
The Influences of Human Capital Organizational Learning and
Organizational Competence on Performance
Winarno and Pribadi Widyatmojo
Universitas Pembangunan Nasional Veteran Yogyakarta
Keywords: Human Capital, Organizational Learning, Organizational Competence, and Organizational Performance
Abstract: This study has investigated the influences of human capital and organizational learning on organizational
competence and organizational performance in Higher Education Institutions. The study followed a survey
design and employed an evaluative quantitative analysis method. The testing model was Structural Equation
Modeling using Partial Least Square method. The results show that intellectual capital is the most important
indicator of human capital in increasing organizational performance that is reflected in the improvement of
learning system, personal skills are the most important indicators of organizational learning in improving
organizational performance as reflected by the improvement in the learning system, and the quality of
education and teaching is the most important indicator of the organizational competence in improving
organizational performance which is reflected by the learning system improvement. The quality of education
and teaching as the most important indicator of organizational competence is capable of mediating the
influence of organizational learning on performance. Organizational competence as the mediating variable of
the influence of human capital and organizational learning on performance is partial, and human capital serves
as a more dominant factor in improving organizational performance than organizational learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
The organization will achieve sustainable
competitive advantage and superior performance if
the organization has the competence (Barney, 1991).
Organizational competencies covering all strategic
assets both tangible and in a tangible asset such as
human capital, organizational reputation, and
managerial capacity (Prahalad and Hamel, 1990;
Rumelt, 1991; Barney, 1991; and Pateraf, 1993).
Intangible assets can contribute more to the
organization than tangible resources (Amit and
Schoemaker, 1993; Barney, 1991; and Conner, 2002).
Higher education that has intangible assets,
particularly the quality of human capital is a critical
success factor in achieving superior performance
organization. Due to the quality of human capital,
then the organization will increase the competence
impact on improving the competitiveness of the
organization
.Research at the University of Cambridge found
that human capital intellectual capital, social capital,
organizational capital, and knowledge) have a
significant effect on performance (Stiles and
Kulvisaechana, 2004). Other empirical evidence
conducted research at 34 universities in Europe
(Germany, Spain, France, Sweden, and the UK),
shows that human capital (education, skills, and
competence) significantly affects the performance of
both public and private universities (Hansson et al.
,2004).
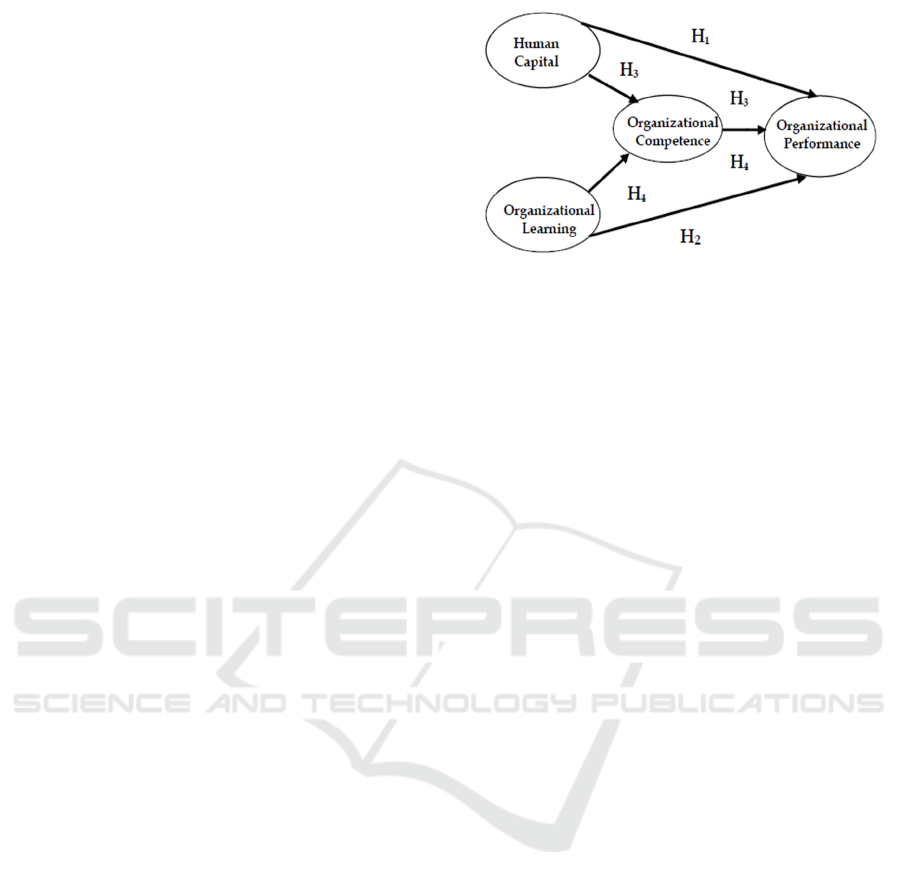
This study aims to examine and analyze the effect
of (1) human capital on organizational performance,
(2) organizational learning on organizational
performance, (3) human capital on organizational
performance is mediated by organizational
competence, and (4) organizational learning on
organizational performance mediated by
organizational competence.
2 LITERATURE
2.1 Human Capital
Human capital is the term human capital is the
recognition that people in organization and business
are important and essential assets that contribute to
development and growth, a similar way as physical
Winarno, . and Widyatmojo, P.
The Influences of Human Capital Organizational Learning and Organizational Competence on Performance.
DOI: 10.5220/0009967605670573
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management (ICBEEM 2019), pages 567-573
ISBN: 978-989-758-471-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
567

assets such as machines and money. The collective
attitude, skills, and abilities of people contribute to
organizational performance and productivity. Any
expenditure in training, development, health, and
support is an investment, not just an expense Stockely
(2003). Edvinson and Malone (1997) define that
human capital is individual knowledge, experience,
capability, skills, creativity, innovativeness.
Knowledge is the academic texts obtained through
education and skills is the ability to work to meet the
practical skills. Knowledge and skills do naturally,
but universities should deliberately increase it
through investment in human capital. Meanwhile
(Ancok,2002) defines that comprehensive human
capital includes :(1) intellectual capital, (2) emotional
capital, (3) social capital, (4) adversity capital, and (5)
moral capital. Therefore, in this study, the dimensions
of capital are capital that will be used from the fifth
dimension are used as an indicator of human capital.
Colleges who scored the pioneer development of this
nation must develop human capital concerns: (a)
intellectual capital, where universities develop the
willingness and ability to think to of something new,
(b) capital emotional, where the college develop a
positive attitude in the face of changes in the
organization, (c) Social capital, where universities
develop cooperation with other organizations to
achieve success, (d) Adversity capital, where
universities develop stoicism in the face of various
challenges, and (e) Moral capital, where the
university develop a good image for the organization.
2.2 Organizational Learning
Organizations that make learning organization is an
organization that has expertise in creating, retrieving,
and transferring knowledge, and modifying its
behavior to reflect new knowledge and experience.
Organizational learning impact on organizational
performance (Amulyoto, 2004; Njuguna, 2008) and
organizational learning as one of the determinants of
success in Non-Governmental Organizations
(Khakina, 2006). These studies concluded that
organizational learning had a positive impact on
organizational performance, but results could not be
generalized to other industries due to differences in
size efficiencies and knowledge needs. Baldwinetal.
(1997) Stated that members of the organization at all
levels, not just top management, continue to observe
the environment in an effort to obtain important
information, change strategies and programs
necessary to obtain the advantage of the changing
environment, and to work with the methods,
procedures, and evaluation techniques continuously
improved. Other research findings, there is an
influence of organizational learning knowledge
acquisition, information distribution, information
interpretation, and organizational memory jointly
positively affect organizational performance (Ouma
and Kombo, 2016). In order to achieve and maintain
a competitive advantage and high performance in a
business environment is changing rapidly,
organizations must be able to increase the capacity of
learning (Marquardt, 1996). This study uses six
dimensions of organizational learning developed by
Marquardt (1996: 30), i.e.:
a. Systems thinking, the conceptual framework, a
person to make the pattern more clearly and to
help him see how to change them effectively.
b. Mental model, the assumptions inherent in-
depth understanding of how the influence of the
outside world, and how people take action.
c. Personal skills, indicating a high level` of skill
or expertise. This requires long-term
commitment to continue to learn so to develop
expertise and skill in an organization devoted.
d. Teamwork, the skill that is focused on the
process of bringing together and building the
capacity of the team to create and produce
learning that members actually expected.
e. Expertise divided into a shared vision, the
expertise that each member of the organization
to focus its efforts on the development of a
vision to build a true commitment.
f. Dialogue, which is the ability to listen, share,
and high-level communication among members
of the organization. This skill requires the
freedom and creativity to explore the issues, the
ability to listen to each other deeply and suspend
his own
2.3 Organizational Competence
Competence can also be perceived as assets derived
intermediate company from increasing the
productivity of its resources, such as strategic
flexibility and protection of products and services the
company (Amit and Schoemaker, 1993).
Organizational competence is the ability to organize
work and deliver value; competencies include
communication, involvement, and commitment to
work along the boundaries of the organization
(Prahalad and Hamel, 1990; Kogut and Zander,
1992).
Competence of higher education in this study was
measured in accordance with the philosophy that
mandated by the government for higher education
institutions, namely: 1) quality of education and, 2)
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
568
quality of research, and 3) quality of service to the
community. An assessment of the level of
performance can be measured from the higher
education success rate in achieving the first goal has
been set, from field activities.
2.4 Organizational Performance
Organizational performance is the effectiveness that
includes the achievement of organizational
objectives, the efficiency of which considers the
relationship between inputs and outputs necessary to
achieve the output, and the adaptations that reflect the
organization's ability to adapt to environmental
changes (Homburg et al., 1999). The performance of
an organization reflects how effective the
products/services produced and how the organization
can deliver to customers. Human resources (HR) in
the organization in charge of designing, producing
and continuing through services (Mathis and Jackson,
2001), therefore one of the objectives of human
resource management (HRM) is to create activities
that contribute to the achievement of superior
performance.
Accreditation standards are benchmarks that must
be met by higher education. Accreditation standard
consists of several parameters (key indicators) that
can be used as the basis of (1) the presentation of data
and information on the performance, the state, and the
higher education, as outlined in the instrument of
accreditation; (2) evaluation and assessment of
quality performance, and the state of college
education, (3) the determination of college eligibility
to hold its programs; and (4) The formulation of
recommendations for improvement and development
quality of higher education. Higher accreditation
standards include two core commitments, the college
commitments the institutional capacity (institutional
capacity) and the effectiveness of educational
programs (educational effectiveness), which
includes 15 accreditation standards, namely: 1)
Leadership, 2) Student, 3) Human resources, 4)
Curriculum, 5)Infrastructure, 6) Funding, 7)
Governance, 8) Management systems, 9) learning
systems, 10) Academic atmosphere, 11) Information
systems, 12) Internal quality assurance system.,13)
Graduates, 14) Research and community service, 15)
Study program.
Figure 1: Research Framework
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research is explanatory research with a
quantitative approach to explain the relationship
between variables through hypothesis testing. The
sampling technique used was purposive sampling,
namely that the sample is based on certain criteria.
Sample grouping criteria are (1) Rector and Vice-
Rector for the University and the Institute, (2)
Director and Vice-Director for the Academy and
Polytechnic. The total population of 116 private
universities, where the sample is based on private
higher education, which has 50% of accredited study
programs as much as 53 private universities. The
method used in this study was Structural Equation
Modeling by using Partial Least Square (Ghozali,
2006). This method was chosen because the study
involved a series of causal relationships between the
variables of human capital, organizational learning,
organizational competence, and performance.
4 ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Analysis of Research Model
Testing the research hypotheses proposed in this
study by using Partial Least Square(PLS). PLS is a
structural equation model (SEM) based on
components or variance (variance). As with SEM,
PLS analysis involves two stages, namely:
The Influences of Human Capital Organizational Learning and Organizational Competence on Performance
569
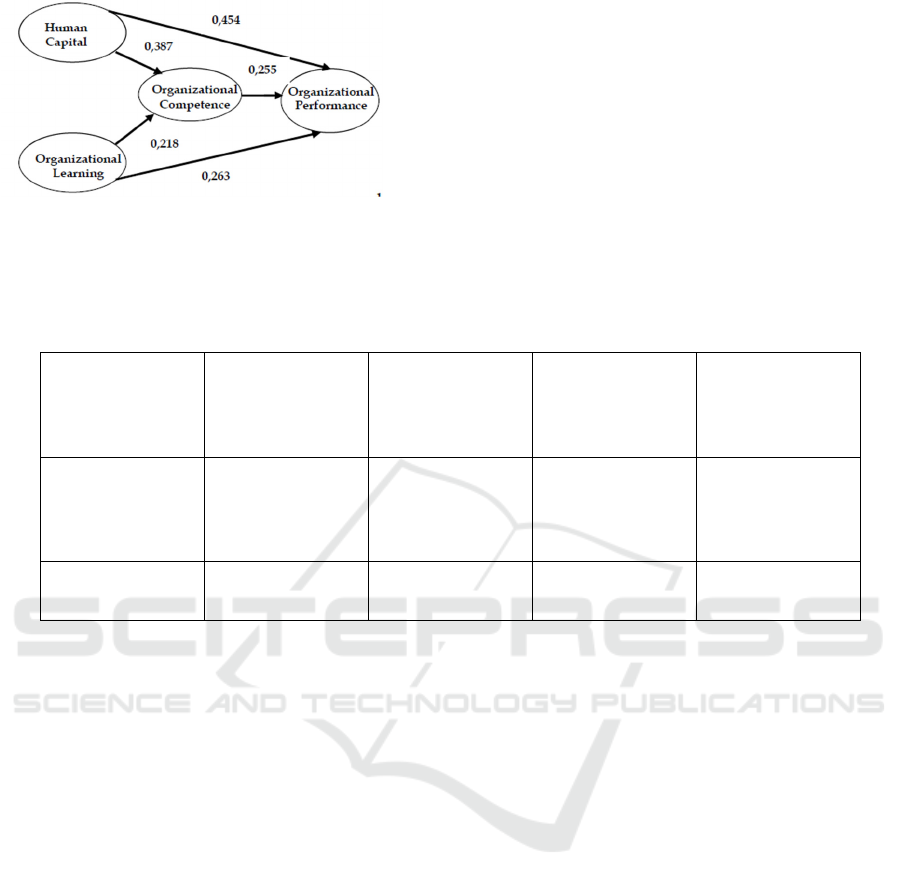
Figure 2: PLS Result of Structural Model
Source: Primary Data Processed, 2018
4.2 Hypothesis Testing
4.2.1 Direct Effect Testing
The results showed that both the direct effect, either
direct effect of human capital on organizational
performanceas as well as a direct effect of
organizational learning on organizational
performanceisa significant (Table 1)
Table 1: Direct Effect Testing in Inner Model.
Influence
Between
Variables
Inner Weight t-statistic P values Description
Human Capital
Organizational
Performance
0.454 9.870 0.000 Significant
0.263 6.262 0.000 Significant
Source: Primary Data Processed, 2014
Table 1 and Figure 2 shows that the results of
hypothesis testing as follows:
a. Testing the direct effect of Human Capitalon
Organizational Performance, inner weight
coefficient values obtained at 0.454, with at-
statistic values for 9,870, and p-value of 0.000.
Since the value of t-statistics > 1.96, and the p-
valueof < 0.05, then there is a positive
significant direct effect between Human
Capitalto Organizational Performance. That is,
the higher quality of human capital, the higher
the Organizational Performance. This shows
that the first hypothesis which the higher the
human capital can improve the organization's
performance proved.
b. Testing the direct effect of Organizational
Learning on Organizational Performance, the
value of weigh coefficient of the inner
workings of 0.263, with at-statistic values for
6,262, and p-value of 0.000. Since the value of
t-statistics > 1.96, and the p-value of < 0.05,
then there is a positive significant direct effect
on Organizational Learning to Organizational
Performance. That is, the higher the Learning
Organization, the higher the Organizational
Performance. This suggests that the second
hypothesis which the higher Learning
Organization can improve the Organization’s
performance proven.
4.2.2 Indirect Effect Testing
a. Organizational Competence Mediates the
Influence of Human Capital On Organizational
Performance
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
570
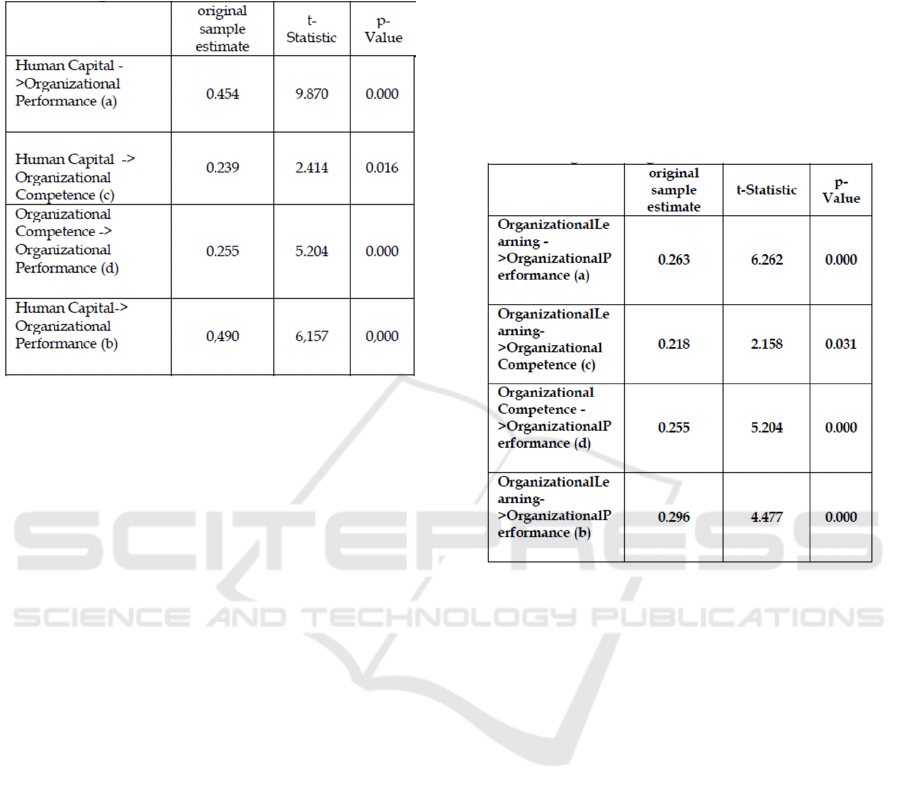
Table 2: Organizational Competence Mediates the
Influence of Human Capital on Organizational
Performance.
Table 2 shows the effect of human capital on
organizational performance( a), the effect of human
capital on organizational competence (c), the
competence of the organization on the organization
performance (d), and the effect of human capital on
organizational performance without organizational
competence (b), where (a) has a smaller coefficient
(down) from the influence of human capital on
organizational performance without organizational
competence(b), it can be said that the organizational
competence as a mediating is partially (partial
mediation). This proves that human capital can
improve organizational performance directly and also
through organizational competence. Thus, it can be
said that the hypothesis (H3) that states the higher
human capital will, the higher organizational
performance mediated by Organization competence
proven.
b. Organizational Competence Mediates the
Influence of Organizational Learning On
Organizational Performance
Table 3 shows the effect of organizational
learning on organizational performance (a), the effect
of organizational learning on organizational
competence (c), the effect of organizational on the
organizational performance (d), and the effect of
organizational learning on organizational
performance without organizational competence (b),
where (a) has a smaller coefficient (down) from the
influence of organizational learning on organizational
performance without organizational competence (b),
it can be said that the organizational competence as a
mediating is partially (partial mediation). This proves
that organizational learning can improve
organizational performance directly and also through
of organizational competence. Thus, it can be said
that the hypothesis (H4) that states the higher
organizational learning will, the higher the
organizational performance mediated by
Organization competence proven.
Table 3: Organizational Competence Mediates the
Influence of Organizational Learning On Organizational
Performance
Source: Primary Data Processed, 2018
5 DISCUSSION
The results of this study found that the learning
organization can directly improve organizational
performance. Besides supporting research Marquardt
(1996) found that the learning organization (systems
thinking, mental models, personal skills, Teamwork,
Expertise shared the vision, and dialogue/discussions
can improve organizational performance.
This research supports previous research
(Khandekar and Sharma, 2006; Wang and Lo, 2003;
Said, 2002; Absah, 2007; and Therin, 2003), which
This study also supports the theory of organizational
learning of Argyris (1976), which reveals that
organizational learning is a process to detect and
correct errors to improve organizational performance.
And also supports the theory of organizational
learning Senge(1990) which revealed that the
organization must continually expand their capacity
to create the desired performance, through new
patterns and development of ideas, where collective
aspiration released, as well as the organization
The Influences of Human Capital Organizational Learning and Organizational Competence on Performance
571

continues to learn how to create learning together.The
implication of this research for organizations is to
improve organizational performance, so
organizations must continue to develop and enhance
organizational learning, including creating a
continuous opportunity to learn, develop inquiry and
dialogue, encourage collaboration and group
learning, establish various systems to obtain and
share learning, empower members of the
organization towards a common vision, and Connect
the organization to its environment.
The results of this study also found that
organizations that invest in improving the quality of
human resources can gain a competitive advantage
and high performance. This research supports
research (Redmon, 2005; Stenberg & Slater, 1982),
who found that human capital (intellectual capital,
emotional/social and moral capital/spiritual)
influence on organizational competence. The findings
also indicate that organizational competencies
mediate the effect of human capital on organizational
performance. Therefore, organizations in the field of
investment in human resources should be able to
increase the competence of an organization in order
to support the improvement of organizational
performance.
Another result of this study also found that
organizational learning and empowering members
can enhance organizational competencies,
organizational competencies which use RBV
consisting of: rare, valuable, not easily imitated and
not easily replaceable, and competence of the
organization can improve organizational
performance. This research support (Said, 2002) that
has been done by the findings that organizational
learning can improve organizational competence (the
ability of market analysis and quality of service) on
the private higher education. While in this study,
although the competence of the organization refers to
the quality of the implementation of the college, in
college, it contains the ability to analyze the market
and good quality services for students and the
community.
Research in public and private universities in
India (Bhatnagar,2006) found that the competence of
the organization includes the teaching and services
that affect the performance of organizations, both
public and private universities. Therefore, of this
research have to find a way to develop a learning
organization that can improve both organizational
competence in the field of education and teaching,
community service, in order to encourage the
improvement of organizational performance.
6 CONCLUSION
Many studies have tried to show the relationship
between human capital and performance. An
important finding of this study is that contingency
models and best practices can complement each other
to create conditions for effective human resource
management. This research found that investment in
human resources is a determinant of organizational
success, especially in higher education. Human
capital conceptualization is related to the
fundamentals of economic and firm performance.
According to this research, organizational
performance influenced positively by human capital
considerations, especially intellectual capital
Organizational learning influences organizational
performance, which reflects an improvement in
learning systems. Thus, the higher the organizational
learning, the higher the organizational performance.
This is consistent with organizational learning theory,
which states that good organizational learning can
improve organizational performance. Quality of
education and teaching is an important organizational
competency in improving organizational
performance reflected increased learning system.
Proven organizational competence partially mediates
the influence of human capital on organizational
performance. In other words, the higher the human
capital can increase organizational performance
mediated increase organizational competence.
Organizational competence as a mediating is partial.
Basically, it is changing the whole workforce as
the most valuable asset, thus creating the way for the
organization for greater achievements through
creativity and innovativeness. Therefore, companies
should bring some effective and useful plans for
investing in the various aspects of human capital and
organizational learning. It not only direct firms to
achieve greater performance but also makes firms to
remain competence for long term survival.
7 RECOMMENDATION
Based on the analysis and discussion, the suggestions
put forward in this study are:
1. The results of this study indicate that human
capital affects the competence and performance
of the organization, so that university leaders
must increase, human capital, especially
intellectual capital through the provision of
study permits or following study assignments
for lecturers to continue their studies both
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
572

Masters (S2) and Doctor (S3), in order to
improve competence (quality of education and
teaching) and its performance.
2. Organizational learning that is carried out by
universities can enhance improve personal
skills. Related to the learning system, such as
personal skills. Therefore, higher education is
recommended to conduct organizational
learning such as character education, scientific
publication training, comparative studies to
other universities, and others.
8 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS
AND FUTURE RESEARCH
This study was conducted on Private Higher
Education, which has accredited programs 50% or
more. Variables examined only the relationship was
human capital and organizational learning to
organizational competence and performance. Future
studies can be conducted on all Private Higher
Education with a wider scope such as Private Higher
Education throughout Indonesia. While the research
can be developed the relationship between human
capital and organizational learning with the
competitive advantage of the organization's
reputation or other company.
REFERENCES
Ancok, D. 1997. Revitalisasi Sumber Daya Manusia dalam
Era perubahan, Kelola: Gadjah Mada University
Business Review, No.8, 104-117.
Ancok, D. 1998. Membangun Kompetensi Manusia dalam
Milenium Ketiga, Psikologika, No. 6, 5-17.
Barney, JB.1986b. Organization Culture: Can it be a
Source of Sustained Competitive Advantage? Academy
of Management Review, Vol.11, pp.656-665.
Damanpour, F. and W.M.Evan.1984.Organizational
Innovation and Performance: The Problem of
''Organizational Lag''. Administrative Science
Quarterly, 1984, 29(3), 392-409
Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, 2003. Undang-Undang
No.20 Tahun 2003 tentang Sistem Pendidikan
Nasional, Jakarta: Departemen Pendidikan Nasional.
Ghozali, I. 2006.Structural Equation Modeling: Metode
Alternatif Dengan Partial Least Square (PLS),
Semarang: Universitas Diponegoro.
Hansson, B.,U.,Johanson and Karl-Heinz, L.2004. The
impact of human capital and human capital Investments
on company performance, Office for Official
Publications of the European Communities, 2004.
Hanssons, B. 2006. Company –based determinants of
training on company performance Result from an
International HRM Survey, Personnel Review, Vol. 36
No. 2, 2007.
Kemp,R.G.M., M. Folkeringa, J.P.J. deJong,and
Wubben,E.F.M.2003. Innovation and firm
performance, SCientific AnaLysis of
Entrepreneurship and SMEs, September 2003
Iannaccone, L. R.2000.Household Production,
Human Capital, and the Economics of Religion” Santa
Clara University, Santa Clara, CA 95053.
Tan, B., Lee, C-K. and. Chiu, J-Z.(2008) The impact of
organisational culture and learning on innovation
performance, International Journal of Innovation and
Learning Issue: Volume 5, Number .4 2008.
Maditinos, D., Sevic, Z., and Tsairidis, C. 2009.Intellectual
Capital and Business Performance: An Empirical study
for the Greek Listed Companies,7th International
Conference on Accounting and Financein Transition
(ICAFT) 23-25 July 2009 Greenwich, London.
Marimuthu, M., Arokiasamy, L. and Ismail,
M. 2009. Human Capital Development And Its Impact On
Firm Performance: Evidence From Developmenta
Economics, The Journal of International Social
Research, Volume 2 / 8 Summer 2009.
Ouma, Ruth, and Kombo, Henry, 2016. Effect of
Organizational Learning on Organizational
Performance of Food Manufacturing Firms in Nairobi
County, Kenya, European Journal of Business and
Management , Vol.8, No.30, 2016
Ravichandran, T., and Troy, N. 2007. IT Competencies,
Innovation Capacity and Organizational Agility:
Performance Impact and the Moderating Effects of
environmental Characteristics, Submitted to CIST,
Ihformation, June 15, 2007.
Segal, G., Borgia, D., &Schoenfeld, J. 2009.Founder
human capital and small firm performance: an
empirical study of founder- managed natural food
stores, Journal of Management and Marketing
Research., 2009
Souleh, S., 2014, The impactof Human Capital
Management on the Innovativeness of research Center:
The Case of Scientific Research Centers in Algeria,
International Journal of Business and Management Vol.
II (4), 2014
Stiles, P. andKulvisaechana, S. 2002.On The Link Between
Humn Capital And Firm Performance, FEP Work
Paper, No. 121 November2002.
Toole, A. A., andCzarnitzki, D.(2007) Exploring the
relationship between scientist human capital and firm
performance: The case of biomedical academic
entrepreneurs, Dis cus si on Paper No. 07-011
Ukenna, Ijouma, Anlionwu and Olise (2010) Effect of
Investment in Human Capital Development on
Organizational Performance, Office for Official
Publications of the European Communities.
Wang, Yand Lo, H., P. (2003) Customer- focused
Performance and the Dynamic Model for Competences
Building and Leveraging: A Resource-based View,
Journal of Management DevelopmentVol. 22 No. 6,
2003
The Influences of Human Capital Organizational Learning and Organizational Competence on Performance
573
