
Enabling Predictive and Preventive Maintenance using IoT
and Big Data in the Telecom Sector
Tahir Mahmood and Kamran Munir
Department of Computer Science and Creative Technologies, Faculty of Environment and Technology,
University of the West of England, Bristol, BS16 1QY, U.K.
Keywords: Predictive Maintenance, Telecom, IoT, Big Data, Prediction Model.
Abstract: Telecom sector has always been working hard to improve network quality to satisfy end user services. Fixing
telecom network errors (hardware and software) precisely and quickly is a main factor to improve quality of
services. Telecom operators are spending a lot of budget on ad hoc maintenance to fix these errors. This paper
presents a framework using internet of things (IoT) and big data to enable predictive and preventive
maintenance, which have been applied in the telecom sector. A telecom network consists of radio nodes,
transport network, switching centres and civil infrastructure; and in this paper, focus is on the maintenance of
Radio Access Network (RAN). A challengeable task for telecom operators has been to maintain radio nodes
as these are installed on different locations. This framework for predictive maintenance is modelled using
active and historical data from telecom equipment as well as data collected from IoT devices and sensors. The
major benefit of implementing this framework has been a control on the time and cost of the maintenance by
pre-planning maintenance activities and related budget.
1 INTRODUCTION
Telecom industry is spending bulk part of their
budget for the maintenance of their network. This
maintenance cost is called operational expenditure
(OPEX). Telecom operators are trying to increase
their profit by reducing the OPEX cost of their
network. Due to competition, technology change and
productivity gains (Ciriani and Jeansjean, 2019), it is
observed that there is variation in growth rate and
profit in all industries related to technology. Also,
telecom industry is becoming less profitable due to
the competition between operators and technology
variation, which is evolving day by day. There is
another reason behind reduction of OPEX cost as it
has no link with the output e.g., whatever telecom
company will spend on maintenance, there is no
guarantee that their sale or profit would increase.
According to an earlier study (Takao and Ryoji, 2002)
presented in the Telecommunication Development
Plan, telecom companies should be trying to reduce
the maintenance cost by re-organisation their field
operation team’s. We aimed to develop a predictive
and preventive maintenance framework for telecom
using IoT and big data. Using this framework telecom
companies can re-design their network maintenance
processes that will help to reduce their operational
cost and increase network stability. We have
developed a list of descriptions related to telecom
operation and maintenance activities and how these
operation and maintenance can be transformed in a
predictive maintenance model. Our work has evolved
around following key aspects: (1) telecom base
station equipment and infrastructure; (2) procedures
to collect data of telecom equipment; (3) telecom
network operation and maintenance departments and
field engineer hierarchy; (4) telecom network errors,
alarms triggering and collection; (5) transformation
of telecom network active maintenance to predictive
maintenance; (6) telecom maintenance engineer
effort and time for telecom network maintenance; and
(7) significant effects of predictive maintenance on
telecom network performance.
2 SYSTEMS MAINTENANCE
Telecommunication is the transmission of voice and
data over the wires and the wireless (radio layers)
network (Gunawardena and Weihua, 2014). It is also
known as the technology that enables one user to
connect
with other user for the exchange of voice and
Mahmood, T. and Munir, K.
Enabling Predictive and Preventive Maintenance using IoT and Big Data in the Telecom Sector.
DOI: 10.5220/0009325201690176
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security (IoTBDS 2020), pages 169-176
ISBN: 978-989-758-426-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
169
data. Base station sites consist of transmitter and
receiver equipment, rectifier to covert AC power to
dc-48 volts, battery banks, air conditioner, RF cables,
Oil storage (used for generators) and generators to
generate electricity in case of commercial electric
power failure. Table 1 shows the equipment which
involves in the building of a base station.
Table 1: Base Station Site Equipment.
Item Name Indoor/ Outdoor Area
Air Conditioner Indoor Civil Infrastructure
AC Power System Indoor Civil Infrastructure
Base Station Indoor Telecom Equipment
Battery Bank Indoor Civil Infrastructure
DC Power System Indoor Civil Infrastructure
Rectifier Indoor Civil Infrastructure
RF Cables In/outdoor Telecom Equipment
RF Combiners Indoor Telecom Equipment
RF Module Indoor Telecom Equipment
Tower Outdoor Civil Infrastructure
Tower Base Outdoor Civil Infrastructure
To control maintenance activities in telecom
network, Hoang and Hai (2013) elaborated that every
telecom operator has a structure of teams who are
involved in telecom base station’s maintenance,
which include:
network operation centre (NOC),
NOC team to monitor alarms 24/7, field operation
team for planned maintenance, field operation team
for reactive maintenance, alarms from telecom
equipment comes to NOC system via management
link. This management link used to perform software
upgrade and downgrade for telecom equipment in
addition of alarms monitoring. Currently, telecom
operators are doing planned and reactive maintenance
of base stations. Current maintenance is carried out
only when NOC team observed one of the following
situations: equipment stops working, equipment starts
to give critical/service effecting alarms, equipment
starts to crash, Software starts to give alarms and
software starts abnormal behaviour.
3 PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE
Predictive maintenance means monitoring the
equipment to avoid future failure and as soon as
equipment performance is degrading then
maintenance is scheduled to avoid down time. Yousef
et al. (2017) proposed a methodology for building a
Node Failure Prediction Model, which can help to
implement node failures predications to take the
precautionary measures. This node is called optical
switch in telecom and used to transport voice and data
traffic. In our work, data collection by real monitoring
of optical switch is explored and then three different
models of machine learning are implemented to
predict the optical switch maintenance. Using the
decision tree, ensemble model and logistic regression,
data is trained and then prediction for optical switch
maintenance is triggered.
In order to build a telecom operator network there
are three types of sections: radio, transport and core
sites. Multiple devices are used to set up an end to end
telecom operator network. However, in the existing
work only one device of transport is considered to
base prediction maintenance. From a telecom
operator point of view, spending money only for one
device maintenance solution is usually not worthy.
Telecom operators are often looking to find a solution
which can cover most part of their maintenance. Our
work considers radio sites which covers most part of
telecom network and optical switches are part of radio
sites. Using the proposed framework, telecom
operators can cover the optical switch maintenance as
well, by adding the data from optical switch to the
predictive model. Our predictive maintenance
framework also has the flexibility to add data from
different sources as well as from optical switch.
3.1 Predictive Maintenance in Power
System
In (Sisman and Mihai, 2017). failure of power supply
system is predicted using a statistical analysis of the
power system. By using a statistical analysis method
(such as the
Pareto analysis, etc.) and failure risk
assessment (through the intelligent techniques e.g.,
fuzzy graphs, artificial intelligent, etc) critical
components can be identified and monitored. Our
work covers power system as well as radio and
transport equipment. The prediction maintenance for
power supply system is not useable for telecom
operators. This is because a framework for predictive
maintenance in telecom, should have the capability to
first merge different kind of data into predive
maintenance system to trigger maintenance flags.
3.2 Framework and Related Data
Availability, Access, Exploration
and Processing
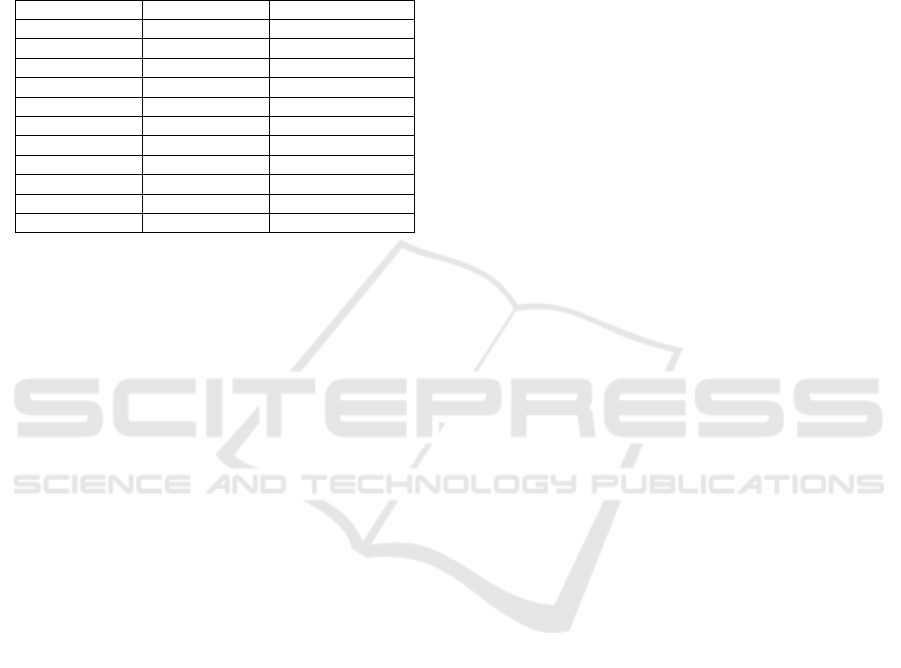
Our framework (as shown in Figure 1) has four steps
to deliver predictions i.e., (a) access and explore
data; (b) process data; (c) develop predictive
framework; and (d) integrate analytics with system.
In this framework, both hardware and software
related data is used for predictive analysis. As
outcomes, notifications are triggered to declare areas
IoTBDS 2020 - 5th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
170
needed maintenance. In terms of access to data, we
have found that it is possible to collect data about
hardware, alarms, key performance indicators (KPI),
IoT (including CCTV, ultrasonic and temperature
sensor) from telecom network equipment and
infrastructure. Moreover, data from maintenance
servers, IoT devices, alarms, key performance
indicators and equipment manufacturers are
combined in the main data server. Processing
included scattering or to rearrange to bring the data
into standardise format, this standard data is then
processed to bring in a meaningful form which can
make sense from the maintenance point of view. In
predictive analysis, data is
processed, and prediction
notification are generated based on the defined
priority area(s) that require maintenance.
Figure 1: Overview of Predictive Maintenance Framework.
This framework for enabling predictive
maintenance suggests integration of the network
alarms and IoT data to storage disks. These storage
disks are integrated with both Hadoop/Hive and
power business intelligence (BI) system. This Power
BI system raises flags when a defined threshold is
crossed. This flag then triggers task(s) for field
engineers for maintenance.
4 METHODOLOGY
Due to the fact that it is impossible to self-raise faults
in Telcom network as no Telecom operator will allow
service suspensions, we have used simulations on the
bases of our theoretical or visible values obtained from
Telecom sector. However, we have collected original
maintenance data from telecom industry equipment as
well as their IoT data. Predictive maintenance default
values are obtained and used as input. This
maintenance input data is then processed i.e., either
degraded or increase in quality, and then predictive
maintenance results are observed. Our observations
were based on varying the input data from the input
sources to see the effects on the predictive maintenance
outcomes. Moreover, data generated by different
resources is analysed. The margin of error in predicted
results is covered by giving prediction using qualitative
input data. These data sources include both hardware
and software counters.
5 ENABLING PREDICTIVE
MAINTENANCE
This section discusses the process adapted to enable
predictive framework for the base station site.
5.1 Predictive Maintenance
Framework Implementation for
Base Station
In a telecom network all base stations are planned and
installed in almost a similar model i.e., their operation
and maintenance activities are similar. Therefore,
evaluating predictive and preventive maintenance for
one base station is largely applicable for all stations.
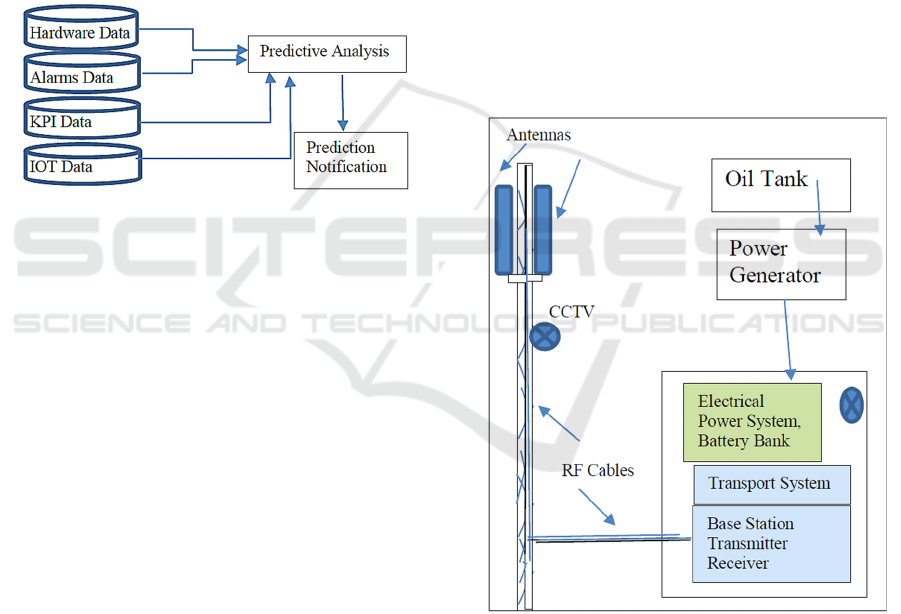
Figure 2: A typical Telecom Network Base Station Site.
As shown in Figure 2, a base station consists of
radio transmitter and receiver, transport system
device (optical switch or microwave link) and electric
power system. Base station transmitter and receiver
are the main equipment responsible for receiving and
transmitting the signals to end users. Electricity is
feed by commercial sources as well generated by on-
site generator. Generator used for electricity
production at site is dependant for oil stored in oil
Enabling Predictive and Preventive Maintenance using IoT and Big Data in the Telecom Sector
171
tank. Therefor maintenance and availability of oil
tank is very important. This electricity is AC
(alternating Current) which is converted to DC (direct
current) by electrifier. This is because base station
and transport system need -48v DC power as
mentioned by Kasper, Bortis, Deboy and Kolar
(2017). Base stations are also equipped with battery
banks which are used to store DC power. In the next
section each part of base station and prediction for
maintenance is explored.
5.2 Base Station Transmitter and
Receiver
Our requirements and design activities have
established that prediction for radio hardware failure
will be found by running diagnostic tests and then the
results will be feed to the big data prediction system.
Diagnostic test run through the hardware, check the
health of the hardware and give immediate outputs. If
a test case result is negative, then it means that the
related hardware or part of that hardware is faulty.
Radio equipment manufacturers have already
added a default capability that when diagnostic test
runs on a radio hardware, it checks the equipment
stability and performance of each part of the radio
module. The outcome of this test is either pass or fail.
Figure 3: Prediction for a Radio Hardware Failure.
Figure 3 shows the diagnostic test and result feed
to predictive maintenance system. For diagnostic
tests, a script is prepared which runs the diagnostic
test on each radio module of the telecom base station
and collect the results of these diagnostic tests. These
results are in text format which are then transmitted
to big data predictive maintenance system. These test
results are in pass or fail format which reflects the
hardware health status. The predictive maintenance
system raises a flag for maintenance if the result is
failed.
5.3 Base Station RF Cables
The RF cables data are collected from two resources.
First from display sensor which shows the RF cable
and connector physical appearance. Human
intervention is required to check the physical
appearance and then to add this data in main database.
Second data for RF cables and connectors are be
collected from IoT devices. This data consists of
actual RF measurements like voltage standing wave
ration (VSWR), cable loss, return loss etc. These
results are collected automatically from base station
equipment and sent to main database. These results
are precise, and each measurement reflect the status
of the RF cable. Analysis triggers flags to predict if
RF cable(s) situation is degrade and going to get
worse if maintenance is not carried out.
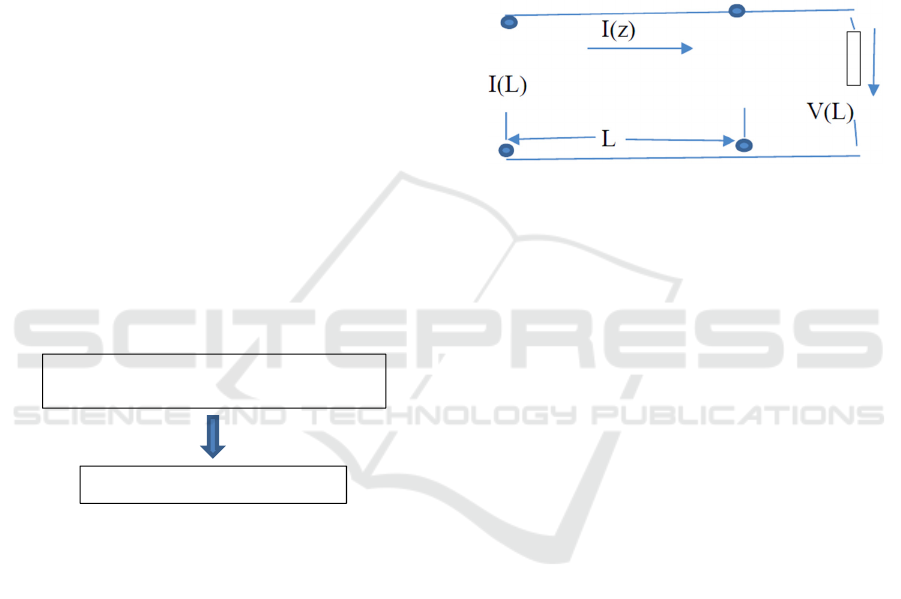
Figure 4: Transmission line terminated with load.
In relation to the power transmission via RF
cables, power is represented by voltage (V) and
current (I). A Voltage V(z) and Current I(z) at any
point z is shown in Figure 4 when it travels through
the RF cables. Voltage and Current can be calculated
in load condition and at any point where it needs to
be measured. This RF power is travelled in sinusoidal
form and can be expressed in phasor form in an
equation 1 & 2 given below:
V(z)dz =− (R + jωL) I(z)
(1)
dI(z)dz = − (G +
j
ωC) V(z)
(2)
Where R is series resistance expressed in
(ohms/m) and L is inductance expressed in
(henrys/m) for both conductors, and G(siemens/m)
and C(farads/m) are shunt conductance and
capacitance per unit length. When RF power is
travelling via RF cable then this is given as follows:
V(z) = V + oe – γz + V− oeγz
(3)
I(z) = I + oe − γz + I – oeγz
(4)
Where Γ = α+jβ=√(R+jωL) (G+jωC) (5)
above is a complex propagation constant, with α
being the attenuation coefficient and β=2π/λ the wave
number, V + o and I + o are the voltage and current
amplitudes of the incident wave along + z direction,
V−o and I−o are the voltage amplitude and current
amplitudes of the reflected wave along−z direction,
and Z0 is the characteristic impedance of the
transmission line and is defined by:
Diagnostic Test on
Radio Hardware
Predictive Maintenance System
IoTBDS 2020 - 5th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
172
Z0 =
√
R + jωLG + jωC
(6)
When Rf signals travel in RF cables then the
output of power at exit end depends on the quality of
the RF cable or the performance of the RF cable. This
quality and performance of RF cables are measured
in form of variable measurements. These
measurements can be variable due to a fault or
leakage in the RF cables. In case of faulty or leaked
RF cable, the respective measurements will change
which eventually will affect the output of RF signals.
The measurements collected in this section for
telecom RF cables health are in digits. These digits
correspond the health of RF cable. High value of digit
corresponds the bad health of RF cable and vice
versa. These results which are in mathematical
structure are feed to predictive maintenance system
which analytical is applied to get prediction for RF
cables maintenance.
5.4 Predictive Maintenance for Civil
Structure
In telecom sector, an important part of base station is
civil infrastructure. Civil infrastructure consists of
cooling systems, electric power from commercial
source, a rectifier to convert AC to DC power, system
for electric power generation (in case of commercial
power failure), battery bank (used in case of
commercial power failure), and concrete base (to
install tower on this). Figure 5 shows various sensors
in our predictive maintenance model, which covers
all areas of a civil infrastructure installed in a telecom
base station. In order to predict maintenance for base
station civil infrastructure, CCTV and sensors are
used which are installed on battery banks and send
live data to main database.
Figure 5: Prediction for base station infrastructure failure.
Base station telecom equipment needs -48 dc
voltage. The sensor on battery bank reads voltage of
battery bank and send these measurements to main
database on daily base. When this dc voltage data is
processed, trends are sent to power BI tool. Power BI
will raise flag if the voltage gets less than -48 volt. The
telecom equipment is considered working fine if
voltage is between the range of -48 to -53 dc volts. In
case a flag is raised for low voltage, maintenance
should be carried out as soon as possible to avoid
outage in a base station service. Moreover, a sensor is
also installed on oil tank to read the oil level. This reads
the oil level and measurements are feed to the system
which raises the flag for inappropriate oil levels.
5.5 Predict Maintenance for Telecom
Network Failure
Most of the telecom equipment vendors have
manufactured their own proprietary server to collect
alarms and log data from their equipment. In these
days major telecom vendors are Nokia, Ericsson and
Huawei. Huawei has main network control system
called U2000/U2020 and Nokia has Net-act. U2000
and net-act are providing statics of the network. These
network statics are called key performance indicator
(KPI). KPI’s given by U2000 and net-act are in same
format. Like both are giving data about calls and
throughput. These data sets include:
Call attempted
Call dropped
Call successful
Call failure
Total Throughput
Throughput in uplink
Throughput in downlink
Packet loss
Packet dropped
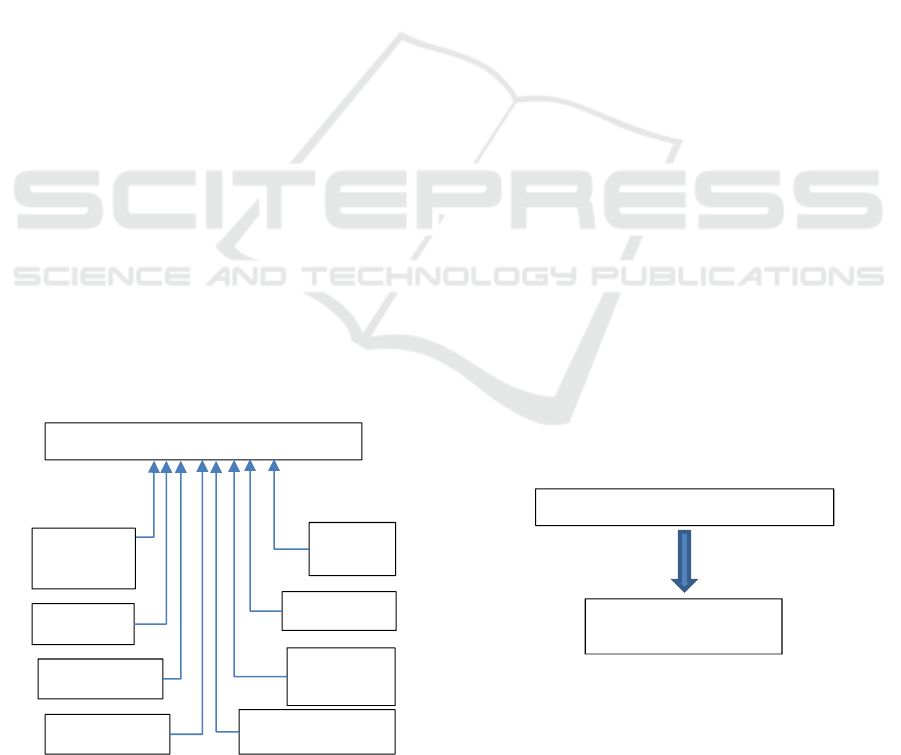
Figure 6: Network KPI’s to Big Data Predictive System.
It is important to note that the KPI’s mentioned in
this section are just example, there are a lot more
KPI’s who reflect the network performance. These
KPI’s are in text format which represent the stability
and performance of the telecom network. As shown
Sensors Data Collection
Power
Generator
Rectifier
Temperature
RF Cable
Battery
Ban
k
Tower/Pole
Oil Tank
Generator
RF Antennas
Network KPI’s (Measurements)
Predictive
Maintenance S
y
ste
m
Enabling Predictive and Preventive Maintenance using IoT and Big Data in the Telecom Sector
173
in Figure 6, KPI’s data generated from network
management system is sent to the predictive
maintenance system, where these data sets are
processed, and flags are raised when performance is
degraded by comparing it to the defined measures.
Once flag is raised, a notification is sent to network
operations team or network optimisation team for
further diagnostics.
6 DISCUSSION, ANALYSIS AND
LIMITATIONS
This section discusses our achievements, limitations,
related issues and prioritise in using an automated
telecom network predictive maintenance
infrastructure.
6.1 Telecom Base Station Equipment
and Infrastructure
In order to achieve predicative maintenance in
telecom sector, equipment and infrastructure
involved in building a telecom base station site is
explored. Figure 2 gives an overview for the telecom
base station equipment as well as civil infrastructure.
The telecom base station outdoor view explains the
tower at base station and antennas installed on tower.
There is one generator installed at the base station site
to generate electricity in case of outage in commercial
electricity. Also, electricity received from
commercial resources or from generator is alternate
current (AC) but telecom equipment needs direct
current (DC). For the purpose to convert AC to DC,
rectifier is used. The base station transceiver system
(BTS) is purely a telecom system, which is
responsible for processing the signals, data and
modulating the transmission and
received signals.
BTS is responsible for communication to end users as
well as to the main control system (Mobile Switching
System). The RF cables are used in base station site,
which connect BTS and antennas. Maintenance of RF
cables are also very important for the performance of
the base station.
6.2 Procedure to Collect Data from
Telecom Equipment
Section 2 presents telecom hardware data which
telecom vendor can provide. This data has full
production history of the equipment manufacturing
record, the batch (it belongs to) and related
manufacturing issues (if faced during the
manufacturing). Normally vendors don’t (fully) share
such information. Vendor usually only release
information about the production data and expiry date
of an equipment. This manufacturing data is stored in
predictive maintenance database to verify the
performance of the related equipment.
Table 2: Hardware Alarms.
Location of
Alarm
Alarm Type
Alarm raised
by Equipment
Historical Alarm on
this equipment
Site A RF module
Major, minor,
Critical
from one-month poor
site performance
Site A
Main
Processor
Major, minor,
Critical
from one-month poor
site performance
In Table 2, various types of alarms that a telecom
equipment can raise are presented. These alarms
feature is usually pre-added by telecom equipment
vendor. Telecom equipment vendor can add and edit
any alarm if necessary, by downloading software
patches. These alarms are in status of minor, major or
critical, depends on the effect of service it provides.
The network stability is measured by various key
performance indicator (KPI), and an example of is
shown in Table 3.
Table 3: KPI’s from base stations.
Location
Call Attempted
Call drop Rate
Data Packet Loss
Call Failure
Call Successful Rate
Handover attempted
Handover failure rate
Call drops due
to hardware failure
A 100 95%
50
packets
95 5% 100 93 95
B 100 100 0 0 100% 100 0 0
This KPI feature can be edited by a telecom
equipment vendor. Normally every telecom vendor is
following 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)
aspects for network performance (Release 15, 2018).
But some KPI’s can be proprietary to a vendor, which
they add to optimise network or these propriety KPI’s
help vendor to improve the network performance.
6.3 Telecom Network Operation and
Maintenance Departments and
Field Engineer Hierarchy
We have explored telecom current maintenance
design and it was found that telecom operators
perform maintenance activities both in planned and
reactive arrangements. Telecom vendor usually spend
a lot of money for their daily operational tasks. There
IoTBDS 2020 - 5th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
174

are usually two teams involved in daily maintenance
task. One does the planned maintenance activities,
who are not responsible to immediate alarms and only
visit the site according to planned date and observe if
there is any maintenance required. The other team is
the one which attend the base station for priority
maintenance e.g., if there
is a service failure alarm
triggered by the base station site.
6.4 Telecom Network Errors, Alarms
Triggering and Maintenance
In telecom sector, usually maintenance is carried out
when there is fault in network. Li, Lansburg and
Cocciantelli (2001) have explored the maintenance and
operations characteristics in telecom application. It is
found that two kinds of maintenance are adopted i.e.,
planned and proactive maintenance. Many telecom
operators have outsourced their operation and
maintenance activities. Takada, Tanji. Seki, Yamagoe,
Soejima and Tahara (2019) has explored the operation
and optimising based on SLA. To avoid the SLA, a
maintenance engineer visits the site according to the
maintenance plan which has been drafted for the site
maintenance, regardless the planned site required
maintenance or not. For proactive maintenance,
maintenance engineer receives the task from the NOC
team that a site raised alarms and needs to be fixed,
usually as soon as possible. Mostly these alarms are
about service failures, which means operator is losing
money due to outage in network. In order to overcome
the outage in the network services and to save the
maintenance engineer time, predictive maintenance
can help these maintenance engineers in upholding the
telecom network.
The key idea behind the predictive maintenance is
to get all possible alarms and historical data from
telecom equipment, including technical and non-
technical areas and make use of all these data sets. Big
data analytics can help getting accurate predictions
for needed maintenance. Data from civil
infrastructure (se discussed in Section 4) need to be
collected via IoT devices, which involved; for
example, sensors and CCTV monitoring. Moreover,
sensors can be used to detect the oil level in oil
storage
tank and to send the measurements back to
the system.
6.5 Issues and Limitations in Enabling
Predictive Maintenance on Telecom
Network
Enabling predictive maintenance could be expansive
in the start, but in the long run telecom operators can
increase their income by reducing the network issues
as well as by decreasing the time and cost for
maintenance. Challenges also arise in testing the
system as it may not be possible to test all live failures
until a failure occurs automatically. Moreover, in
order to enable this framework in telecom industry,
telecom operators need to plan implementation in
various small steps. Moreover, they will need to keep
running their manual (existing) maintenance
operations and structure. Even after enabling an
automated framework for predictive maintenance,
telecom operators will need to optimise this
framework to get accurate and quick predictions for
future maintenance. We cannot ignore the chances of
wrong of misleading predications made by the
automated system at-least in the initial period.
Therefore, there will still be a need to verify the
performance of the base station site when predictive
maintenance system triggers a required maintenance.
This usually done by verifying the counters and KPI’s
of the site, and manual verification is performed for
the civil infrastructure installed at a telecom site.
6.6 Verifications from Telecom Experts
We conducted a survey from senior telecom
professional engineers to get their opinion about the
need of predictive maintenance and its possible
effects on telecom network. Here is a partial snapshot
of the key results obtained from our survey:
72% (21 out of 29) telecom field engineers agree
that predictive maintenance is better option for
telecom industry
97% (28 out of 29) telecom field engineers has
agreed that predictive maintenance can bring
benefit for telecom industry.
93% (27 out of 29) telecom field engineers has
recommended that predictive maintenance can
improve the stability in telecom network.
97% (28 out of 29) telecom field engineers has idea
that predictive maintenance can reduce time and
cost for telecom network maintenance.
100% (29 out of 29) telecom field engineers agree
that historical alarms are beneficial for future
planning in telecom network.
97% (28 out of 29) telecom field engineers agree
that KPI (voice and data measurements) are helpful
for future planning in telecom network
100% (29 out of 29) telecom field engineers has
recommended that enabling predictive maintenance
system for power infrastructure can improve the
outage in telecom network.
Enabling Predictive and Preventive Maintenance using IoT and Big Data in the Telecom Sector
175

100% (29 out of 29) telecom field engineers that
combining network alarms, KPI and environment
data are helpful for predictive maintenance in
telecom network.
97% (28 out of 29) telecom field engineers agree
that predictive maintenance is helpful in generating
more revenue for telecom industry.
7 CONCLUSIONS
Predictive maintenance in telecom can bring stability
in the network and increase in revenue. For the
purpose of incorporating predictive maintenance in
telecom network, research is carried out about active
maintenance structure and network entities which
require maintenance. Research is also carried to find
different sensors / IoT devices to monitor the telecom
network base station temperature, power system,
generator and oil. This framework for predictive
maintenance is modelled using active and historical
data from telecom equipment as well as data collected
from IoT devices and sensors. A survey is also carried
out to confirm that senior professional engineers
working in telecom network agree with the benefits
obtained through predictive maintenance in telecom
network. Results also show that enabling this
predictive maintenance framework in telecom
network can increase the stability and performance of
network which can lead to decrease in maintenance
cost and increase profit.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We acknowledge the huge support provided by the
engineers from British telecom (BT), EE Limited
Mobile, Ericsson and related third parties for sharing
requirements, data sets, equipment sheets,
images and
all related outcomes that are presented in this paper.
REFERENCES
A. H. Yousef, A. F. Fahmy and H. K. Mohamed, "On the
use of predictive analytics techniques for network
elements failure prediction in telecom operators," 2017
13th International Computer Engineering Conference
(ICENCO), Cairo, 2017, pp. 250-255.
A. Takada, N. Tanji. T. Seki, K. Yamagoe, Y. Soejima and
M. Tahara, "SLA Driven Operation - optimizing
telecom operation based on SLA, "2019 20th Asia-
Pacific Network Operations and Management
Symposium (APNOMS), Japan, 2019.
Berggren, C and Bengtsson, L. (2004) Rethinking
Outsourcing in Manufacturing: A Tale of Two Telecom
Firms. European Management Journal [online]. 22 (2)
[Accessed 10 December 2019].
Ciriani, S. Jeansjean, F (2019) Competition, technological
change and productivity gains. [Online]
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3
410912
Hong, I. and Hai, D. (2013) Maintenance Support System
for Telecommunication Equipments [online]. Vietnam:
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/472e/de85e3666f0781
3fabf368db55ed42e20432.pdf. [Accessed 10
December 2019].
Gunawardena, S. and Weihua, Z. (2014). Modeling and
Analysis of Voice and Data in Cognitive Radio
Networks [online]. Canada: Springer International
Publishing. [Accessed 10 December 2019].
Kasper Matthias, Bortis Dominik, Deboy Gerald, Johann
W. Kolar, “Design of a Highly Efficient (97.7%) and
Very Compact (2.2 kW/dm3) Isolated AC-DC Telecom
Power Supply Module Based on the Multi-cell ISOP
Converter Approach”, IEEE Transactions on Power
Electronics, 2017, 32 (10), pp.7750-7769.
Release 15. (2018) 3GPP TS 32.401 – Telecommunication
management; Performance Management (PM);
Concept and requirements, 2018.
Sisman, G., Mihai, O. (2017) Monitoring the parameters of
the electronics devices to assure the predictive
maintenance of equipment, Bucharest, Romania, 23-25
March 2017. IEEE explore Digital Library.
Saini, M and Shlonsky, A (2012) Systematic synthesis of
qualitative research. 1st edition ed. United Kingdom:
Oxford University Press.
Stuart Lansburg, Jean-Michel Cocciantelli, "Ni-Cd Field
Experience Confirms Low Maintenance and Their
Operating Characteristics in Telecom Applications",
Proceedings of Intelec, 2001.
Takao Kawakami, Ryoji Sasaki, "The study on
Telecommunication development plan in Ethiopia",
JICA and ETC, 2002.
IoTBDS 2020 - 5th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
176
