
Expression of MicroRNA-155 and Suppressor of Cytokines Signaling
1 (SOCS1) mRNA in Plasma Breast Cancer Patients
Dwi Nur Indah Sari
1
1
, Dina Rahmina
2
2
, Sumadi Lukman
3
3
, Artanto Wahyono
3
4
,
Indwiani Astuti
4
5
, Sofia Mubarika
5
6
and Teguh Aryandono
3
7
1
Department of Biomedicine, School of Dentistry, Faculty of Medicine, Jenderal Soedirman University, Purwokerto,
Indonesia
2
Graduate Student Biomedical Science, Faculty of Medicine, Nursing and Public Health, Universitas Gadjah Mada,
Yogyakarta, Indonesia
3
Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Nursing and Public Health, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta,
Indonesia
4
Derpartment of Pharmacology and Therapy, Faculty of Medicine, Nursing and Public Health, Universitas Gadjah Mada,
Yogyakarta, Indonesia
5
Department of Histology and Cell Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Nursing and Public Health, Universitas Gadjah Mada,
Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Breast cancer, plasma, microRNA-155, SOCS1 mRNA.
Abstract: Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women worldwide. miR-155 has been discovered to have an
important role in the development of breast cancer. miR-155 targets many mRNAs of tumor suppressor genes,
one of them is SOCS1. The discovery of miRNA in body fluids provides a novel alternative for the
development of minimally invasive biomarker in cancer. However, limited study has been reported on the
expression of miR-155 and SOCS1 mRNA in plasma breast cancer patients especially in Indonesian
population.This study analyzed expressions of miR-155 and SOCS1 mRNA in plasma breast cancer patients
This study was conducted using cross-sectional design, 32 plasma samples were collected from Dr.Sardjito
Hospital. RNA was extracted from plasma and then cDNA was synthesized from RNA samples. Real-time
qPCR was used to detect expression of miR-155 and mRNA SOCS1. Both expression was analyzed using
Livak's method. The significance of the results were tested statistically using independence T-test. Expression
of miR-155 at advanced stage was 2.43 higher than the early stages (p=0.047), while the mRNA expression
of SOCS1 at advanced stage was 1.29 lower than early stage (p=0.170). Expression of miR-155 in ER, PR,
& HER2 status revealed differences among subgroups, while the mRNA expression of SOCS1 was not
significantly different. Other result showed that miR-155 expression was higher in triple negative tumor, while
SOCS1 higher in luminal A tumor. Nevertheless, the difference was also not statistically significant (p value
> 0,05). This study showed that expressions of miR-155 and SOCS1 mRNA was deregulated in breast cancer
plasma and it believed to have an important role in breast cancer.
1
https://orcid.org/0000- 0003-4691-9840
2
https://orcid.org/0000- 0003-0125-8604
3
https://orcid.org/0000- 0002-2607-6682
4
https://orcid.org/0000- 0001-6870-4475
5
https://orcid.org/0000- 0001-7008-9192
6
https://orcid.org/0000- 0001-7205-652X
7
https://orcid.org/ 0000-0003-4998-0006
Indah Sari, D., Rahmina, D., Lukman, S., Wahyono, A., Astuti, I., Mubarika, S. and Aryandono, T.
Expression of MicroRNA-155 and Suppressor of Cytokines Signaling 1 (SOCS1) mRNA in Plasma Breast Cancer Patients.
DOI: 10.5220/0010490402230230
In Proceedings of the 1st Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference in conjunction with the 5th Annual Scientific Meeting (Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia
(JIMC 2020), pages 223-230
ISBN: 978-989-758-499-2
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
223
1 INTRODUCTION
MicroRNAs (miRNA) are short non-coding RNA
molecules that play important role as regulators of
various cellular processes in post-transcriptional
process (Ying et al. 2008). The role of miRNA is
mediated by inhibition of translation or target
mRNAs degradation. The mechanism of interaction
between miRNA and mRNA is based on sequence
complementation (Iorio & Croce 2009). Several
biological processes are modulated by miRNAs,
therefore deregulation of miRNAs expression is
associated with various disease. Deregulation of
miRNA expression has also been widely reported in
various cancers, including breast cancer (Singh & Mo
2013; Iorio & Croce 2012; Ventura & Jacks 2009;
Garzon et al. 2006).
Based on the target mRNAs, miRNA are divided
into oncogenic miRNAs (oncomirs) and tumor
suppressive miRNAs (Cho, 2011; Garzon et al.
2006). miR-155 plays as oncomir, and its
overexpression is frequently reported in a number of
malignant diseases (Higgs & Slack 2013; Johansson
et al. 2013; Zhang et al. 2013; Jiang et al. 2012; Kong
et al. 2010; Faraoni et al. 2009). Overexpression of
miR-155 is reported during early development and
progression of breast cancer. The expression of miR-
155 has been studied that it has correlation with
SOCS1 expression. It was reported that SOCS1,
tumor suppressor gene, become target of miR-155
(Zhao et al. 2013; Huang et al. 2013; Cho, 2011; Jiang
et al. 2010).
SOCS1 (Suppressor of cytokines signaling 1) is a
negative feedback pathway regulator of Janus-
activated kinase (JAK) / signal transducer and
activator of transcription signaling (STAT) (Fujimoto
& Naka 2010; Croker et al. 2009). Activation of JAK
/ STAT stimulates cells to proliferate, migrate or
undergo apoptosis (Murray 2007; Rawlings et al.
2004). In the mammary gland, JAK / STAT plays role
in the development of the mammary gland
(particularly JAK1 and JAK2). Uncontrolled
activation of JAK / STAT lead to tumorigenesis
(Santillán-Benítez et al. 2014; Wagner & Schmidt
2011). SOCS1 regulates activation of JAK / STAT in
order to maintain breast cells in homeostasis.
The initial study of the miR-155 and SOCS1 was
reported in pancreatic cancer cells by Huang et al.
(Huang et al., 2013). They reported that miR-155
played an important role in the regulation of invasion
and migration of cancer cells via modulation of
STAT3 and SOCS1 (Huang et al. 2013). The
discovery of miRNA in body fluids represents a new
alternative for the development of minimally invasive
biomarker in breast cancer in addition to the use of
Ca-153 which is not specific ( Zheng et al. 2011;
Corcoran et al. 2011; Brase et al. 2010). Previous
studies showed that the expression of miR-155 in the
serum of breast cancer patients was associated with
clinical stages, molecular types, proliferation index
and p53 expression ( Zeng et al. 2014; Zheng et al.
2012). However, no study reported the expression of
miR-155 and SOCS1 mRNA in the plasma of breast
cancer patients especially for the Indonesian
population. Expressions of miR-155 and SOCS1
mRNA from plasma of breast patients were
performed in this study.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was designed as observational study and
cross sectional study.
2.1 Sample
Plasma samples of breast cancer patients were
obtained from Dr. Sardjito Hospital. Samples were
collected from patients that clinically and
pathologically confirmed have breast cancer, not have
another cancer, have not received any treatment, and
aged 30-70 years.
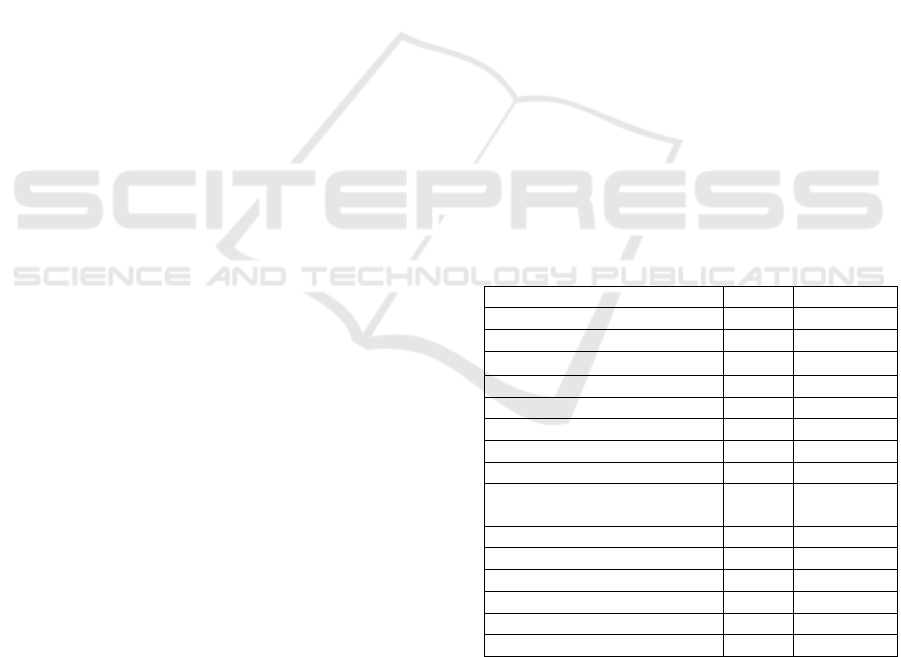
Table 1: Characterics of samples
Characteristic N %
Sta
g
e
Earl
y
sta
g
e
(
I-II
)
10 31,25%
Advanced stage (III-IV)
22 68,75%
Receptor
ER Positive 17 60,71%
ER Ne
g
ative 11 39,29%
PR Positive 13 50,00%
PR Ne
g
ative 13 50,00%
HER2 Positive
10
40,00%
HER2 Ne
g
ative 15 60,00%
Molecular subtype
Luminal A 10 35,71%
Luminal B 8 28,57%
HER2 overex
p
ression 4 14,28%
Tri
p
le ne
g
ative 6 21,42%
2.2 RNA Extraction and cDNA
Synthesis
RNA extraction was performed using RNA Isolation
Kit miRCURY-Biofluid according to the
manufacturer’ protocol. After RNA isolation, cDNAs
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
224

were synthesised using cDNA Synthesis kit II, 8-64
rxns. Each reaction was incubated 42°C for 60
minutes, 95°C for 5 minutes and followed by
indefinite incubation at 4°C in PCR themal cycler
(Biorad c1000).
2.3 Real Time-quantitative PCR
(qPCR) of miR-155
qPCR was performed using ExiLent SYBR Green
master mix (Cat No. 203402, Exiqon) and miRCURY
LNATM Universal RT microRNA PCR for hsa-miR-
155-5p. one reaction was mixed according to the
manufacturer’s protocol. Each reaction was then
incubated with following programs : denaturation
95°C for 10 minutes, 40 cycles amplification : 95
o
C,
58
o
C for 10 seconds in Biorad CFX 96. MiR-16 was
used as reference gene for miR-155-5p
quantification. Relative expression was calculated
according to the comparative Livak’s Method : 2
-∆∆Cq
.
If the fold change <1, value of fold decreased was
calculate by 1/fold change.
2.4 Real Time PCR mRNA SOCS1
One-Step qRT-PCR using KAPA™ SYBR® kit was
used to analyze SOCS1 mRNA expression. One
reaction was mixed according to the manufacturer’s
protocol. qPCR program were performed on Biorad
CFX 96. cDNA synthesis 45
o
C for 5 minutes, RT
inactivation 95°C for 3 minutes, denaturation 95° C
for 10 s, annealing for 30 seconds 59,4°C
amplification of 45 cycles : 95°C for 10 seconds and
59 , 4 °C for 30-second ramp-rate 1,6°C / s Optical
read and melting curve analysis. Beta Actin mRNA
was used as reference gene for SOCS1 mRNA
quantification. Relative expression was calculated
according to the comparative Livak’s Method : 2
-∆∆Cq
.
If the fold change <1, value of fold decreased was
calculate by 1/fold change.
2.5 Statistical Analysis
All of the miR-155 and SOCS1 expression
differences among breast cancer subgroup was then
analyzed statistically using Independent T-tests.
Statistical significance was determined when P value
≤ 0.05.
3 RESULT
3.1 Interaction Analysis of miR-155
with mRNA SOCS1 (in silico)
Interaction analysis of miR-155 with its target mRNA
was carried out through bioinformatic analysis on
miRanda/mirtarbase
(www.mirtarbase.mbc.nctu.edu.tw). One of the
targets for mir-155 is mRNA SOCS1. The SOCS1
mRNA sequence has a length of 1216 base pairs with
the region predicted to interact with miR-155 being in
the 3'UTR (untranslated region) of SOCS1 mRNA.
Possible interaction of miR-155 with 3'UTR mRNA
SOCS1 occur at three site, at 15-34 nucleotides withal
Minimum Free Energy (MFE) -15,50 kj/mol, at 218-
242 nucleotides withal MFE -15,90 kj/mol and at
nucleotides 404-425 withal MFE -9,13 kj/mol (see
figure 1).
Figure1. Binding site of miR-155 on 3’UTR region
mRNA SOCS1
3.2 Expression of miR-155 and mRNA
SOCS1
Expressions of miR-155 and SOCS1 mRNA were
analyzed by qRT-PCR as previously described.
Expression of miR-155 was calculated defined from
Cq value. Cq value represents first cycle in PCR when
the quantitative graph increased exponentially. The
small Cq value means concentration of PCR product
is high in the sample. Then Cq value were used to
calculated the expression of miR-155 and SOCS1
mRNA using Livak’s Method. The fold change (FC)
value could upregulated (FC>1) or downregulated
(FC<1). If the fold change <1, value of fold decreased
was calculate by 1/fold change.
Expression of miR-155 in advanced stage of
breast cancer patients was significantly higher than
TGACCGGCAGCGCCCGCCGTGCACGCAGCATTAAC
TGGGATGCCGTGTTATTTTGTTATTACTTGCCTGG
AACCATGTGGGTACCCTCCCCGGCCTGGGTTGGAG
GGAGCGGATGGGTGTAGGGGCGAGGCGCCTCCCGC
CCTCGGCTGGAGACGAGGCCGCAGACCCCTTCTCA
CCTCTTGAGGGGGTCCTCCCCCTCCTGGTGCTCCC
TCTGGGTCCCCCTGGTTGTTGTAGCAGCTTAACTG
TATCTGGAGCCAGGACCTGAACTCGCACCTCCTAC
CTCTTCATGTTTACATATACCCAGTATCTTTGCAC
AAACCAGGGGTTGGGGGAGGGTCTCTGGCTTTATT
TTTCTGCTGTGCAGAATCCTATTTTATATTTTTTA
AAGTCAGTTTAGGTAATAAACTTTATTATGAAAGT
Expression of MicroRNA-155 and Suppressor of Cytokines Signaling 1 (SOCS1) mRNA in Plasma Breast Cancer Patients
225
early stage. Expression of miR-155 in advanced stage
of breast cancer was 2.43 times higher than the early
stage. In addition, expression of SOCS1 in early stage
was higher than advanced stage. Fold change
expression of SOCS1 in advanced stage of breast
cancer was 0.77 times to early stage. It was mean
expression of SOCS1 in advanced stage of breast
cancer was 1.29 fold decreased from early stage
However, the differences were not statistically
significant (See Table 2).
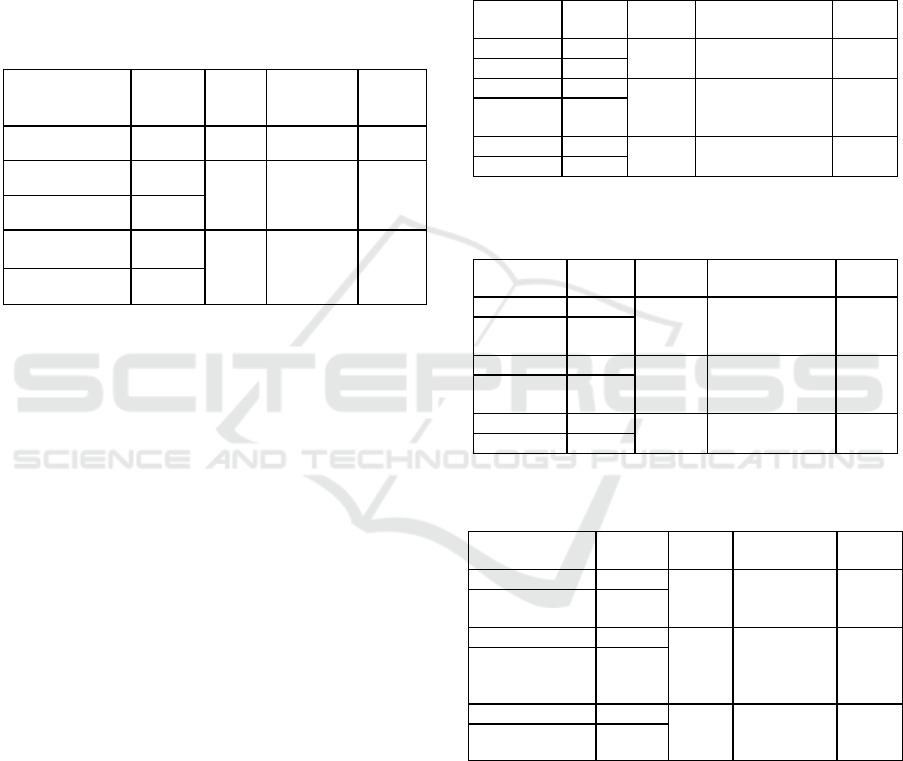
Table 2: miR-155 and SOCS1 mRNA expression
according to clinical stage
Sample
Mean
(ΔCq)
∆∆Cq
Fold
change
(2
-∆∆Cq
)
P
value
#
miR-155
Advanced stage
11.51
-1.28
2.43
(up-
regulated)
0.047
Early stage
12.79
SOCS1 mRNA
Advanced stage
4.90
0.38
0.77
(down-
regulated)
0.170
Early stage
4.53
#
p value were analyzed with independent t-test
We subclassified samples by their estrogen
receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and HER2
receptor. Expression of miR-155 was not
significantly different between ER + and ER -. Fold
change expression miR-155 in PR - was 0.76 times to
PR +. It was mean that expression miR-155 in PR -
was 1.31 fold decreased from PR +. Expression of
miR-155 in HER2 - was higher 2.55 times from
HER2 +. However, the different miR-155 expression
was not statistically significant (see Table 3).
The expression of SOCS1 mRNA was also
analyzed according ER, PR, and HER2 status. The
results showed that expression of SOCS1 were not
different in both in ER + and ER - and also in HER2
+ and HER2 -. But in PR - was slightly lower than in
PR +. However, that were not statistically different
between different ER, PR, and HER2 status (see
Table 4).
Subtypes of breast cancer have been implicated to
determine prognosis. We subclassified breast cancer
patients according to the subtypes. Our result showed
expression of miR-155 was higher in triple negative
than the other subtypes, while the highest expression
of SOCS1 mRNA was in Luminal A subtype and the
lowest was in triple negative subtype.
Then, we compared expression of miR-155 and
SOCS1 mRNA between Luminal A and other
subtypes. The result showed that miR-155 in Luminal
A was upregulated/higher than Luminal B dan HER2
overexpressions subtype, but lower than Triple
negative subtype. However, the differences were not
statistically significant. Our result also showed that
expression of SOCS1 mRNA in Luminal A subtype
was higher than in the other subtypes but that were
not statically significant.
Table 3. miR-155 expression according to ER, PR,
HER2
Sample
Mean
(ΔCq)
∆∆Cq
Fold change (2
-
∆∆Cq
)
P
value
#
ER- 11.47
-0.17 1.13 0.838
ER+ 11.64
PR- 11.84
0.39
0.76
(downregulated)
0.648
PR+ 11.45
HER2- 11.17
-1.35
2.55
(upregulated)
0.074
HER2+ 12.52
#
p value were analyzed with independent t-test
Table 4. SOCS1 mRNA expression according to ER, PR,
and HER2 expression
Sample Mean
(ΔCq)
∆∆Cq Fold change
(2
-∆∆Cq
)
P
value
ER- 4.74
0.01 0.99 0.994
ER+
4.73
PR- 5.04
0.32
0.80
(down-
regulated)
0.482
PR+
4.72
HER2- 4.87
-0.10 1.07 0.830
HER2+ 4.97
#
p value were analyzed with independent t-test
Table 5 miR-155 expression in subtype
Subtype
Mean
(ΔCq)
∆∆Cq
Fold change
(2
-∆∆Cq
)
P
value
#
Luminal A 10.94
-0.68
1.60
(up-
regulated)
0,506
Luminal B
11.62
Luminal A 10.94
-0.94
1.92
(up-
regulated)
0,547
HER2
overexpression 11.88
Luminal A 10.94
0.92
0.53
(down-
regulated)
0,461
Triple negative 10.02
#
p value were analyzed with independent t-test
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
226
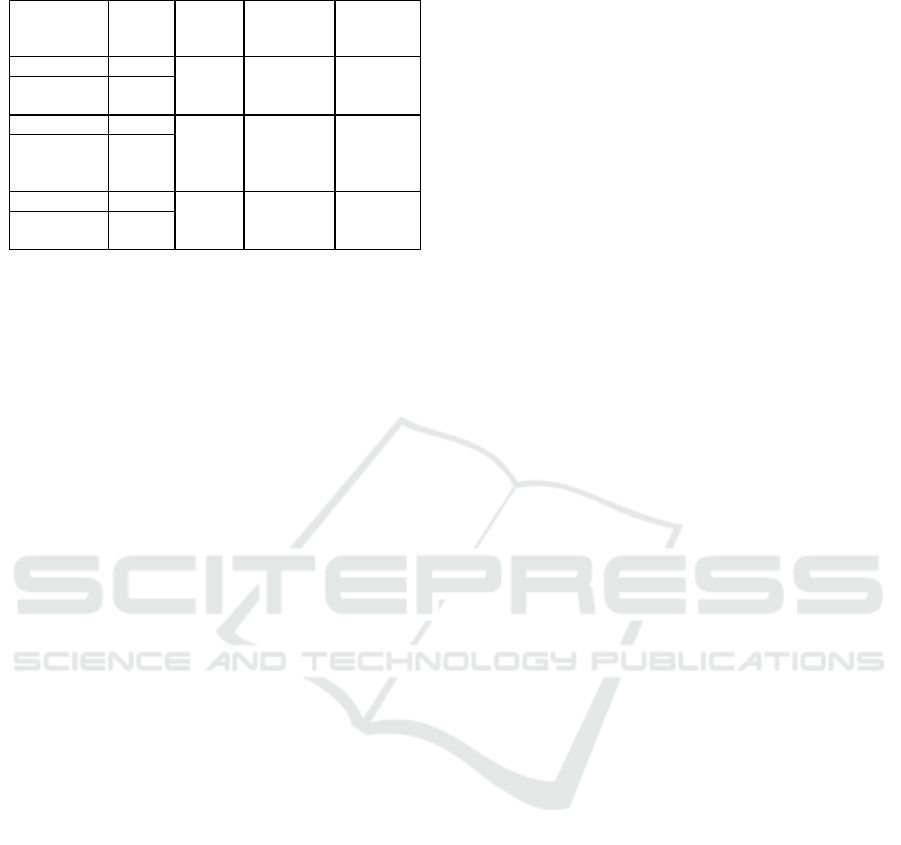
Table 6 SOCS1 mRNA expression in subtype
Subtype
Mean
(ΔCq)
∆∆Cq
Fold
change (2
-
∆∆Cq
)
P value
#
Luminal A 4.59
-0.27
1.21
(up-
regulated)
0,570
Luminal B
4.86
Luminal A 4.59
-0.57
1.48
(up-
regulated)
0.353
HER2 over
expression
5.16
Luminal A 4.59
-0.61
1.52
(up-
regulated)
0.380
Triple
negative
5.20
#
p value were analyzed with independent t-test
4 DISCUSSION
MicroRNAs (miRNA) are short non-coding RNAs
that play an important role in the regulation of gene
expression post-transcriptionally (Ying et al. 2008).
In bioinformatics analysis, miR-155 targets many
genes, one of which is SOCS1 mRNA. miR-155
interacted with SOCS1 mRNA at 3'UTR. The
strongest interaction between miR-155 and SOCS1
mRNA might be in 218-242 base of 3'UTR SOCS1
which was indicated by the most negative mfe value.
Ragan et al. (2011) reported that the mfe value
indicates the free energy used to break the structure
of the interactions that occur between miR and target
mRNA. The more negative mfe value will make it
difficult to break this structure. This means that the
structure has high stability (Chan & Zhang, 2009).
The high stability of the miR-mRNA interaction
structure allows the role of miR-155 in the regulation
of SOCS1 mRNA expression.
Our study has been performed with plasma of
breast cancer patients and the expression of
microRNA can be detected in this samples. It showed
that microRNA in plasma was relatively stable and
provides to be potential alternative for minimal
invasive cancer biomarkers (Zheng et al. 2011;
Kosaka et al. 2010). MiRNAs are relatively stable in
body fluids because miRNAs are protected in lipid
complex or lipoprotein such as apoptotic bodies,
microvesicle, or exosome (Cortez et al. 2011; Kosaka
et al. 2010) or presence in a modified structure
(methylation, adenylation, uridilasi) (Chen et al.
2012).
Our results also showed SOCS1 mRNA can be
detected in plasma samples. This might occur because
SOCS1 mRNA was also protected within
microvesicle (Kosaka et al. 2010; Marini et al. 2006).
In this study, expression of miR-155 was
significantly higher (2.43 times) at an advanced stage
than early stages of breast cancer patients (p=0,047).
Other study showed overexpression of miR-155 both
at an early stage and advanced stage breast cancer
compared with healthy controls. In the advanced
stage breast cancer, expression of miR-155 was
significantly higher compared with than early stages
(p <0.05) (Wang et al. 2012). Studies by Zheng et al.
and Liu et al showed increased expression of miR-
155 in breast cancer patients. They found that the
expression of miR-155 correlated with proliferation
index, lymph node infiltration, and advanced stage
(Zheng et al. 2012; Zeng et al. 2014).
miR-155 has been reported as regulator in the
growth stimulating factor and metastasis (Sun et al.
2012). The role of microRNA in metastasis is
suggested by the presence of microRNA within
exosome in circulation. Exosomal microRNAs plays
a role in the intercellular communication
(Schwarzenbach et al. 2014; Cortez et al. 2011).
Plasma miR-155 is thought to be uptaked by recipient
cells, causing changes in the expression of mRNA
targets of miR-155 in these cells (Cheng, 2015). The
cancer cells might be utilized miRNA to influence
their development and has been reported to have a
strong correlation with cancer invasion and
metastasis (Sun et al., 2012; Cheng et al., 2015).
One of the miR-155 targets is SOCS1 mRNA.
SOCS1 is a major regulator JAK-STAT pathway that
affects expression of various genes involved in cancer
progression (proliferation, invasion, migration,
apoptosis resistance, and angiogenesis) (Huang et al.
2013). Our study showed that expression of SOCS1
at an advanced stage was lower than in the early stage
of breast cancer. Our results were similar with a study
by Sasi et al, that SOCS1 expression decreased in the
higher-stage breast cancer and positively correlated
with the clinical outcome of patients (Sasi et al.
2010). Jiang et al. (2010) reported that in breast
cancer cell line, the decreased expression of SOCS1
was thought to be due to SOCS1 mRNA being
targeted by miR-155. Huang et al. (2013) reported
that miR-155 plays an important role in regulating the
invasion and migration of cancer cells by decreasing
SOCS1 expression, resulting in continuous STAT3
activation.
In this study, we also demonstrated that
expression of miR-155 in different of ER, PR and
HER2 status. The result was not statistically different
both ER status. miR-155 was higher in PR + than PR-
breast cancer, and was higher in HER2- than HER2 +
breast cancer. Expression of miR-155 on PR + might
be affect the growth of breast cancer. Tanos et al.
Expression of MicroRNA-155 and Suppressor of Cytokines Signaling 1 (SOCS1) mRNA in Plasma Breast Cancer Patients
227

(2012) reported that through binding to its receptor,
progesterone induces STAT3 activation in breast
cancer via the JAK and Src pathways. Absence or
reduction of negative regulator (SOCS1), resulting in
continuously active STAT3 leading to cancer
progression. However, this result is not supported by
fold change of SOCS1 mRNA. This might occur
because miR-155 targets other PR-related mRNAs.
Expression of SOCS1 in both PR+ and PR- breast
cancer was similiar in our study. This result was
different with the study conducted by Sun et al. Sun
and colleagus showed that progesterone up regulated
SOCS1 expression through induction of LPS (Sun et
al. 2012).
In this study, miR-155 expression appeared to be
higher in patients with HER2- than HER2+, whereas
SOCS1 mRNA expression was almost the same in
both HER2 states. Bischoff et al. (2015) reported that
miR-155 might be act as a negative regulator of
HER2 signaling. miR-155 was reported to decrease
HER2-induced Akt activity, but miR-155 played a
role in increasing basal Akt activity. This is in line
with reports that miR-155 is positively correlated
with basal PI3K activation by targeting PI3K negative
regulators (p85α and SHIP) (Huang et al., 2013), and
upstream negative regulator PI3K (SOCS1) (Jiang et
al., 2010).
In subtype breast cancer, our result showed that
expression of miR-155 was elevated in Triple-
negative breast cancer. However, the result showed
not statistically significant. This result was same as
result of a study by Blenkiron et al. (2007) that
documented elevated miR-155 expression in the
triple negative breast cancer. Lu et al (2012) also
reported that expression of miR-155 in plasma also
showed significant differences among the subtypes of
breast cancer with the highest expression was seen in
triple negative subtype followed by HER2
overexpression, Luminal B, and Luminal A (p =
0.027).
In Triple negative breast cancer, expression of ER,
PR, and HER2 is negative. A microRNA profiling
study by Gasparini et al. (2014) showed that there
were 4 miRNAs that were correlated with triple
negative subtypes, one of them was miR-155. The
high expression of miR-155 in triple negative subtype
might be associated with BRCA1 (Chang & Sharan
2012). BRCA1 is a gene that is frequently mutated in
breast cancer, especially in the triple negative subtype
(Bange et al. 2001). Davis et al reported that silencing
of BRCA1 leads to reduced expression of ER and PR
(Davis et al , 2014).
SOCS1 expression was higher in luminal A. The
luminal subtype is the subtype with the best
prognosis. This is in accordance with Sasi et al.
(2010) who reported that the expression of SOCS1
was positively correlated with good outcomes (the
lowest recurrence and the lowest mortality rate). (Sasi
et al. 2010).
5 CONCLUSIONS
In plasma of breast cancer patients, expression of
miR-155 in advanced stage was higher than in the
early stages, while the expression of SOCS1 mRNA
in advanced stage was lower than the early stage.
MiR-155 was differentially expressed according to
ER, PR, HER2 while the expression of SOCS1 was
not different according to ER, PR, HER2. miR-155
expression was higher in triple negative, while
SOCS1 was higher in luminal A. However, the
differences were not statistically significant.
Deregulation of miR-155 dan SOCS1 expressions is
believed to have important role in breast cancer
progressivity.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was support by a grant from the PUPT
2014 grants, Universitas Gadjah Mada. Researchers
supervisor: Prof. dr. Sofia Mubarika H., M.Med.Sc,
Ph.D and Prof. Dr. dr. Teguh Aryandono Sp.B (K)
Onk; Research Advisor: dr. Artanto Wahyono, Sp.B.,
Dr.med. dr. Indwiani Astuti; Prof. Dr. Mustafa, Apt.,
Kes; dr. Ahmad Hamim Sadewa, Ph.D., Drs. Zulaela,
Dipl. Med. Stat., M.Si. dr. Ahmad Ghozali, Sp.PA(K)
for analized immunohistochemistry data’s patients.
Laboratory supervisor : Risky Oktriani, S. Si, M.
Biotech, dr. Sumadi Lukman A., Ph.D., dr.
Zulrachman Erlangga, Nihayatus Saadah, S. Si,
M.Sc. and the entire members of the study group
mikroRNA (genomiR).
.
REFERENCES
Bange, J., Zwick, E. & Ullrich, A., 2001. Molecular targets
for breast cancer therapy and prevention. Nat Med,
7(5), 548–52.
Berishaj, M., Gao, S. P., Ahmed, S., et al., 2007. Stat3 is
tyrosine-phosphorylated through the interleukin-6 /
glycoprotein 130 / Janus kinase pathway in breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res, 9(3), 1–8.
Bischoff, A., Bayerlova, M., Strotbek, M., Schmid, S.,
Beissbarth, T., & Olayioye, M. O. 2015. A global
microRNA screen identities regulators of the ErbB
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
228

receptor signaling network. Cell Comm Sig. 13 (5): 1-
15.
Blenkiron, C., Goldstein, L. D., Thorne, N. P., et al., 2007.
MicroRNA expression profiling of human breast
cancer identifies new markers of tumor subtype.
Genome Biol, 8(10), 214.1–.16.
Brase, J.C., Wuttig, D., Kuner, R., et al., 2010. Serum
microRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for cancer.
Mol Cancer, 9(1), 1–9.
Chan, H. S., & Zhang, Z. 2009. Liaison amid disorder: non-
native interactions may underpin long-range coupling
in proteins. Journal of Biology. 8(3): 27.
Chang, S. & Sharan, S.K., 2012. BRCA1 and microRNAs:
emerging networks and potential therapeutic targets.
Mol. Cells, 34(5), 425–32.
Chen, X., Liang, H., Zhang, J., et al., 2012. Secreted
microRNAs: a new form of intercellular
communication. Trends in cell biology, 22(3), 125–32.
Cheng, G. 2015. Circulating miRNAs: roles in cancer
diagnosis, prognosis and therapy. Advanced Drug
Delivery Reviews. 81: 75–93.
Corcoran, C., Friel, A. M., Duffy, M. J., et al., 2011.
Intracellular and extracellular microRNAs in breast
cancer. Clin Chem, 57(1), 18–32.
Cortez, M.A., Bueso-ramos, C., Ferdin, J., et al., 2011.
MicroRNAs in body fluids—the mix of hormones and
biomarkers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 8(8), 467–77.
Croker, B.A., Kiu, H. & Nicholson, S.E., 2009. SOCS
regulation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Semin
Cell Dev Biol, 19(4), 414–22.
Faraoni, I. Antonetti, F. R., Cardone, J., et al., 2009. MiR-
155 gene: a typical multifunctional microRNA.
Biochim Biophys Acta, 1792(6), 497–505.
Fujimoto, M. & Naka, T., 2010. SOCS1 , a negative
regulator of cytokine signals and TLR responses , in
human liver diseases. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2010,
1–7.
Garzon, R. Marcucci, G., & Croce, C. M. 2006. MicroRNA
expression and function in cancer. J Mol Med, 12(12),
580–7.
Gasparini, P., Cascione, L., Fassan, M., & Lovat, F. 2014.
MicroRNA expression profiling identifies a four
microRNA signature as a novel diagnostic and
prognostic biomarker in triple negative breast cancers.
Oncotarget. 5(5): 1174–84.
Gupta, N. & Mayer, D., 2013. Interaction of JAK with
steroid receptor function. JAK-STAT, 2, 37–41.
Higgs, G. & Slack, F., 2013. The multiple roles of
microRNA-155 in oncogenesis. J Clin Bioinformatics,
3, 1–8.
Huang, C. Li, H., Wu, W., et al., 2013. Regulation of miR-
155 affects pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness and
migration by modulating the STAT3 signaling
pathway through SOCS1. Oncol Rep, 30, 1223–30.
Iorio, M. V & Croce, C.M., 2012. MicroRNA dysregulation
in cancer : diagnostics , monitoring and therapeutics .
A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med, 4, 143–59.
Iorio, M. V & Croce, C.M., 2009. MicroRNAs in cancer:
small molecules with a huge impact. J Clin Oncol,
27(34), 5848–56.
Jiang, S. et al., 2012. A novel miR-155/miR-143 cascade
controls glycolysis by regulating hexokinase 2 in
breast cancer cells. EMBO J, 31(8), 1985–98.
Jiang, S., Zhang, H. & Lu, M., 2010. MicroRNA-155
functions as an oncomiR in breast cancer by targeting
the Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 gene. Cancer
Res, 70, 3119–27.
Johansson, J. et al., 2013. MiR-155-mediated loss of
C/EBPβ shifts the TGF-β response from growth
inhibition to epithelial-mesenchymal transition,
invasion and metastasis in breast cancer. Oncogene,
32(50), 5614–24.
Kong, W. He, L., Coppola, M., et al., 2010. MicroRNA-155
regulates cell survival, growth, and chemosensitivity
by targeting FOXO3a in breast cancer. The Journal of
biological chemistry, 285(23), 17869–79.
Kosaka, N., Iguchi, H. & Ochiya, T., 2010. Circulating
microRNA in body fluid: a new potential biomarker
for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci,
101(10), 2087–92.
Liu, J. Mao, Q., Liu, Y., et al., 2013. Analysis of miR-205
and miR-155 expression in the blood of breast cancer
patients. Chin J Cancer Res, 25(1), 46–54.
Lu, Z. Ye, Y., Jiao, D., et al., 2012. MiR-155 and miR-31
are differentially expressed in breast cancer patients
and are correlated with the estrogen receptor and
progesterone receptor status. Oncology Letters, 4(5),
1027–32.
Marini, A. et al., 2006. Epigenetic Inactivation of Tumor
Suppressor Genes in Serum of Patients with
Cutaneous Melanoma. J Invest Dermathol, 126, 422–
431.
Martin, E.C. Rhodes, L. Elliot, S., et al., 2014. microRNA
regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin
expression and activity controls estrogen receptor
function and RAD001 sensitivity. Mol Cancer, 13(1),
1–13.
Murray, P.J., 2007. The JAK-STAT signaling pathway:
input and output integration. J Immunol, 178,.2623–
29.
Ragan, C., Zuker, M., Ragan, M.A. 2011. Quantitative
prediction of miRNA-mRNA interaction based on
equilibrium concentrations. PLoS Compt Biol. 7 (2):
e10001090.
Rawlings, J.S., Kristin, M. & Harrison, D.A., 2004. The
JAK / STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Sci, 1(117),
1281–83.
Santillán-Benítez, J.G. Mendieta-Zeró, H., Gómez-Oliván,
L. M., et al., 2014. JAK2, STAT3 and SOCS3 gene
expression in women with and without breast cancer.
Gene, 547(1), 70–6.
Sasi, W. Jiang, W. G., Sharma, A., et al., 2010. Higher
expression levels of SOCS 1 , 3 , 4 , 7 are associated
with earlier tumour stage and better clinical outcome
in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer, 10(178), 1–13.
Sasi, W. Sharma, A. K., Mokbel, K., et al., 2014. The role
of Suppressors of Cytokine Signalling in human
neoplasms. Mol Biol Int, 2014, 1–24.
Expression of MicroRNA-155 and Suppressor of Cytokines Signaling 1 (SOCS1) mRNA in Plasma Breast Cancer Patients
229

Schwarzenbach, H., Nishida, N., Calin, G. A., et al., 2014.
Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs
in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 1–12.
Singh, R. & Mo, Y.-Y., 2013. Role of microRNAs in breast
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther, 14(3), 201–12.
Sun, Y. Wang, M., Lin, G., et al., 2012. Serum microRNA-
155 as a potential biomarker to track disease in breast
cancer. PloS One, 7(10), 1–8.
Tanos, T., Rojo, L. J., Echeverria, P., & Brisken, C. 2012.
ER and PR signaling nodes during mammary gland
development. Breast Can Res. 14:210
Ventura, A. & Jacks, T., 2009. MicroRNAs and cancer:
short RNAs go a long way. Cell, 136(4), 586–91.
Wagner, K.-U. & Schmidt, J.W., 2011. The two faces of
Janus kinases and their respective STATs in mammary
gland development and cancer. (published online)
Wang, H. Tan, G., Dong, L., et al., 2012. Circulating miR-
125b as a marker predicting chemoresistance in breast
cancer. PloS one, 7(4), 1–8.
Ying, S.-Y., Chang, D.C. & Lin, S.-L., 2008. The
microRNA (miRNA): overview of the RNA genes that
modulate gene function. Mol Biotechnol, 38(3), 257–
68.
Zeng, H. Fang, C., Nam, S., et al., 2014. The
clinicopathological significance of microRNA-155 in
breast cancer: a meta-analysis. BioMed research
international, 2014, 724209.
Zhang, C.-M., Zhao, J. & Deng, H.-Y., 2013. MiR-155
promotes proliferation of human breast cancer MCF-7
cells through targeting tumor protein 53-induced
nuclear protein 1. J Biomed Sci, 20, 1–10.
Zhao, X. Zhang, W., Liang, H., et al., 2013. Overexpression
of miR -155 Promotes Proliferation and Invasion of
Human Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma via
Targeting SOCS1 and STAT3. PloS one, 8(2), 1–11.
Zheng, D. et al., 2011. Plasma microRNAs as novel
biomarkers for early detection of lung cancer. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol, 4(6), 575–86.
Zheng, S.-R. Guo, G.-L., Zhang, W., et al., 2012. Clinical
significance of miR-155 expression in breast cancer
and effects of miR-155 ASO on cell viability and
apoptosis. Oncology reports, 27(4), 1149–55..
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
230
