
Hard Tissue Surgical Treatment with Embedded Dental Condition of
Tuberosity Maxillary
Bambang Tri Hartomo
1
a
, and Rizka Rachmatika Dewi
2
b
1
Dental Medicine Study Program, Faculty of Medicine, Jenderal Soedirman University, Purwokerto, Indonesia
2
Student of Dental Medicine Study Program, Faculty of Medicine, Jenderal Soedirman University, Purwokerto, Indonesia
Keywords: Hard tissue surgical, embedded, tuberosity maxillary.
Abstract: An embedded tooth is a tooth condition that cannot erupt due to obstruction by bone. The state of a hidden
tooth located near the nerve will cause pain due to persistent pressure on the nerve. The extraction of the
hidden tooth is performed by surgery, namely odontectomy. This case report aimed to know the hard tissue
surgical treatment performed in an embedded tooth in maxillary tuberosity. The case report is about a 23 years
old woman with frequent headaches since five years ago and pain in the left temple area and the left maxillary
region. The results of the palpation examination on the left temporal site are tender. The supporting
examination results in panoramic radiological radiographs were obtained from tooth 27, which had a
horizontal class IIIC impacted with the crown distally. The removal of the embedded tooth was performed by
odontectomy procedure and administration of medication antibiotics and analgesics.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Indonesian citizen's level of awareness regarding
oral and dental health is still deficient, so it is often
found that patients come for treatment when they are
already experiencing unbearable pain. Patients who
come for treatment when they already experience
unbearable pain dramatically affect the treatment plan
carried out by the dentist. Conditions for tooth decay,
such as teeth with extensive caries and leaving
minimal tooth structure, require several treatment
types to get maximum results (Taufiqurrachman and
Mulyo, 2016).
Hard tissue surgery is a branch of oral surgery in
dentistry that studies things related to hard tissue
surgery in the oral cavity. Some of the oral surgery
treatments are tooth extraction, and odontectomy in
an impacted an embedded tooth. The bone reduction
to assist in the extraction of teeth with difficult
conditions and alveolectomy in exostotic conditions.
Tooth extraction can be performed using two
methods: the intra alveolar extraction technique and
the trans alveolar extraction technique or surgery. The
trans alveolar extraction technique is used to extract a
tooth with difficult conditions, such as teeth with root
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9791-1200
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4583-2145
deformities, namely dilation and fusion,
hypersementosis, ankylosis, and the tooth that enter
the maxillary sinus. Extraction of a tooth with
difficult conditions is an extraction that requires
opening the soft tissue flap, removing bone or cutting
the tooth (Lande et al., 2015).
Hard tissue surgery is a surgical procedure in the
field of oral surgery to eliminate the infection in the
tooth and hard tissue in the patient's oral cavity.
Several kinds of conditions in the tooth and oral
cavity that require hard tissue surgery include the
state of the impacted tooth, buried root tooth and
exostosis. Impaction is a tooth condition that cannot
erupt in the jaw arch at the time of eruption (Arisetiadi
et al., 2017).
The embedded tooth is tooth conditions that
cannot erupt due to obstruction by bone. Extraction is
performed when embedded tooth causes various
symptoms that can interfere with the patient's
activities, such as disrupting the chewing function
and causing complications. Complications include
pathological resorption of the adjacent tooth, the
formation of follicular cysts, pericoronitis and
neuralgic pain (Saleh et al., 2015). The condition of
the embedded tooth located near the nerve will cause
pain due to persistent pressure on the nerve (Hupp et
278
Hartomo, B. and Dewi, R.
Hard Tissue Surgical Treatment with Embedded Dental Condition of Tuberosity Maxillary.
DOI: 10.5220/0010491402780283
In Proceedings of the 1st Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference in conjunction with the 5th Annual Scientific Meeting (Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia
(JIMC 2020), pages 278-283
ISBN: 978-989-758-499-2
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

al., 2019). Embedded conditions can cause
complaints such as pain so that the patient feels
uncomfortable and disturbed. The pain results from
persistent pressure on the nerves around the
embedded tooth. Pain that occurs as a result of dental
problems is included in myofascial pain. Myofascial
pain is a condition of muscle pain or facial pain, acute
and chronic and interferes with sensory and motor
functions (Bahrudin, 2017). The tooth that is often
impacted or embedded in the posterior tooth,
including mandibular third molars, maxillary third
molars, mandibular premolars, and maxillary
premolars. Anterior tooth such as canines and incisors
can also be impacted on either the maxilla or the
mandible. The maxillary second molar's Impaction is
relatively rare, with a prevalence rate of 0.08%
(Zakaria, 2015).
The angulation positions of the impacted teeth of
the maxillary and mandibular third molars had the
opposite degree of difficulty. The most difficult to
remove for the maxillary third molar was
mesioangular angulation (directly opposite to the
impacted mandibular third molar) versus vertical or
distoangular angulation. The mesioangular impact is
the most challenging difficulty to remove because the
bone lining or covering the impacted tooth requires
removal or expansion in the tooth's posterior aspect.
Access to the teeth in the mesioangular position is
complicated to reach if the maxillary second molar's
eruption is in place.1 The angulation of impacted
teeth of the maxillary and mandibular third molars
have the opposite degree of difficulty. The most
difficult to remove for the maxillary third molar was
mesioangular angulation (directly opposite to the
impacted mandibular third molar) versus vertical or
distoangular angulation. The mesioangular impact is
the most challenging difficulty to remove because the
bone lining or covering the impacted tooth requires
removal or expansion in the tooth's posterior aspect.
Access to the teeth in the mesioangular position is
complicated to reach if the maxillary second molar's
eruption is in place (Tammama, 2018).
The extraction of the embedded tooth is
performed by surgery. Extraction with a surgical
technique is called omentectomy (Fitri et al., 2016).
Odontectomy is a treatment performed to remove a
tooth that can erupt, partially erupt and non-erupted
tooth (Fakhrurrazi et al., 2015). Odontectomy is a
surgical extraction procedure that requires creating a
mucoperiosteal flap and removing the bone blocking
the tooth. This action requires good preparation and
accuracy in planning. It is done not to cause unwanted
complications, such as oedema, trismus and
paresthesia (Roi et al., 2019). The aim of this case
report is knowing the hard tissue surgical treatment
performed in the condition of embedded tooth in
maxillary tuberosity.
2 CASE
A 23 years old female patient came with complaints
of frequent headaches since five years ago. Patients
often feel pain in the left temple area as well as the
left maxilla area. The patient has a habit of chewing
using both sides of the jaw. The extraoral examination
results, when the palpation examination was carried
out in the left temporal area, there was mild
tenderness. A temporomandibular joint investigation
found no abnormalities and pain. The intraoral study
results were no teeth 18, 17, 27, 28, and 38.
Examination of palpation in the left maxillary
tuberosity felt a slight bulge in the distal part.
Analysis of the vestibule of tooth 27 showed mild
tenderness. It was found that both maxillary second
molars had horizontal class IIIC impactions with the
crown distally and there were no images of the right
and left third molars in the upper jaw and the lower
left third molar.
Figure 1. Panoramic radiograph
The diagnosis in the case was embedded tooth 37.
The treatment plan, in this case, was odontectomy.
The odontectomy procedure begins with
performing asepsis of the work area using povidone-
iodine. The buccal anaesthesia in the space of tooth
was performed. An anaesthetize posterior superior
alveolar nerve and tooth 27 to anaesthetize palatinus
major nerve was conducted in the palatal region.
Anaesthesia checks are carried out using an excavator
or tweezers by comparing the area under anaesthesia
with the area that was not anaesthetized. The next step
was to make an incision to create the mucoperiosteum
flap and the left maxillary second molar. The flap is
opened using a raspatorium, and then the alveolar
processus is taken from the buccal part that covers the
tooth with a bone bur. The visible tooth was removed
Hard Tissue Surgical Treatment with Embedded Dental Condition of Tuberosity Maxillary
279
using beins and extraction forceps. The socket where
it was removed is debrided by taking the granulation
tissue and smoothing the sharp bone. The next step is
to perform irrigation using sterile saline and continues
with suturing. The patient is instructed to bite the
tampon. The patient was given postoperative
instructions and medication in the form of antibiotics
and analgesics.
Figure 2. The left maxillary second molar after
omentectomy
3 DISCUSSION
A hard tissue surgery is a branch of oral surgery that
studies things related to hard tissue surgery in the oral
cavity, such as odontectomy in the case of impacted
and embedded tooth, bone reduction to help the
extraction process of the tooth with challenging
conditions and alveolectomy in cases exostosis or
bony prominence (Haggerty and Laughlin, 2015).
The state of an impacted tooth is a condition of the
tooth which partially or cannot fully erupt due to
obstruction or obstruction by an adjacent tooth or
pathological tissue (Lande et al., 2015).
The embedded tooth is a tooth condition that
cannot wholly erupt due to obstruction by bone. The
implanted root is a condition where the remaining
root of the tooth is not treated when the tooth is
necrotic so that over time the alveolar and gingiva
will cover the remaining root of the tooth. The
embedded tooth usually occur in mandibular third
molars and maxillary third molars (Saleh et al., 2015).
The tooth cannot erupt because of the tooth's small
arch or horizontal position (Roi et al., 2019). The
tooth that is often impacted or embedded in the
posterior tooth, including mandibular third molars,
maxillary third molars, mandibular premolars and
maxillary premolars. Anterior tooth such as canines
and incisors can also impact either the maxilla or the
mandible (Zakaria, 2015).
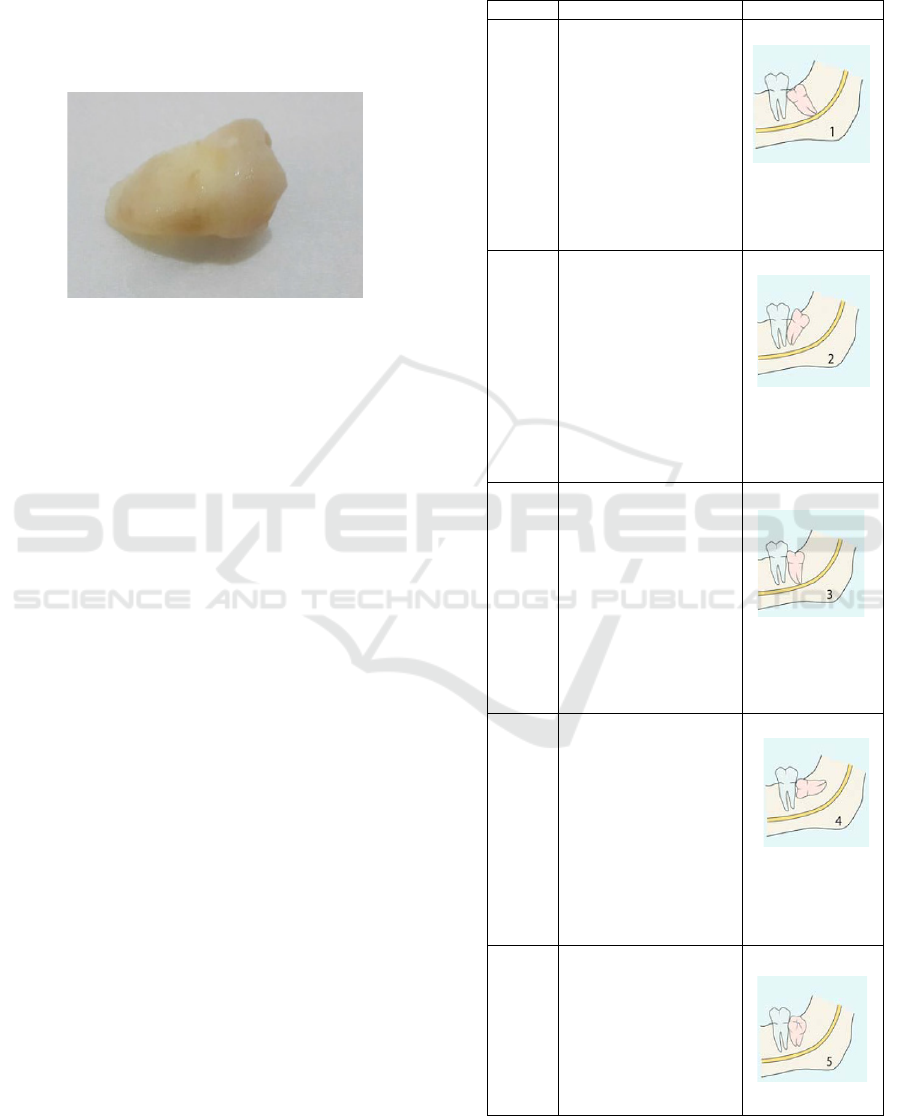
Winter's classification divides the conditions of
impacted mandibular third molars based on the long
axis of the tooth or the position of the impacted
mandibular third molar against the mandibular
second molar, among others:
Table 1. Winter Classification
Class Description Figure
Class 1 It is called a
mesioangular impacted
tooth, or it is oblique to
the mesial direction
because the third molar is
tilting the second molar
in a mesial direction.
Figure 2. Class 1
Source: Hupp et
al. (2019)
Class 2 It is called a distoangular
or tilted distally impacted
tooth because the
condition of the third
molar's long axis is
directed distally or
posteriorly so that it is
away from the second
molar.
Figure 3. Class 2
Source: Hupp et
al. (2019)
Class 3 It is called a vertical
impacted tooth because
of the third molar points'
long axis in the same
direction as the second
molar axis.
Figure 4. Class 3
Source: Hupp et
al. (2019)
Class 4 It is called a horizontally
impacted tooth because
the third molar's long axis
is flat or horizontal to the
second molar's long axis.
Figure 5. Class 4
Source: Hupp et
al. (2019)
Class 5 It is called a bucoangular
impacted tooth because
the long axis of the third
molar is directed buccal
to the second molar's
long axis.
Figure 6. Class 5
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
280
Source: Hupp et
al. (2019)
Class 6 It is called a
linguoangular impacted
tooth because the long
axis of the third molar
points lingually towards
the second molar's long
axis.
Figure 7. Class 6
Source: Hupp et
al. (2019)
Class 7 It is called an inverted
impacted tooth because
the third molar is
embedded with the third
molar's long axis
pointing apically.
Figure 8. Class 7
Source: Hupp et
al. (2019)
(Hupp et al., 2019)
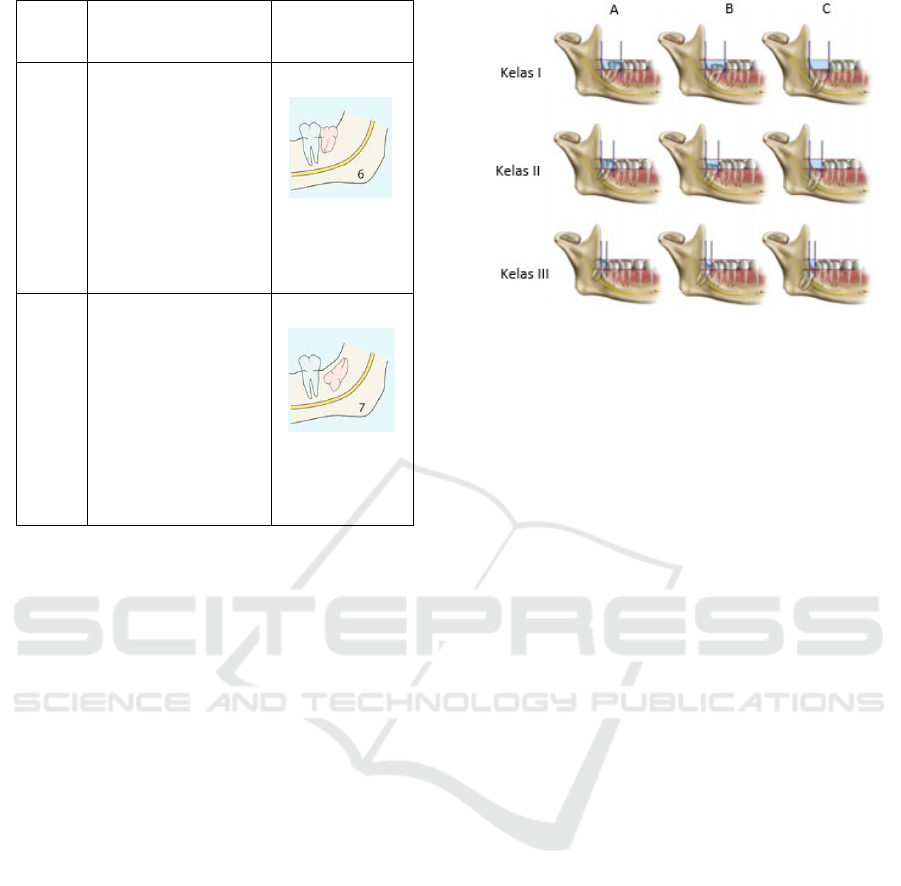
Pell and Gregory's classification divided the
impacted conditions of the third molars based on two
factors: the relationship of the ramus to the space
available and the relative depth of the third molars.
The relationship between the ramus and the available
space is divided into three classes, including class I,
class II, and class III. Class I is the space available
between the mandibular ramus and the mandibular
second molar's distal surface, sufficient for the
mesiodistal size of the mandibular third molar crown.
Class II, the space available between the mandibular
ramus and the mandibular second molar's distal
surface is smaller than the mesiodistal size of the
mandibular third molar crown. Class III, namely that
there is no space available between the ramus of the
mandibular and the distal surface of the mandibular
second molar so that the tooth is mostly or entirely
located in the ramus. Based on the third molar's
relative depth, it is divided into three positions,
namely position A, position B, and position C.
Position A is that the occlusal plane of the third molar
is at the same level as the occlusal plane of the second
molar. Position B is the third molar's occlusal plane
between the occlusal plane and the cervical line of the
second molar. Position C, which is the third molar's
occlusal plane, is below the cervical line of the second
molar (Lita and Hadikrishna, 2020).
Figure 9. Pell and Gregory classification
Source: Lita and Hadikrishna (2020)
The embedded tooth condition occurs because the
crown cannot erupt either partially or entirely. After
all, it is blocked by bone. According to Winter, the
implanted tooth in the classification is included in
class 7, whereas according to Pell and Gregory, the
embedded tooth are in class IIC and class IIIC (Hupp
et al., 2019).
Embedded conditions can cause complaints such
as pain so that the patient feels uncomfortable and
disturbed. The pain results from persistent pressure
on the nerves around the embedded tooth. Pain that
occurs as a result of dental problems is included in
myofascial pain. Myofascial pain is a condition of
muscle pain or facial pain, acute and chronic and
interferes with sensory and motor functions. Pain
occurs due to tissue damage that secretes histamine
and bradykinin so that C fibres will increase the
response to the peripheral areas by serotonin,
prostaglandins, thromboxane and leukotrienes
(Bahrudin, 2017). Substance P is released in the
periphery, and increase peripheral vasodilation,
sensitisation C fibres. C fibres will deliver impulses
to the spinal cord's dorsal horn (Atmadja, 2016).
The procedure for the embedded tooth is
odontectomy. This treatment aims to prevent the
occurrence of a pathological condition originating
from the follicle and infection caused by the inability
to erupt or not fully erupt so that it can cause various
kinds of pain complaints (Domingos et al., 2019).
Odontectomy is a tooth extraction procedure for a
tooth that cannot erupt, partially erupt or a tooth that
cannot be extracted (Fakhrurrazi et al., 2015).
The odontectomy procedure begins with
investigations, flap creation, bone reduction and tooth
extraction. Studies are needed before an odontectomy
is performed. The supporting examination function is
to find out the anatomy around the tooth to be
Hard Tissue Surgical Treatment with Embedded Dental Condition of Tuberosity Maxillary
281

performed, the condition around the bones, the shape
of the roots, the number of roots, the length of the
roots, and whether there is hypersementosis or not.
The supporting examination used before an
odontectomy is taking extra-oral X-rays using a
panoramic technique (Saptadi et al., 2019).
Odontectomy for embedded tooth requires precision
and precision when extracting tooth using beins and
extraction forceps. Anatomical structures such as
blood vessels and sinuses and nerves around the tooth
also need to be considered in the odontectomy of the
embedded tooth. The management of odontectomy in
the implanted tooth's condition begins with the
asepsis procedure followed by anaesthesia (Sahetapy
et al., 2015).
The stage after the supporting examination is
making a flap. A flap is a surgical procedure that
separates the mucosa from the underlying tissue. The
flap aims to obtain visitability and accessibility to the
alveolar bone. The flap in surgery has several
conditions, including forms with a surgical incision,
must have an adequate blood supply, sufficient flap
size, have good visualization, flap design does not
damage the anatomical structure, can return the tissue
to its original or initial position and can be sutured
with a sound healing process. There are various
classifications of flaps, namely based on thickness
and based on an outline. Based on the thickness, there
are two types of flap: full-thickness flap or
mucoperiosteal flap and partial thickness flap of the
mucosal flap. A full-thickness flap is a flap used to
gain access to the bone surface by separating the
bone's soft tissue. This flap consists of the gingiva,
mucosa, submucosa and alveolar periosteum (Yolcu
and Acar, 2015).
The next step was to make an incision to create
the mucoperiosteum flap, and the flap was opened
using a raspatorium, and then the alveolar process
was taken that covered the teeth using a bone bur. The
visible tooth is cut into two parts to make it easier to
retrieve. A tooth that has been cut is removed using a
bein and extraction forceps. The socket where it was
removed was debrided in taking granulation tissue
and smoothing the sharp bone and then doing
irrigation using sterile saline. The next step was
suturing the socket, and the patient was instructed to
bite the tampon. The patient was given postoperative
instructions and medication in antibiotics and
analgesics (Sahetapy et al., 2015).
Medication after hard tissue surgery is needed to
prevent post-surgical complications. Medicines used
after hard tissue surgery are antibiotics, analgesics
and anti-inflammatory. Antibiotics, analgesics and
anti-inflammatory agents in postoperative and simple
tooth extraction procedures are slightly different. The
difference in medication is in choosing the type of
medicine, which is the size or not the wound healing
after the action. Antibiotic medication can be given as
a prophylaxis to prevent infection in patients with a
high risk of disease. It can be given post-surgery to
prevent infection after the procedure(Lukito, 2019).
Analgesic medication is given after surgery to
relieve pain or relieve pain. A few hours after the
surgery, the numbness or numbness from anaesthesia
will slowly return to normal, causing pain. The pain
that appears can be reduced if given analgesic
medication. Analgesics are divided into two groups,
namely non-opioid anaesthetics and opioid
analgesics. Non-opioid painkillers, also called
NSAID analgesics, are the anaesthetics most often
used in dentistry. NSAID anaesthetics inhibit
cyclooxygenase, where cyclooxygenase synthesizes
prostaglandins, thromboxane and prostacyclin which
are pain mediators. Based on the way NSAID
analgesics work, it can be used as a drug to treat pain
due to inflammation after extraction and surgery
(Taufiqurrachman and Mulyo, 2016).
4 CONCLUSIONS
The tooth condition that has been impacted,
embedded, exostotic, and the state of the tooth with
complications, namely having variations in the roots'
anatomical shape, such as bent or macerated roots,
mostly cause complaints and pain. Pain and
complaints can be relieved by taking care or treatment
for these conditions. The treatment that can be given
is by performing hard tissue surgery.
Hard tissue surgery that can be done is extraction
with surgical techniques, namely odontectomy. The
odontectomy procedure aims to remove the infection
source so that complaints of pain and discomfort will
disappear. Providing medication in the form of
prophylactic medication and post-surgery
significantly affects infection prevention, wound
healing process, and overcoming patients' pain after
surgery.
REFERENCES
Arisetiadi, K. N. ., Hutomo, L. ., & Septarini, N. . (2017).
Hubungan Antara Gigi Impaksi Molar Ketiga dengan
Kejadian Karies Molar Kedua Berdasarkan Jenis
Kelamin dan Usia pada Mahasiswa Fakultas
Kedokteran Universitas Udayana. Bali Dental Journal,
1(1), 29–38.
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
282

Atmadja, A. S. (2016). Sindrom Nyeri Myofasial. Cermin
Dunia Kedokteran, 43(3), 176–179.
http://www.cdkjournal.com/index.php/CDK/article/do
wnload/29/26
Bahrudin, M. (2017). Patofisiologi Nyeri (Pain). Saintika
Medika, 13(1), 7–13.
https://doi.org/10.22219/sm.v13i1.5449
Domingos, J., Suwarman, & Kestriani, N. D. (2019).
Pengaruh Deksametason 0,2 mg/KgBB sebagai
Adjuvan Analgesia terhadap Waktu Kejadian Nyeri
Pascaoperasi Odontektomi dengan Nrs>3. Jurnal
Anestesi Perioperatif, 7(3), 168–174.
Fakhrurrazi, Hakim, R. F., & Rifani, R. (2015). Hubungan
Tingkat Kesulitan dengan Komplikasi Post
Odontektomi Gigi Impaksi Molar Ketiga Rahang
Bawah pada Pasien di Instalasi Gigi dan Mulit
RSUDZA Banda Aceh. Cakradonya Dent J, 7(1), 761–
767. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
Fitri, A. M., Kasim, A., & Yuza, A. T. (2016). Impaksi gigi
molar tiga rahang bawah dan sefalgia. J Ked Gi Unpad,
28(3), 148–154.
https://doi.org/10.24198/jkg.v28i3.18691
Haggerty, C. J., & Laughlin, R. M. (2015). Atlas of
Operatie Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. WILEY
Blackwell.
https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118993729.ch2
Hupp, J. R., Ellis, E., & Tucker, M. R. (2019).
Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (7th
ed.). Elsevier.
https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
Lande, R., Kepel, B. J., & Siagian, K. V. (2015). Gambaran
Faktor Risiko Dan Komplikasi Pencabutan Gigi Di
Rsgm Pspdg-Fk Unsrat. Jurnal E-GIGI, 3(2), 476–481.
https://doi.org/10.35790/eg.3.2.2015.10012
Lita, Y. A., & Hadikrishna, I. (2020). Klasifikasi Impaksi
Gigi Molar Ketiga Melalui Pemeriksaan Radiografi
sebagai Penunjang Odontektomi. Jurnal Radiologi
Dentomaksilofasial Indonesia, 4(1), 1–5.
https://doi.org/10.32793/jrdi.v4i1.467
Lukito, J. I. (2019). Antibiotik Profilaksis pada Tindakan
Bedah. Cermin Dunia Kedokteran, 46(12), 777–783.
Roi, C. I., Ianes, E., Gaje, P. N., Nica, D. F., Roi, A., & Roi,
A. (2019). The predictability of Difficultness of Lower
Third Molar Odontectomy. REV.CHIM, 70(4), 1342–
1345. https://doi.org/10.37358/rc.19.4.7123
Sahetapy, D. T., Anindita, P. S., & Hutagalung, B. S. P.
(2015). Prevalensi Gigi Impaksi Molar Tiga Partial
Erupted Pada Masyarakat Desa Totabuan. Jurnal E-
GIGI, 3
(2), 641–646.
https://doi.org/10.35790/eg.3.2.2015.10810
Saleh, E., Prihartiningsih, & Rahardjo. (2015).
Odontektomi Gigi Molar Ketiga Mandibula Impaksi
Ektopik dengan Kista Dentigerous secara Ekstraoral.
Majalah Kedokteran Gigi Klinik, 1(2), 85–91.
https://doi.org/10.22146/mkgk.11956
Saptadi, A., Lilies, D. S., Menik, P., & Latief, B. S. (2019).
Evaluation of Impacted Mandibular Third Molar
Position in Relation to Mandibular Canal on Panoramic
Radiography compared to Cone-Beam Computed
Tomography. Journal of International Dental and
Medical Research, 12(2), 591–596.
Tammama, T. (2018). Impaksi Horizontal Gigi Molar
Kedua Maksila Bilateral Simptomatis yang
Menyebabkan Nyeri Kepala Rekuren Horizontal
impaction of symptomatic bilateral maxillary second
molar causing recurrent headache. J Ked Gi Unpad,
30(3), 158–161.
https://doi.org/10.24198/jkg.v30i3.18082
Taufiqurrachman, T., & Mulyo, K. (2016). Perbandingan
Pengaruh Pemberian Analgetik Etoricoxib Dengan
Natrium Diclofenak Terhadap Rasa Nyeri Pasca
Odontektomi (Impaksi Kelas 1, Molar 3 Rahang
Bawah). Jurnal Kedokteran Diponegoro, 5(3), 222–
234.
Yolcu, U., & Acar, A. H. (2015). Comparison of a New
Flap Design with The Routinely used Triangular Flap
Design in Third Molar Surgery. International Journal
of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 1–8.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2015.07.007
Zakaria, K. (2015). Sistem Pakar Diagnosa Penyakit THT
Menggunakan Metode Dempster Shafer. Prosiding
Seminar Informatika Aplikatif Polinema, 175–178.
https://doi.org/10.22219/repositor.v2i9.776
Hard Tissue Surgical Treatment with Embedded Dental Condition of Tuberosity Maxillary
283
