
Profile of Tinea Capitis in Skin and Gender Poly
at RSUD Dr. Rm Djoelham Binjai Periode
1 Januari 2014 – 1 September 2018
Hervina
1*
1
Department of Dermatology and Venereology Medical Faculty Muhammadiyah University Of North Sumatera
Keywords: Tinea Capitis, risk factors
Abstract: Introduction: Tinea capitis ( ringworm of the scalp) is a disorder of the skin and the hair of the head caused
by a species of dermatophyte. This disorder is characterized by scaly lesions, reddish tint, alopecia to
kerion.
(1)
Tinea capitis usually occurs, especially in children, although there are also cases in adults are
usually infected with Trichophyton tonsurans. Tinea capitis can also be seen in adults with AIDS.
(2)
Objective: To determine the overall incidence of Tinea Capitis in the general hospital, Dr. RM.
DJOELHAM THE CITY OF BINJAI
.
Research method: This research uses a descriptive method with a
retrospective approach. Data obtained from the medical records of patients of Tinea Capitis the period 1
January 2014 – 1 November 2018
.
Result : On 1 January 2014 – 1September 2018 in the polyclinic of the
health of the skin and venereal Hospital DR RM DJOELHAM the City of Binjai an incident the highest
incidence of Tinea Capitis at the age of 1-20 years (52,4%), and to incidence of most common of Tinea
Capitis occurs in women that is of 66.7% compared to men of 33.3%, based on the work, student / school
have a high risk factor to be exposed to Tinea Capitis i.e. 61,9%. Conclusion: Based on the results of the
research overview of the incidence of Tinea Capitis in the Polyclinic of the Health of the Skin and Venereal
Hospital DR. RM DJOELHAM the City of Binjai much happens in women that is of 66.7% compared to
men of 33.3%, at the age of 1-20 years (52,4%), based on the work, student/school have a high-risk factor to
be exposed to Tinea Capitis 61,9%.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tinea capitis ( ringworm of the scalp) is a disorder
of the skin and the hair of the head caused by a
species of dermatophyte. This disorder is
characterized by scaly lesions, reddish tint, alopecia
to kerion (Budimulja et al, 2016). Tinea capitis is a
disorder on the scalp caused by fungi
dermatophytes. Tinea capitis usually occurs,
especially in children, although there are also cases
in adults are usually infected with Trichophyton
tonsurans. Tinea capitis can also be seen in adults
with AIDS (Verma et al, 2008).
Tinea capitis can be divided into different types,
namely: gray patch ringworm → papule billion
around the estuary of the hair, hair easily is broken,
leaving alopecia brown. Black dot ringworm →
fungal infection in the hair (endotriks) or outside a
hair (ektotriks), the hairs break off, leaving a
macular blackish brown. Kerion → .the skin of the
head seen small ulcers with squama. Tinea Favosa
→ red spots yellowish covered crusting cup-shaped
(skutula), foul-smelling (mousy odor), the hair on
top of it broken up and easily removed (Siregar,
2014).
The spread of infection of tinea capitis can be
spread by species zoophilic, geophilic, and
anthropophilic. Species zoophilic generally found in
the body of an animal but is transmitted to the
human body. Animals and pets are the primary
sources of infection in urban areas (for example, M.
canis in dogs and cats). Transmission can occur
through direct contact with animals that are specific
or indirectly when the hair of infected animals
carried in a shirt or contained in the building or
contaminated food. The area exposed such as the
scalp, beard, face, and hands. Dermatophytes are
inflamed usually caused by an infection caused the
organism zoophilic (Verma et al, 2008).
As for the treatment of tinea can be given a
topical therapy in the form of selenium sulfide,
Hervina, .
Profile of Tinea Capitis in Skin and Gender Poly at RSUD Dr. Rm Djoelham Binjai Periode 1 Januari 2014 – 1 September 2018.
DOI: 10.5220/0009991304490454
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease (ICTROMI 2019), pages 449-454
ISBN: 978-989-758-469-5
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
449

povidone-iodine, or ketoconazole, or systemic
therapy with griseofulvin (Verma et al, 2008;
Siregar, 2014).
Based on the background above, with the number
of incidence of Tinea Capitis, the researcher
interested in doing research about the profile of the
incidence of Tinea Capitis in the Clinic of Skin and
Venereal HOSPITAL DR RM Djoelham the City of
Binjai in the period of 1 January 2014 – 1
September 2018.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
RESEARCH
This research uses a descriptive method with a
retrospective approach. Data obtained from the
medical records of patients of Tinea Capitis the
period 1 January 2014 – 1 September 2018. By
using the examination of KOH 10%.
2.1 Definition
Tinea capitis ( ringworm of the scalp) is a
disorder of the skin and the hair of the head
caused by a species of dermatophyte. This
disorder is characterized by scaly lesions,
reddish tint, alopecia to kerion
(Budimulja et al,
2016
)Tinea capitis is a disorder on the scalp
caused by fungi dermatophytes. Tinea capitis
usually occurs, especially in children, although
there are also cases in adults are usually
infected with Trichophyton tonsurans. Tinea
capitis can also be seen in adults with AIDS.
(Verma et al, 2008). Tinea Capitis is a superficial
fungal infection that affects the scalp and hair.
(
Siregar, 2014).
2.2 Etiology
Infection on the scalp by the dermatophytes is
usually the result of transmission from person to
person. These organisms remain alive on combs,
brushes, couches, and sheets for a long time. Species
of dermatophytes only specific endemic in parts of
the world sure In general, M. Audouinii is the
causative agent of classical in Europe and America
and M. Ferrugineum most common in Asia, T
violaceum also is common in Romania, Italy,
Portugal, Spain, and the former Soviet Union, as
well as in Yugoslavia. In Africa, T violaceum, T
schoenleinii, and M canis is commonly isolated.
(6)
T. violaceum and M. canis is the agent that is
prevalent in Asia. T schoenleinii is common in Iran
and Turkey, while M canis is common in Israel.
Epidermophyton floccosum and T concentricum not
attack the skin of the head of hair. Trichophyton
rubrum, which is the dermatophyte most commonly
isolated in the whole world, is not a common cause
of tinea capitis On infections ectothrix,
fragmentation of the mycelium into spores occurs
just below the cuticle. Different from infection
endothrix, the destruction of the cuticle occurs. This
type of infection is caused by T verrucosum, T
mentagrophytes, and all species of
Microsporum.(Kondo et al, 2006)
2.3 Epidemiology
The incidence of tinea capitis is still unknown, but it
is usually found in children aged 3 - 14 years, rarely
occurs in adults. Tinea capitis is found in many
children of African descent, the Transmission
increases with reduced hygiene personal, the area of
residence are dense, and low socioeconomic status.
Patients with a carrier symptomatic often found, and
this causes tinea capitis challenging to eradicate.
(2,4)
2.4 Risk Factors
1. Age
Tinea capitis often appears in children between the
ages of 3-14 years. But in adults rarely occur due to
changes in the PH of the scalp and an increase in
fatty acids that are useful as protection against fungi.
(Verma et al, 2008;Welsh et al,2006)
2. Gender
Tinea capitis is often encountered in children than
adults. (Verma et al, 2008;N Rebollo et al,2008)
3. Environment
Hygiene poor, population density, and low
socioeconomic increase transmission of the fungi.
(Verma et al, 2008;N Rebollo et al,2008)
2.5 Diagnosis
1. Anamnesis
a. Grey patch ringworm
Tinea capitis, usually caused by the genus
Microsporum and are often found in children. The
cause in the form of the organism anthropophilic
ektotric such as M. audounii or M. canis. Form of
ICTROMI 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease
450
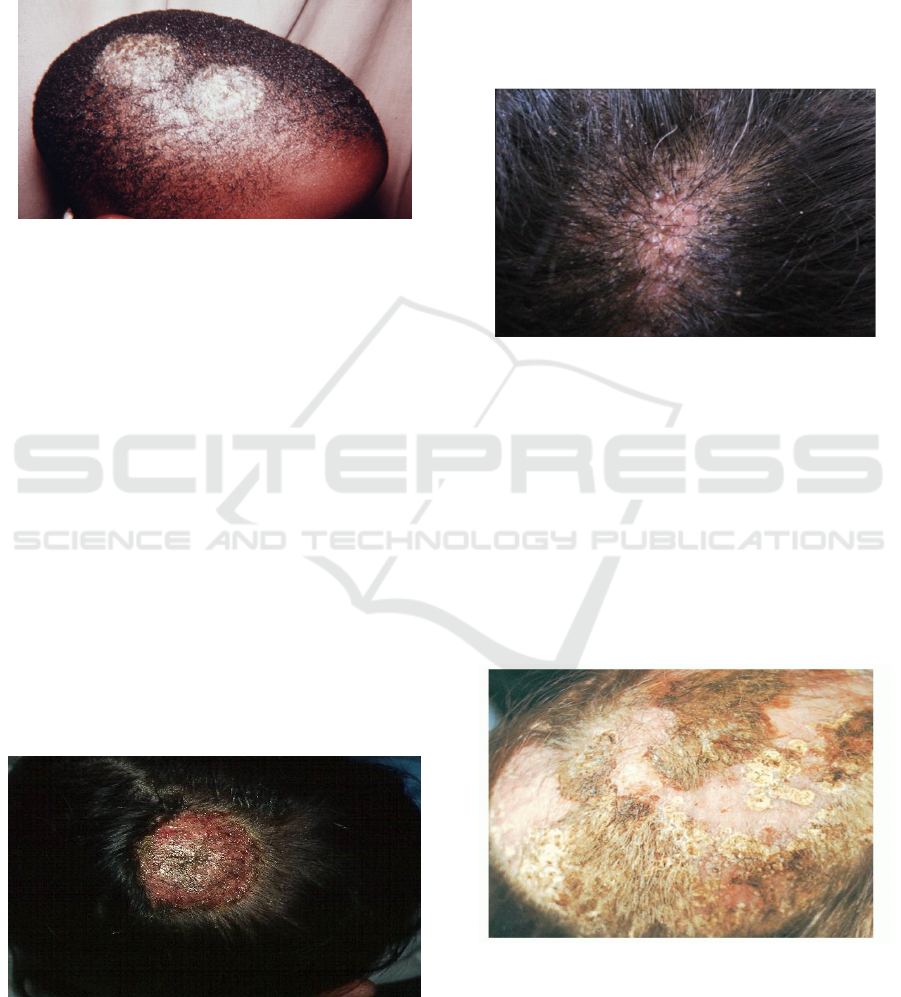
tinea capitis is also known as a form of seborrheic
dermatitis of the squama that stands out.
Inflammation is minimal. The infected hair becomes
gray and dull in the sheath arthroconidia, and hair
breaking off at the top of the scalp (Verma et al,
2008;James et al.,2006)
Figure 1: Grey patch ringworm
b. Kerion celcii
Is the reaction of inflammation weight in tinea
capitis, in the form of swelling which resembles a
honeycomb with inflammation of the dense
surrounding. When the cause is Microsporum canis
and Microsporum gypseum, the formation of a
kerion is often seen. Reduced when the cause
Trichophyton tonsurans, and fewer when the cause
is Trichophyton violaceum. This type is as a result
of the reaction of hypersensitivity to infection. The
spectrum of inflammatory diseases can occur
ranging from folliculitis postular up to a kerion,
which gives the picture such as "mud," the
inflammatory with a sprinkling of damaged hair and
orifice follicular that secrete pus. Inflammatory
lesions usually pruritic, and may also pain, the
presence of lymphadenopathy cervical posterior,
fever, and lesions on the scalp that are bald. .(Verma
et al, 2008;James et al.,2006)
Figure 2: kerion
c. Black dot ringworm
Mainly caused by the Trichophyton tonsurans and
Trichophyton violaceum. At the beginning of the
disease, the clinical picture resembles the
abnormalities caused by the genus Microsporum.
Hair exposed to the infection of the broken right on
the estuary of the follicle, and what's left is the ends
of the hair which is full of spora.(Verma et al,
2008;James et al.,2006)
Figure 3: Black dot ringworm
d. Tinea favus
Tinea favus is an infection of the clinical
dermatophytes of the head, the skin is no hair, and or
nails, characterized crusting dry and thick hair
follicles that cause scarring alopecia. Tinea favus
generally suffered before the adults continued adults,
and is associated with malnutrition and poor
nutrition. The most common cause is T. scholeinii,
occasionally T. violaceum, and M. gypseum.
.(Verma et al, 2008;James et al.,2006)
Figure 4: Tinea Favus
Profile of Tinea Capitis in Skin and Gender Poly at RSUD Dr. Rm Djoelham Binjai Periode 1 Januari 2014 – 1 September 2018
451
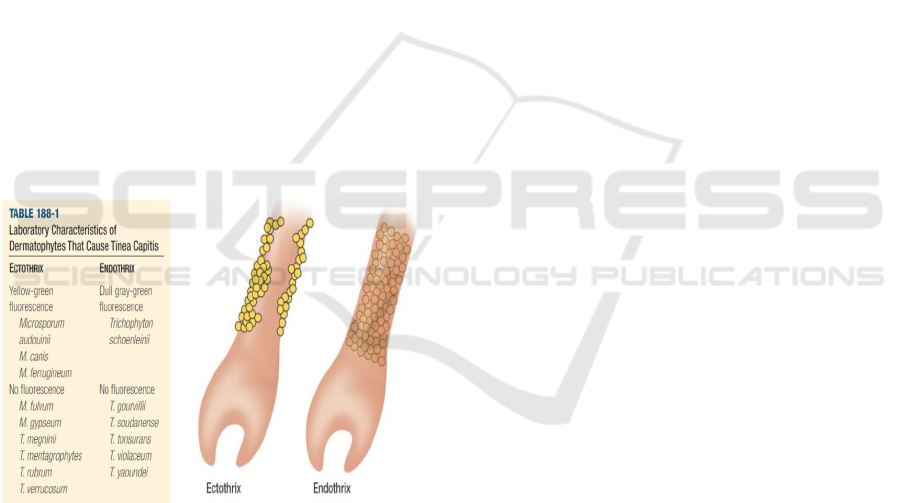
3 INVESTIGATIONS
- Ray Wood
Flouresensi positive infected by Microsporum
audouinii, Microsporum canis, Microsporum
femgineum, Microsporum distorturn, and
Trichophyton schoenleinii. In a room that is dark
skin under the lights, this flouresensi slightly blue.
Dandruff is generally a bright bluish-white. The
infected hair flouresensi bright green or greenish-
yellow while the organisms endotrik, Trichophyton
tonsurans does not seem flouresensi.(Verma et al,
2008;Siregar,2014)
- KOH 10%
Visible hyphae or spores and mycelium. Preparation
directly from the hair can be visible hyphae or
spores inside a hair (endotriks) or outside a hair
(ektotriks). (Siregar,2014)
Positive results there are 2 possibilities:
1.Ektotrik: looks arthroconidia small or large form a
layer surrounding the outside of the hair shaft.
2.Endotrik: looks arthroconidia in the hair
shaft.(Verma et al, 2008)
3.1 Culture Examination
Speciation of fungi is based on the characteristics of
the microscopic, macroscopic, and metabolism of
the organism. Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA)
media is the most common insulation used.
(Siregar,2014)
3.2 Pathogenesis
Infection endotrik and ektotrik except arthroconidia
still contained in the hair shaft, replacing the keratin
intrapilari, and reduce the intake with the cortex. As
a result, hair is easily broken and separated on the
surface of the head whereby the walls of the
follicular does not support, leaving a small black
dot. (Verma et al, 2008)
3.3 Pathofisiologi
The period of incubation of tinea capitis antropofilik
is 2 to 4 days, Hyphae growing towards the follicle,
the hair surface, and hyphae intrafollicular broken
down into a chain of spores. The period of the
deployment (4 days to 4 months) occurred during
the lesions enlarge and appear new lesions. Three
weeks hair started off a few millimeters above the
surface of the skin. In the hair, hyphae into the top of
the zone keratogenous and on the zone this is
Adamson's "fringe" is formed day 12. There are no
new lesions appear during a refractory period (4
months to several years). (Verma et al, 2008;Welsh
et al,2006)
3.4 Differential Diagnosis
1. Alopecia areata (with the shape of the black dot),
usually the skin looks slippery and brown.
2. Dermatitis Seboroika (with the form of tinea
favosa), the hair looks oily, the skin of the head
seemed covered squama oily.
3. Psoriasis ( with a form of tinea favosa), scales
(squama) thick, white, shiny and are kronik residif.
(Siregar,2014)
3.5 Therapy
Systemic :
Griseofulvin with a dose of 0.5 – 1g for adults and
0.25 to 0.50 g for the children a day or 10-25 mg/kg.
Given 1-2 times/day with long pengebotan
depending on the location, cause and clinical, healed
continue treatment for up to 2 weeks.
Ketoconazole 200 mg/day for ten days to 2
weeks the morning after a meal. Replace
ketoconazole with itraconazole 2x 100-200 mg/ day.
Terbinafine for 2-3 weeks, doses of 62.5 mg – 250
mg/day depending on weight.
(Budimulja et al,
2016).
Topical
Wash the head and hair with shampoo disinfectant
antimikotik such as a solution of salicylic acid,
ICTROMI 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease
452
benzoic acid, and sulfur presipitatum. Derivatives of
imidazole 1-2% in cream or solution can cure,
ketoconazole cream 2 %.(Siregar,2014)
4 RESULT
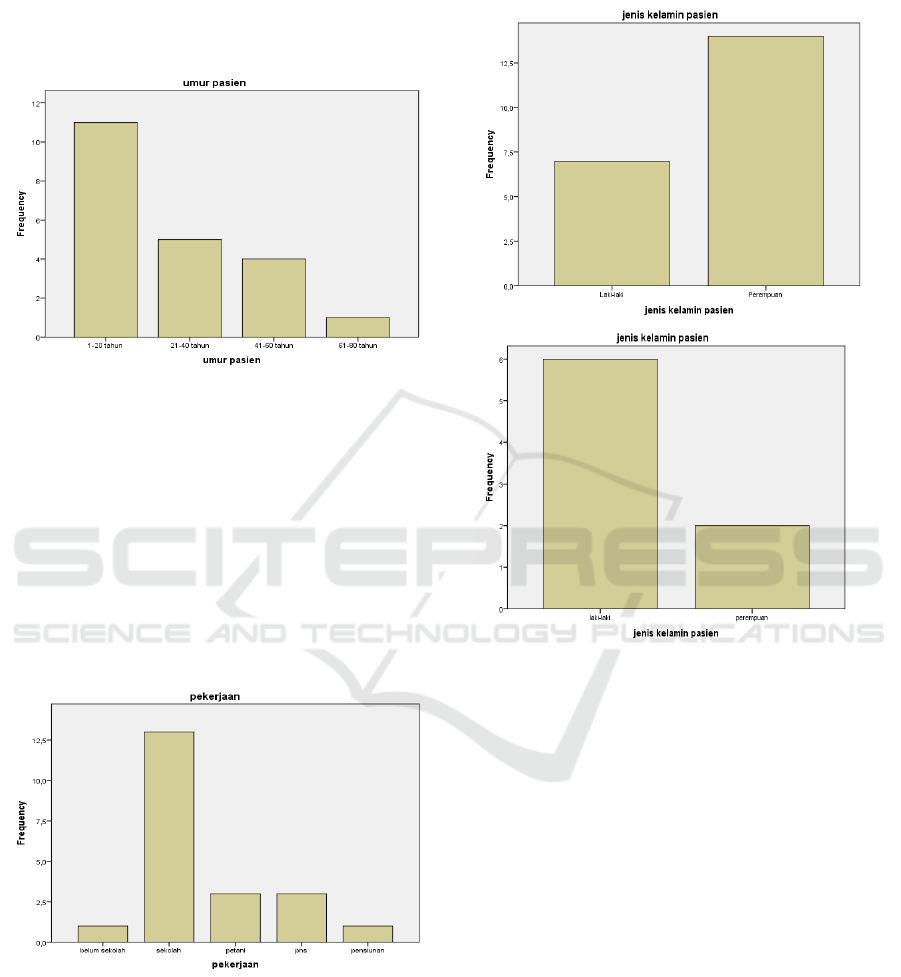
Figure 4.1 The incidence of tinea capitis is based on age
On 1 January 2014 – 1 September 2018 in the
Polyclinic of the Health of the Skin and Venereal
Hospital DR. RM. Djoelham the City of Binjai, the
highest incidence of Tinea Capitis, are in the age
range 1-20 years (52,4%), then at the age of 21 - 40
years (23,8%), aged 41-60 years (of 19.0%), and
ages 61 - 80 (of 4.8%). This is in accordance with
the theory described by Siregar, where the incidence
of Tinea Capitis a lot happens before the age of 20
years. (Siregar,2014)
Figure 4.2 Occurrence of Tinea Kapitis based on work
The incidence of Tinea Capitis seen based on the
work in getting that student/school have risk factors
the risk of developing Tinea Capitis this is affected
by the dirty environment and the air hot and humid,
the results obtained,(61,9%) compared to farmers
(14.3 %), civil servants (14.3 %), retired (4.8 %),
and schools (4.8 %).
Figure 4.3 The incidence of tinea capitis by sex
Based on the diagram 4.3 the incidence of
Tinea Capitis in a poly skin and venereal
HOSPITAL DR. RM DJOELHAM the CITY of
BINJAI more common in women (66,7%) than men
(33,3%), for the year 2014, and in 2016 more
common in men (28,6 %), and women (9.5 percent)
and for years the incidence of tinea capitis is
suffered by many women. This statement is
inversely proportional to the research that has been
done by Siregar in the study also found that men
more often suffer from Tinea Capitis than females
(3)
. On the poly skin and venereal in hospital, Dr.
RM DJOELHAM the CITY of BINJAI encountered
many patients of Tinea Capitis sex women seeking
treatment than men, and this is because women
usually tend to be more worried about the change of
the pigmentation of their skin and the impact on
their social life.
Profile of Tinea Capitis in Skin and Gender Poly at RSUD Dr. Rm Djoelham Binjai Periode 1 Januari 2014 – 1 September 2018
453

5 DISCUSSION
In a study done at the polyclinic the health of the
skin and venereal HOSPITAL DR. R. M.
DJOELHAM the CITY of BINJAI in the Years
2014-2018 the patients with Tinea Capitis most in
the age range 1-20 years, with female gender and
employment status as a student/school. The same
thing obtained in the research carried out in RSUP
Sanglah Denpasar to get age group the highest in the
5-14 years (45,45%), while in RSU dr. Soetomo
Surabaya age group the highest at the age of under
14 (93,33%).(Putu et al,2008;Suyoso et al,2008)
Research in Spain gain of 0.33% of school
children with culture-positive tinea capitis in 1994
and in London reported a prevalence of 2.5 % in
1995. The prevalence of tinea capitis in the United
States ranged from 3% to 8% in the child population
.(Mohrenschlager et al,2005) from Indonesia that
comes from RSUP Sanglah Denpasar to get to
0.32% of patients with tinea capitis were treated
during the period January 2004 to December 2006.
(
Putu et al,2008) Other Data in the poly
Dermatomikosis Unit Outpatient Skin and Venereal
HOSPITAL dr. Soetomo Hospital Surabaya, there is
0,31-1,55% of new cases of tinea capitis between the
years 2001-2006.(Suyoso et al,2008)
6 CONCLUSION
Tinea capitis ( ringworm of the scalp) is a disorder
of the skin and the hair of the head caused by a
species of dermatophyte. This disorder is
characterized by scaly lesions, reddish tint, alopecia
to kerion.
(Budimulja et al, 2016) The cause of the
tinea capitis is a dermatophyte fungus. Tinea capitis
usually occurs, especially in children, although there
are also cases in adults are usually infected with
Trichophyton tonsurans the most common cause
Verma et al, 2008) incidence of Tinea capitis in the
Polyclinic of the Health of the Skin and Venereal
HOSPITAL DR. RM DJOELHAM the CITY of
BINJAI In the year 1 January 2014 - 1 November
2018 more common in women that is of 66.7%
compared to men of 33.3%, achieved the number of
patients of Tinea Capitis as many as 50 people, with
the age group is the largest 1 -120 of the year
amounted to 52.4%, and a lot of students/school
(61,9%).
REFERENCES
Budimulja . U, Widaty S. (2016). Dermatofitosis (tinea
kapitis). Dalam : Menaldi S.L SW, Bramono. K,
Indriatmi W, editors. Ilmu Penyakit Kulit dan
Kelamin. Edisi Ketujuh. Jakarta: Badan Penerbit FK
UI. hal.109-113.
Health Protection Agency. 2007. Tinea Capitis in The
United Kingdom: A report on its diagnosis,
management and provention. Lomdon: Health
Protection Agency, March.
Hryncewicz-Gwozdz A, Beck-Jendroscheck V, Brasch J,
Kalinowska K, Jagielski T. 2011. Tinea capitis and
tinea corporis with a severe inflammatory response
due to trichophyton tonsurans. Acta Derm Venerol
Vol. 91, Hal 708-710
James.WD, Berger TG, Elston DM. 2006. Disease
resulting from fungi and yeasts. Andrew’s Diseases of
The Skin : Clinical Dermatology. 10
th
Ed. Canada .
Hal. 297-299.
Kondo M, Nakano N, Shiraki Y, Hiruma M, Ikeda S,
Sugita T.A. 2006. Chinese-Japanese boy with black
dot ringworm due to Trichophyton violaceum. J
Dermatol. Mar. 33(3): 165-8. Available from :
https/emedicine.medscape.com.updated : jun13, 2018.
Author Handler, MZ. Fellow in Mohs Micrographic
Surgery, Skin Laser and Surgery Specialists of NY
and NJ.
Mohrenschlager M, Seidl HP, Ring J, Abeck D. 2005.
Pediatric tinea capitis recognition and management.
Am J Clin Dermatol. 5 : 203-13.
N. Rebollo, dkk. 2008. Tinea Capitis.Review article. Acts
Dermosifiogr. 99:91-100.
Putu DWL, Made B, Made SA. 2008. Tinea kapitis di
RSUP Sanglah Denpasar. MDVI. 35: 15-8s.
Robin Graham-Brown, Tony Burns. 2005. Dermatologi.
Edisi. 8. Jakarta: Erlangga. p,35.
Seebacher, C, Bouchara, JP, Mignon, B. 2018. Updates on
the epidemiology of dermatophyte infections.
Mycopathologia 2008 Nov-Dec. 166 (5-6) : 335-52.
Available From :
https/emedicine.medscape.com.updated : jun13.
Author Handler, MZ. Fellow in Mohs Micrographic
Surgery, Skin Laser and Surgery Specialists of NY
and NJ.
Siregar R,S. (2014). Saripati Penyakit Kulit dan Kelamin.
Jakarta : EGC. Hal. 13-15.
Suyoso S. 2008. Tinea Kapitis pada bayi dan anak. Dalam
: Kelompok Studi Dermatologi Anak. Penyakit
papuloeritroskuamosa dan dermatomikosis
superfisialis pada bayi dan anak. Semarang: Badan
Penerbit Universitas Diponegor. Hal. 49-88.
Verma, S. Heffernan, MP. (2008). Fungal Disease.
Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine 8
th
Ed.
Vol. 1 & 2. New York, USA. Hal. 1807-1818.
Welsh O, Welsh E, Ocampo-Candiani J, Gomez M, Vera
Cabrera L. 2006. Dermatophytoses in Monterrey,
Mexico. Mycoses. Vol. 49, Hal. 119-123
ICTROMI 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease
454
