
Validity of Pab Tennis Ball Catch- Throw Test for
Volleyball in Selabora
Sb. Pranatahadi
1
, Moh Aditya Nur Aziz
1
1
Sport Coaching Department, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Jl. Colombo No.1 Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Validation of Tennis Ball Throwing Test, Volleyball Playing Ability
Abstract: This research has objectives to determine the validity of the PAB tennis ball throwing test (eye-hand
coordination test) and to determine the relationship of the tennis ball throwing test and the ability to play
volleyball for beginner male athletes of Selabora UNY. This research employs survey method with
observation technique by judge. The sample in this study is 30 beginner male athletes of Selabora UNY, with
a sampling technique applying purposive sampling. Instruments applied in this research are as follows: (1).
Hand eye coordination test, (2). Volleyball ability test. Data analysis techniques used correlation test,
normality test, Aiken test and objectivity test. The results showed that (1). The validity of the tennis ball
throwing test (eye-hand coordination test), with the Aiken test calculation validity of = 0.78. (2). The
objectivity of volleyball ability to play with Pearson correlation = 0.684 (Sig 0.00 <0.05) is significant. (3)
Hand eye coordination is not significantly related to volleyball playing ability with r = 0.321 and p: (0.084).
1 INTRODUCTION
In the process of practicing, if started at an early age,
the basic technique will show better result. There are
four basic techniques in volleyball namely bottom
passing, top passing, block, smash and service.
Managing exercises for children is quite difficult for
coaches, because they have to create a sense of fun
for volleyball. The main purpose of training for
children is not mere achievement, but also increases
fitness, raises feelings of pleasure, and practices basic
techniques and correct tactics. Physical improvement
from an early age needs to be done in stages, or it can't
be done instantly. When athletes are still young, they
need to be trained aspects including strength,
endurance, flexibility, speed and coordination of
motion. It is recommended that all training units use
a play or integrated approach.
Kinesthetic intelligence is the basis of the ability
to learn motion of various skills. Kinesthetic
intelligence needs to be developed from an early age
or a beginner athlete, so that the child's motor can
develop optimally. Good kinesthetic intelligence is
very important when children do training activities in
sports that require a lot of coordination (Gardner,
Howard, 2003), (Tadkiroatun Musfiroh, 2007).
Children who possess kinesthetic intelligence will
tend to be more skillful in doing the various
techniques needed in playing volleyball.
Volleyball requires the athletes to play the ball
while it is still in the air, before falling and touching
the floor. The athletes must approach the ball
precisely. The athletes must stop near the ball and
play it with parts of the body. In playing the ball they
have to jump, with a short and precise time, so as to
reach the maximum height in hitting the ball. There
are still many skills that must be mastered in playing
volleyball. Children who have good movement
learning will find it easier to master a variety of basic
techniques. The trainer should teach the basic
movements first so that the technique is quickly
mastered when teaching techniques to beginner
athletes. There is a possibility that the trainer has not
trained the basic movement skills to the best of his
athletes. Thus when an athlete has to master high
techniques there will be various obstacles.
Kinesthetic intelligence is one of the many
intelligence possessed by a child. Children with high
kinesthetic intelligence, will have the same potential
as children who have other intelligence if developed.
Kinesthetically intelligent children can also be
successful individuals. If accompanied by the
potential for high body posture, high physical fitness
components, through practicing volleyball the
children will also be successful. Many children with
760
Pranatahadi, S. and Aditya Nur Aziz, M.
Validity of Pab Tennis Ball Catch- Throw Test for Volleyball in Selabora.
DOI: 10.5220/0009895207600763
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 760-763
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

high posture potential who learn the movements do
not appear to be skillful at an early age. This has
become a problem for volleyball coaches. In Gifted
Education (PAB) for volleyball, problems often
occur. At the beginning of the education, children
with high posture potential do not show good
development in learning techniques. Children who
have a short posture are very fast in mastering various
volleyball techniques. When they grow up, children
with high posture show their skillful eminence in
playing the game.
Children or beginner athletes who have good
motor educability need to be find by conducting tests.
Children with good kinesthetic intelligence have high
coordination, agility, and balance. Development of
the basic motion of kinesthetic intelligence needs to
be trained since they are young (Tadkiroatun
Musfiroh, 2027). Thus, when they grow up, they will
be able to master techniques in sports well,
particularly volleyball. In volleyball game
intelligence is highly required, because this sport
requires complex abilities in each of its movements.
Harmony between motion and mind is needed in
volleyball games, so when playing the game the
athletes can dynamically move.
Tennis ball throwing tests have often been used
for the selection process, various selection processes
for prospective athletes, even for college entrance
exams with a sports background. The tennis ball
throwing test may still use logical validation, not yet
quantitatively validated particularly for volleyball.
The throwing test with a tennis ball to find out the
children’s learning needs to be evaluated, whether it
is valid or not yet. If it is invalid it can be harmful for
volleyball coaching, because children with high
posture potential can be knocked out by the test.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
2.1 Research Type
This research is a descriptive research, which is
directed to provide symptoms, facts, or events
systematically and accurately, regarding the
characteristics of a particular population or area
(Zuriah, 2005). The method used is a survey, data
collection by observation by the judge. The ability of
hand-eye coordination measured using a tennis ball
catch test, and evaluated by a judge. The ability to
play volleyball is also measured by the judge's
observations, and by the scoring sheet instructions.
2.2 Research Time and Place
The research was conducted at the Sepak Takraw
Field, and at the UNY Badminton Hall, located at
Jl.Colombo No.1, Caturtunggal, Depok, Sleman,
Special Region of Yogyakarta.
The research was conducted on September 22-26,
2018. The sample of this research was 30 beginner
male volleyball athletes from UNY Selabora.
Saturday, Tuesday and Wednesday at 3:30 p.m. to
6:00 p.m. and Sunday 7:00 a.m to10:00 a.m.
2.3 Sample
The sample in this study were 30 beginner male
athletes from UNY Selabora. The characteristics of
the sample are as follows: (a) Beginner male athletes
from UNY Selabora. (b) Willing to be sample. (c)
Age range between 10-13 years. (d) Minimum age of
exercise was 12 months.
2.4 Instruments and Data Collection
Techniques
2.4.1 Volleyball Skill Testing
Data collection methods in research using
observations and tests. Athletes playing 3 against 3
selected randomly. Judge made observations when
both teams played. In each rally, all six players were
given a base value of 50. When the rally ended, two
judges were entitled to give a score of + or - to an
athlete.
The following provisions are as follows (1) A total
of 30 children selected (2) Grouped into 10, each
group consisted of 3 people) randomly selected. (3)
Using a field with a size of 12 m x 6 m with a net of
2.15 m. height. (4) Two sets of random groups were
compared (5) Service implementation in play must
took turns in accordance with rotation. (6)Judge
Assessment: The judge would give a (+) score to the
child who could be the key to getting points, or give
a (-) score to the child who is the key to removing
points. Each rally judge only gave a - or + score for
once. For example:
(a) Child A does a very deadly service, and it is
unacceptable that the player gets a + service
performer score, the receiver does not get a score. If
on the other hand, child A does light service, missed
by child B, then the one who gets a - score is child B.
(b) Child A does a hard smash and missed by child B
or the smash directly falls to a hard floor then the one
who gets the + score is the smasher, otherwise child
Validity of Pab Tennis Ball Catch- Throw Test for Volleyball in Selabora
761
A does the slow smash and missed by child B then the
one who gets a - score is child B. (c) Child A does a
service to child B, but the service is not good (too
close to the net or too far) so that child B fails to
smash then the child who does the service gets a -
score otherwise if Child A plays good (not near the
net and not far net), but child B fails to make a smash
out or snagged on the net, the smasher gets - score.
(d) The last child to touch, or plays the ball when
mistake happens does not get a - score, if the previous
child makes difficulty for the next player. Children
who get - score is difficulty maker.
(7) Judge scored as much as rally that occurs
during 2 sets (8) The final score was the initial score
(50) plus the number of + scores or the initial score
(50) minus the - score.
Table 1: Assessment worksheet of objectivity of volleyball
playing skill of the two judges with a pearson correlation of
0.684, with sig. 0,00 (significant).
N
o
Chest
numbe
r
Nam
e
Judg
e
score
Tota
l
Initia
l
Score
Final
Scor
e
+ -
1 50
2 50
3 50
4 50
5 50
6 50
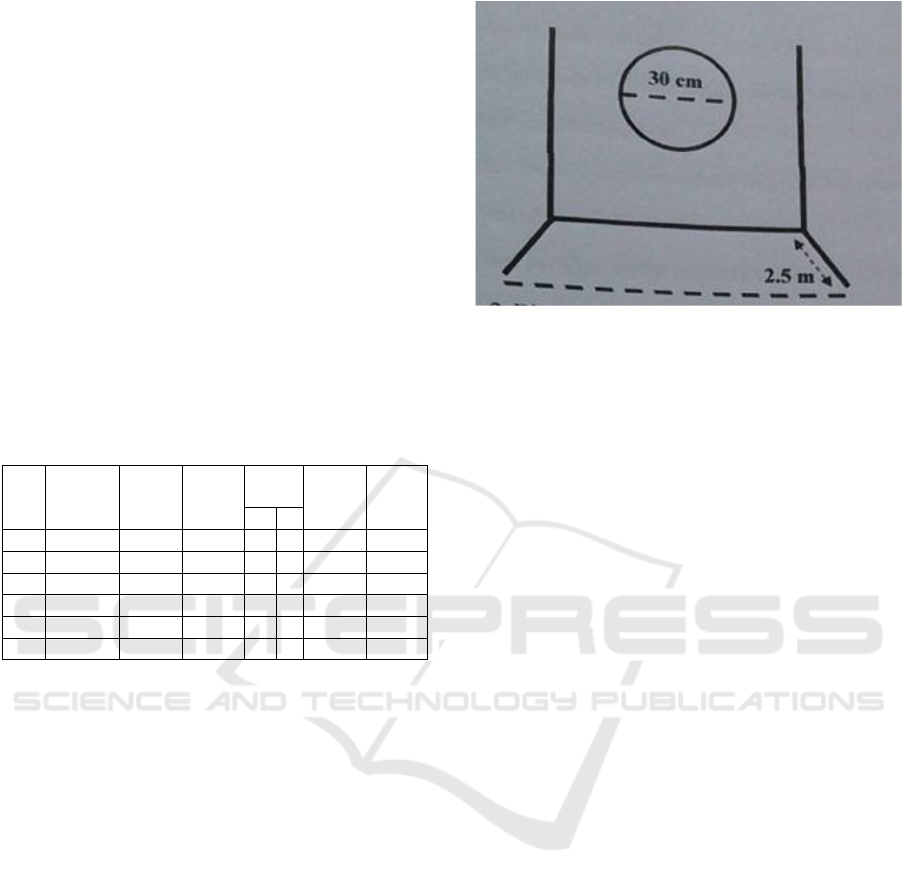
2.4.2 Tennis Ball Throwing Test
(1) Objective: to measure eye - hand coordination. (2)
Target: male and female aged 10 years old and over.
(3) Equipment: tennis ball, target wall, markers. (4)
Implementation: (a) Throws with one hand and
catches with the other. (b) Before doing the test, the
respondents may try first until they feel to get used to
it (c) The target is 30 cm in diameter, the distance
from the wall is 2.5 meters. (5) Assessment : Every
throw that hits the target and gets caught by another
gets one score. (6) To get 1 score: (a) The ball must
be thrown from the bottom (under arm). (b) The ball
hits the target. (c) The ball must be able to be caught
immediately without any obstruction beforehand. (d)
Respondents don't go forward or move outside the
boundary line to catch the ball. (e) Throws 20 times,
10 first throws and 10 second throws with a maximum
score of 20.
Figure 1: Image of target of tennis ball throwing test
(Ismaryati, 2006)
2.5 Data Analysis Technique
Data analysis technique applies the normality test as
a parametric statistical requirement. Objectivity and
validity test with Pearson correlation, except for the
validity of tennis ball throwing with the Aiken test.
3 RESEARCH METHODS
The age of Exercise of UNY Selabora of Beginner
Male Athletes. The age of the research subjects: 12-
18 months 12 athletes (46%), 19-24 months 8 athletes
(26.67%), 25-31 months 4 athletes (13.33%), 35-41
months 3 athletes (10 %).
3.1 Tennis Ball Throwing Test Validity
Result
The validity of the tennis ball throwing test (eye-hand
coordination test) obtained a result of 0.78 with the
Aiken test by 4 judges or experts. The objectivity of
volleyball playing skills tests, from the two judges
with a Pearson correlation of 0.684 (Sig 0.00) is
significant.
3.2 Relationship between Volleyball
Skill Tests and Tennis Ball
Throwing Tests
The validity of the coordination test with the ball
throwing in tennis balls, to learn motion or eye-hand
coordination in volleyball training, found by
correlating between the two instruments. With
Pearson's correlation yields r = 0.321 and Sig. 0.084,
besides the correlation coefficient is small, also not
significant. Thus the results of the tennis ball
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
762

throwing test, is not significantly related, with the
result of volleyball playing skill tests.
4 DISCUSSION
An assessment to determine the validity of the tennis
ball throwing test carried out by 4 judges. The results
of the data obtained there is an understanding of the
assessment of items and test items among 4 judges so
that the validity result obtained with the Aiken test of
0.78
The correlation coefficient (0.321) means that the
relationship is low. On the correlation between hand
eye coordination and volleyball skill Sig> α (0.084>
0.05), it means that the results of the tennis ball
throwing test is not significantly related to the test
result of the ability to play volleyball. Test result
shows that there are high result on tennis on ball
throwing test results but low test result of volleyball
skill.
In volleyball game the physical biomotor
demands not only eye hand coordination. There are
several other biomotor such as power, reaction speed,
stamina, agility, and motion coordination (Suharno,
1981). From the result of research conducted shows
that it is not significant, it is possible in playing
volleyball the coordination test is less contributing to
volleyball playing techniques, such as smash, block,
service and passing.
With the result above, the instrument for testing
existing giftedness on PAB, namely eye coordination
for Selabora FIK UNY is not relevant. If used it must
be given a small weight. If eliminated it will be more
economical and efficient for Selabora. The form of
the test might be used as a way to improve kinesthetic
intelligence.
For children who potentially will have a high
posture, usually their skills will be steps behind
compared to potentially short-postured children.
Children who are going to be taller have longer body
segments, so that their angular inertia is large. To be
able to move requires a greater force. If the
coordination test is used in determining the volleyball
athlete candidate, it is possible for children who will
have a high posture to exclude. The current posture
for volleyball determines achievement.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The relationship between the tennis ball throwing
test, with the volleyball skill test for beginner male
athletes at Selabora, or its validity "Low and
insignificant" r of 0.321, and Sig. 0,084 > 0,05).
REFERENCES
Gardner, H., 2003. Kecerdasan Majemuk Teori dalam
Praktek. (Alih bahasa: Drs. Alexander Sindoro).
Penerbit Interaksara. Batam Center.
Ismaryati, 2006. Tes & Pengukuran Olahraga. UPT
Penerbit Percetakan UNS. Surakarta.
Suharno. 1981. Metodik Melatih Permainan Bola Volley.
IKIP Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta.
Musfiroh, T., 2017. Pengembangan Kecerdasan Majemuk.
Universitas Terbuka. Tangerang Selatan.
Yunus, M., 1992. Olahraga Pilihan Bola Voli. Yogyakarta
Zuriah, N., 2005. Metodologi Penelitian Sosial dan
Pendidikan. Bumi Aksara, Jakarta.
Validity of Pab Tennis Ball Catch- Throw Test for Volleyball in Selabora
763
