
Expert System for Measuring the Level of Spinach Freshness using
Certainty Factor Method
Marchello William
1
, Jason Kristanto
1
, Jansen Sampurna
1
, Edrick
1
and Melvin Hendronoto
1
1
Informatics Student, Multimedia Nusantara University, Tangerang, Indonesia
Keywords:
Spinach, Certainty Factor, Prototype, Expert System, Freshness Level.
Abstract:
Expert system for measuring the level of spinach freshness is made because spinach is one of the vegetables
that has a good nutritions and often consumed by people, especially in Indonesia. Spinach that will be con-
sumed must be check first the freshness level. However, not everyone know how to find out the level of spinach
freshness Therefore, an expert system is needed to measure the level of spinach freshness. Expert system for
measuring the level of spinach freshness is also rarely found, especially in Indonesia. The measurement of
level of spinach freshness can be seen from several factors or symptoms, such as soft texture, leaf color be-
tween light green and green, and no white spots on the leaves. These factors or symptoms determine the level
of spinach freshness or spinach quality whether the spinach is good or normal. Expert system created in this
study uses the Certainty Factor method because this method has been widely used in several other studies and
gives good results. This research still uses prototype system, but it cant give good results, namely the system
made to show the quality calculation of the level of spinach freshness in accordance with manual calculations.
Test result on expert get 90% accuracy.
1 INTRODUCTION
This research will discuss the level of spinach fresh-
ness using Certainty Factor method with the help of
an expert system. Artificial intelligence are every-
where, perform in so many sector such as security
using biometric, health etc (Alexander et al., 2018).
Expert system is part of artificial intelligence that
combines knowledge from the research of an expert
who has knowledge of a field to help make a deci-
sion(Islam and Mishra, ). It has been implemented in
many fields including health (Kusnadi, 2013), educa-
tion (Futra, 2014) and others.
Spinach contains vitamin K, iron, flavonoids,
carotene, vitamin C, and other good nutrients. These
nutrients are good for the body and can prevent sev-
eral diseases such as cancer, presbyopia, cataract, and
other diseases. This has been proven from an inter-
national research journal entitled Nutritional Value of
Spinacia Oleraecea Spinach which states that spinach
is good for the body (Singh et al., 2016). In addition,
these benefits make people become interested in con-
suming spinach, including Indonesian.
Indonesia has abundant natural resources, includ-
ing spinach. Based on data from Statistics Indone-
sia regarding spinach production in Indonesia, the in-
crease level of spinach production in Indonesia is in-
creasing almost every year (Statistik, 2019). The in-
crease in spinach production each year is between
10.000 and 20.000 per ton. This shows that spinach is
in demand by Indonesian people. Therefore, the qual-
ity of spinach also needs to be considered. Before
spinach is consumed, it is better to check the fresh-
ness level first so that the nutrients in spinach can be
beneficial to the body. The level of spinach fresh-
ness is generally seen from the physical condition.
However, not everyone knows how to check the level
of spinach freshness. Therefore, an expert system is
needed to help people in giving advice on choosing
fresh spinach.
Spinach that is good to be consume is fresh
spinach and useful substances in spinach can still be
utilized. Checking the level of spinach freshness is
generally seen from the physical condition of spinach.
However, not everyone knows how to check the level
of spinach freshness. Therefore, an expert system
is needed to help people in giving advice on choos-
ing fresh spinach. Currenlty in Indonesia there are
not many system for measuring the level of veg-
etable freshness, especially spinach. Based on this,
an expert system for measuring the level of spinach
freshness needs to be made. Expert system that
William, M., Kristanto, J., Sampurna, J., Edrick, E. and Hendronoto, M.
Expert System for Measuring the Level of Spinach Freshness using Certainty Factor Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0009909703190324
In Proceedings of the International Conferences on Information System and Technology (CONRIST 2019), pages 319-324
ISBN: 978-989-758-453-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
319

will be created is to use the certainty factor method.
This method was chosen because there are already
many research journals that use this method, such
as Sistem Pakar Mendiagnosa Penyakit Tanaman Kol
Menggunakan Metode Certainty Factor (Rayuwati,
2013), Sistem Pakar Diagnosa Penyakit Tomat den-
gan Metode Certainty Factor (Rohmah, 2017), Sistem
Pakar Mendiagnosa Penyakit Kolesterol pada Remaja
dengan Metode Certainty Factor Berbasis Web (Si-
hotang, 2017), and other researches. Based on these
researches, certainty factor method can provide good
suggestions to users.
The system that will be created will receive input
from the user to select factors or symptoms that exist
in spinach that will be checked for the freshness. Af-
ter that, the user fills in the certainty level (CF User)
on each factor or symptom. The system will calcu-
late the CF factor to get the freshness percentage of
spinach. Based on the testing result expert system
was successfully made with 90% accuracy so it can
be useful to help people or users who have difficulty
in choosing fresh spinach. Therefore, people or users
can choose spinach that is good for the body and get
maximum benefits from the spinach.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Level of Spinach Freshness
The level of spinach freshness can be seen from the
color of spinach leaves which are still integrated with
the stem. Spinach leaves that are suitable for con-
sumption are spinach leaves that are green or dark
green while spinach that is not suitable for consump-
tion is spinach with yellow leaves and also on the sur-
face of a good spinach leaf there are no white spots
(fungus) (Zhang and Zhang, 2014).
2.2 Certainty Factor Method
The following are literature review of researches us-
ing Certainty Factor method.
1. Sistem Pakar Mendiagnosa Penyakit Tanaman
Kol Menggunakan Metode Certainty Factor by
Danil Iskandar in 2017. This research diagnosed
cabbage plant diseases that can provide advice to
users and farmers and provide solutions that are
appropriate to the symptoms experienced by cab-
bage.
2. Sistem Pakar Diagnosa Penyakit Tomat dengan
Metode Certainty Factor by Siti Nur Romah in
2017. This research produced a system that can
provide disease indication results based on the
selected symptoms and the level of confidence.
Validity testing is done by using system calcula-
tion and manual calculation by finding highest CF
value that is equal to confidence value 93.77%. So
the system can be declared as valid.
3. Sistem Pakar Mendiagnosa Penyakit Kolesterol
pada Remaja dengan Metode Certainty Factor
Berbasis Web by Hengki Tamando Sihotang in
2014. This research simplify and provide a calcu-
lation of the completion of how certain the users
are aware of teenage cholesterol disease.
2.3 Results Validation
System testing is done by comparison result of man-
ual testing with those calculated through the system.
This research will be testing the highest CF value.
The following are literature review of research test-
ing.
1. Sistem Pakar Diagnosa Penyakit Tomat dengan
Metode Certainty Factor by Siti Nur Romah in
2017. This research examines the highest CF
value with confidence value of 93.77%.
There are also rules that determine the level of
spinach freshness that is influenced by the color of
leaf, the amount of mold, and the texture of the leaf.
The test result are in the form of a comparison be-
tween manually calculated Certainty Factor and sys-
tem calculated using system.
Certainty Factor can be calculated using the fol-
lowing formula.
CF[H, E] = MB[H, E]–MD[H, E] (1)
Variables:
CF[H,E] : Certainty factor hipotesis which is
influenced by evidence e known with certainty.
MB[H,E]: Measure of belief against hypothesis H, if
given evidence E (between 0 and 1).
MD : Measure of disbelief
P : Probability
E : Evidence
The basic formula is used if there is no CF value
for each spinach fact. The Certainty Factor used to
measure the quality of spinach is as follows.
1. Certainty Factor for rules with a single
premise/factor
CF f actor = CF[user] ∗CF[expert] (2)
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
320
2. If there are more than factors, then it will be de-
termined by the following equation.
CFcombination = CFold +CF f actor
∗ (1 −CFold) (3)
3. Whereas to calculate the percentage of quality
freshness can use the following equation.
CF percentage = CFcombination ∗ 100 (4)
3 SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT
METHOD
The method used to develop this system is pro-
totype method due to one of the advantages of pro-
totype method because this method able to take con-
crete needs and can be developed into largescale sys-
tem but only the simplified version was made (bam-
bang hermawan, 2015). System only accepts input in
the form of confidence percentage in a spinach quality
category. The steps of this method are as follows:
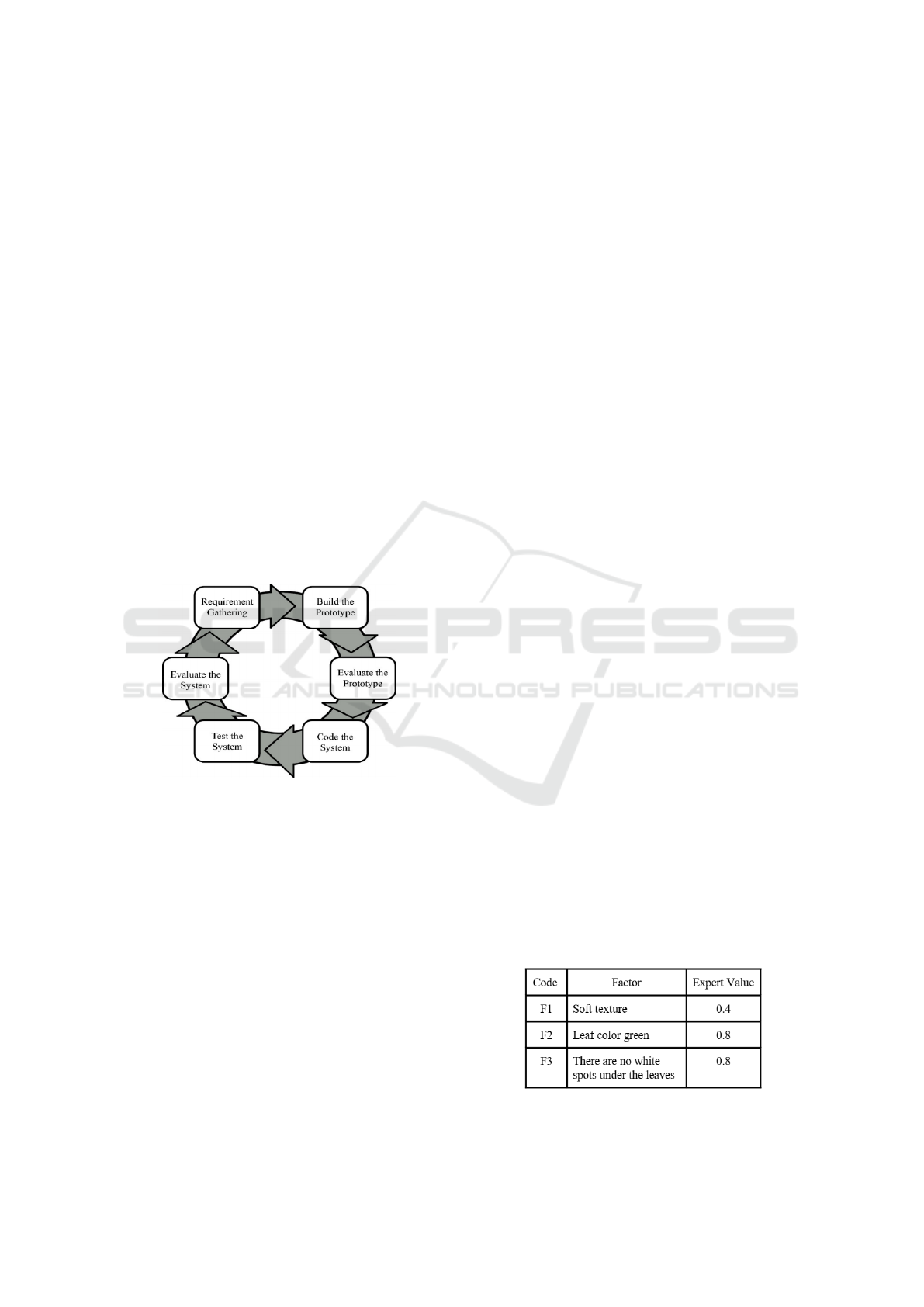
Figure 1: Prototype Method
1. Requirements gathering
Identify all the requirements and system out-
line that will be made. Requirements are ex-
plored with stakeholders to define software re-
quirements.
2. Build the prototype
After gathering requirements, temporary design
will be made for the user. The temporary design
consist of input, process, and output that can be
seen by the user.
3. Evaluate the prototype
Evaluate the prototype to find out if it has fulfilled
all the necessary requirements. If not, then the
developer must gather requirements more deeper
and prototype must be designed and built or de-
veloped so that it suits the overall requirements.
4. Code the system
Prototype that has been approved will be code into
certain programming language.
5. Test the system
System has become a software and must be tested
using either White Box, Black Box, and other test-
ing.
6. Evaluate the system
Sistem will be evaluated and quality of the system
will be checked. If quality of the system is still not
according to user expectations, then system will
be code and test again. When system is ready to
be use, system can measure the level of spinach
freshness. If there is an update, then there will be
requirements gathering again.
System will be made with C/C++ programming
language with CodeBlock editor. System will accept
2 inputs number with float data type where the value
of the inputs are probability value that range from -
1 to 1 and each input comes from experts and users.
System has 3 criteria for determining the quality of
spinach, those are the state of spinach leaves, the color
of spinach leaves, and the number of white mold un-
der the spinach leaves. Each criterion receives 2 in-
puts, namely from the experts and the users, so that
the total input is 8 kinds. System will process input
data from users and experts to measure certainty fac-
tor based on the level of certainty, the level of uncer-
tainty, and probability then processed using the for-
mula described in the previous chapter. Output from
the system is the value of a certainty factor that ranges
from -1.0 to 1.0 (certainly not to very certain) to de-
termine whether spinach leaves are suitable for con-
sumption or not.
4 RESEARCH RESULT
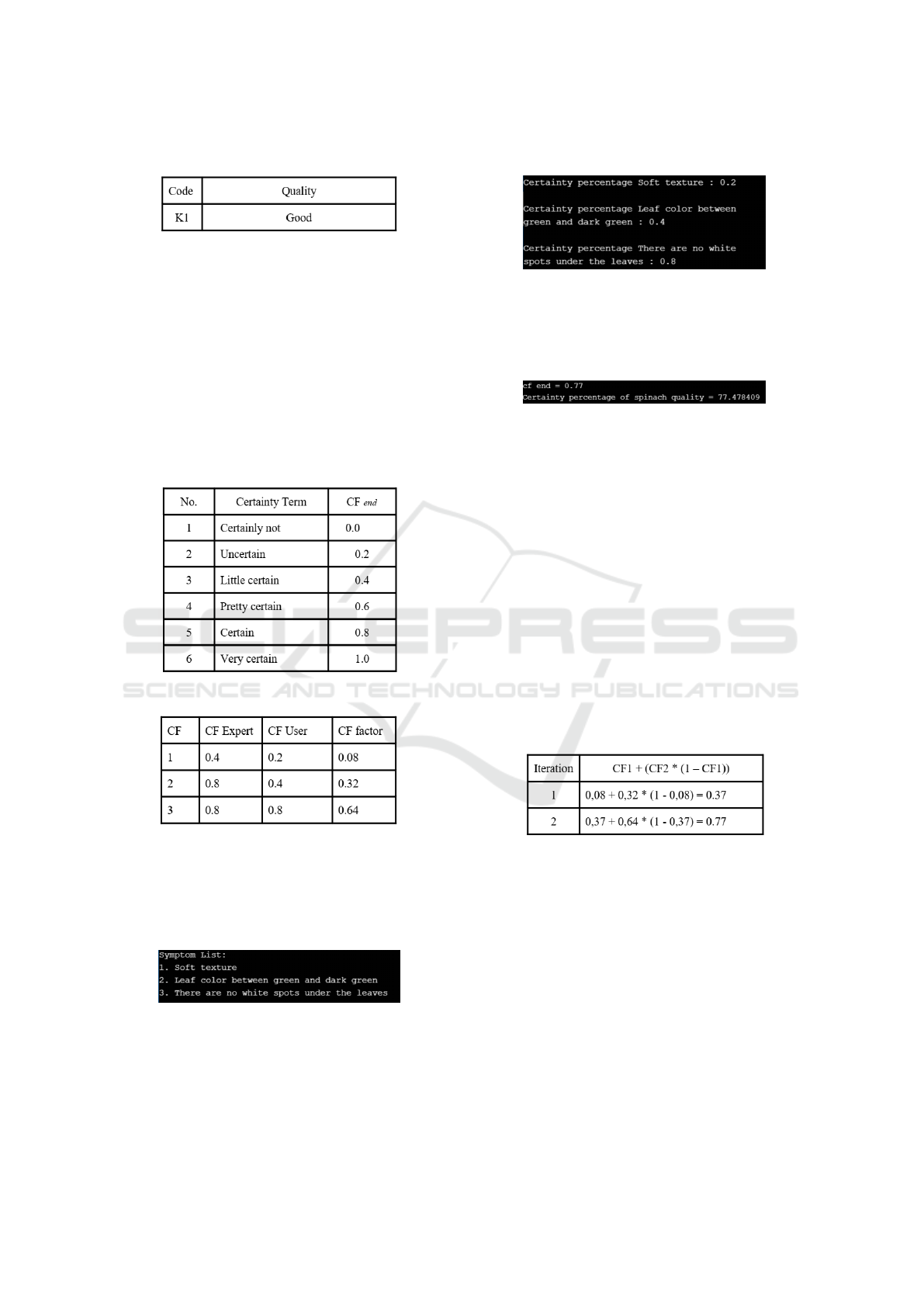
4.1 Knowledge Base
Research conducted by interviewing experts who
have experience in understanding the level of spinach
freshness. The following are the categories of symp-
toms and quality in spinach obtained from experts.
Figure 2: Symptoms Category.
Expert System for Measuring the Level of Spinach Freshness using Certainty Factor Method
321
space
Figure 3: Quality Category.
To determine certainty factor information from the
expert, seen from CF combination based on the CF
term table.
4.2 Rule CF
The application of the Certainty Factor method re-
quires several rules in form of variables and weight
values given by experts. The weight value needed for
each symptom can be seen in Figure 4. CF rules that
contain symptoms and weight values from experts for
each disease are shown in Figure 5.
Figure 4: Symptoms Percentage.
Figure 5: Test case calculation.
4.3 Implementation
System will display list of symptom criteria consist-
ing of 3 types which can be seen in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Symptoms criteria
User will input their certainty level about symp-
toms found in spinach with inputs ranging from 0
(certain), 0.2 (not certain), 0.4 (little certain), 0.6
(pretty certain), 0.8 (certain), 1.0 (very certain) as in
Figure 7.
space
Figure 7: Input certainty factor
If the user has finished inputting all certainty about
symptoms found, then the application will issue a
certainty percentage of spinach quality which can be
seen in Figure 8.
Figure 8: Result certainty percentage of spinach quality
4.4 Application Calculations
Application calculations are used to determine the
quality of spinach freshness. The calculation method
used is Certainty Factor.
The first step of using CF method in the calcula-
tion process based on symptoms that have been in-
putted by the user in figure 3 is to multiply 2 proba-
bility values namely weight given by the user with the
weight value rule given by the expert. The results of
multiplication are shown in Figure 5.
The next step is the combination of the multipli-
cation results of each symptom from the product in
table 4 with each combined iteration show in Figure 9
where the good spinach has 77% percentage value of
spinach quality which can be seen in Figure 8.
Figure 9: Symptoms Percentage.
4.5 System Testing
System testing is done to determine the accuracy be-
tween the calculation of the certainty percentage of
spinach freshness from the system equal to the man-
ual calculation. The system is tested by giving users
to input CF which can be seen in Figure 5. The results
of calculations on the system can be seen from figure
4 and the results of manual calculation can be seen
in Figure 9. From these calculations were shown to
experts and checked by experts to know the accuracy
level. The level of accuracy is obtained from com-
patibility between the spinach that is checked for the
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
322
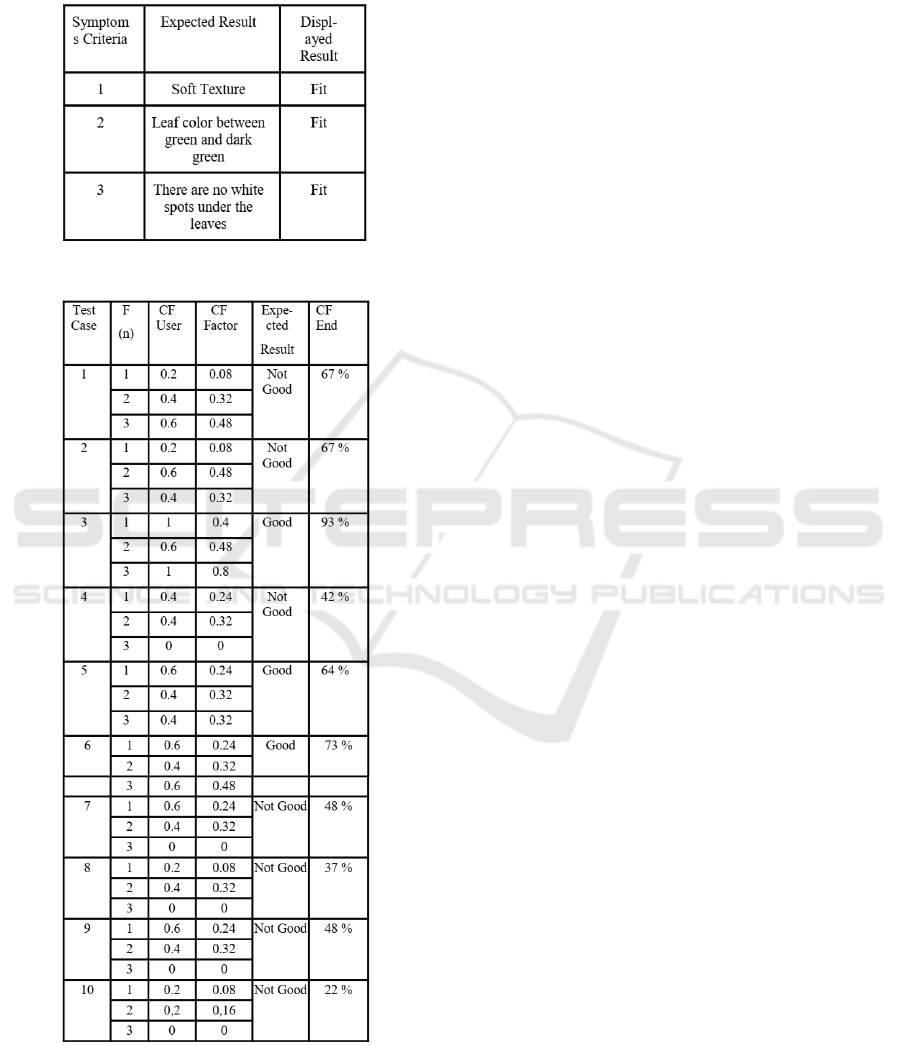
level of freshness manually by experts and those that
are checked with the system. From the test result it
can be said that the accuracy is 90% which can be
seen in Figure 11.
Figure 10: Symptoms Criteria Testing.
Figure 11: Expert Test Result.
Result from Figure 11 can produce 90% accuracy
because out of 10 test cases, there was one wrong test
case, that was test case 5, where the expected result
is different from result checked in system. Test case
5 included in category not good because CF end is
under 70%. Failure might be caused by expert give
inputs or weight that are not quite right.
From the research conducted there are still weak-
nesses in several aspects. This research might be de-
veloped to give maximum result, such as add more
criteria or expert value that can be checked with other
experts.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on research conducted, the expert system with
the Certainty Factor method can be implemented well
for the measurement of the level of spinach fresh-
ness. Calculations made with the system that are
made compared with calculations done manually. The
results of the comparison done are same. So that the
system created can help to see the quality of spinach
from the symptom entered by user. With this system,
it is expected to be useful for people who want to see
the spinach quality or spinach freshness.
Expert System for Measuring the Level of Spinach Freshness using Certainty Factor Method
323

REFERENCES
Alexander, L., Kusnadi, A., Wella, W., Winantyo, R., and
Pane, I. Z. (2018). Authentication system using 3d
face with algorithm dlt and neural network. In 2018
Joint 10th International Conference on Soft Comput-
ing and Intelligent Systems (SCIS) and 19th Inter-
national Symposium on Advanced Intelligent Systems
(ISIS), pages 186–189. IEEE.
bambang hermawan (2015). Apa saja tahapan-tahapan
dalam prototyping ?
Futra, I. (2014). Rancang bangun sistem pakar prediksi
stres belajar dengan neural network algoritma back-
propagation. PhD thesis, Universitas Multimedia Nu-
santara.
Islam, S. and Mishra, R. Expert system shell for developing
multi crop expert systems.
Kusnadi, A. (2013). Perancangan aplikasi sistem pakar un-
tuk mendiagnosa penyakit pada manusia. Ultimatics:
Jurnal Teknik Informatika, 5(1):1–8.
Rayuwati, E. G. (2013). Sistem pakar mendiagnosa
penyakit tanaman kopi. In Seminar Nasional
Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi, page 3.
Rohmah, S. N. (2017). SISTEM PAKAR DIAGNOSA
PENYAKIT PADA TANAMAN TOMAT DENGAN
METODE CERTAINTY FACTOR. PhD thesis, STMIK
Sinar Nusantara Surakarta.
Sihotang, H. T. (2017). Sistem pakar mendiagnosa penyakit
kolesterol pada remaja dengan metode certainty factor
(cf) berbasis web. Jurnal Mantik Penusa, 15(1).
Singh, S., Jain, S., Alok, S., Chanchal, D., Rashi, S., and
Pradesh, U. (2016). A review on ficus religiosa-an
important medicinal plant. Int J Life Sci Rev (IJLSR),
2(1):1–11.
Statistik, B. P. (2019).
Zhang, L. and Zhang, B. (2014). Quotient space based
problem solving: a theoretical foundation of granular
computing. Newnes.
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
324
