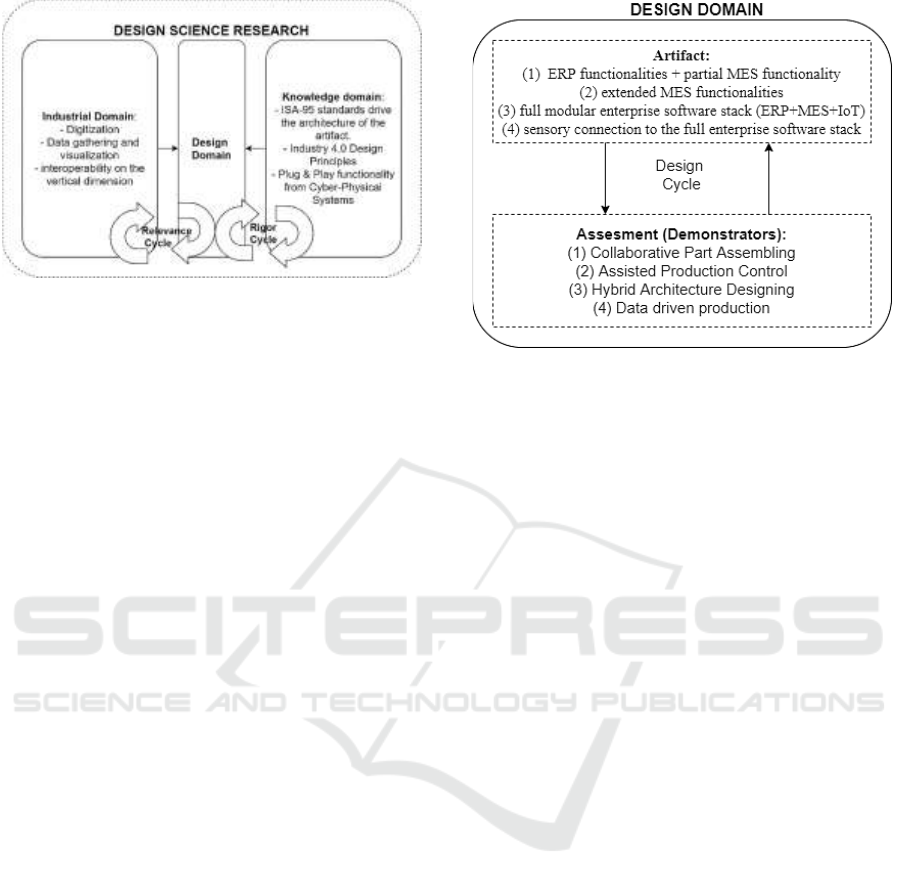
Figure 2: DSR Research Overview presenting the three
domains and relevance/rigour cycles.
Application is underlined by providing a means to
have industrial demonstrators built on top of the
physical instantiation presented in this research. The
demonstrators take place because there is interest
from industrial partners. It is important to note that
the artifact (enterprise software stack) and its
abstraction (the platform) should be used as a means
to an end, which is a concrete solution to a
demonstrator project, and not as an end of itself, thus
the measurement by which the artifact is assessed is
by how easy it is to build industrial demonstrators
around it.
There are a set of high-level requirements that
drive the design and development of the
platform. They are: (1) the use of open source is
mandatory; (2) no hard coding necessary; (3)
inclusion of ERP, MES, and IoT; (4) the architecture
must be modular; (5) real-time capability is required
(6) allow virtualization and information
transparency.
Moreover, the design and development of the
artifact is constrained by external factors: (1) the
artifact should be tested at our Smart Lab, because it
will be used there; (2) be easily customizable or
programmable; (3) allow Plug and Play feature.
The artifact evolved because of specific needs
from four previous demonstrator projects, each of
them guiding the development from specific
perspectives having different scopes and
requirements, but still acting as a stage of iterative
development. The contextualization of each
demonstrator is presented in figure 3, and in the
further section.
3.1 Demonstrators Scenario
The platform evolved through as a result of four
demonstrators, which are presented further.
Figure 3: The Design Domain from DSR, presenting the
design cycle.
1) Collaborative Part Assembling: In this scenario,
the MES provides the instruction to the mobile robots
to deliver the materials to different robot cells to assist
product assembling. The production line consists of
two robot cells, one mobile robot and materials (i.e.,
PCB). In this scenario, the MES receives the
production order from the Odoo Sales (part of Odoo
ERP) module and checks the mobile robot’s state to
see if it is available or not. After receiving the
command from the MES, the mobile robot will pick
up the specific PCB and deliver it to the robot cell.
This task requires the MES to be able to communicate
with the mobile robots through OPC UA protocol.
The order information and mobile operations are set
as parameters transferring between MES and mobile
robots.
2) Assisted Production Control: The second scenario
we tested relates to the task of production control.
There are four pieces of equipment involved in this
scenario, counting machine one, counting machine
two, robot station, and manual station. This task
simulates the LEGO bricks assembling process. The
counting machine one and two counts two types of
bricks separately and put them to the pallet according
to the work order. The robot station can select the
other three types of bricks for assembling. All the
bricks in the pallet will be assembled at the manual
station. In this task, MES helps to schedule the
production, balance the workload of the equipment,
and control the production process. To synchronize
the order states and avoid the same order is produced
at the same time, MES also introduces a synchronize
mechanism to create a production sequence of the
work order.
ICEIS 2021 - 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
710
3) Hybrid Architecture Designing: The third scenario
is focused on a hybrid architecture that provides an
integration solution that introduces the IoT platform
(Thingworx is chosen as the IoT platform in this case)
to the traditional hierarchical model. The proposed
architecture follows the Industrial standards ISA-95
and includes the key activities of different functional
hierarchy layers. It defines the several interfaces to
support data collection and transformation between
the MES and IoT platform. The integration between
MES and IoT platform is through the ISA-95 middle
layer which helps to generate an industrial standard
followed, standardized, and formalized data
structure.
4) Data Driven Production: The fourth scenario is
focused on creating a simple monitoring system for
production lines with outdated machinery without
compromising or infiltrating the legacy systems
already in place. A Node-Red (simple programming
tool) instantiation was installed on a Raspberry Pi,
and was receiving vibration sensory data from
ESP8266 microcontrollers, that were mounted on a
conveyor, that would declare if a machine is
functioning or idle. Moreover, a fully customizable
dashboard accessible from PC would present the
necessary data, which was also collected in a database
for statistical purposes. The setup is modular and
easily customizable with minimum programming
knowledge.
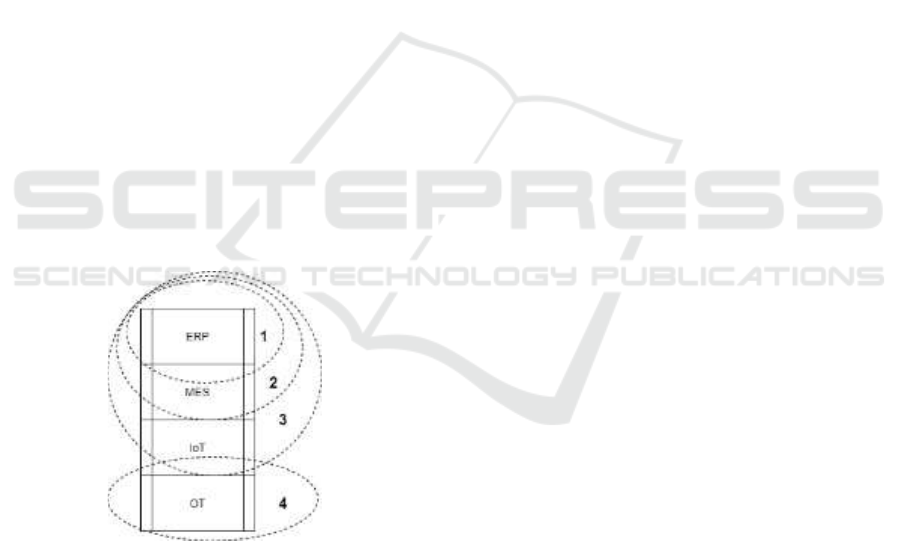
Figure 4: Levels of the hierarchical model, detailing where
the demonstrators’ scope correlated with the enterprise
stack.
3.2 Development
Based on the knowledge acquired from these
demonstrators, an architecture was proposed, and an
instantiation of a platform was developed that would
facilitate further demonstrators. Figure 4 presents the
levels of the platform's architecture, and specifically
where previous demonstrators augmented the design
of it. The next chapter presents in detail the road to
designing and developing the platform.
4 STAGES IN THE EVOLUTION
OF THE PLATFORM
The Smart Lab is the learning factory at our research
institution. It is the foundation on which new industry
4.0 concepts are tested, and artifacts designed and
deployed as part of industrial demonstrators. It has a
proprietary MES solution, and at procurement it had
an ERP system from SAP, which was discontinued
due to the inability to customize it. This is the outset
from which we start our journey. The direction of our
journey is top to bottom from the vertical integration
perspective, and the demonstrators mirror this
approach.
4.1 Design Cycles
The first step was to replace the SAP system with
something that is customizable, modular, and easy to
deploy. The Odoo ERP system was considered
(formerly Open ERP). The community edition of
Odoo ERP is open source and can be deployed both
onsite and in the cloud. Odoo is structured in
modules, each of which has a specific authority.
In the (1) Collaborative part assembling
demonstrator the Odoo Sales and Odoo
manufacturing modules were tested. Odoo
manufacturing was customized specifically to fit the
Smart Lab, and specifically this demonstrator.
Through OPC-UA (OPC-Unified Architecture) the
manufacturing module would check the availability
of resources (in this case, mobile robots) and assign a
task to them. On completion, it would receive a signal
and take the next task. Through this demonstrator, we
observed that Odoo fits the need of the Smart Lab and
thus it was decided to use it further.
In the (2) Assisted production control
demonstrator, we further tested the customizability of
the Odoo manufacturing module by designing a
production planning operation that would
synchronize the order states and balance the workload
of the resources used. Through this, we also tested the
real-time capabilities of the system, deemed it
acceptable for our purposes.
Further, in (3) Hybrid architecture designing
demonstrator we complete the vertical integration of
information systems by introducing an IIoT platform
(Thingworx). The integration follows the industrial
standard ISA-95 through a middle layer that supports
An Open Platform for Smart Production: IT/OT Integration in a Smart Factory
711
standardized and structured data. The solution was
deployed on the Cloud and represented a modular
software with a digital backbone that was
customizable, and quickly deployable. However,
customizing the IIoT platform required a lot of hard
coding and with each new use case the legacy would
grow, thus bringing complexity into maintaining the
platform. Thus, it was decided that Thingworx is not
fully suited for our purposes, and that testing another
solution is required. Although there are other open
source IIoT platforms (FIWARE, Mobius,
SiteWhere, Kaa, DeviceHive), we decided to test an
IoT platform designed for automating your house,
Home Assistant, because it has a much larger
audience and is designed specifically for ease of use.
In the last couple of years, Home Assistant was
appreciated with grants and awards from open-source
societies for its flexibility and ease of integration with
smart resources and third-party software. Although it
was criticized in the beginning for its file-specific
integration (the use of YAML setup files), presently,
it shifted to a more web-based GUI. Home Assistant
was tested on the premises of the Smart Production
Lab by creating a local version on a raspberry pi and
connecting it to the Festo CP factory, through OPC-
UA.
In (4) Data driven production demonstrator, we
tested the possibility of using a cheap setup of
vibrational sensor and ESP32 (cheap microcontroller
architecture) to bring smartness to old machinery. An
often-cited motive for the difficulty to integrate
machinery into a central system (like an IoT platform)
was the lack of functionality and connectivity
embedded in its system. We bypassed this problem by
adding inexpensive smart sensors instead that are
easy to install and connect, thus completing the
skeleton of vertical integration.
Finally, the platform was tested and evaluated at
our facility. Our artifact, which constitutes a skeleton
of a full enterprise automation stack, is able to fully
control and monitor the state of the order and
machinery.
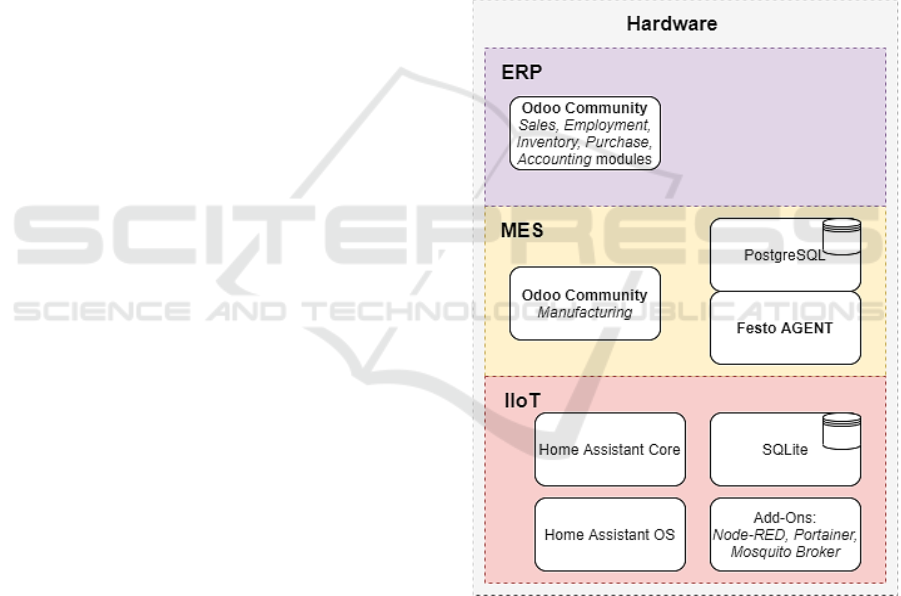
4.2 Target Architecture and Workflow
The artifact is designed to correspond to the levels of
functionality dictated by the ISA-95 standard. At each
layer there are containers with relevant applications.
Figure 5 presents an overview of the architecture.
It was decided to have a clear hierarchical model,
but also to divide the functionalities in separate
containers in order to be able to migrate them either
to the Cloud or to the edge according to our needs and
keep the distinct integration protocols in place.
The ERP layer includes Odoo Community
edition, deployed locally as the MVP (minimum
viable product) with sales, employment, inventory,
purchase, and accounting modules. It is considered to
deploy the enterprise edition on the Cloud in the
future release. The MES layer includes another
module from Odoo called manufacturing, which was
customized according to our needs and maybe further
changed to fit specific demonstrator scopes. There is
also the Festo Agent, which is a python based
program that acts as a control layer for the machines
through OPC-UA. The IIoT layer includes an
instance of Home Assistant core running add-ons like
partainer, ESPHome, and Node-RED in separate
containers, and a Home Assistant OS.
Figure 5: High Level Architecture of the enterprise software
stack.
Figure 6 presents the workflow of the order, detailing
the course from sales to execution. It represents a
generic order flow that can be applied in any
manufacturing context, thus ensuring the relevance of
the research. The logical blocks (different colors)
correspond with specific functionalities from ERP
(Purple and Blue), MES (Yellow), and IIoT (Red)
layers.
ICEIS 2021 - 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
712
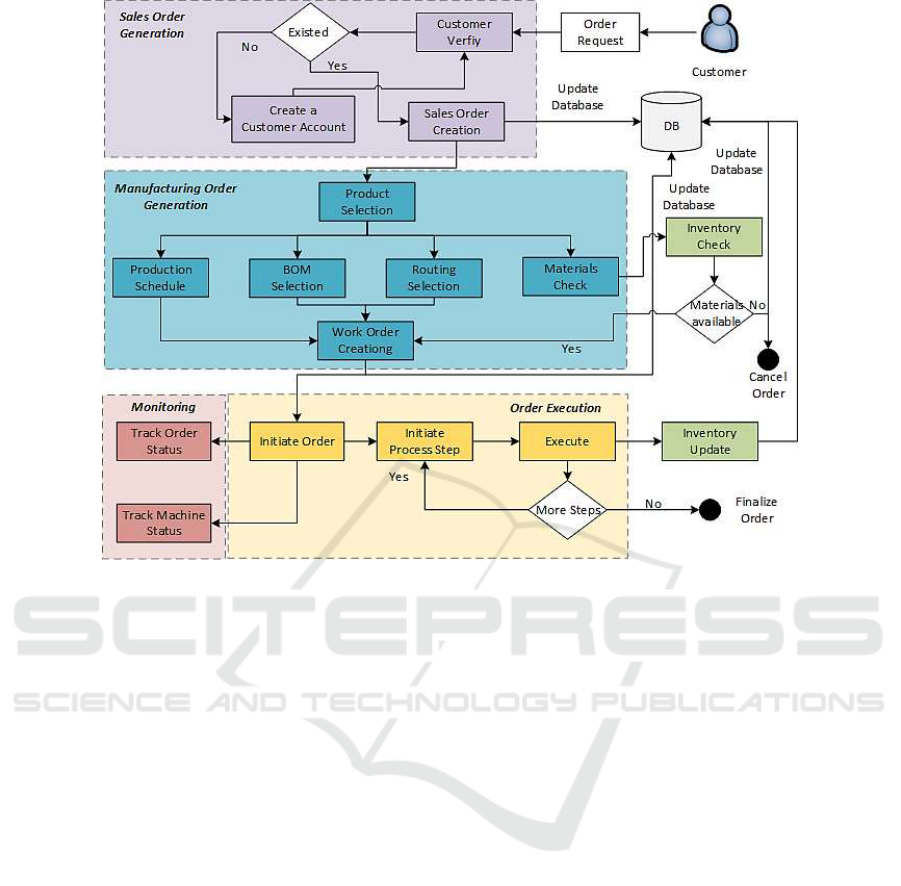
Figure 6: Generic Order Workflow model.
5 DISCUSSION
In the next couple of months, AAU plans to host
several industrial demonstrators with multiple
industrial partners. In this section, we will argue that
the presented artifact will facilitate the creation of the
demonstrators by specifically pointing out the
processes that it will perform for each project. First
demonstrator is titled Mass Customization. The outset
of the project is to demonstrate the capability of a
simple setup, to receive an order for a customized
product (made by the customer through a
configurator), sort the correct components, and
package them. The resources include but are not
limited to feeders with counting devices, grippers,
and robots. Our artifact has a major role, specifically
controlling the order management through the ERP
layer, and production processes through the MES
layer. The IoT will collect machine status and order
data for a statistical reason and strategic decision
making. The secondary scope is to demonstrate
traceability and quality assurance. Second
demonstrator titled Paperless Production is directed
toward companies that are at the beginning of the
digitization journey and have no or minimal gain
from using information systems at their site. The
scope is to demonstrate the capabilities of digital tools
through the whole spectrum of the hierarchical stack;
thus, our artifact will be used extensively in this
demonstrator, especially for collecting data. Some of
the goals are: (a) automatic capturing and storage of
information from machines, devices, and employees;
(b) aggregation and visualization of information for
decision support; (c) automatic model-based
decision; (d) reporting and publishing insights for
actions. Third demonstrator titled Predictive
Maintenance has scope is to create a base for
intelligent maintenance of machines and devices
through diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive
analytics. For this, a stable data collection and storage
procedure should be in place, which is provided by
our platform.
The OP4SP will be the facilitator for conducting
these planned demonstrators and will allow for quick
setup according to new requirements for each
demonstrator.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have stated that our research
institution uses its facility, the Smart Lab, to create
An Open Platform for Smart Production: IT/OT Integration in a Smart Factory
713

industrial demonstrators for showcasing Industry 4.0
concepts and technologies. We argue that the Smart
Lab misses a digital backbone that would allow us to
easily collect data and track the production. This
digital backbone would help us as researchers to
explore new concepts and create industrial
demonstrators faster. The digital backbone entails a
full enterprise automation stack (as explained in ISA
– 95 standard) developed from open-source tools. The
architecture includes an ERP system (Odoo ERP), a
MES (MES – based on Odoo Manufacturing), and an
IoT Platform (Home Assistant), which was the result
of a DSR approach with 4 design cycles. Our artifact
is not the final state and will continue to be refined as
it will be used in the upcoming industrial
demonstrators.
The presented platform fulfills almost all the
requirements presented earlier. It is composed of
open-source tools (1), has little hard coding involved,
only in the FESTO Agent (2) , includes ERP, MES,
and IoT (3), has a modular architecture through the
containers that hold the programs (4), the response is
close to real-time (5), the virtualization and
information transparency is in place (6). Further
development also seeks to fully complete the
requirements (2) and (5).
The contribution of this paper includes proposed
architecture of the enterprise software stack, a
concrete instantiation of the platform, and the generic
order workflow model.
It is also planned that the OP4SP will be used
further in the context of helping small and medium
sized enterprises (SMEs) by providing minimum
necessary enterprise functionalities and observe their
digitization journey. Moreover, the stack will
facilitate research into implementation of industry 4.0
technologies, with respect to SMEs as well.
REFERENCES
Awouda, A. et al. (2019) ‘Practical Implementation of
Industry 4.0 Based on Open Access Tools and
Technologies’, in IFIP Advances in Information and
Communication Technology. Springer, pp. 94–103.
Franzosa, R. (2019) Magic Quadrant for Manufacturing
Execution Systems. Available at: https://www.gartner
.com/en/documents/3970825/magic-quadrant-for-man
ufacturing-execution-systems (Accessed: 18 December
2020).
De Jong, E., Lalla-Sewgoolam, B. and Vainberg, G. (2019)
Unlocking the full power of automation in industrials.
Kagermann, H. (2015) ‘Change through digitization—
value creation in the age of industry 4.0’, in
Management of Permanent Change. Springer
Science+Business Media, pp. 23–45.
Kim, M., Lee, J. and Jeong, J. (2019) ‘Open Source Based
Industrial IoT Platforms for Smart Factory: Concept,
Comparison and Challenges’, in Lecture Notes in
Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes
in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in
Bioinformatics). Springer Verlag, pp. 105–120.
Li, C., Mantravadi, S. and Møller, C. (2020) ‘AAU Open
Source MES Architecture for Smart Factories -
Exploiting ISA 95’, Ieee International Conference on
Industrial Informatics.
Madsen, O. and Møller, C. (2017) ‘The AAU Smart
Production Laboratory for Teaching and Research in
Emerging Digital Manufacturing Technologies’,
Procedia Manufacturing. Elsevier B.V., 9, pp. 106–
112. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2017.04.036.
Mantravadi, S. et al. (2020) ‘Securing IT/OT Links for Low
Power IIoT Devices: Design Considerations for
Industry 4.0’, IEEE Access, 8, pp. 200305–200321. doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3035963.
Mantravadi, S., Jansson, A. D. and Møller, C. (2020) ‘User-
Friendly MES Interfaces: Recommendations for an AI-
Based Chatbot Assistance in Industry 4.0 Shop Floors’,
in Nguyen, N. T. et al. (eds) Intelligent Information and
Database Systems. Cham: Springer International
Publishing, pp. 189–201.
Martin, J. L. et al. (2010) ‘Preface: Technologies for a
Smarter Planet’, IBM Journal of Research and
Development. doi: 10.1147/JRD.2010.2051498.
Møller, C. (2005) ‘ERP II: a conceptual framework for
next-generation enterprise systems?’, Journal of
Enterprise Information Management. JAI Press, 18(4),
pp. 483–497. Available at: https://vbn.aau.dk/da/
publications/erp-ii-a-conceptual-framework-for-next-g
eneration-enterprise-syst (Accessed: 18 December
2020).
Nardello, M. ; Madsen, O. ; and Møller, C. (2017) The
smart production laboratory A learning factory for
industry 4.0 concepts, CEUR Workshop Proceedings.
CEUR Workshop Proceedings. Available at:
http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1898/paper13.pdf (Accessed:
27 November 2020).
Queiroz, M. M. et al. (2020) ‘Smart production systems
drivers for business process management improvement:
An integrative framework’, Business Process
Management Journal. Emerald Group Holdings Ltd.,
26(5), pp. 1075–1092. doi: 10.1108/BPMJ-03-2019-
0134.
Ross, J. W. and Weill, D. P. (2006) Enterprise Architecture
as Strategy-Creating a Foundation for Business
Execution. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/
publication/236972734 (Accessed: 14 December
2020).
Williams, T. J. (1994) ‘The Purdue enterprise reference
architecture’, Computers in Industry, 24(2–3), pp. 141–
158.
ICEIS 2021 - 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
714
