
Dose-dependent Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract Administration
Improved Hyperglycemia through Modulation of IRS-1 and GLUT-4
Genes Expression in Metabolic Syndrome Rat Model
Dwi Adi Nugroho
11
, Mifetika Lukitasari
22
Marlita Marlita
33
Mohammad Saifur Rohman
44
,
Nashi Widodo
55
, Inggita Kusumastuty
66
and Nur Ida Panca Nugrahini
77
1
Department of Herbal Medicine, Cardiovascular research group, Faculty of Medicine, Brawijaya University, Malang,
Indonesia.
2
Department of Nursing, Faculty of Medicine, Brawijaya University,Malang, Indonesia.
3
Department of cell culture, Animal Physiology, Structure and Development Laboratory, Faculty of Mathematics and
Natural Science, Brawijaya University, Malang, Indonesia.
4
Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Brawijaya University-Saiful Anwar General
Hospitalt, Malang, Indonesia.
5
Department of Biology, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Brawijaya University,, Malang, Indonesia.
6
Department of Nutrition, Faculty of Medicine, Brawijaya University, Malang, Indonesia.
7
Departement Agricultural Product Technology, Brawijaya University, Malang, Indonesia.
Keywords: Green tea, Hyperglycemia, IRS-1, GLUT-4, Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract: Hyperglycemia is a major disorder in metabolic syndrome. Skeletal IRS-1 dan GLUT-4 expression are the
key target in hyperglycemia improvement. This study aimed to investigate green tea extract's effect on
hyperglycemia improvement in metabolic syndrome rat models. Twenty Sprague Dawley Metabolic
Syndrome Rat Model weighed 300 – 400 grams were divided into GTE 200 (n=5) and GTE 400 (n=5) groups.
Moreover, as control groups, ten rats were divided into normal control (NC) (n=5) and metabolic syndrome
(MS) (n=5) groups. Rats in the GTE 200 and 400 groups were treated once daily with green tea extract at a
dose of 200 and 400 mg/bw.t, respectively. The extract was administered for 9 weeks through oral gavage.
RT-PCR methods analyzed skeletal IRS-1 and GLUT-4 gene expression. This study showed that the fasting
blood glucose of GTE 200 dan GTE 400 was significantly lower than those of the MS group (p<0.001 and
p<0.001, respectively). In addition, GTE 400 group had the lowest fasting blood glucose. Moreover, skeletal
IRS-1 dan GLUT-4 gene expression was significantly higher in the GTE 200 and GTE 400 group than those
of the MS group. In contrast, the GTE 400 group's gene expression was the highest among all groups (p<0.000
and p<0.002, respectively). Administration of green tea extract improved hyperglycemia in a metabolic
syndrome rat model in a dose-dependent manner through skeletal IRS-1 dan GLUT-4 gene expression
modulation.
1
https://orcid.org/0000- 0002-6195-9771
2
https://orcid.org/0000- 0002-3971-7418
3
https://orcid.org/0000- 0001-7955-1320
4
https://orcid.org/0000- 0001-6461-2223
5
https://orcid.org/0000- 0002-1126-498X
6
https://orcid.org/0000- 0002-0481-4541
7
https://orcid.org/0000- 0003-2781-2554
Nugroho, D., Lukitasari, M., Marlita, M., Rohman, M., Widodo, N., Kusumastuty, I. and Panca Nugrahini, N.
Dose-dependent Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract Administration Improved Hyperglycemia through Modulation of IRS-1 and GLUT-4 Genes Expression in Metabolic Syndrome Rat Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0010487900690074
In Proceedings of the 1st Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference in conjunction with the 5th Annual Scientific Meeting (Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia
(JIMC 2020), pages 69-74
ISBN: 978-989-758-499-2
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
69

1 INTRODUCTION
Metabolic syndrome (MS) is a complex multifactorial
disorder that increases the risk of cardiovascular
disease and diabetes mellitus type 2. MS prevalence
ranges between 10% and 84%, depending on the age,
gender, race, ethnicity, and MS criteria.(Alberti et al.,
2009) The World Health Organization, International
Diabetes Federation, and National Cholesterol of
Adult Treatment Panel III (NCEP-ATP III) have
determined specific criteria for MS, which includes
central obesity, high blood pressure, high triglyceride
(TG) levels, low high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and
high glucose levels.(Grundy, 2016) There is no single
treatment for MS, and natural products have gained
attention as potential treatments have
increased.(Cerezo et al., 2013; Rohman, 2011)
Tea, the most widely consumed beverage
globally, has attracted significant public interest for
its potential health benefits.(Cheng et al., 2020;
Department of Biology, College of Science,
University of Baghdad, Baghdad-Iraq & Al-Hilfy,
2012).
Green tea contains caffeine and polyphenolic
compounds, known as catechins. The most abundant
catechin found in green tea is (−)-epigallocatechin-3-
gallate (EGCG). Tea catechins are also thought to be
useful for their antiobesity, antioxidant,
antihypertensive, anticarcinogenic, and
hypocholesterolemic action. Several studies have
described the beneficial effects of tea constituents in
animal models of MS.(Ding et al., 2017; Gan et al.,
2015; Riegsecker et al., 2013).
Moreover, the skeletal insulin receptor substrate
(IRS)/glucose transporter-4 (GLUT-4) pathway has
shown to improve hyperglycemia in metabolic
disorders in animal models.(Casanova et al., 2019;
Cheng et al., 2020) A previous study reported that
oral administration of green tea extract (GTE)
significantly improved hyperglycemia and increased
insulin sensitivity in patients with metabolic
disorders.(Wu et al., 2004)
Previous study by Cao et al suggested that green
tea extract administration with the dose of 1-2 g/body
weight increased IRS1 and GLUT4 mRNA level in
skeletal tissue of high fructose diet rats. Moreover,
Wu et al suggested that intravenous administration of
0,5 g/100 ml green tea extract alleviated
hyperglycemia and increased GLUT mRNA in high
fat diet induced rat model for 12 weeks. However, as
our knowledge there were limited data regarding the
effect of green tea administration on metabolic
syndrome rat model.
Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the
effect of decaffeinated green tea extract in high fat,
high sucrose diet, and low dose streptozococin
induced metabolic syndrome rat model for 9 weeks.
We hypothesized that decaffeinated GTE modulates
IRS/GLUT-4 gene expression and improves
hyperglycemia in MS rats.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Extraction of Green Tea
Green tea was extracted from the young leaves of
green tea. Green tea leaves were sorted to obtain high-
quality seeds. A dryer cabinet set at 50°C was used to
dry 500 g of green tea leaves for 8 h to obtain
simplicia with 8%–10% water content. The simplicia
was mashed with a blender and macerated with
methanol to produce a crude extract. The crude
extract was then filtered using a filter cloth to separate
the liquid from the solid phase. The liquid phase was
concentrated using a rotary evaporator at a
temperature of ±40°C. The concentrated liquid phase
was partitioned using butanol, water, and
acetilacetate Finally, column chromatography was
performed using silica gel as the static phase, and the
filtered product was evaporated.(Banerjee &
Chatterjee, 2014).
2.2 Animal Care and Experimental
Protocol
Twenty male Sprague Dawley rats were purchased
from the National Agency of Drug and Food Control
of Indonesia. They were housed in standard cages and
placed in a room where temperature was maintained
at 25°C ± 1°C and relative humidity at 50% ± 1%,
with a 12 h light/dark cycle. During a 1-week
acclimatization period, all rats consumed a normal
pellet diet and tap water ad libitum. The rats then
received a high sucrose, fat, and sodium diet for 9
weeks and an intraperitoneal streptozotocin injection
(30 mg/body weight [BW]) in the second and third
weeks. Rats with >126 mg/dL blood glucose, >150
mg/dL triglyceride, high systolic blood pressure
(≥140 mm/Hg), and reduced HDL levels (<40 mg/dL)
were confirmed as MS rats based on NCEP-ATP III
criteria.(Saifur Rohman et al., 2017) The rats were
divided into four weight-matched groups (𝑛 = 5): the
normal control (NC), Metabolic syndrome (MS),
metabolic syndrome with 200 mg/b.wt GTE (GTE
200), and metabolic syndrome with 400 mg/bw.t GTE
(GTE 400). The extract was given via oral gavage
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
70
daily. Extract dose was given in milliliters based on
the weekly BW measurement. Food and water intake
were recorded daily. At the end of the experimental
period, animals were anesthetized with ether
following a 12 h fasting period. Blood samples were
drawn from the heart into a micro-centrifuge tube,
and serum samples were obtained by centrifugation at
4000 × g for 15 min at 4°C. The protocol was
reviewed and approved by the ethics committee of the
Faculty of Medicine, Brawijaya University.
2.3 Physiological Measurement
Daily food and fluid intake were measured on
everyday basis, and BW was measured weekly. Food
and fluid intake of each rat was measured by
subtracting the amount initially provided by the
remaining amount in the cage.
2.4 Biochemical Analysis
The serum concentrations of fasting blood glucose,
TG, and HDL cholesterol were measured
enzymatically using commercial kits (Biolabo,
France).
2.5 Blood Pressure Measurements
Blood pressure was measured using the tail-cuff
method with a sphygmomanometer at baseline and at
the end of the experiment. Three readings were taken
consecutively, which were averaged to provide a final
systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) reading.
2.6 Gene Expression Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from skeletal tissues with
TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, USA). The total RNA (2
g) was reverse transcribed using the SuperScript
First-Strand Synthesis System (Invitrogen, USA).
Primers were designed according to the sequences in
GenBank as follows: -actin F: “TAC AAC CTC
CTT GCA GCT CC,” R: “GGA TCT TCA TGA
GGT AGT CAG TC;” IRS-1 F: “AAG CAC CTG
GTG GCT CTC TA,” R: “TCA GGA TAA CCT
GCC AGA CC;” and GLUT-4 F: “CTT CCT TCT
ATT TGC CGT CCT C,” R: “GCT GCT GTT TCC
TTC ATC CTG.” Standard 25 L polymerase chain
reaction (PCR) with 2 L of the reverse transcriptase
was performed using the following parameters: 95°C,
40 s, annealing temperature, 40 s, 72°C, 45 s, for 27
cycles with TaKaRa Ex Taq Hot Start Version
(TaKaRa, Japan) in an MJ Research PTC-200 Peltier
Thermal Cycler. The PCR reaction product (10 L)
was separated using 2% agarose gels by
electrophoresis. Densitometric quantification of the
band intensities was conducted using NIH Image J
software.
2.7 Statistical Analysis
All data were analyzed using Statistical Package for
Social Sciences (version 22) and are presented as
mean ± standard deviation. The data were subjected
to a one-way analysis of variance, independent t-test,
and paired t-test and used a significance level of p <
0.05.
3 RESULTS
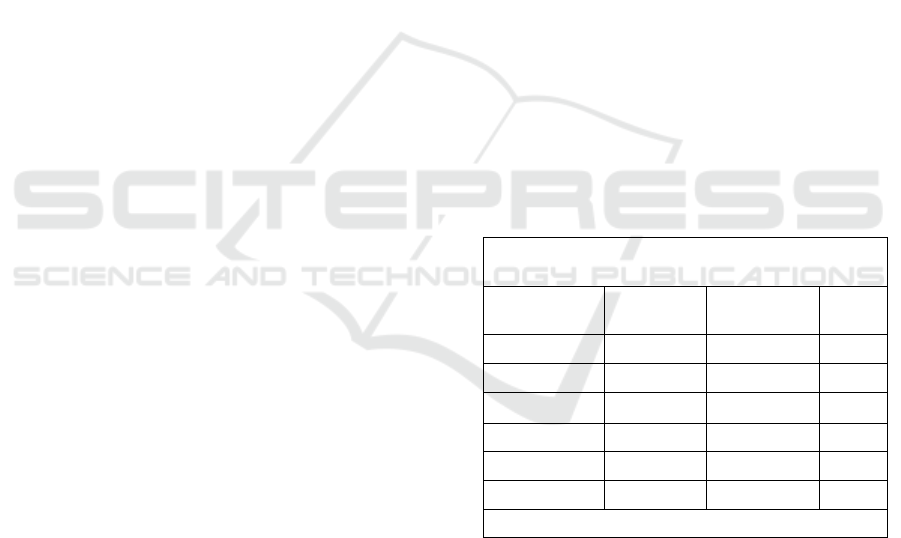
3.1 Baseline Characteristics
Before treatment, the MS rats were characterized by
obesity, high systolic blood pressure, high TG,
hyperglycemia, and low HDL cholesterol, as shown
in Table 1. These characteristics were similar to the
MS characteristics observed in humans, according to
the NCEP-ATP III criteria.
Table 1. Baseline Characteristics Metabolic Syndrome Rat
Model.
Experimental group
Paramater
NC MS p
Body Weight
295,80±5,11 366,2±7,59 0,012
Food Intake
19,40±0,66 22,6±1,67 0,000
Water Intake
26,85±1,92 45,4±14,02 0,001`
Blood Glucose
101,2±4,32 250±40,74 0,000
Triglyceride
81,20±6,76 252,8±66,83 0,000
HDL
44,00±3,46 31,40±6,87 0,000
Blood pressure
124,6±5,5 152,6±7,12 0,000
Values are mean ± SD, n = 5. data was analyzed by
dependent t-test.
NC : Normal Control;
MS : Metabolic syndrome Induces
3.2 Effects of GTE on Fasting Blood
Glucose Levels
The effect of GTE on fasting blood glucose levels in
the experimental animals is presented in Table 2. The
level of fasting blood glucose was not significantly
Dose-dependent Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract Administration Improved Hyperglycemia through Modulation of IRS-1 and GLUT-4
Genes Expression in Metabolic Syndrome Rat Model
71
different between any of the groups at baseline.
Following 9 weeks of intervention, fasting blood
glucose levels in all GTE groups significantly
decreased from baseline (p < 0.001). Furthermore, all
interventional groups showed greater decrease in
fasting blood glucose levels compared to that of the
MS group (p < 0.05). The GTE 400 group had the
lowest fasting blood glucose level.
Table 2. The comparison of fasting blood glucose among
groups.
Experimental
group
Fastin
g
Blood Glucose
Pre Post
NC 101,2±4,32 92,40±9,50
MS 250±40,74 283,2±31,92*
GTE 200 243,89±29,21 196,41±19,19*a
GTE 400 223,40±18,69 181,95±14,95*ab
Values are mean ± SD, n = 5. data was analyzed by
dependent t-test.
* : significant between pre test and postest ( p < 0,05)
a : significant compared to that MS group ( p < 0,05)
b : significant compared to that GTE 200 group ( p < 0,05)
NC : Normal Control;
MS : Metabolic syndrome Induces
EGCG 200 : Metabolic syndrome with green tea
extract
200 mg/kg.bw.t
EGCG 400 : Metabolic syndrome with green tea
extract
400 mg/kg.bw.t
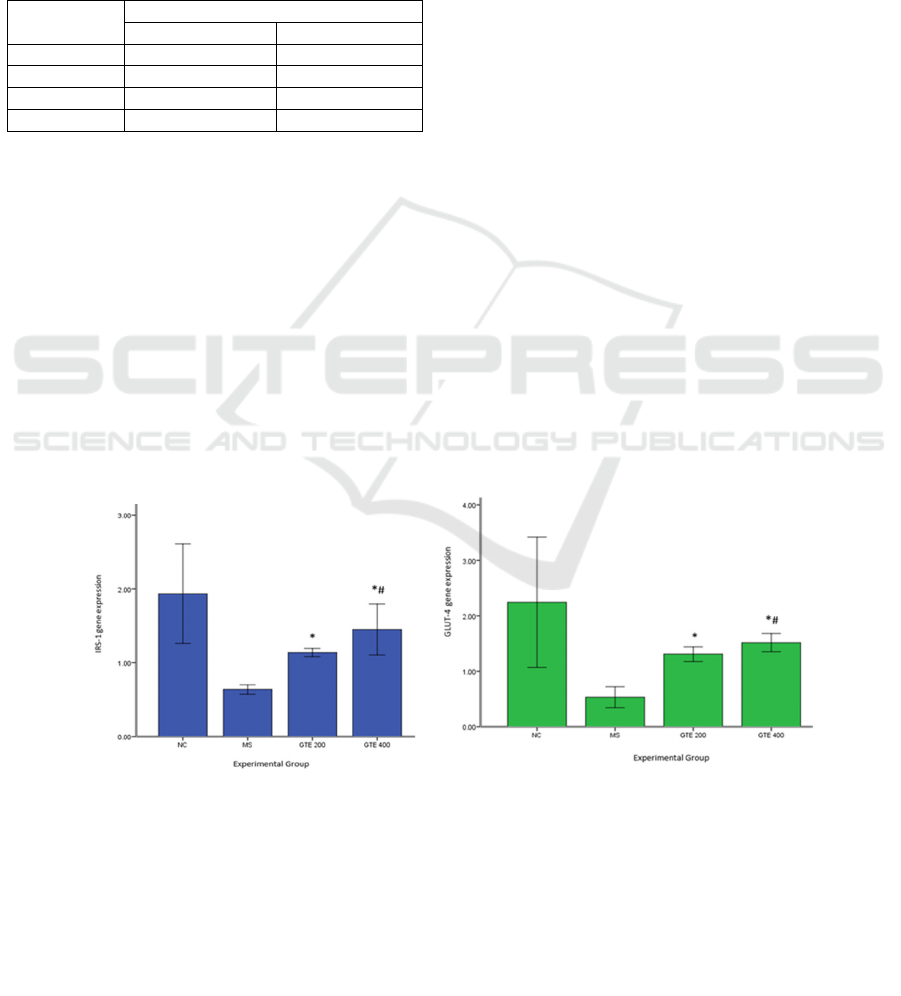
3.3 Effect of GTE on IRS-1 and
GLUT-4 Gene Expression
We examined skeletal mRNA gene expression to
determine the effect of 9 weeks of decaffeinated GTE
administration on IRS-1 (Figure 1a) and GLUT-4
gene expression (Figure 1b). In skeletal tissue, IRS-1
and GLUT-4 gene expression were significantly
higher in all GTE groups compared with those of the
MS group (p < 0.001 and p < 0.002, respectively).
Moreover, gene expression in the GTE 400 group was
the highest among all groups.
4 DISCUSSION
We investigated the effect of decaffeinated GTE on
hyperglycemia by modulation of IRS-1 and GLUT-4
gene expression. A recent study was conducted in a
rat model that the criteria of MS (hyperglycemia,
elevated triglyceride level, decreased HDL level, and
hypertension) as presented in baseline characteristics
in Table 1.(Saifur Rohman et al., 2017) MS was
confirmed by high IRS-1 and GLUT-4 gene
expression and significant reduction in fasting blood
glucose levels in the GTE 200 and GTE 400 groups.
The development of metabolic syndrome rat model in
this study was different from previous study that used
high fructose diet or high fat diet only or genetically
modified rat model. In fact, the rat model in this study
represented the features of metabolic syndrome in
human, such as hyperglycemia, hypertension, and
dyslipidemia.
Hyperglycemia improved after 9 weeks of
decaffeinated GTE administration. Furthermore, we
(a) (b)
Figure 1. Effects of green tea extract on IRS-1 (a) and Glut-4 gene expression (b).
Values are mean ± SD, n = 5. data was analyzed by independent t-test.
* : significant compared to that MS group (p< 0,05)
# : significant compared to that GTE 200 group (p< 0,05)
NC : Normal Control;
MS : Metabolic syndrome Induces
EGCG 200 : Metabolic syndrome with green tea extract 200 mg/kg.bw.t
E
GCG
4
00
:
M
etabo
li
c
sy
n
d
r
o
m
e
w
i
t
h
g
r
ee
n
tea
e
x
t
r
act
4
00
m
g/
k
g.bw.t
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
72

revealed that one mechanism of hyperglycemia
improvement was via the skeletal IRS/GLUT-4
pathway.(Boucher et al., 2014; Chang et al., 2004)
Modulation of IRS-1 may have increased GLUT-4
translocation, which induced the reuptake of plasma
glucose and improved hyperglycemia. A study by
Jang showed that EGCG in green tea reduces fasting
glucose and increases insulin and GLUT-4 expression
levels in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue.(Fu et al.,
2017; Jang et al., 2013) Another study showed that
the administration of GTE regulated the expression of
genes involved in insulin-signaling pathways in the
muscle tissue of rats with MS induced by a high-
fructose diet.(Wu et al., 2004) GTE significantly
increased mRNA levels of IRS1 and GLUT4 in the
muscle tissue. An in vitro study by Zhang showed that
GTE-rich EGCG improved IRS-1 and GLUT-4 gene
expression in L6 muscle cells after dexamethasone
induction (Zhang et al., 2010).
A study by Cao showed that GTE at 1 or 2 g/kg
BW regulates IRS-1 and GLUT-4 gene expression in
rats that are fed a fructose-rich diet. Moreover,(Cao et
al., 2007) a study by Cheng et al. showed that
administration of 200 mg/b.wt green tea extract
decreases fasting glucose, enhances the expression
and translocation of GLUT-4, and activates IRS-1
through decreased pSer612IRS-1 expression.(Cheng
et al., 2020)
Hyperglycemia alleviation after green tea extract
administration might achieved through other pathway
such as adiponectin receptor-AMPK pathway,
inflammation inhibition pathway by inhibiting
gluconeogenesis factor such as FOX-O and PEPCK
in hepatic, skeletal, and adipocyte tissue.
Our study showed that GTE 400 had a larger
effect on hyperglycemia compared to that of GTE
200, demonstrating a dose effect.(Lukitasari et al.,
2018) We used decaffeinated grren tea extract
because caffeine may induce palpitations and
increase blood homocysteine, which reduced the
antioxidant effect of EGCG that was abundantly
obtained from tea. Therefore, decaffeinated GTE
might minimize these side effects.(Roberts et al.,
2015)
5 CONCLUSIONS
Our study revealed the beneficial effect of
decaffeinated GTE on hyperglycemia via the
modulation of IRS-1 and GLUT-4 receptor gene
expression in the MS rat model.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Thanks to Cardiovascular Research Group, Medical
Faculty of Brawijaya University, Biology
Mathematics and Natural Sciences Faculty of
Brawijaya University, and the Ministry of Research,
Technology, and Higher Education of the Republic of
Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Alberti, K. G. M. M., Eckel, R. H., Grundy, S. M., Zimmet,
P. Z., Cleeman, J. I., Donato, K. A., Fruchart, J.-C.,
James, W. P. T., Loria, C. M., Smith, S. C.,
International Diabetes Federation Task Force on
Epidemiology and Prevention, Hational Heart, Lung,
and Blood Institute, American Heart Association,
World Heart Federation, International Atherosclerosis
Society, & International Association for the Study of
Obesity., 2009. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome:
A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes
Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and
Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute;
American Heart Association; World Heart Federation;
International Atherosclerosis Society; and International
Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation,
120(16), pp. 1640–1645.
Banerjee, S., & Chatterjee, J., 2014. Efficient extraction
strategies of tea (Camellia sinensis) biomolecules.
Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(6), pp.
3158-68 ,
Boucher, J., Kleinridders, A., & Kahn, C. R. (2014). Insulin
Receptor Signaling in Normal and Insulin-Resistant
States. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology,
6(1).
Cao, H., Hininger-Favier, I., Kelly, M. A., Benaraba, R.,
Dawson, H. D., Coves, S., Roussel, A. M., & Anderson,
R. A., 2007. Green Tea Polyphenol Extract Regulates
the Expression of Genes Involved in Glucose Uptake
and Insulin Signaling in Rats Fed a High Fructose Diet.
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55(15),
pp. 6372–6378.
Casanova, E., Salvadó, J., Crescenti, A., & Gibert-Ramos,
A., 2019. Epigallocatechin Gallate Modulates Muscle
Homeostasis in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity by
Targeting Energetic and Redox Pathways: A Narrative
Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,
20(3).
Cerezo, C., Segura, J., Praga, M., & Ruilope, L. M., 2013.
Guidelines Updates in the Treatment of Obesity or
Metabolic Syndrome and Hypertension. Current
Hypertension Reports, 15(3), pp. 196–203.
Chang, L., Chiang, S.-H., & Saltiel, A. R., 2004. Insulin
Signaling and the Regulation of Glucose Transport.
Molecular Medicine, 10(7–12), pp. 65–71.
Cheng, J., Tan, Y., Zhou, J., Xiao, L., Johnson, M., & Qu,
X., 2020. Green tea polyphenols ameliorate metabolic
Dose-dependent Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract Administration Improved Hyperglycemia through Modulation of IRS-1 and GLUT-4
Genes Expression in Metabolic Syndrome Rat Model
73

abnormalities and insulin resistance by enhancing
insulin signalling in skeletal muscle of Zucker fatty rats.
Clinical Science, 134(10), pp. 1167–1180.
Department of Biology, College of Science, University of
Baghdad, Baghdad-Iraq, & Al-Hilfy, J. H. Y., 2012.
Effect of Green Tea Aqueous Extract on Body Weight,
Glucose Level, and Kidney Functions in Diabetic Male
Albino Rats. Journal of Al-Nahrain University Science,
15(3), pp. 161–166.
Ding, S., Jiang, J., Yu, P., Zhang, G., Zhang, G., & Liu, X.,
2017. Green tea polyphenol treatment attenuates
atherosclerosis in high-fat diet-fed apolipoprotein E-
knockout mice via alleviating dyslipidemia and up-
regulating autophagy. PLOS ONE, 12(8), e0181666.
Fu, Q.-Y., Li, Q.-S., Lin, X.-M., Qiao, R.-Y., Yang, R., Li,
X.-M., Dong, Z.-B., Xiang, L.-P., Zheng, X.-Q., Lu, J.-
L., Yuan, C.-B., Ye, J.-H., & Liang, Y.-R., 2017.
Antidiabetic Effects of Tea. Molecules (Basel,
Switzerland), 22(5).
Gan, L., Meng, Z., Xiong, R., Guo, J., Lu, X., Zheng, Z.,
Deng, Y., Luo, B., Zou, F., & Li, H., 2015. Green tea
polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates
insulin resistance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
mice. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 36(5), pp. 597–605.
Grundy, S. M., 2016. Metabolic syndrome update. Trends
in Cardiovascular Medicine, 26(4),pp. 364–373.
Jang, H.-J., Ridgeway, S. D., & Kim, J., 2013. Effects of
the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate on
high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and endothelial
dysfunction. American Journal of Physiology-
Endocrinology and Metabolism, 305(12), pp. E1444–
E1451.
Lukitasari, M., Nugroho, D. A., & Rohman, M. S., 2018.
Green Tea Extract Administration Had A Beneficial
Effect On Ppar Alpha And Ppar Gamma Gene
Expression In Metabolic Syndrome Rat Model: Journal
of Hypertension, 36, e9.
Riegsecker, S., Wiczynski, D., Kaplan, M. J., & Ahmed, S.,
2013. Potential Benefits of Green Tea Polyphenol
EGCG in the Prevention and Treatment of Vascular
Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Life Sciences,
93(8), pp. 307–312.
Roberts, J. D., Roberts, M. G., Tarpey, M. D., Weekes, J.
C., & Thomas, C. H., 2015. The effect of a
decaffeinated green tea extract formula on fat
oxidation, body composition and exercise performance.
Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition,
12.
Rohman, M. S., 2011. Patogenesis dan Terapi Sindroma
Metabolik. Jurnal Kardiologi Indonesia, 28(2), pp. 86–
94.
Saifur Rohman, M., Lukitasari, M., Adi Nugroho, D.,
Nashi, W., Ida Panca Nugraheini, N., & Wahyu
Sardjono, Teguh., 2017. Development of an
Experimental Model of Metabolic Syndrome in
Sprague Dawley Rat. Research Journal of Life Science,
4(1), pp. 76–86.
Wu, L.-Y., Juan, C.-C., Hwang, L. S., Hsu, Y.-P., Ho, P.-
H., & Ho, L.-T., 2004. Green tea supplementation
ameliorates insulin resistance and increases glucose
transporter IV content in a fructose-fed rat model.
European Journal of Nutrition, 43(2), pp. 116–124.
Zhang, Z. F., Li, Q., Liang, J., Dai, X. Q., Ding, Y., Wang,
J. B., & Li, Y., 2010. Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate
(EGCG) protects the insulin sensitivity in rat L6 muscle
cells exposed to dexamethasone condition.
Phytomedicine: International Journal of Phytotherapy
and Phytopharmacology, 17(1), pp. 14–18.
JIMC 2020 - 1’s t Jenderal Soedirman International Medical Conference (JIMC) in conjunction with the Annual Scientific Meeting
(Temilnas) Consortium of Biomedical Science Indonesia (KIBI )
74
