
Development of an Internet of Things System for Measuring
the Direction of Use of Body Pressure Dispersion Cushions
using Radio Frequency Identifier
Ryoma Seto
1a
, Hirona Okudaira
2
and Toshitaka Inoue
3
1
Healthcare Informatics, Faculty of Healthcare, Tokyo Healthcare University, Tokyo, Japan
2
Faculty of Sports and Health Science, Daito Bunka University, Saitama, Japan
3
Faculty of Health and Social Welfare Sciences, Nishikyushu University, Saga, Japan
Keywords: Pressure Ulcer Prevention, Pressure Distribution Cushion, IoT (Internet of Things), RFID (Radio Frequency
Identifier), NIS (Nursing Information System).
Abstract: Pressure ulcer prevention guidelines recommend repositioning within 4 hours. For encouraging
implementation, IoT technology was used to design a pressure distribution cushion with an embedded radio
frequency identifier (RFID) tag and a prototype Android smartphone application to read the tag. As a result
of the RFID tag reading experiment, 83% without blanket and 13% with blanket could read the correct posture
successfully. In addition, the position was correctly read by the system. With this prototype, the body position
could be detected appropriately.
1 INTRODUCTION
Prevention of pressure ulcers as part of long-term
nursing care is extremely important in ensuring the
quality of life of the elderly. It has various
precautionary measures; one of them is pressure
dispersal, which is crucial. Pressure ulcer prevention
guidelines recommend that postural change be
performed every 4 hours or less (The Japanese
Society of Pressure Ulcers Guideline Revision
Committee, 2016).
For the proper distribution of body pressure, the
date and time of the postural change and the person
performing the postural change should be recorded as
accurately as possible. The use of ICT to prevent
pressure ulcers has been extensively investigated.
Several studies perform the following: (1) Detecting
pressure ulcer risk factors using electronic medical
record data and communicating them to nurses (Park,
2019) (Davidson, 2019), (2) Gathering information
on pressure ulcer occurrence and using it as an index
for quality evaluation.
In recent years, with the spread of machine
learning, research integrating (1) and (2) have been
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6154-9342
attempted (Cramer, 2019). Thus, pressure ulcer
prevention based on data is progressing.
Meanwhile, only few research use such
information technology for body pressure
distribution, which is a more basic means of
preventing pressure ulcers. The reason is that postural
variance is excessively analogous and requires less
ICT participation.
Therefore, from the viewpoint of the Internet of
things (IoT), we report on the development of a
system that implants an IC chip in a postural change
cushion and enables detection and recording of the
postural position.
2 METHODS
2.1 Aim for Development
We aimed to develop this system to be able to
automatically record the position, date, and time of
the position change, and the nurse who performed the
position change. Hence, we have developed a postural
change cushion with an embedded IC chip.
Seto, R., Okudaira, H. and Inoue, T.
Development of an Internet of Things System for Measuring the Direction of Use of Body Pressure Dispersion Cushions using Radio Frequency Identifier.
DOI: 10.5220/0009567200990102
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AWE 2020), pages 99-102
ISBN: 978-989-758-420-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
99
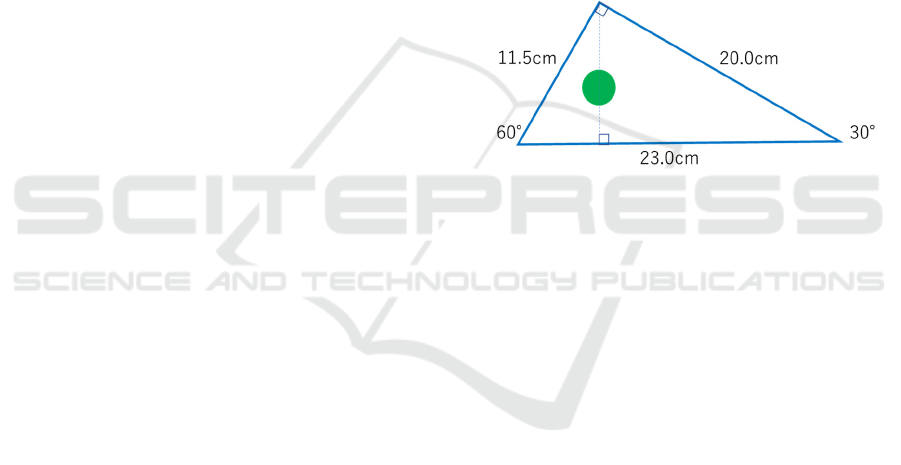
2.2 Design of the Body Pressure Partial
Pressure Cushion
The body pressure distribution mattress has a
structure in which a scapula is lifted to distribute the
weight of a patient. The angle at which the scapula is
lifted is 30°, so the cross section of the mattress is a
right triangle of 30°-60°–90°.
Therefore, we could specify whether the patient
was in the right or in the left lateral position according
to the base of the right triangle, which is either above,
or below the body. To specify such position, we
assigned a function in radio frequency identifier
(RFID).
The performance and position of the RFID tag
were designed so as not to affect the abovementioned
positional relationship.
2.3 Design of the Position Detection
System
The information system for reading the body pressure
dispersion cushion with the RFID tag was designed
for Android.
At present, according to reviews in other clinical
fields, many mobile terminals used for observing
symptoms are for Android smartphones (Choi, 2018).
Hence, the environment used by the authors for
design was Android, and the software used for
reading the IC chip was a highly versatile
middleware.
2.4 Method for Evaluating the
Prototype of This System
For this prototype of the body pressure dispersion
cushion and the body position detection system, we
constructed a sleeping environment virtually. The
validity of reading the IC chip and the absence of
malfunction were verified.
Considering that this verification is performed in
a virtual environment, government approval based on
the Pharmaceutical Machinery Act or approval of the
ethics committee at the university is unnecessary.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Outline of the Newly Developed
Body Pressure Dispersion Cushion
and Body Position Detection
System
The body pressure dispersion cushion was made of
urethane sponge, and its length was 40 cm. The cross
section was a right triangle, with the hypotenuse at the
bottom. RFID tags were attached to both ends of the
cross section. This RFID tag measured 22 mm in
diameter and 0.6 mm in thickness (Figure 1).
The format of the RFID tag is NTAG213, which
is a 13.56 MHz-band passive tag. An RFID tag of this
standard has an effective distance of 10 cm, with 144
bytes of user memory.
Figure 1: Cross section of the body pressure dispersion
cushion (circle in the center represents the RFID tag).
The reading system employs a general-purpose
RFID tag reading system that runs on an Android
smartphone; when a user touches a tag attached to a
cushion, the body position is displayed in a pop-up
(Figure 2).
3.2 Reading Result of the RFID Tag
Attached to the Cushion
We placed the humanoid model in the right lateral
recumbent position and inserted a body pressure
dispersion cushion equipped with an RFID tag to
maintain this posture.
In this environment, the RFID tag on the head
(written information: postural change to the right
recumbent position) was read in an environment
without a blanket. Consequently, 25 out of 30 trials
(83%) were correctly read.
When a similar reading test was performed with
a blanket placed on the humanoid model, reading was
successful only four times (13%) and failed 26 times
(87%).
In both situations with and without a blanket, the
RFID tag placed on the foot (written information:
repositioning to the left lateral position) was never
read by mistake (Table 1).
ICT4AWE 2020 - 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
100

Figure 2: Pop-up screen when reading an RFID tag attached
to a cushion with Android smartphone.
Table 1: Success rate of reading an RFID tag attached to a
cushion (number of trials: 30).
Head side tag Foot side tag
Without blanket 25 (83%) 0 (0%)
With blanket 4 (13%) 0 (0%)
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Availability of the Position
Detection System
This system is the first to record postural change
using IoT technology for postural dispersal cushions
among bedridden patients.
In a virtual environment experiment using a
humanoid model, reading can be possibly correct
80% of the time in an environment without blankets.
This percentage may be insufficient, but at least, false
readings may not occur in general.
Conversely, when a blanket was used, the
reading success rate decreased to approximately 10%.
Peeling off the blanket is indispensable to perform the
repositioning; however, this reading success rate is
appropriate for a system that records the proper
performance of repositioning.
Next, the validity of the RFID tag is considered.
Regarding NTAG213 (ISO14443 type-A) used this
time, related literature cannot be found in PubMed.
Therefore, comparing it with other cases is difficult,
but it is still appropriate because of the absence of
false reading of RFID in this experiment. Given that
the effective distance of NTAG213 is approximately
100 mm, the tag of the foot is not read when reading
the tag of the head.
According to a previous study of pressure ulcer
prevention using IoT technology, a device can detect
excessive body pressure by attaching it at the center
of a wheelchair (Tavares C, 2019).
I have no intention to deny such a sophisticated body
pressure detection tool. However, extremely simple
tools, such as those proposed herein, are also useful,
and we suggest that they will be used for pressure
ulcer prevention.
4.2 Considerations for Implementing a
Posture Detection System
This system is the first to record postural change
using the IoT technology for postural dispersal
cushions in bedridden patients.
In this experiment, we only developed a postural
change cushion equipped with an RFID tag, and we
verified the effectiveness of reading by using a
general-purpose software. To implement this system
in an electronic medical record system or the like, we
need to consider a message format.
Thus, we will discuss the message format by
using the Master of Nursing terms certified by the
Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan. This
master consists of nursing observation and nursing
action, both of which have the expressions “right side
supine” and “left side supine.”
In any case, the information to be written to the
RFID tag is either “right side supine” or “left side
supine,” and this master can express it with one code.
Therefore, in this study, we leave judgment on
whether to use the Master of Nursing observation or
nursing action. Hence, writing a code that specifies
left and right on the RFID chip is necessary, so that it
can be used for three-point authentication (Figure 3).
Development of an Internet of Things System for Measuring the Direction of Use of Body Pressure Dispersion Cushions using Radio
Frequency Identifier
101
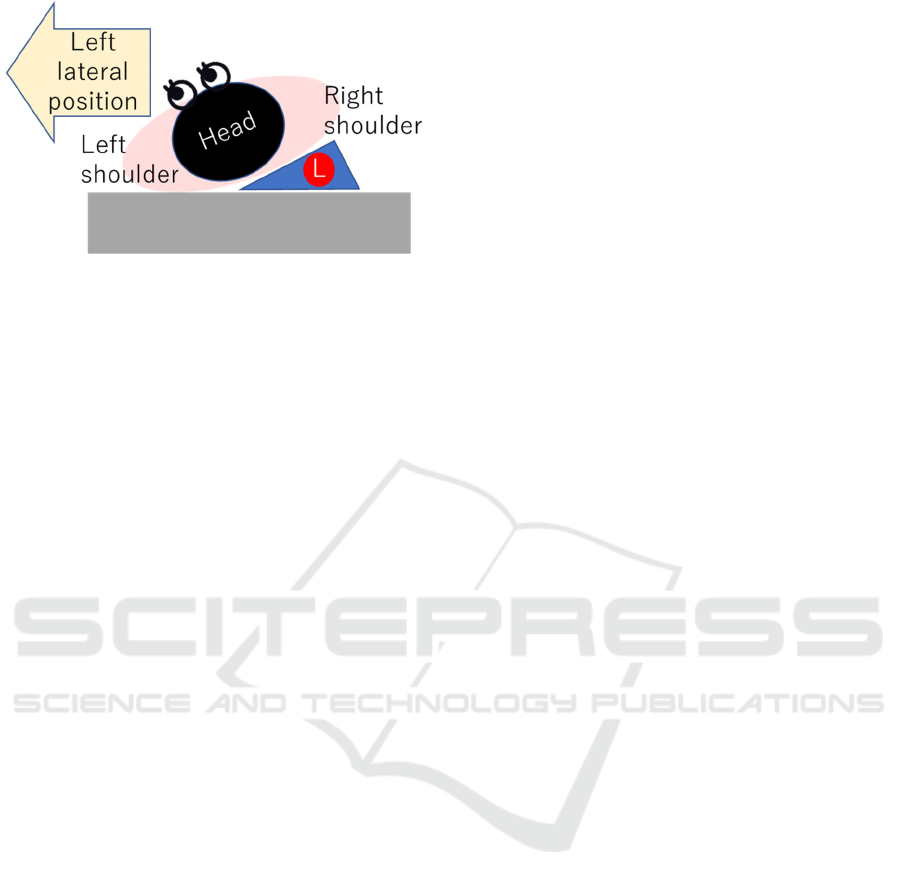
Figure 3: Image of an RFID tag with left side-lying
information (L symbol).
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, a prototype of a postural change cushion
and a reading system using the IoT technology were
developed to accurately record postural changes
necessary for pressure ulcer prevention.
By devising the effective range of the RFID tag,
we verified that constructing a system that enables
position detection is possible. The developed system
can also be applied to other nursing situations. For
example, the date, and time of changing clothes can
be recorded by attaching an RFID tag to a hospital
garment. We will continue to consider various uses.
This model has been registered as a utility model
in Japan (registration number:3225058) by Japan
Patent Office.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by Japan Society for the
Promotion of Science; Grant-in-Aid for Scientific
Research (C) 19K11180.
REFERENCES
Choi, Y.K., Demiris, G., Lin, S.Y. et al. 2018. Smartphone
applications to support sleep self-management: review
and evaluation. J Clin Sleep Med.; 14(10):1783-1790
Cramer, E.M., Seneviratne, M.G., Sharifi, H., et al. 2019.
Predicting the incidence of pressure ulcers in the
intensive care unit using machine learning, EGEMS
(Wash DC).; 7(1):49
Davidson, C., Loganathan, S., Bishop, L., et al. 2019.
Scalability of an IT intervention to prevent pressure
ulcers in nursing homes, J Am Med Dir Assoc.;
20(7):816-821
Park, S.K., Park, H.A., Hwang, H., 2019. Development and
evaluation of electronic health record data-driven
predictive models for pressure ulcers, J Korean Acad
Nurs.; 49(5):575-585
Tavares, C., Domingues, M.F., Paixão, T., et al., 2019.
Wheelchair pressure ulcer prevention using fbg based
sensing devices, Sensors (Basel).;20(1). pii: E212.
The Japanese Society of Pressure Ulcers Guideline
Revision Committee. JSPU Guidelines for the
Prevention and Management of Pressure Ulcers (4th
Ed.), Japanese Journal of Pressure Ulcers 2-16; 18(4):
455-544
ICT4AWE 2020 - 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
102
