
Cost Analysis Monotherapy of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in
RSUD. Prof. Dr. Margono Soekarjo
Fajar Wahyu Pribadi
1a
, Afifah
1b
, and Catharina Widiartini
2c
1
Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Jenderal Soedirman, Purwokerto, Indonesia
2
Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Jenderal Soedirman, Purwokerto, Indonesia
Keywords: cost analysis, type 2 diabetes mellitus, INA-CBG's rates, monotherapy, effectiveness.
Abstract: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (D.M.) is a metabolic syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia due to decreased
insulin sensitivity. High prevalence and long-term treatment to be burdened on the health economy indicate
that D.M. therapy must be cost-effective. The study aimed to know the cost analysis monotherapy of type 2
Diabetes Mellitus patients. Twenty-three patients without complications were given monotherapy and
followed six months from D.M.'s initial diagnostic in a descriptive study. Data was taken from medical
records, clinical pathology laboratory and finansial data between January 1, 2016, and June 30, 2018. The
cost analysis therapy was compared between monotherapy Insulin, Metformin, Glimepiride and Pioglitazone.
Of the 23 patients monotherapy of the study population, nine patients received Insuline; 8 patients received
Metformin; 3 patients received Glimepirid, and three patients received Pioglitazone. The analysis showed that
the total cost INA-CBG's rates Rp9.0189 million; Rp7.9648 million; Rp2.9609 million and Rp2.9633 million.
Effectiveness therapy rates 44.44%; 70.83%; 50% and 66.67%. CER Rp202925; Rp112444; Rp59218 and
Rp44449. As a conclusion, Pioglitazone is more cost-effective when compared to Insulin, Metformin and
Glimepiride. Our findings suggest it needed to assess the total costs effectiveness of therapy with more and
longer periods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus is caused by insulin
insensitivity to the cells. It requires long-term therapy
to reduce the risk of complications (ADA, 2015). The
prevalence of D.M. in Indonesia is 6.2% or 10.7
million sufferers, and it is estimated that in 2035 it
will increase to 14.1 million sufferers (IDF, 2020).
Data from the 2015 World Economic Forum,
Indonesia has the potential to experience losses due
to non-communicable diseases such as diabetes
mellitus for the 2012-2030 period of 34.47 trillion
dollars, and specifically, in 2015, 33% of JKN
expenditure was used to finance health care for
diabetes mellitus and its complications (Kemenkes,
2016). In research conducted at UPT. Puskesmas
Dawan II in Klungkung Regency in 2015-2016,
apparently there is no significant difference in the
effectiveness of the drugs given (Udayani dan
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9706-8110
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5703-7061
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2789-5292
Herleeya, 2016). The high incidence of D.M. cases,
high D.M. health care costs and no significant
difference in the effectiveness of the drug will affect
the analysis of the cost of two-drug combination
therapy in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients. By
knowing this analysis, it can provide input in
selecting the most cost-effective drug in the therapy.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This descriptive study used a total sampling method
from all the secondary data archives of medical
records, financial records (INA-CBGs) and clinical
pathology laboratory of Prof. Dr Margono Soekarjo
Purwokerto. Patient of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
without complications from a BPJS (national health
insurance) participant followed for the next six
months. The variables used were the type of drug
Pribadi, F., Afifah, . and Widiartini, C.
Cost Analysis Monotherapy of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in RSUD. Prof. Dr. Margono Soekarjo.
DOI: 10.5220/0010488100810083
In Proceedings of the 1st Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference in conjunction with the 5th Annual Scientific Meeting (Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia
(JIMC 2020), pages 81-83
ISBN: 978-989-758-499-2
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
81
given, the Cost of therapy, and the Effectiveness of
blood sugar levels.
3 RESULTS
From January 1, 2016, to December 31, 2017, twenty-
three new patients were on combination therapy with
two drugs. These diabetes mellitus patients were then
followed for the next six months.
Characteristics of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
patients, including gender, age, Body Mass Index
(BMI), and type of drugs were presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Characteristics
n%
Gende
r
Man 10 43,5
Woman 13 56,5
A
g
e
<50 5 21,74
50-59 9 39,13
≥60 9 39,13
IMT
Underwei
g
h
t
3 13,04
N
ormal 4 17,39
Overwei
g
h
t
7 30,44
Obesitas 9 39,13
Monotherap
y
Insulin 9 39
Metformin 8 35
Glimepiride 3 13
Pio
g
litazone 3 13
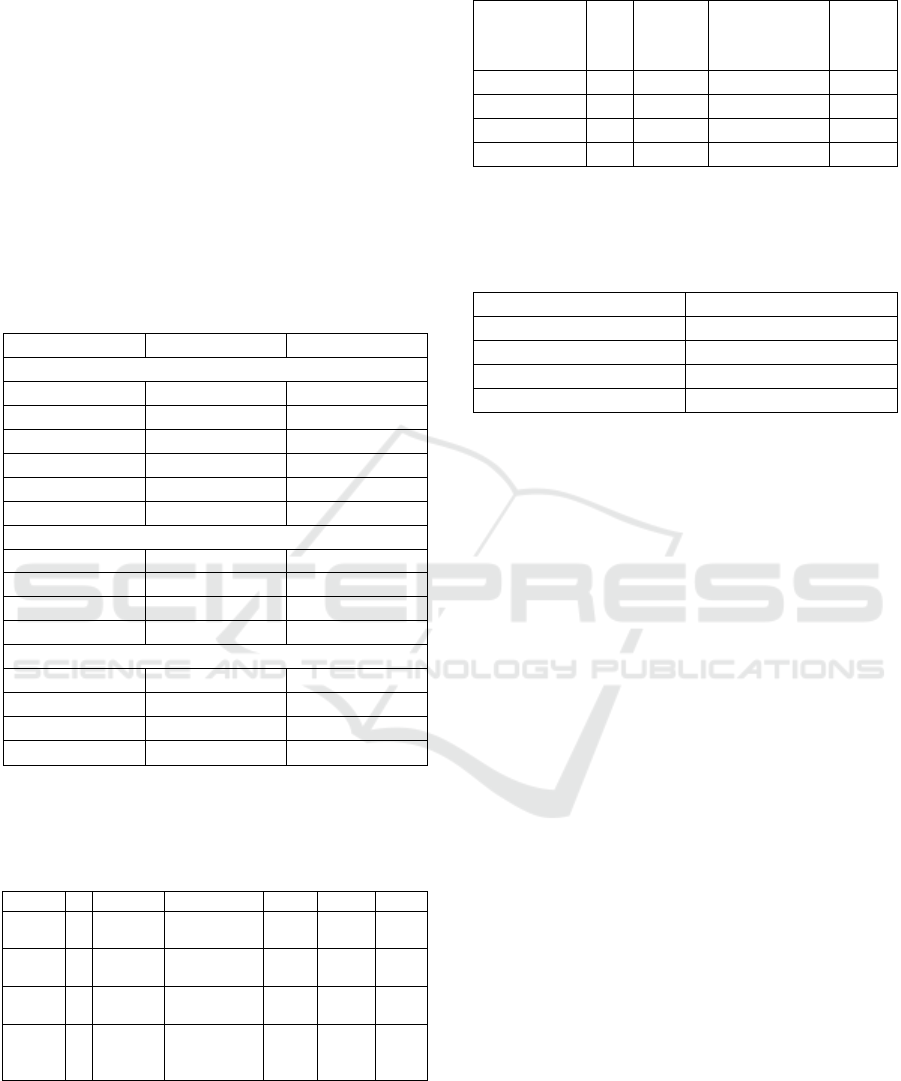
Total Cost Based On INA-CBGs of type 2 Diabetes
Mellitus patients were presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Total cost (in thousands of rupiah)
Drugs n Total Mean Med Min Max
Insuli
n
9 9.018,9 143,16±12,
03
142,
2
135,9 198,
9
Metfor
min
8 7.964,8 142,23±10,
89
142,
2
135,9 183,
3
Glimep
iride
3 2.960,9 140,99±14,
68
142,
2
135,9 202,
5
Piogli
tazon
e
3 2.963,3 141,11±8,6
3
142,
2
135,9 165,
4
Effectiveness Therapy Rates of type 2 Diabetes
Mellitus patients were presented in Table 3.
Table 3. Effectiveness therapy rates
Drugs n Reach
the
tar
g
e
t
Total
examination
%
Insuline 9 24 54 44,4
Metformin 8 34 48 70,83
Glimepiri
d
39 18 50
Pio
g
litazon 3 12 18 66,67
Cost-Effectiveness Ratio of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
patients, as presented in Table 4.
Table 4. Cost-Effectiveness Ratio (in thousands of rupiah)
Dru
g
sCER
Insuline 202,925
Metformin 112,444
Glimepiride 59,218
Pio
g
litazone 44,449
4 DISCUSSIONS
This characteristic is under research from Lestari
(2013) in a study conducted at Fatmawati General
Hospital in 2012 which shows that the distribution of
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus sufferers is more dominated
by women and research from Gautam (2009)
regarding the quality of life of type 2 D.M. patients in
India also has results. Most of the sufferers are
female. According to the American Diabetes
Association (ADA), gender may be an indirect risk
factor for D.M. since their personalities like lack of
physical activity, obesity, and a history of diabetes
during pregnancy (PERKENI, 2015; Smeltzer et al.,
2008).
This age characteristic is slightly different from
Lestari's research (2013) conducted at Fatmawati
General Hospital in 2012, which shows that at the age
of 50-59 years, the most Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
sufferers are 35%. However, according to Smeltzer et
al. (2008), insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes
mellitus tends to increase in the elderly or aged 40-65
years.
This BMI characteristic follows Lestari's (2013)
research, which shows that the distribution of Type 2
Diabetes Mellitus sufferers is more dominated by
obesity by 38%. Obesity is one of the risk factors for
type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Due to overweight or
obesity, fat cells are also fat, and cells like this will
produce several substances classified as
adipocytokines which are more in number. These
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
82

substances cause resistance to insulin (Smeltzer et al.,
2008; Hartini, 2009).
In this study, the effectiveness of therapy was
similar according to Priharsi (2015) research at Dr
Moewardi Surakarta in 2014, which stated that
Metformin had the highest effectiveness (58.33%) to
other drugs. And according to the American Diabetes
Association (2015), Metformin is safe for the elderly,
accompanied by decreased physiological function.
For CER data, when compared with each therapy,
the most cost-effective is Pioglitazone therapy
because the cost of this therapy is cheaper than other
therapies. And according to Jameson (2012) and
Nathan, et al. (2008) Pioglitazone can reduce insulin
resistance by binding to the gamma Peroxisome
Proliferator Activator receptor (PPAR-gamma) found
in muscles, fat tissue, liver, and vascular.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Pioglitazone is more cost-effective when compared to
Insulin, Metformin, and Glimepiride. However,
further research is needed with a larger sample, over
a more extended period and using GD2PP and
HbA1C
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
I am grateful to Lantip Rujito for writing this article,
Director of RSUD Prof. Dr Margono Soekarjo, Dean
and Head of the Pharmacology Section of the Faculty
of Medicine and Head of LPPM, Jenderal Soedirman
University, for allowing this research to be carried
out.
REFERENCES
American Diabetes Association (ADA), 2015. Standards of
Medical Care in Diabetes-2015. Diabetes Care 2015
Jan; 38 (Supplement 1): S4.
https://doi.org/10.2337/dc15-S003
Gautam, Y., 2009. A Cross-Sectional Study of QOL of
Diabetic Patient at tertiary Care Hospital in Delhi.
Indian Journal of Community Medicine., 34(4): 346-
350.
Hartini, S., 2009. Diabetes Siapa Takut, Panduan Lengkap
untuk Diabetes, Keluarganya dan Profesional Medis.
Penerbit Buku Qanita, Jakarta.
International Diabetes Federation (IDF), 2020, Diabetes
Atlas, https://www.idf.org/our-network/regions-
members/western-pacific/members/104-
indonesia.html
Jameson, J.L., 2012. Harrison Endocrinology Ed 2. USA:
McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 267-313.
Kemenkes RI, 2016. Mari Kita Cegah Diabetes dengan
Cerdik (online),
https://www.kemkes.go.id/article/print/16040700002/
menkes-mari-kita-cegah-diabetes-dengan-cerdik.html.
Lestari, W.P., 2013, Gambaran Efektivitas Penggunaan
Obat Antidiabetik Tunggal dan Kombinasi dalam
Mengendalikan Gula Darah Pada Pasien Diabetes
Mellitus Tipe 2 di RSUP Fatmawati Tahun 2012. UIN
Syarif Hidayatullah, Jakarta.
Nathan, M.N., J.B. Buse, B.D. Mayer, E. Ferrannini, R.R.
Holman, R. Sherwin, et al. 2008. Medical management
of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes A consensus
Algorithm for the Initiation and Adjustment of
Therapy. A consensus statement of the American
Diabetes Association and the European Association for
the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008. 31:1-11.
Perkumpulan Endokrinologi Indonesia (PERKENI), 2015.
Konsensus Pengelolaan dan Pencegahan Diabetes
Melitus Tipe 2 di Indonesia 2015, PB PERKENI.
Jakarta.
Priharsi, A., 2015. Analisis Efektivitas Biaya Antidiabetik
Oral pada Penderita Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 Rawat
Jalan Peserta Bpjs di Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah Dr.
Moewardi Tahun 2014, Universitas Muhammadiyah
Surakarta.
Smeltzer,S.C., E. Monica, B. Bare, A. Waluyo, 2008. Buku
Ajar Keperawatan Medikal Bedah Brunner dan
Suddart, EGC. Jakarta.
Cost Analysis Monotherapy of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in RSUD. Prof. Dr. Margono Soekarjo
83
