
A SWOT Analysis of Big Data in Healthcare
Cristiana Dias, Manuel Filipe Santos and Filipe Portela
Algoritmi Research Center, University of Minho, Guimarães, Portugal
Keywords: Big Data, Healthcare, Swot Analysis.
Abstract: Nowadays, organizations in the most distinct sectors of activities, are generating enormous amounts of data,
at high velocity and high variety. This phenomenon dictated a growing technological development, called big
data, which is already recognized as one of the most important areas of the future of information. Due to this
fact, organizations have been looking for new solutions to improve their services and take advantage of these
new technologies. The reality in the healthcare industry is similar to the phenomenon described above. It is a
sector where large amounts of data have been stored digitally and with enormous benefits from these new
technologies. Despite this, there are very few health-related organizations making investments in big data and
taking advantage of it. This article will address a SWOT analysis, more specifically the strengths, weaknesses,
opportunities and threats of big data in healthcare in order to help organizations to evaluate its potential.
1 INTRODUCTION
Big data is a contemporary phenomenon, more and
more electronic data are being generated in the world
and will continue to increase. Due the smartphones,
sensors that turn real-world phenomena into data,
smart home appliances, computer systems and other
internet of things systems that produce and stream
huge amounts of different types of electronic data
(Lee, 2017).
The development of big data also includes new
ways of collecting, storing and processing
information in order to make it available and useful.
Beyond that, big data has raised the capability of data
analysis and reasoning to unprecedented levels
(Maciejewski, 2017). The digitization of information
along computing power create powerful possibilities
to convert information into knowledge that helps
organizations achieve their goals (Murdoch &
Detsky, 2013).
In the health sector, the reality is no different.
Historically, this industry has also generated large
amounts of data from record keeping, regulatory
requirements and patient care (Raghupathi &
Raghupathi, 2014). It’s evident that within these
amounts of data there is occult knowledge that can
change a patient life or, who knows, the world.
According to (BDV, 2016), extracting this knowledge
is fastest, least costly and most effective path to
improving population health. The potential of big
data can impact positively technology, economic and
society, boosting innovations and leading to the
improvement of business models. However, the path
to extract knowledge from big data brings challenges
and it’s important to understand them in order to be
successful.
Having as motivation all the aspects mentioned
above, the purpose of this article is to provide a
SWOT analysis, which allows to evaluate the
potential of big data in healthcare. Therefore, in this
document are included five sections. Firstly,
background, which explains big data definition and
characteristics. In second place, a SWOT analysis for
big data in healthcare, where are described the
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
Lastly, the discussion and conclusion, which contains
a reflection on the analysis previously presented and
final considerations, respectively.
2 BACKGROUND
Despite being a recurring term nowadays, due to its
complexity and heterogeneity, there is no clear
definition of the term (Dave & Kamal, 2017).
According to a questionnaire conducted by SAP, in
2012, the majority define Big Data focusing only on
the huge growth in the amount of data generated and
processed (Gandomi & Haider, 2015). A good
example is McKinsey & Company that define big
256
Dias, C., Santos, M. and Portela, F.
A SWOT Analysis of Big Data in Healthcare.
DOI: 10.5220/0009390202560263
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AWE 2020), pages 256-263
ISBN: 978-989-758-420-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
data as datasets whose size compromises the
competence of traditional database software for the
storage, management and analysis of data (McKinsey
& Company, 2011).
Obviously, in sequence of the previous definition,
the characteristic that is most easily associated with
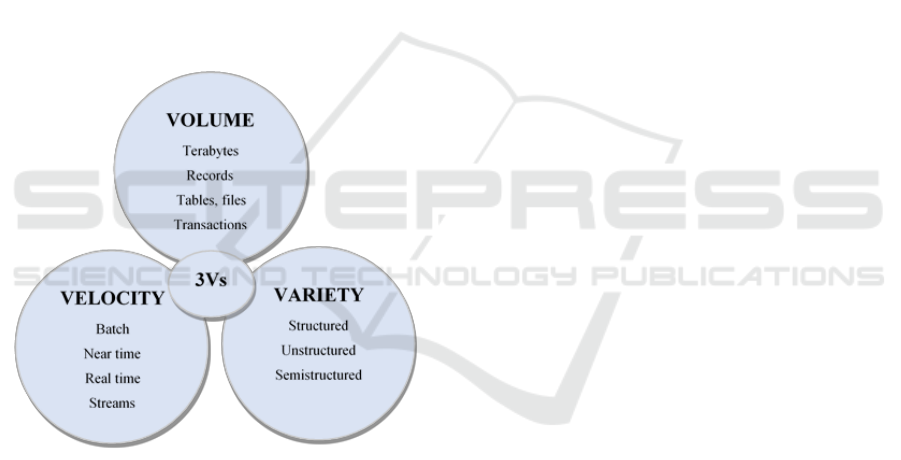
big data is volume, but there are others. Doug Laney,
in 2001, created the 3Vs of big data that emerged as
the most common and accepted way to characterize
big data (Dave & Kamal, 2017), as described after
and showed in figure 1.
▪ Volume: Corresponds to the amount of data
that is collected or generated by organizations
or an individual (Lee, 2017);
▪ Variety: Corresponds to the type of existing
data which may be of the structured, semi-
structured and unstructured type (Lee, 2017);
▪ Velocity: Corresponds to the high rate and
speed at which data is created, captured,
refreshed and shared from milliseconds to
hours (Ambigavathi & Sridharan, 2020).
Figure 1: 3Vs of Big Data.
Subsequently, two new characteristics were identified
by IBM and Oracle, which complements the 3V
model previously described. These new discoveries
have led to the creation of the Big Data 5V model,
which contains, beyond the dimensions already
known, Veracity and Value. Each of them will be
described below:
▪ Veracity: Represents the lack of reliability and
uncertainty inherent in some data sources, these
may suggest due to imprecision, inconsistency
and subjectivity in data (Gandomi & Haider,
2015). For example, consumers' feelings are
not reliable since they include the subjectivity
of their opinion (Lee, 2017). On the other hand,
it’s defined as the combination of data
consistency and data trustworthiness which is
necessary to provide effective results of a data
analysis (Ambigavathi & Sridharan, 2020).
▪ Value: Corresponds to the value that big data
can bring to organizations.
3 SWOT ANALYSIS FOR BIG
DATA IN HEALTHCARE
In healthcare, data are disorganized and distributed
from diverse sources, internal and external, often in
multiple formats in multiple locations (Ambigavathi
& Sridharan, 2020). So, when we talk about
healthcare data, it can be physiological, behavioral,
molecular, clinical, medical imaging, medication
prescription history, nutrition and many more (Mehta
& Pandit, 2018). Despite all this dispersion, it is based
on these sources of information that health
professionals make decisions and provide appropriate
and efficient treatments.
Due to this phenomenon that is upon us, it’s
important to explore solutions that fit the clinical
context, allowing to enjoy the many advantages and
opportunities in this sector. Doing that successfully,
can be determined by how well we understand the
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of
big data in healthcare (Ahmadi, Dileepan, &
Wheatley, 2016).
Considering a bibliographic review based on a
articles and researches of various platforms such as
“Google Scholar” or purely “Google”, we conducted
a SWOT Analysis for big data in healthcare. In this
research the following restrictions were considered:
articles only written in Portuguese or English and
with the year of publication less than ten years.
As definition, a SWOT analysis can be described
as a technique used to determine and define the
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in
order to assessing the performance, competition, risk
and potential of a business (Grant, 2019).
3.1 Strengths
The fundamental strength of big data can be easily
associated with the three Vs it represents: volume,
velocity, variety. Regarding volume and velocity,
over years, the health sector has generated and
collecting large amount of data from record keeping,
regulatory requirements and patient care which has
been costly and time-consuming (Ahmadi et al.,
2016). Essentially because most data were stored on
A SWOT Analysis of Big Data in Healthcare
257

paper, but now the trend is toward digitization of this
large amount of data. Nowadays, when it comes to
data generated by these organizations in this industry,
this includes prescribing data, administrative data,
patient data in management systems, sensor data,
social networking data, blogs, medical journal
articles, and more (Raghupathi & Raghupathi, 2014).
According to (Mehta, Pandit, & Kulkarni, 2020),
healthcare has seen a transition from clinical-centric
care model to consumer-driver care model. In the
consumer-driver care model, the patients won greater
responsibility for their own health with a lot of digital
applications to control health. This increase pace of
generation of data brought an explosion of digital
healthcare data, velocity and heterogeneity (Mehta et
al., 2020). This real-world evidence has all the
potential to make the system more efficient of care
because open datasets mean that people from
different areas can analyze data and test hypotheses,
bringing fresh perspectives and open collaboration
(Collins, 2016).
Analyzing these data volumes, through big data
analytics, can add value to the organization, for
example, discovering new correlations between
things never thought before, patterns, and trends with
data, thereby improving care, saving lives, and
lowering costs (Raghupathi & Raghupathi, 2014). In
a smaller view, providing access to relevant and high-
quality data, healthcare providers and patients have
better conditions to make decisions in the daily bases.
Big data will continue to grow in all areas fueled
by the continuing growth of internet of things and this
is one of its natural strengths (Ahmadi et al., 2016).
Another strength of big data, that is a complement of
all previously referred, is providing a big sample of
data that permits validate the performance of
statistical models developed. This strength is very
important in healthcare sector because treatment
models have changed in order to use data-driven
findings to predict and solve a problem before is too
late.
3.2 Weaknesses
To accomplish the benefits that big data can deliver
it’s necessary to define effective policies and
procedures for handling and maintaining big data
(Ahmadi et al., 2016). In order to deal with big data
is required new infrastructures able to address
volume, variety and velocity regarding data. It’s also
necessary scalability, capacity of operating and
support immediate response for a large amount of
medical data, including images, in order to reduce
medical error (Sarkar, 2017).
As it is known, healthcare data is
multidimensional and highly segmented. The
possible lack of synchronization, generation of data
in real-time or near real-time, amongst data sources
can create gaps and misleading information (Mehta et
al., 2020). The unification of data from multiple
sources, including the conversation into common
formats, is also another challenge of data acquisition.
Added to this, storage data from multiple sources
leads to data redundancy problems and it’s difficult to
aggregate data, considering separate useful
information and discard redundant or irrelevant data
(Mehta et al., 2020).
Another major weakness of big data is the risk of
poor quality insights gathered from the data (Ahmadi
et al., 2016). The accuracy and integrity of data is a
concern because healthcare has a lot of different
formats and sources of data. There is a need for
information extraction process capable of selecting
the essential information and present it in an adequate
form for analysis, which is a technical challenge
(Mehta et al., 2020). In order to be capable to produce
meaningful use of data, cleaning and normalization
by removal noise or irrelevant data is imperative
(Mehta et al., 2020). In this sector, is extremely
necessary to have reliable and reproducible results
data, especially in medical and pharmaceutical
research where gathering data is very expensive. With
new analysis methods being developed quickly, the
origin and quality of data can be significantly
important to have good results (BDV, 2016).
Regarding data access and sharing, there are barriers,
technical and organizational, that limit the
distribution of healthcare data among different
institutions. The data collected is not shared between
institutions, not even between departments (BDV,
2016). This leads to data that are not fully exploited
and consequently, insights that can’t be done.
The digitalization of healthcare service lead to a
generation of very large volumes of data and
heterogeneity, which is a consequence of multiple
information systems and data sources. This scenario
led to a lack of interoperability and coordination
between medical service providers and consumers,
causing erroneous diagnostics, greater operating costs
or even, non-adherence top treatment plans by the
patients (Satti et al., 2020). By definition,
interoperability represents the policies and guidelines
that can bridge the gap between systems and services.
Data interoperability is a part that focuses on
resolving integration, exchange and consumption of
data (Satti et al., 2020). In healthcare, this is a
weakness because some healthcare information
management systems do not utilize any format
ICT4AWE 2020 - 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
258

standard to build their schemas. And, in order to be
able to use data effectively, the devices should be able
to communicate in a standard and compatible format
with other devices (Mehta et al., 2020).
Lastly, according to Nathan Eagle, cited by
(BDV, 2016), there are not enough trained
professionals comfortable to deal with petabytes of
data, until this factor is remedied, this will remain a
serious weakness. The skills required are not simple,
they involve data mining, analysis, manipulation and
other techniques expensive for most small firms to
master (Hong et al., 2018).
3.3 Opportunities
Without any doubt big data has the potential to cause
impact in technology, economic and society, boosting
innovation and improving business models.
According to (BDV, 2016), big data will open new
opportunities and enable breakthroughs in very
different perspectives:
1. Descriptive to answer what happened;
2. Diagnostic to answer the reason why
happened:
3. Predictive to understand what will
happen;
4. Prescriptive to detect how we can make it
happen.
Regarding prevention and health promotion, big
data can improve lifestyle support providing effective
tools for behavioral change and provide a picture of
what influences progress and reverse in any therapy.
A great example is mobile health that has the
capability to personalize interventions, using lifestyle
data (sleep, nutrition and activity) from large
reference populations (BDV, 2016). With these
technologies it’s possible to expand recording
medical data not only to hospitals and doctors but also
to home care models. Combining smart home
technologies, wearables, periodic vital sign
measurements, home care providers will be supported
by a big healthcare infrastructure, while individuals
are encouraged to live longer on their own (BDV,
2016).
Public health is another area that will benefit from
the application of big data, using a nationwide patient
and treatment database, public health can ensure the
rapid, coordinated detection of infectious diseases
and improve response (McKinsey & Company,
2011). According to the European Center for Disease
Prevention and Control, cited by (BDV, 2016), 100
000 patients are estimated to acquire a healthcare
associated infection in Europe each year. At least 37
000 deaths occur as a direct consequence of these
infections. Combining information from informal
(social networks, forums, chats, social sensors,
internet of things devices) and formal sources
(surveillance, diagnostic data) also provide earlier
detection of disease outbreaks and information for
understanding transmission in order to coordinate
quarantine and vaccination responses (BDV, 2016).
Big data has given healthcare a huge opportunity
to improve the quality of treatment. As it’s showed,
ultimately, the aim of big data in healthcare is to
provide the patient’s health data to make major
decisions considering their needs, in order to be more
efficient from the start. However, much more can be
explored starting from research and development,
which involves predicative modeling for new drugs
and determine the most efficient allocation of
resources, using of statistical tools to improve the
design of clinical trials and analyze disease patterns
and trends to model future demand and costs
(McKinsey & Company, 2011). Certain
developments or outcomes may be predicted and/or
estimated based on vast amounts of historical data
(Raghupathi & Raghupathi, 2014). Even in regular
clinical operations the use of data is important to
conduct a research to determinate which treatment
will work best for specific patients, deploying clinical
decision support systems to improve the quality of the
operations and analyzing data to identify performance
opportunities (BDV, 2016).
It’s essential for a healthcare organization
integrate multiple data, in order to allow more
efficient decision-making, productivity and
consequently, optimizing workflows. With big data
technologies is not also possible to integrate all
systems like electronic medical records, patient
monitors and laboratory data but also implement
automated systems for fraud detections and explore
new business models (McKinsey & Company, 2011).
The first type of new business model is one that
aggregates and analyzes patient records to provide to
third parties. Other potential business is online
platforms and communities (McKinsey & Company,
2011).
Lastly, but also very important is the economic
potential of big data in healthcare. According to a
study conduct by Accenture in 2014, a third of
European hospitals had reported operating losses
(BDV, 2016). This is due the fact of being extremely
difficult to provide good quality care at reasonable
costs. However, big data has the potential to disrupt
this industry and optimize quality, access and cost
simultaneously (BDV, 2016).
A SWOT Analysis of Big Data in Healthcare
259
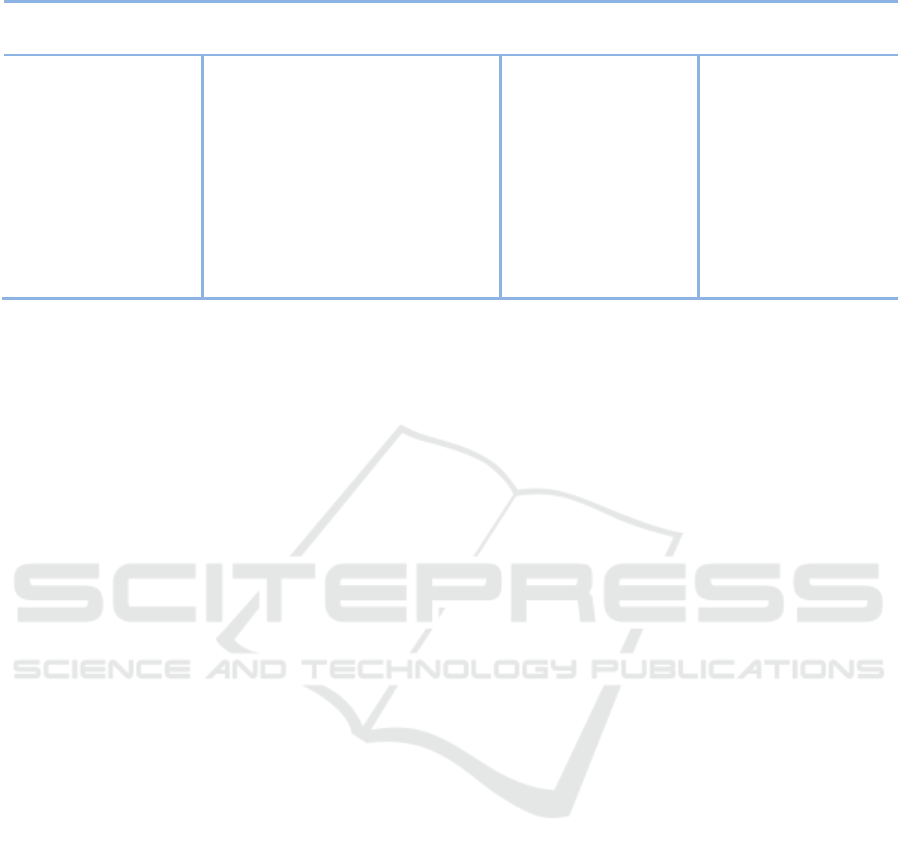
Table 1: SWOT analysis of big data in healthcare.
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
• Volume;
• Variety;
• Velocity;
• Value to
organizations;
• Better decision
making;
• More efficiency;
• Continuous
growth.
• Lack of adequate
infrastructure;
• Data acquisition;
• Data aggregation and storage;
• Data access and sharing;
• Interoperability;
• Risk of poor quality insights;
• Lack of trained professionals.
• Improve lifestyle
support;
• Improve public
health;
• Reduce costs;
• New business
models;
• Fraud detection;
• Patient-adjusted
treatments.
• Data privacy;
• Data security;
• Lack of incentive;
• Ethical/moral
questions;
• Misuse of
information;
3.4 Threats
Is crucial to store health data in a secure and privacy-
respecting database. According to study conducted by
(Alexandru, Radu, & Bizon, 2018) the main concern
when discussing big data in healthcare is privacy and
security of health-related data. Security breaches,
hackings, phishing attacks and ransomware episodes
happen, and healthcare data are more sensitive than
other types of big data, that’s why data security is a
priority for healthcare organizations. After noticing
an array of vulnerabilities was developed a list of
technical safeguards by protected health information
(PHI). Termed as HIPAA Security Rules, these rules
help guide organizations with storing, transmission,
authentication protocols, controls over access,
integrity and auditing (Dash, Shakyawar, Sharma, &
Kaushik, 2019). Anonymization and
pseudonymization approaches are also a valid
solution to guarantee privacy.
By users, there is a lot of skepticism regarding
“where the data goes to”, “by whom it is used” and
“for what purpose” is present in most citizens and
public opinion because the divulgation of medical
information or lifestyle data can compromise
individuals or their families (BDV, 2016).
An important issue that must be addressed as a
threat is the lack of incentive for organizations to face
technological challenges. The key question that any
health organization faces is what is the return on
investment for my hospital to implement big data?
(Adibuzzaman, DeLaurentis, Hill, & Benneyworth,
2017). Even the current model of pay-per-service
does not make sense, once big data will be able to
carry out preventive analyzes in order to reduce or
mitigate diseases. Thus, healthcare organizations
would bill less, which is not an advantage for
themselves.
The growth of information available to the user,
if not well managed, can cause in some cases anxiety
and stress. Since there will be a greater understanding
about individual risk of diseases, in particularly for
diseases with no treatment available, can create
unnecessary concern in people. The use of all of this
information can raise ethical/moral questions and
lead to misuse of data by insurers because companies
will soon be able to predict healthcare cost using big
data applications. This threat might cause a backlash
in health economics if people feel that their data are
being misused or being over-monitored (Collins,
2016).
4 DISCUSSION
Big data and big data analytics, particularly in health,
are some of the hottest buzzwords at the moment.
However, nobody really knows how to do it but
everyone thinks everyone else is doing it (Health,
2016).
Based on the previous literature review and
SWOT analysis, big data in healthcare is a field with
more strengths and opportunities when comparing
with weaknesses and threats. Analyzing Table 1, it’s
possible to visualize that were identified seven
strengths, seven weaknesses, six opportunities and
five threats.
Regarding strengths and weaknesses, big data in
healthcare can provide better decisions making and,
consequently, efficiency of care. But some strengths
can turn into weaknesses. For example, the three Vs
of big data (volume, velocity and variety) are a major
strength because the amount of data generated, at high
speed, in various data types can generate knowledge
and value to organizations but also cause
infrastructure issues, risk of poor quality data and data
ICT4AWE 2020 - 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
260

aggregation challenges. However, there are more and
more tools and techniques for storing, processing and
analyzing big data, as is the case of Hadoop – a open
source framework. In the case of the lack of
professionals specialized in big data to implement
these systems tailored to organizations, there are
companies that provide big data solutions depending
on monthly payments. Addressing interoperability
problems, healthcare providers will need to develop a
big data exchange ecosystem that provides
trustworthy, timely and meaningful information by
connecting all members of the care continuum. Time,
commitment and communication would be required
(Dash et al., 2019). Another weakness mentioned
above is the lack of trained professionals but it’s
important to reminder that is a temporary situation
once the world is preparing for big data, educating
more and more big data experts and data scientists.
Comparing opportunities and threats, opportunities
are vast, in multiple areas, from financial to more
quality healthcare. On the other hand, threats are
based in two areas, privacy of personal data and lack
of incentive to implement big data. To solve security
and privacy issues, many businesses are trying to
invest in processes and protocols in order to guarantee
privacy and, consequently prevent massive data
breaches. Common measures like up-to-date antivirus
software, firewalls, encrypting sensitive data and
multi-factor authentication can save a lot of trouble
(Dash et al., 2019).
In general, despite the weaknesses and threats
discussed here, cannot be denied the potential that big
data has to offer in healthcare. The application of real-
time data may have preventive effects, permitting
faster identification of problems and, consequently a
earlier application of the treatment. This can be
extremely important to reduce the mortality rate and
prepare medical staff to possible peak of workloads
in situations like the flu and pandemic infections. But,
how exactly can big data reduce waste and
inefficiency? In several ways, as mentioned in the
previous chapter, through big data it is possible to
diagnose and treat patients more effectively in terms
of clinical procedures and cost. It’s also possible to
make predictive modeling that allows the production
of new devices and drugs more quickly with the
intention of enhancing the reduction of possible
failures and a better combination between treatment
and patient’s disease. In addition, big data facilitates
pattern analysis and disease monitoring to increase
the speed of response, faster vaccine development
and turn large amount of data into relevant
information to identify needs, provide services,
predict and prevent crises or event the rapid analysis
of medication reimbursement requests in order to
reduce fraud. The combination of financial,
operational and clinical data constitutes a very
important asset provided by the application of this
revolutionary technological concept.
Considering everything mentioned in this article,
the main requirements needed for realizing the
potential of big data are, in first place, evaluate
commercially and affordable tools or services that
enable scaling up the use of big data analytics in
healthcare. In second, it’s important to choose a big
data platform that support the key functions necessary
to overcome weaknesses, threats and that responds to
the needs of the business. The criteria for evaluating
the best big data platform/technology should focus on
ability to manipulate data at different levels of
granularity, data privacy, security, scalability, quality
assurance and easy to use. With this, value and
information will be added for decision making and
the resistance to change will be less. In third, make
sure that exist a solid exchange ecosystem between
all members of care community, in order to ensure
data access and sharing. Lastly, an incentive to
exploit data. According to (Health, 2016), healthcare
providers have been compensated on a fee-for-service
model. However, this does not incentivize moving to
a pre-emptive care model once it can be expressed in
a lesser visit to medical services and consequently,
less financial returns. A model like fee-for-value
would motivate more healthcare providers to invest in
big data.
Globally, healthcare is seeing a surge of interest
in the use of big data. According to (Schroer, 2019),
big data is already taking on some of the biggest
challenges in healthcare, as it’s possible to analyze in
the following examples of companies/organizations
that are already extracting knowledge from big data:
1. Flatiron Health (New York): Utilizes
billions of data points from cancer patients
in order to gain new insights for patient care.
Their solution enables multiple players
(oncologists, hospitals, academics,) to learn
from each patient. Flatiron partners with
over 280 community cancer practices, 7
major academic research centers and over 15
of the top therapeutic oncology companies
(McCall, 2020).
2. Pieces Technologies (Dallas, Texas): Is a
cloud-based software company that collects
data from patients in order to improve
quality and cost of care. Their platform
makes decisions and recommendations
based on the most varied data such lab
results and vitals;
A SWOT Analysis of Big Data in Healthcare
261

3. Amitech (St. Louis, Missouri): Utilizes
data for population health management
solutions, combining health data to identify
risks and engage patients in their own
healthcare;
4. Apixio (San Mateo, California): Utilizes
information from millions of files, claims,
PDFs and other health records to provide
more accurate risk adjustment for healthcare
providers.
5. Innoplexus (Hoboken, New Jersey):
creator of iPlexus that organizes millions of
publications, articles, clinical trials and more
documentation into a concept-based
research platform. The purpose of this tool is
to help pharmaceutical companies finding
relevant information for new drug
discovery.
6. Ellipsis Health (San Francisco,
California): Offers a different approach,
tackling depression and anxiety. Using a few
minutes of speech per participant, analyzing
audio, is developing a vital sign tool for
mental health and wellness that detects
depression and anxiety (McCall, 2020).
And many more, from analyzing patients with
cancer to organizing millions of documentations,
companies with high-tech approaches are growing
and harnessing big data in health. However, there is
still a long way to go. According to (Turea, 2019), a
Dimensional Insight study found that 56% of
hospitals and medical practice, in United States, do
not have appropriate big data governance or long-
term analytics plans and 71% of the people surveyed
said they have found inconsistencies in data.
5 CONCLUSIONS
With the realization of this article it was possible to
highlights the urgent need to understand the economic
and strategic impact that big data brings to healthcare.
This paper introduces a SWOT analysis in healthcare,
where the main strengths, weaknesses, opportunities
and threats are addressed. In addition, we summarize
the main requirements needed for realizing the
potential of big data and the criteria for evaluating the
best big data platform/technology. In general, big data
in healthcare faces a lot of weaknesses and threats,
since interoperability to data privacy. However, the
right and affordable investment adjusted with a
favorable incentive to healthcare organizations and a
data sharing ecosystem can bring innumerous
strengths and opportunities. Among the many
advantages, it is important to highlight the production
of new devices, drugs, discovery of patterns, trends
and associations with data able to improve care
efficiency, provide better decision making, save lives,
decrease costs and provide patient-adjusted
treatments. As a future work is important to
understand the difficulties of organizations in this
transition in order to investigate ways to overcome
these problems. We believe that big data will add-on
and bolster healthcare, instead of misuse of
information and anxiety/stress due the information
available to the user. Together, big data will facilitate
healthcare by reducing waste and inefficiency.
REFERENCES
Adibuzzaman, M., DeLaurentis, P., Hill, J., &
Benneyworth, B. D. (2017). Big data in healthcare - the
promises, challenges and opportunities from a research
perspective: A case study with a model database. AMIA
... Annual Symposium Proceedings. AMIA Symposium,
2017, 384–392.
Ahmadi, M., Dileepan, P., & Wheatley, K. K. (2016). A
SWOT analysis of big data. Journal of Education for
Business, 91(5), 289–294. https://doi.org/10.1080/
08832323.2016.1181045
Alexandru, A., Radu, I.-M., & Bizon, M. (2018). Big Data
in Healthcare - Opportunities and Challenges.
Informatica Economica, 47–58. https://doi.org/
10.12948/issn14531305/22.2.2018.05
Ambigavathi, M., & Sridharan, D. (2020). A survey on big
data in healthcare applications. Advances in Intelligent
Systems and Computing, 989(January), 755–763.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8618-3_77
BDV. (2016). Big Data Technologies in Healthcare. Big
Data Technologies in Healthcare Needs, Opportunities
and Challenges, 31. Retrieved from
http://www.bdva.eu/sites/default/files/Big Data
Technologies in Healthcare.pdf
Collins, B. (2016). Big Data and Health Economics:
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats.
PharmacoEconomics, 34(2), 101–106. https://doi.org/
10.1007/s40273-015-0306-7
Dash, S., Shakyawar, S. K., Sharma, M., & Kaushik, S.
(2019). Big data in healthcare: management, analysis
and future prospects. Journal of Big Data, 6(1).
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-019-0217-0
Dave, M., & Kamal, J. (2017). Identifying Big Data
Dimensions and Structure. 163–168.
Gandomi, A., & Haider, M. (2015). Beyond the hype: Big
data concepts, methods, and analytics. International
Journal of Information Management, 35(2), 137–144.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2014.10.007
Grant, M. (2019). Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, and
Threat (SWOT) Analysis. Retrieved from
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/swot.asp
ICT4AWE 2020 - 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
262

Health, K. (2016). Big Data in Healthcare – What is the
Hype All About? Retrieved from
https://kaikuhealth.com/big-data-healthcare-hype/
Hong, L., Luo, M., Wang, R., Lu, P., Lu, W., Lu, L., &
Musterman, M. (2018). Big Data in Health Care:
Applications and Challenges. 1(2), 122–135.
Lee, I. (2017). Big data: Dimensions, evolution, impacts,
and challenges. Business Horizons, 60(3), 293–303.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2017.01.004
Maciejewski, M. (2017). To do more , better , faster and
more cheaply : using big data in public administration.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0020852316640058
McCall, B. (2020). 15 ways Silicon Valley is harnessing
Big Data for health. Nature Medicine, 26(1), 7–10.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0708-8
McKinsey & Company. (2011). Big data: The next frontier
for innovation, competition, and productivity.
McKinsey Global Institute, (June), 156. https://doi.org/
10.1080/01443610903114527
Mehta, N., Pandit, A., & Kulkarni, M. (2020). Elements of
Healthcare Big Data Analytics. In Big Data Analytics
in Healthcare. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-
31672-3_2
Murdoch, T., & Detsky, A. (2013). The Inevitable
Application of Big Data to Health Care. JAMA
Evidence, 309(13), 1351–1352. https://doi.org/
10.1001/jama.2013.393
Raghupathi, W., & Raghupathi, V. (2014). Big data
analytics in healthcare: promise and potential. Health
Information Science and Systems, 2(1), 3.
https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-2501-2-3
Sarkar, B. K. (2017). Big data for secure healthcare system:
a conceptual design. Complex & Intelligent Systems,
3(2), 133–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-017-
0040-1
Satti, F. A., Ali Khan, W., Ali, T., Hussain, J., Yu, H. W.,
Kim, S., & Lee, S. (2020). Semantic Bridge for
Resolving Healthcare Data Interoperability. 2020
International Conference on Information Networking
(ICOIN), 86–91. https://doi.org/10.1109/
icoin48656.2020.9016461
Schroer, A. (2019). From fighting cancer to preventing
disease, big data in healthcare might save your life.
Retrieved from 2019 website: https://builtin.com/big-
data/big-data-in-healthcare
Turea, M. (2019). Ultimate Guide To Big Data In
Healthcare. Retrieved from
https://healthcareweekly.com/big-data-in-healthcare/
A SWOT Analysis of Big Data in Healthcare
263
