
Improve The Performance and Security of Medical Records using
Fingerprint and Advance Encryption Standart
Ach. Khozaimi, Sigit Susanto Putro and Ainul Yaqin
Informatics Engineering Department, University of Trunojoyo Madura East Java, Indonesia
Keywords: Electronic medical records, Cryptography, Biometrics, Data security, Advance encryption standard.
Abstract: Medical record (MR) is privacy and sensitive data. MR can be read by a doctor, nurse, and that patient only.
MR must be store in safety documents and protected from others. MR is stored and identified by a patient's
unique id. In Public Health Center Socah, Bangkalan East Java Indonesia uses card medical treatment as a
patient's unique id to determine their medical record data. The patient's card medical treatment is easy to lose.
In this study will be implemented Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) 256 to protect data electronic medical
record, because AES has better performance than Data Encryption Standard (DES), 3DES and RSA (Rivest–
Shamir–Adleman). On the other hand, the biometric fingerprint is used as a patient's unique id because the
fingerprint is not easy to lose from patients. From the result, this system more efficient in time consumption
by 61% when compared to using the administrative system and writing medical record data manually, besides
that this system also protects the patient's EMR data from irresponsible parties, because the Electronic medical
record (EMR) data is encrypted by AES 256, so EMR data cannot be read directly.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to the regulations Minister of Health
Indonesia No. 269/Menkes/PER/III 2008, Medical
Record is data containing patient information
includes: patient identification, examination,
treatment, administration actions, and other services
performed by medical personnel to the patient (Rusli
et al., 2006). Medical record data is sensitive data and
confidential (Dubovitskaya et al., 2017), medical
records can be used for various purposes, such as for
Memory aid, Communication devices, Quality
assurance instrument, Risk reduction aid,
reimbursement aid, Evaluation tool and Research tool
(Dehn & Asprey, 2007). In addition, medical record
data can be used to plan treatment or further
examination in the future (Marutha et al., 2017).
Besides, the electronic medical record is also used as
evidence of disease diagnosis and medical care of
patients.
Based on Indonesian law and the importance of
medical record data, the data must be stored and
protected, so it cannot be accessed by unauthorized
parties (Benaloh et al., 2009). Medical record data is
stored based on each patient's unique code,
handwritten into sheets of paper, and has not used a
database (Putra & Mulyono, 2013). Much research
has been done to overcome this problem, one of
which is to provide an identity card that is listed with
a medical record number (RM). But this method is
still not effective enough, because it risks losing the
card. This also happened in the public health center
Socah, Bangkalan Regency, Indonesia.
This research will apply two methods, namely
biometric fingerprint authentication and Advance
Encryption Standard (AES). This research use AES
256, because 256 AES is more secure than the other
types (Pancholi & Patel, 2016). The biometric
fingerprint algorithm is used as a unique code that
will mark the medical records of each patient because
the fingerprint is an authentication technology based
on individual physiological and behavioural
characteristics (Soni & Goyani, 2018)(S. Tarare,
2015). So that the unique code will always be there
with the owner and will not be lost, AES 256
cryptography algorithm is used to encrypt medical
record data because AES 256 has better performance
than Data Encryption Standard (DES), 3DES, and
RSA (Ahmed Khalid & Rihan, 2017) The acronym
of RSA stands for Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman, the
inventors of the technique, so medical record data is
safe and cannot be read directly. Including the case of
theft of medical records database.
Khozaimi, A., Putro, S. and Yaqin, A.
Improve the Performance and Security of Medical Records using Fingerprint and Advance Encryption Standart.
DOI: 10.5220/0010333102850290
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical (HIMBEP 2020), pages 285-290
ISBN: 978-989-758-500-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
285
2 BACKGROUND
In this section, we will discuss the theoretical basis
and methods used in this study. Theories and methods
that will be discussed include medical records, public
health centers, fingerprints, cryptography, and
advanced encryption standards (AES).
2.1 Medical Record
Data privacy of medical records of each patient
consists of personal data, medical history, and others.
The medical record is sensitive of data and privacy
(Dubovitskaya et al., 2017), medical record data can
be used for various purposes, such as for Memory aid,
Communication devices, instrument Quality
Assurance, Risk reduction aid, aid reimbursement,
Evaluation and Research tool (Dehn & Asprey,
2007). Besides, medical record data can be used to
plan further treatment or investigation at a later date.
Medical record data is also used as evidence of
disease diagnosis and medical care of patients.
The benefits of medical records very much, and it
is essential for the well-managed so that these
benefits can be felt by the service provider and the
service recipient. Benefits include medical records,
first as a basis for planning treatment, care, and
preventive action. Secondly, to improve the quality of
service and to protect medical personnel. The third
medical records can be used for education and
research. Fourth, care financing will be more
transparent and accountable. Fifth medical records
can be used as health statistics. Sixth medical record
data can be used for evidentiary law, discipline, and
ethics of health personnel (Dehn & Asprey, 2007).
2.2 Public Health Center
Puskesmas stand for public health center, According
to the DEPKES-RI Puskesmas Work Guidelines, the
Puskesmas is a functional health organization which
is a center for community health development which
also fosters community participation in addition to
providing comprehensive and integrated services to
the community in its working area in the form of main
activities. puskesmas has three main functions:
1. As a centre for community health development
in the working area. The Puskesmas is in the
middle of a community that can quickly find
out the successes and obstacles faced in
building public health.
2. Fostering community participation in the
working area for increasing the ability to live
healthy.
3. Providing comprehensive and integrated health
services to the community in its working area.
2.3 Fingerprint
The fingerprint is a technology that can easily identify
someone. Even today fingerprints are widely used by
the world's technological development because the
use of fingerprints is relatively safe, accurate and
convenient for the authentication process compared
to other authentication methods, this is because the
fingerprint is feasible, distinct, permanent, accurate,
reliable, and acceptable(S. Tarare, 2015).
Fingerprint has a function as a verification
medium, just like a password or pin. It's just that the
fingerprint uses a human fingerprint pattern as the
primary key stored in the database (Sifaunajah, 2015).
The work process of the fingerprint is to compare the
current fingerprint feature with some fingerprint
features that have been stored in the database before
(Ngantung et al., 2014). Many methods can match the
current fingerprint with the fingerprint that has been
stored in the database (Soni & Goyani, 2018)(H.
kumar, 2013), such as template matching (Leksono et
al., 2011), Bank Gabor Filter (Verifikasi et al., 2009),
Minutiae Feature (H. kumar, 2013), and so on.
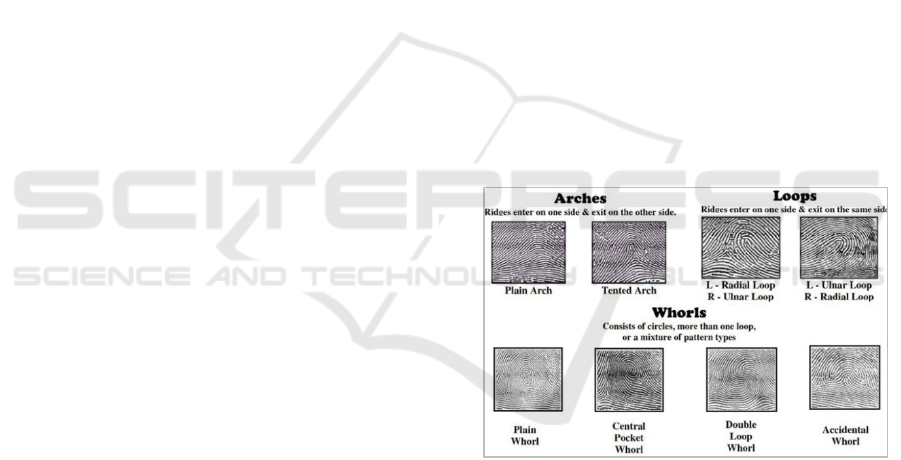
Figure 1: Fingerprint Patterns
Template matching is an image processing
technique to find small parts of the image that
matches a model that has saved previously. The
essential idea template matching explains how the
brain recognizes re-shapes or patterns that known
before. The Bank Gabor Filter method works by
finding fingerprint features based on the Average
Absolute Deviation (AAD) value of the fingerprint
image. These features are known as finger codes
(Verifikasi et al., 2009). Minutiae are some lines that
form a pattern of the fingerprint pattern. At one
fingerprint may be formed of hundreds of minutiae as
an individual characteristic.
HIMBEP 2020 - International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical
286
Fingerprint has three characteristics, i.e.,
Perennial nature, Immutability, and individuality.
Based on the pattern, fingerprints classified into three
forms, namely arch, loop, and whorl (Leksono et al.,
2011). A fingerprint is widely used for security access
and authentication method.
2.4 Cryptography
Cryptography is a technique for hiding and protecting
data information and messages, so that data or
messages cannot be read by unauthorized user. The
main function of cryptography is not only to protect
data, but also to provide solutions for other problems
like: data integrity, authentication, non-repudiation
(Sharma & Gupta, 2017). Cryptography can be used
and implemented in various media, such as software,
graphics and. Figure 2 can be seen the cryptography
process.
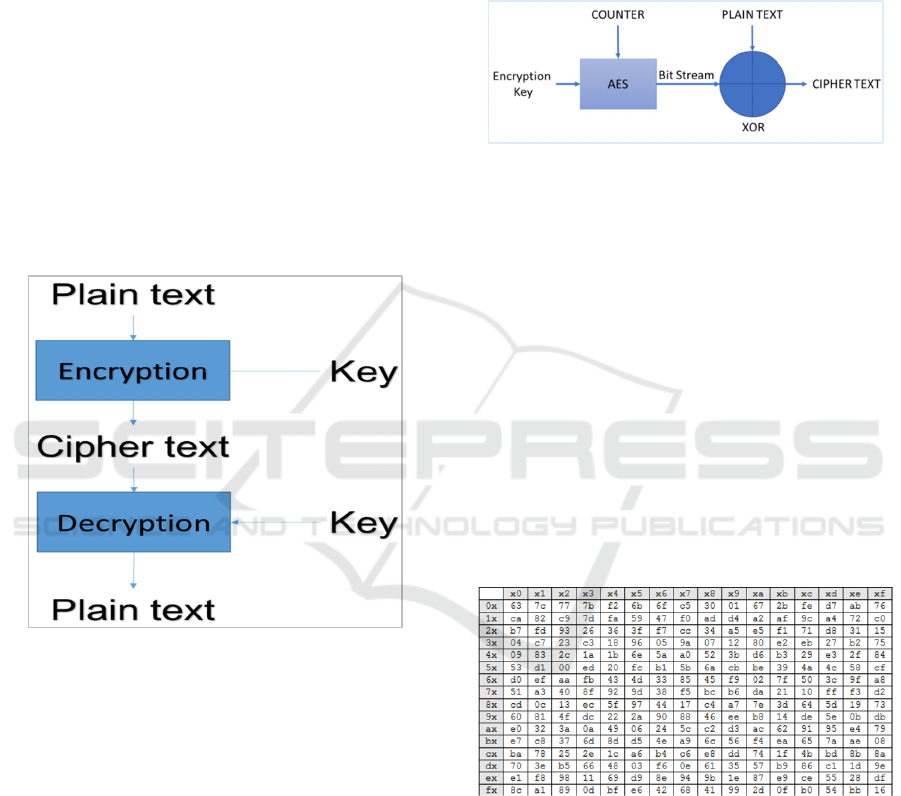
Figure 2: Cryptography Process
There are two key based cryptography techniques
used are: symmetric encryption such as DES, 3DES,
AES and asymmetric encryption such as RSA, DSA,
ECC. Symmetric encryption also called secret key
encryption and the second one called public key
encryption.
2.5 Advanced Encryption Standard
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a
cryptography algorithm to secure and protect files or
data information. AES was developed by Vincent
Rijmen and John Daemen from Belgia, and it's called
the Rijndael algorithm (Ahmed Khalid & Rihan,
2017). AES is a symmetric-key algorithm to encrypt
and decrypt data or information. Advanced
encryption standard (AES) is the next generation of
Data Encryption Standard (DES), and AES is
deference than DES (Ahmed Khalid & Rihan, 2017).
In 1997, the National Institute of Standard and
Technology (NIST) of the United States had released
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) to replace
Data Encryption Standard (DES), because DES has
been deemed insecure.
Figure 3: AES Illustration
AES can be implemented in hardware and
software, especially in the small device (Emori,
1973), AES has the same performance in both
(Padmavathi & Kumari, 2013). AES has a better
performance than another cryptography algorithm
such as DES, 3DES, and RSA in time consumption,
throughput (Patil et al., 2016)(Darma Udayana &
Sastra, 2016) , and CPU Usage (Ahmed Khalid &
Rihan, 2017).
AES is a block cipher algorithm with a
permutation (P-Box) and substitution(S-Box) system.
AES is deference than the usual block cipher system.
They are three kinds of AES, i.e., (Darma Udayana &
Sastra, 2016):
• . AES-128 with 10 rounds.
• AES-192 with 12 rounds.
• AES-256 with 14 rounds
Figure 4: S-BOX of AES Algorithm
Figure 5. Show the step of the AES algorithm to
encryption and decryption. AES Encryption step has
four states in each round, i.e., SubBytes, ShiftRows,
Mixcolumns, and AddRoundKey.
• SubBytes: Byte substitution using S-Box
(Figure 4).
• ShiftRows: Shifting lines are wrapping state
array.
Improve the Performance and Security of Medical Records using Fingerprint and Advance Encryption Standart
287
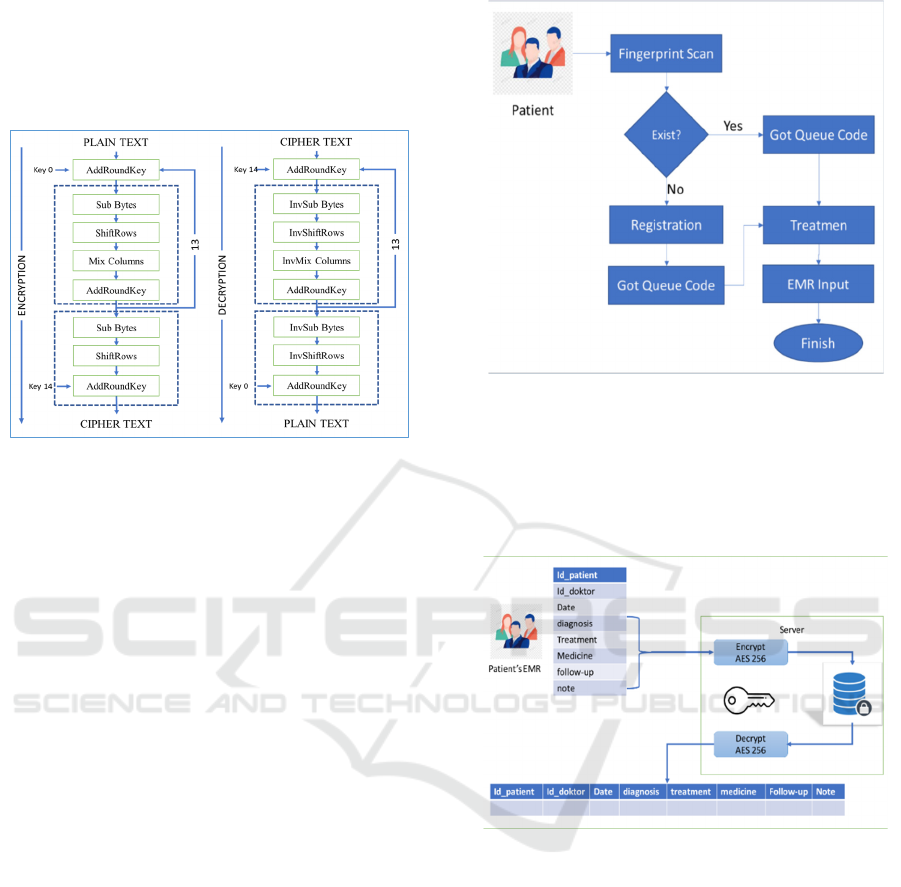
• MixColumns: scrambles the data in each
column of the array state.
• AddRoundKey: do XOR between the first step
(plain text) and cipher key. This step also called
initial round Sub Bytes.
Figure 5. AES Encryption and Decryption
AES Decryption Process is a cipher
transformation that is in the opposite direction of the
encryption process. It’s called an inverse cipher.
Transportation proses that used in the inverse cipher
are InvShiftRows, InvSubBytes, InvMixColumns,
and AddRoundKey (Muharram et al., 2018).
3 IMPLEMENTATION
In this study, two special methods used to identify and
protect the electronic medical record. First, the
fingerprint is used to identify the patients and their
data electronic medical records. Fig. 4. Second, the
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) 256 Algorithm
to encrypt Patient's Electronic Medical record (EMR)
that stores in the database Figure 6.
The fingerprint is used to identify patients and
their electronic medical records, the fingerprint is
implemented in this system. When a patient comes to
Public Health Center Socah Bangkalan, they will be
scanned their finger to identify they have ever visited
and get treatment before or not. If they ever visited,
they will get the queue code and will get treatment.
But if the new patient first came to Public Health
Center Socah Bangkalan, then the patient will
fingerprint is scanned and registered in advance.
After the data collection process and the registration
is completed, the patient will receive a code queue.
Figure 6: Fingerprint as patient's id
The process of health services will be given if the
patient had had his share. All information on the
results of testing, treatment, and all the services that
have been granted is inserted into the electronic
medical record database.
Figure 7: AES 256 to Encrypt the patient's EMR.
Each patient’s information after got treatment
from the doctor, such as diagnosis, treatment,
medicine, follow-up, and other information will be
encrypted and stored to the database using the AES
algorithm. AES will protect the electronic medical
record. Data electronic medical record that stores in
the database can be read by the user whose AES key.
See Figure 7.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
This session will explain the result of the application
and discussion. In this system, the verification and
authentication process uses fingerprint, see figure 8.
HIMBEP 2020 - International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical
288
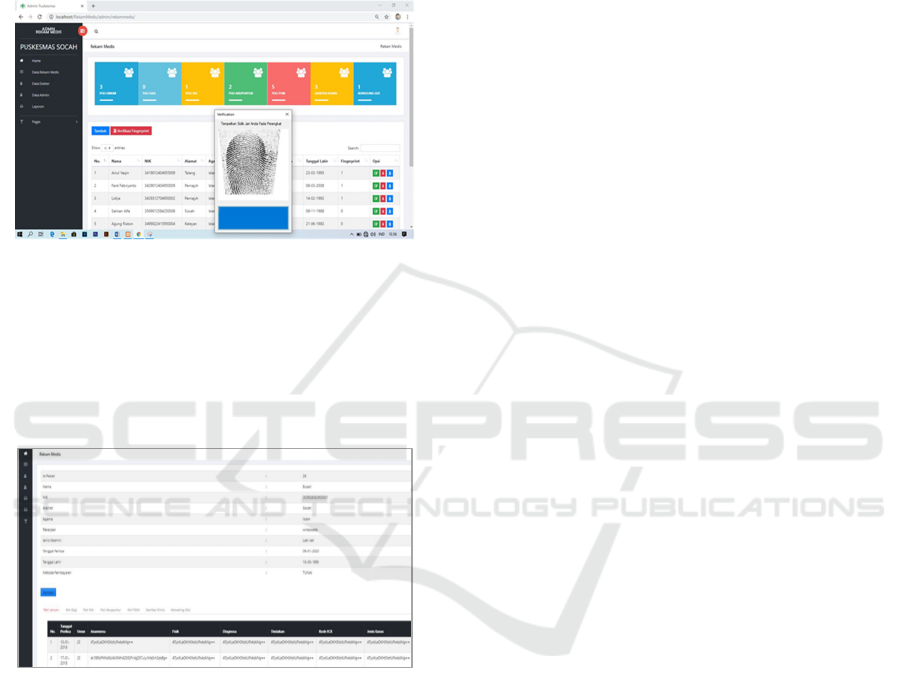
if the patient has visited and treated at public health
center Socah Bangkalan, Indonesia, before, he will be
directed to the Poly registration page, and they will
get queue code. However, if they have never visited
and treated before, it will be directed to the new
patient registration page. After registration is
complete, the patient will be registered at the
destination poly and will get the queue code.
Figure 8: Authentication Process using fingerprint
The results of the examination and treatment of
each patient's medical records will be generated.
Medical record data entered into the database is
encrypted using the Cryptographic Algorithm
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) 256. See
Figure 9.
Figure 9: EMR Encrypted by AES 256
5 CONCLUSION
This application can improve the performance of the
service since it can efficiency time by 61% when
compared to the service without the system. In
addition, this system can increase the number of
services each day.
This application can secure the patient's electronic
medical record. Electronic medical records that store
in the database can be read by the user who has the
key only. It’s mean the data in the database cannot be
read directly.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thanks delivered to the Informatics Engineering
Department, the University of Trunojoyo Madura,
who has supported this research. Special thanks to the
director of the Public Health Service Socah
Bangkalan, Indonesia as a case study of the research.
REFERENCES
Ahmed Khalid, & Rihan, S. D. (2017). A Performance
Comparison of Encryption A Performance Comparison
of Encryption Algorithms AES and DES. International
Journal of Engineering Research & Technology
(IJERT), 4(November), 151–154.
Benaloh, J., Chase, M., Horvitz, E., & Lauter, K. (2009).
Patient controlled encryption: Ensuring privacy of
electronic medical records. Proceedings of the ACM
Conference on Computer and Communications
Security, 103–114.
https://doi.org/10.1145/1655008.1655024
Darma Udayana, I. P. A. E., & Sastra, N. P. (2016).
Comparison of LPSE Backup File Security
Performance Using DES and AES Algorithms. Majalah
Ilmiah Teknologi Elektro, 15(1), 111–117.
https://doi.org/10.24843/mite.1501.19
Dehn, R. W., & Asprey, D. P. (2007). Essential Clinical
Procedures. In Essential Clinical Procedures.
https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4160-3001-0.X5001-1
Dubovitskaya, A., Xu, Z., Ryu, S., Schumacher, M., &
Wang, F. (2017). Secure and Trustable Electronic
Medical Records Sharing using Blockchain. AMIA ...
Annual Symposium Proceedings. AMIA Symposium,
2017, 650–659.
Emori, R. I. (1973). Scale models of automobile collisions
with breakaway obstacles - Investigation indicates that
scale models can be used to show the motion of
breakaway signposts and lightposts after being struck
by automobiles. Experimental Mechanics, 13(2), 64–
69. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02322384
H. kumar, V. P. and K. J. (2013). Fingerprint Matching
Using Minutiae Feature. International Journal of
Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT), 2(11),
49–53.
Leksono, B., Hidayatno, A., & Isnanto, R. R. (2011).
Application of Matching Template Method for
Fingerprint Classification. Aplikasi Metode Template
Matching Untuk Klasifikasi Sidik Jari, 13(1), 1–6.
https://doi.org/10.12777/transmisi.13.1.1-6
Marutha, N. S., Ngoepe, M., Africa, S., & Ngoepe, M.
(2017). The role of medical records in the provision of
public healthcare services in the Limpopo province of
South Africa Research problem. South African Journal
of Information Management, December 2011, 1–8.
Muharram, F., Azis, H., & Manga, A. R. (2018). Algorithm
Analysis of File Encryption and Decryption Process
Using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
Improve the Performance and Security of Medical Records using Fingerprint and Advance Encryption Standart
289

Prosiding Seminar Nasional Ilmu Komputer Dan
Teknologi Informasi, 3(2), 112–115.
Ngantung, K. A., Najoan, M. E. I., Sugiarso, B. A., &
Paturusi, S. D. E. (2014). Design and Implementation
of Fingerprint Attendance System in Campus Network
and Integrated with Elementary Information System. E-
Journal Teknik Elektro Dan Komputer, 3(1), 81–86.
https://doi.org/10.35793/jtek.3.1.2014.4050
Padmavathi, B., & Kumari, S. R. (2013). A Survey on
Performance Analysis of DES, AES and RSA
Algorithm along with LSB Substitution Technique.
International Journal of Science and Research, 2(4),
2319–7064. www.ijsr.net
Pancholi, V. R., & Patel, B. P. (2016). Enhancement of
Cloud Computing Security with Secure Data Storage
using AES. International Journal for Innovative
Research in Science & Technology (IJIRST), 2(09), 18–
21.
Patil, P., Narayankar, P., Narayan, D. G., & Meena, S. M.
(2016). A Comprehensive Evaluation of Cryptographic
Algorithms: DES, 3DES, AES, RSA and Blowfish.
Procedia Computer Science, 78(December 2015), 617–
624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2016.02.108
Putra, D. K., & Mulyono, S. (2013). Designing an
Outpatient Registration Information System at the
Clinic dr. Sri Widatik Sukoharjo Web-based. Jurnal
Rekam Medis, VII(2), 18–36.
Rusli, A., Rasad, A., Enizar, Irdjati, I., Subekti, I., Suprapta,
I. P., & Mohammad, K. (2006). Manual Rekam Medis.
Jurnal Rekam Medis, 2(10), 3–6.
https://doi.org/10.1163/_q3_SIM_00374
S. Tarare, A. A. and H. T. (2015). Fingerprint Based Gender
Classification Using DWT Transform. International
Conference on Computing Communication Control and
Automation, 689–693.
Sharma, S., & Gupta, Y. (2017). Study on Cryptography
and Techniques. International Journal of Scientific
Research in Computer Science, Engineering and
Information Technology © 2017 IJSRCSEIT, 1(2),
2456–3307. www.ijsrcseit.com
Sifaunajah, A. (2015). Integration Fingerprint Technology
in Payroll Systems. 1.
Soni, U. A., & Goyani, M. M. (2018). A Survey on State of
the Art Methods of Fingerprint Recognition.
International Journal of Scientific Research in Science,
Engineering and Technology, 4(2), 189–200.
Verifikasi, S., Jari, S., & Metode, D. (2009). Fingerprint
Verification System Using Gabor Filter Bank Based
Matching Method. Majalah Ilmiah Teknologi Elektro,
5(2), 20–25. https://doi.org/10.24843/10.24843/MITE
HIMBEP 2020 - International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical
290
