
Digital Banking, Customer Experience and Islamic Bank Financial
Performance in Indonesia
Vera Vebiana
1
1
Post Graduate Program of Islamic Finance and Banking , Politeknik Negeri Bandung, Bandung, Indonesia
Keywords:
Digital Banking, Customer Experience, Loyalty, Customer Satisfaction, Financial Performance.
Abstract:
This research aims to look at the relationship between Convenience, Functional Quality, Digital Banking
Service Quality, Brand/ Trust, Employee Customer Engagement, Digital Banking Innovation, Customer Ex-
perience, Customer Satisfaction, Customer Loyalty, and Financial Performance of Islamic Banks.Customer
experience in digital banking can be determined through the service quality so the uses and risks can be expe-
rienced directly. This study used primary data taken directly by using questionnaire with 229 respondents. The
analysis technique used was path analysis with Partial Least Square Structural Equation Model (PLS-SEM).
The results of this study indicate that Convenience, Brand / Trust, Employee Customer Engagement, and digi-
tal banking innovation have an influence on customer experience, but not with Functional Quality and Digital
Banking Service Quality. The results of this study can be used as consideration for companies to improve the
bank performance in serving customers and bank employees must have a friendly attitude for customers to
feel comfortable.
1 INTRODUCTION
In fulfilling customer needs in enhancing the growth
of banking and financial banking, the bank seeks to
maximize the services through digital banking, which
in the modern era can become the main alternative
for mobile banking users. In implementing this digi-
tal banking, Islamic banks must be able to change the
marketing and management model of Islamic banks.
The challenge for Islamic banks in developing digital
banking is customer reluctancy caused by bad expe-
riences. For this reason, the development of service
marketing theory in digital banking requires an under-
standing of customer preferences which can be seen
from customer satisfaction and loyalty (Mbama and
Ezepue, 2018).
Customers choose the service providers based on
importance ratings and after enjoying the service they
tend to compare it with what they expect previously
(Suhartanto, 2008). If the services they get are far be-
low their expectation, the customer will leave the ser-
vice providers. Therefore, increasing customer needs
will increase the bank’s financial performance and
will have a positive impact on the bank itself.
Service quality can be interpreted as customer’s
assessment of the superiority or privilege of a prod-
uct or service as a whole. Service quality is a com-
prehensive customer evaluation process regarding the
perfection of service performance (Assauri, 2015). It
includes the sense of security and comfort for the
customers. Banks can improve this service by im-
plementing Digital Banking (DB). Digital Banking
is a service provided by banks with the development
of electronic banking services in order to serve cus-
tomers easily, quickly, and comfortably according to
customer needs (customer experience), so as to facili-
tate customers to conduct banking activities indepen-
dently (POJK, 2018).
Based on a survey conducted on various bankers
in Indonesia, around 66% of them have developed
digital banking as a strategy for banking companies.
It proves that digital influences in the banking world
have increasingly developed and made digital banking
a part of the company’s strategy (Indonesia, 2018).
However, there is only a small proportion of banks in
Indonesia which has implemented digital banking, of
80 banks only two of them actually implement a to-
tal digital banking system. The rest still apply only a
small part of the program. (Kompas, 2018).
Vebiana, V.
Digital Banking, Customer Experience, and Islamic Bank Financial Performance in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0009868002490255
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism and Information Management (ICCETIM 2019) - Creativity and Innovation Developments for Global
Competitiveness and Sustainability, pages 249-255
ISBN: 978-989-758-451-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
249

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Digital Banking
Rapid technological developmentleads banks to fur-
ther improve their services by forming digital bank-
ing. It aims so that banks can maximize their services
to customers and improve their operational quality.
It is expected that banks can develop their own dig-
ital banking. Digital banking is designed so that cus-
tomers can carry out transactions independently, such
as: opening an account, obtaining information, doing
transactions, closing accounts and conducting other
needs of customers (OJK, 2018).
The advantage that banks can take to advance dig-
ital banking is to utilize the huge penetration of cell-
phones. Up until now, mobile users in this coun-
try have reached 95% of the total population of In-
donesia, while those who can access banking facilities
are only at 20% (Zahiruddin, 2015). Digital banking
allows banks to develop services to customers, pro-
vide an alternative to give information directly to cus-
tomers and reduce direct interaction at branch offices.
Today customers expect the same level of interaction
through digital banking and social media (Dootson
et al., 2016). Digital banking is an orientation of
service, it makes the theory of service marketing im-
portant in its conceptualization (Mbama and Ezepue,
2018).
In line with technological development in the
banking sector, it is also important to consider about
24 hours banking services. One of them is the Auto-
mated Teller Machine (ATM) service. Customers ex-
pect to get information or consult through telephone
or e-mail as soon as possible. It proves the role of ser-
vice quality in the bank so that people feel satisfied
with the bank services (Yilmaz et al., 2018).
2.2 Convenience
Convenience arises as a result of individual’s per-
ception about happiness in using the services pro-
vided. It makes convenience becomes an important
factor to consider by the banks before providing dig-
ital banking services that meet customers expectation
(Paganta, 2015). Convenience can be seen from the
extent to which banks can provide simple, easy to use
and intuitive access for customers (Larsson and Vi-
itaoja, 2017). Convenience can also be felt directly
by the customers, judging by how well the bank pro-
vides services in the form of location (Wu, 2011)
and parking spaces so as to give comfort and avoid
customer dissatisfaction (Culiberg and Roj
ˇ
sek, 2010).
H1: There is a positive relationship between Conve-
nience and customers experience.
2.3 Functional Quality
Functional quality is the process of presenting
services by the service providers to customers
(Gr
¨
onroos, 2007). Functional quality is an attitude /
behavior that shows intelligence, responsiveness, hos-
pitality, professionalism carried out by bank employ-
ees in serving customers (Mulyanti, 2011). It is re-
lated to customers’ judgment toward the services pro-
vided in order to reach customers satisfaction. Func-
tional quality is considered good if it can exceed cus-
tomer expectations. Functional quality also measures
how efficiently banks operate and can be accepted by
customers (Keisidou et al., 2013).
H2: There is a positive relationship between func-
tional quality and customer experience.
2.4 Digital Banking Service Quality
Service is not just about serving but also feeling.
The feeling felt by the customer will open customers’
heart share and it leads to customer loyalty toward the
company’s products (Zainal et al., 2017). The main
services provided through digital banking are online
balance checks and fund transfers. These services can
provide boost for banks in conducting strategic ser-
vice marketing (Mbama and Ezepue, 2018). Banks
must also be able to guarantee customer satisfaction
in order to encourage them to buy other products (Yil-
maz et al., 2018).
H3: There is a positive relationship between Dig-
ital Banking Service Quality and Customer Experi-
ence.
2.5 Brand/Trust
If customers have good expectation toward the brand
of a company, they then believe that the products and
company are also good. This brand trust can increase
customer trust in the company. This arises from the
experience felt by the previous customers so that it
can affect the sales. Brand credibility is considered
reliable if the level of proposition information can
be trusted by customers (Keisidou et al., 2013). The
tendency of consumers towards a brand as a psycho-
logical function is a perspective of customers attitude
(Senjaya, 2013).
H4: There is a positive relationship between
Brand/ Trust and Customer Experience.
ICCETIM 2019 - International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism Information Management
250

2.6 Employee Customer Engagement
Employee engagement is an employee’s involvement
in meeting organization’s goals in the form of ef-
fort, initiative and perseverance (Macey et al., 2011).
The existence of employee customer engagement in a
company will improve relationships and close phys-
ical involvement between employees and customers.
It can bring positive attitudes / behavior towards the
company from both employees and customers. The
thing that must be considered in the service and pro-
curement of complaints is that a good interaction be-
tween customers and bank employees the can create
good connection between the two (Karatepe and Aga,
2016).
H5: There is a positive relationship between Cus-
tomer Engagement Employees and Customer Experi-
ence.
2.7 Digital Banking Innovation
Banks get benefit from digital banking innovation in
improving their performance. This innovation can be
used by customers so that it is beneficial for both par-
ties. Although this innovation is important for bank
services, customers use the innovation independently.
It shows that digital banking innovation must focus
on what customers feel and the impact of innovation
on customers will be a benefit for the banks (Mbama
and Ezepue, 2018). The latest innovations offered by
banks in technology must be able to improve the qual-
ity of services that are equipped with speed, safety
and comfort (Kennedy and Harefa, 2018).
H6: There is a positive relationship between Dig-
ital Banking Innovation and Customer Experience.
2.8 Customer Experience
A new model is always needed in digital banking be-
cause the customers may not get direct services such
as courtesy, friendliness, and personal care. There-
fore, there is a measurement of new service quality
that moderates customer satisfaction in digital bank-
ing (Jun and Palacios, 2016). This study uses sev-
eral measures of service quality (experience, satisfac-
tion, and loyalty). It allows a significant relationship
between digital bank marketing and financial perfor-
mance. Customer experience is a series of interac-
tions between customers, products and companies, or
parts of the organization that give rise to reactions
(e.g. rational, emotional, sensoric, physical, and spir-
itual) (Meyer et al., 2007). H7: There is a relationship
between Customer Experience and Customer Satis-
faction. H8: There is a relationship between Cus-
tomer Experience and Customer Loyalty.
2.9 Customer Loyalty and Financial
Performance
Loyalty is the customer’s trust in a service provider
or service company that allow them to give recom-
mendation to others and give benefit to the company
(Haryeni et al., 2017). The existence of loyal cus-
tomers is needed by the company. Customer loyalty
will greatly help the company’s growth, especially in
the current market competition. Loyal customers are
those who will continually repurchase goods and ser-
vices from the company and will try to recommend
them to others (Hastuti and Nasri, 2014). Loyalty
refers to the customers behavior of making repeated
purchases of goods and services chosen from a com-
pany (Griffin and Herres, 2002).
Financial performance is the result obtained by
management through cooperation with certain par-
ties to collect funds and use them efficiently. Finan-
cial performance is a subjective measure of how well
a company uses existing assets to generate revenue
(Prakarsa, 2016). Financial performance can be mea-
sured by using financial ratios. One of the bank’s fi-
nancial ratios is profitability. The profitability ratio
aims to find out the ability of banks to generate profits
for a certain period (Indonesia, 2014). The ratios re-
lated to earnings are Return on Assets (ROA), Return
on Equity (ROE), and Net Interest Margin (NIM).
H9: There is a positive relationship between Cus-
tomer Experience and Financial Performance H10:
There is a positive relationship between Customer
Satisfaction and Financial Performance. H11: There
is a positive relationship between Customer Loyalty
and Financial Performance.
2.10 Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is customer’s feeling towards
the impression or performance given by the company
which relates to customer expectations of a product.
If the reality is better than the expectations, the service
provided is considered very satisfying and vice versa
(Febriana, 2016).
Customer satisfaction is the overall customer ex-
perience. Positive customer experience depends on
customer satisfaction that is felt directly and raises
customer loyalty towards the bank (Mbama and
Ezepue, 2018) Customer satisfaction is the main thing
that must be considered by banking service providers
because customer satisfaction is an important aspect
Digital Banking, Customer Experience, and Islamic Bank Financial Performance in Indonesia
251
of the company’s image. Customer gives a large con-
tribution to the bank’s income, both directly and indi-
rectly, so as to support the existence of the company
(Febriana, 2016).
Researchers who study customer satisfaction and
loyalty do not always consider customer experience
(Mbama and Ezepue, 2018). Some previous studies
discuss the influence of customer loyalty with cus-
tomer satisfaction as a moderator and gives positive
relationship (Saleem et al., 2016). H12: There is a
positive relationship between Customer Satisfaction
and Loyalty.
3 METHODS AND EQUIPMENT
This research aims to look at the relationship between
Convenience, Functional Quality, Digital Banking
Service Quality, Brand / Trust, Employee Customer
Engagement, Digital Banking Innovation, Customer
Experience, Customer Satisfaction, Customer Loy-
alty, and Financial Performance of Islamic Banks.
Customer experience in digital banking can be de-
termined through the quality of service so the uses
and risks can be experienced directly. This study used
primary data by distributing questionnaires to sharia
bank customers who use digital banking. The pop-
ulation in this study were customers of 13 Islamic
Commercial Banks in Indonesia, with 229 respon-
dents. This study used accidental sampling. Acci-
dental Sampling is a technique of sampling by chance
(Sugiyono, 2017).
Data analysis technique used in this study was
path analysis by applying PLS-SEM (Partial Least
Square-Structural Equation Modeling) method. This
study was processed by using WarpPLS 6.0 which
was run using computer media.
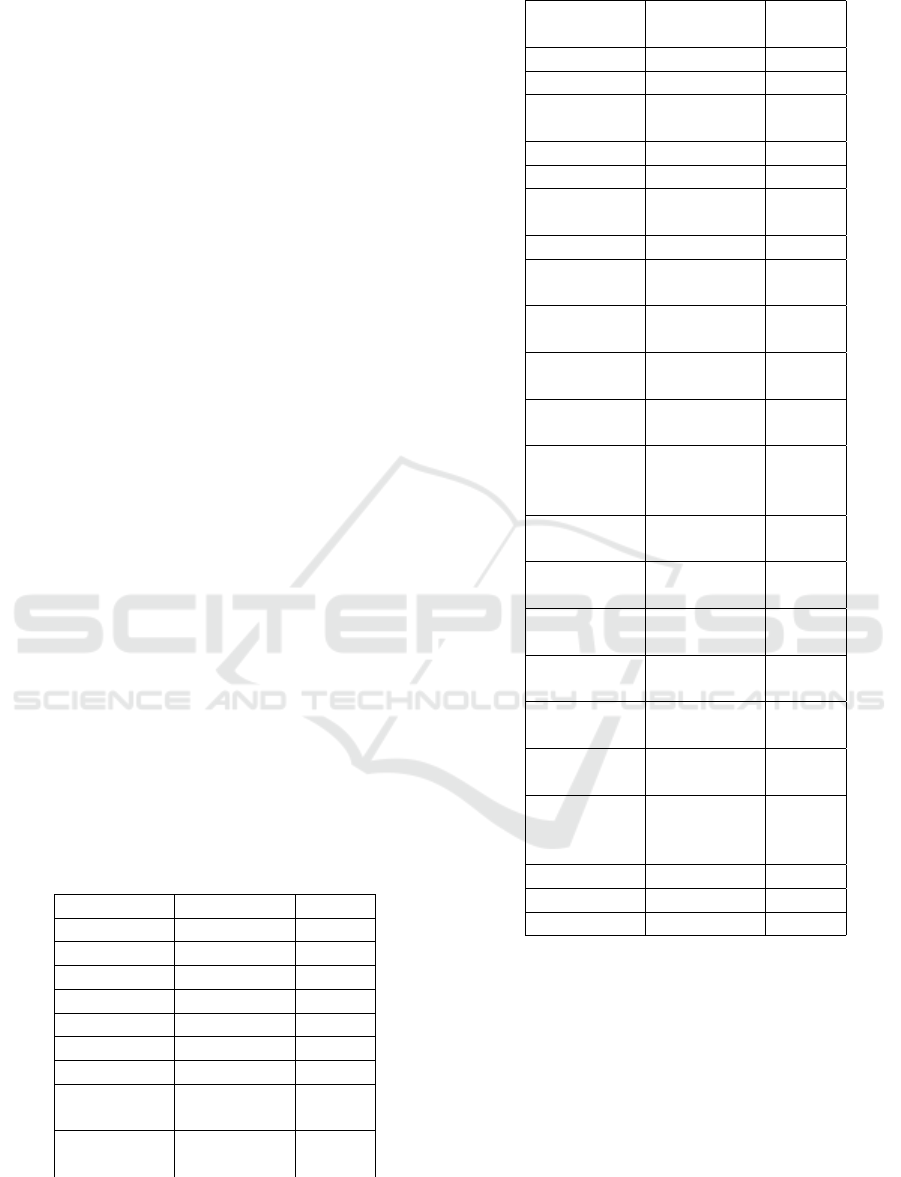
Table 1: Respondent demographic character
Respondent demographic character
Gender Male 66
Female 163
Age 20-24 185
25-29 24
30-34 9
35-39 6
>40 5
Educational
level
High
School
71
Bachelor/
Diploma
142
Post gradu-
ate
16
Job Civil Servents 15
Enterpreneur 22
Private em-
ployees
71
Student 98
Others 23
Customers
by Bank
BSM 83
Muamalat 20
BRI
Syariah
28
Aceh
Syariah
4
Victoria
Syariah
0
Bukopin
Syariah
1
Panin
Dubai
Syariah
0
BNI
Syariah
86
BJB
Syariah
3
BCA
Syariah
1
Mega
Syariah
0
BTPN
Syariah
3
MayBank
Syariah
0
Length of
time being
customer
< 1 year 67
1-2 years 72
3-4 years 48
> 4 years 42
4 RESULT
The validity and reliability assessment refers to the
value of the loading factor with the calculation results
at > 0.5. The rule of thumb used is if the value of
the loading factor is greater and equal to 0.5, it is con-
sidered sufficient for fulfilling the criteria (Haryono,
2017). The reliability assessment of all items or ques-
tions in this study used the Cronbach Alpha coeffi-
cient formula. The value of Cronbach Alpha used was
0.6 with the assumption that the questionnaire instru-
ment is considered reliable if the value of Cronbach
ICCETIM 2019 - International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism Information Management
252
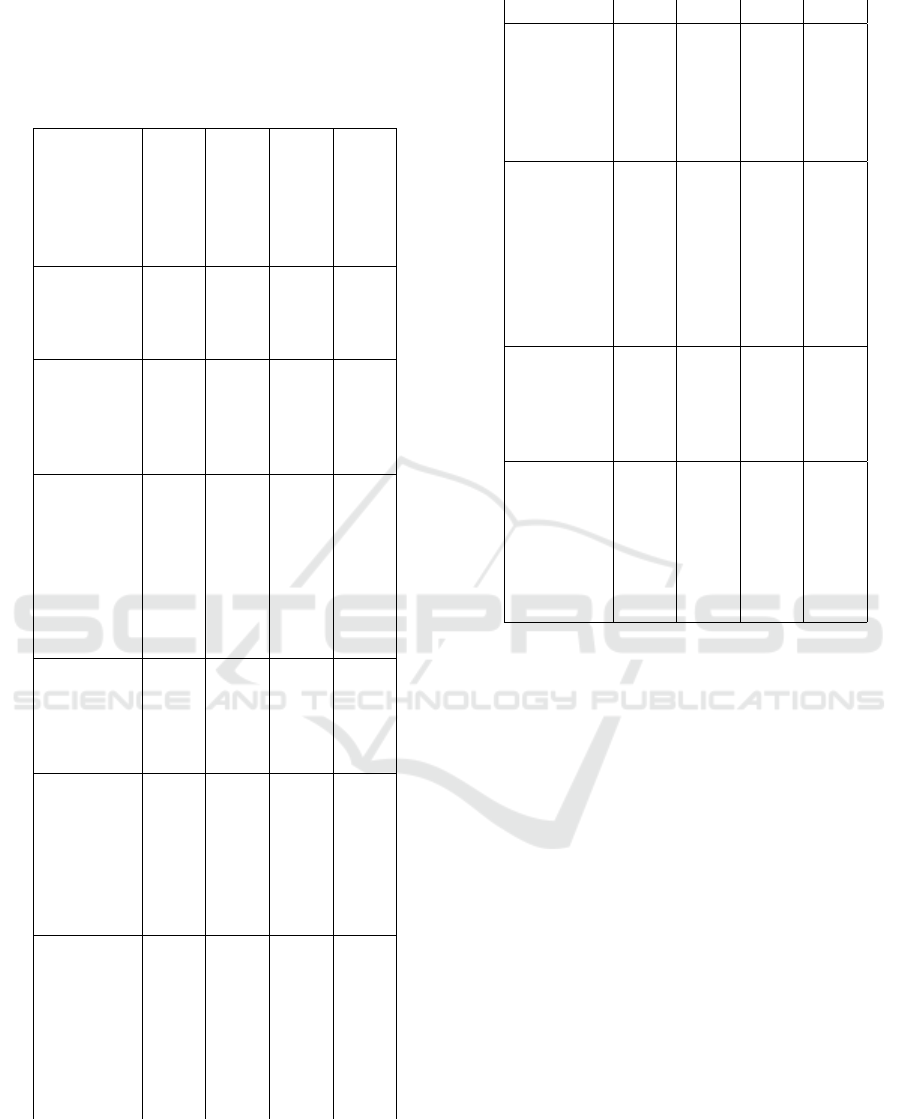
Alpha ≥ 0.6 (Imam, 2005) composite reliability value
≥ 0.70 and AVE value > 0.50 (Widarjono, 2015). Ta-
ble 2 shows that all variable indicators have met the
criteria and can be said to be valid and reliable.
Table 2: Validity and Reliability Value
Indicator Load
ing
Fac-
tors
Comb
rach
α
Comp
osite
Re-
lia-
bil-
ity
AVE
Convenience 0.695 0.831 0.621
Q1 0.783
Q2 0.811
Q3 0.770
Functional
Quality
0.818 0.892 0.733
Q1 0.853
Q2 0,877
Q3 0.839
Digital
Banking
Service
Quality
0.902 0.932 0.773
Q1 0.900
Q2 0.895
Q3 0.823
Q4 0.896
Brand/Trust 0.864 0.907 0.711
Q1 0.803
Q2 0.829
Q3 0.881
Q4 0.857
Employee
Customer
Engage-
ment
0.899 0.937 0.831
Q1 0.911
Q2 0.911
Q3 0.914
Digital
Banking
Innova-
tion
0.884 0.916 0.685
Q1 0.812
Q2 0.836
Q3 0.886
Q4 0.793
Q5 0.807
Customer
Experi-
ence
0.867 0.919 0.790
Q1 0.864
Q2 0.886
Q3 0.916
Customer
Satisfac-
tion
0.898 0.925 0.711
Q1 0.886
Q2 0.846
Q3 0.790
Q4 0.848
Q5 0.843
Customer
Loyalty
0.855 0.912 0.775
Q1 0.874
Q2 0.918
Q3 0.848
Bank
Financial
Perfor-
mance
0.707 0.843 0.653
ROA 0.833
ROE 0.982
NIM 0.549
5 DISCUSSION
The validation of the structural model is carried out
to see the R-square value (ARS) which is equal to
0.463, with P <0.001. Average block VIF (AVIF)
with a value of 2.371, this value is acceptable because
it is ≤5, ideally ≤3.3. Average full collinearity VIF
(AVIF) with a value of 2.818 is also accepted because
it is ≤5, ideally 3.3. Furthermore, the value of Tenen-
haus GoF (GoF) is 0.581. Sympson’s paradox ratio
(SPR) has a value of 1,000 which can be accepted be-
cause the value is greater than ≥ 0.7 ideally = 1. The
R-square contribution ratio (RSCR), Statistical sup-
pression ratio (SSR) and nonlinear bivariate causal-
ity direction ratio (NLBCDR) values is = 1,000 each
which is also acceptable.
The final results of conclusions obtained from the
results of data processing using WarpPLS are shown
below
From the results of testing model above, it can
be seen that Convenience, Brand / Trust, Employee
Customer Engagement, and digital banking innova-
tion have a positive and significant influence on cus-
tomer experience with a significance value of 0.05.
Meanwhile, the Functional Quality and Digital Bank-
Digital Banking, Customer Experience, and Islamic Bank Financial Performance in Indonesia
253

Figure 1: Result of Testing Model
ing Service Quality variables do not have a significant
effect on customer experience. Customer experience
has a positive and significant influence on Customer
Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty with a significance
value of ≤0.01. On the other hands, Customer Ex-
perience, Customer Satisfaction, and Customer Loy-
alty variables do not have a significant effect on Is-
lamic Bank Financial Performance, with a signifi-
cance value of 0.05 0.10 and 0.07 respectively. It
shows that the Customer Experience, Customer Satis-
faction and Customer Loyalty do not affect the Bank’s
Financial Performance.
6 CONCLUSION, LIMITATION
AND FUTURE RESEARCH
The results of the entire study show that Convenience,
Brand / Trust, Employee Customer Engagement, and
digital banking innovation have an influence on cus-
tomer experience, but not with Functional Quality
and Digital Banking Service Quality. It proves that
the functional quality and Digital Banking Service
Quality cannot provide a separate experience for cus-
tomers who do transaction in Islamic banks. Even
so, banks need to improve the convenience in ser-
vice. The bank employees must have a friendly at-
titude for customers to feel comfortable. On the other
hands, Customer Experience, Customer Satisfaction,
and Customer Loyalty variables have no influence on
the Financial Performance of Islamic Banks.However,
the bank must still give a good impression to the cus-
tomers so that the customer remains loyal to the Is-
lamic bank.
This study was only limited to certain time and
place, in which it is aimed at customers of Islamic
banks. Due to this research, the researcher was only
able to collect data from sharia bank customers in sev-
eral regions in Indonesia such as Medan, Bandung,
Jakarta, Semarang, and Kalimantan. Therefore, it is
expected that further researchers can conduct a direct
survey to some other regions in Indonesia so that a
comparison can be obtained.
REFERENCES
Assauri, S. (2015). Manajemen pemasaran (empat belas).
Jakarta: Rajawali Pers.
Culiberg, B. and Roj
ˇ
sek, I. (2010). Identifying service qual-
ity dimensions as antecedents to customer satisfac-
tion in retail banking. Economic and business review,
12(3):151–166.
Dootson, P., Beatson, A., and Drennan, J. (2016). Finan-
cial institutions using social media–do consumers per-
ceive value? International Journal of Bank Market-
ing, 34(1):9–36.
Febriana, N. I. (2016). Analisis kualitas pelayanan bank ter-
hadap kepuasan nasabah pada bank muamalat indone-
sia kantor cabang pembantu tulungagung. An-Nisbah:
Jurnal Ekonomi Syariah, 3(1):145–168.
Griffin, J. and Herres, R. T. (2002). Customer loyalty: How
to earn it, how to keep it. Jossey-Bass San Francisco,
CA.
Gr
¨
onroos, C. (2007). Service management and marketing:
customer management in service competition. John
Wiley & Sons.
Haryeni, Mulyati, Y., Laoli, E. F., et al. (2017). Kuali-
tas pelayanan, kepercayaan dan kepuasan nasabah dan
pengaruhnya terhadap loyalitas nasabah pada tabun-
gan bank rakyat indonesia (persero) tbk kantor cabang
khatib sulaiman. Jurnal Ekonomi dan Bisnis Dharma
Andalas, 19(2):189.
Haryono, S. (2017). Metode sem untuk penelitian manaje-
men dengan amos lisrel pls. Luxima: Jakarta.
Hastuti, T. and Nasri, M. (2014). Kualitas pelayanan,
kepuasan, dan loyalitas nasabah: Aplikasi servqual
model pada lembaga keuangan mikro syariah kota
malang. Jurnal Manajemen dan Akuntansi, 3(3).
Imam, G. (2005). Aplikasi analisis multivariate dengan pro-
gram spss. Semarang: Badan Penerbit Universitas
Diponegoro.
Indonesia, I. B. (2014). Memahami bisnis bank syariah.
Gramedia Pustaka Utama.
Indonesia, P. (2018). Pwc survey: Digital banking in in-
donesia 2018. PWC.
Jun, M. and Palacios, S. (2016). Examining the key di-
mensions of mobile banking service quality: an ex-
ploratory study. International Journal of Bank Mar-
keting.
Karatepe, O. M. and Aga, M. (2016). The effects of or-
ganization mission fulfillment and perceived organi-
zational support on job performance. International
Journal of Bank Marketing.
Keisidou, E., Sarigiannidis, L., Maditinos, D. I., and Tha-
lassinos, E. I. (2013). Customer satisfaction, loyalty
and financial performance. International Journal of
Bank Marketing.
ICCETIM 2019 - International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism Information Management
254

Kennedy, P. S. J. and Harefa, A. A. (2018). Financial tech-
nology, regulation and banking adaptation in indone-
sia. Fundamental Management Journal, 3(1):1–11.
Kompas (2018). ojk baru 2 bank yang benar benar terapkan
digital banking.
Larsson, A. and Viitaoja, Y. (2017). Building customer loy-
alty in digital banking. International Journal of Bank
Marketing.
Macey, W. H., Schneider, B., Barbera, K. M., and Young,
S. A. (2011). Employee engagement: Tools for anal-
ysis, practice, and competitive advantage, volume 31.
John Wiley & Sons.
Mbama, C. I. and Ezepue, P. O. (2018). Digital banking,
customer experience and bank financial performance.
International Journal of Bank Marketing.
Meyer, C., Schwager, A., et al. (2007). Understand-
ing customer experience. Harvard business review,
85(2):116.
Mulyanti, K. (2011). Pengaruh kualitas teknis dan kualitas
fungsional terhadap kepercayaan nasabah (studi kasus
nasabah bank bukopin cabang bekasi). Optimal: Jur-
nal Ekonomi dan Kewirausahaan, 5(1):51–70.
OJK (2018). Panduan penyelenggaraan digital branch oleh
bank umum.
Paganta, D. R., H. . R. D. (2015). Pengaruh kepercayaan,
persepsi kemudahan, persepsi kegunaan, persepsi
kenyamanan, dan persepsi risiko terhadap minat
menggunakan internet banking. fakultas ekonomi, vol
7, no. 1.
POJK (2018). Peraturan otoritas jasa keuangan nomor
12/pojk.03/2018.
Prakarsa, L. M. (2016). Pengaruh kepuasan pelanggan ter-
hadap kinerja keuangan melalui loyalitas pelanggan
sebagai variabel intervening pada berbagai sektor pe-
rusahaan di indonesia. Business Accounting Review,
4(1):361–372.
Saleem, M. A., Zahra, S., Ahmad, R., and Ismail, H. (2016).
Predictors of customer loyalty in the pakistani banking
industry: a moderated-mediation study. International
Journal of Bank Marketing.
Senjaya, V. (2013). Pengaruh customer experience qual-
ity terhadap customer satisfaction & customer loyalty
di kafe excelso tunjungan plaza surabaya: Perspektif
b2c. Jurnal Strategi Pemasaran, 1(1).
Sugiyono, P. (2017). Metode penelitian bisnis: Pendekatan
kuantitatif, kualitatif, kombinasi, dan r&d.
Suhartanto, D. (2008). Perilaku konsumen: Tinjauan ap-
likasi di indonesia. Penerbit: Guardaya Intimarta.
Bandung.
Widarjono, A. (2015). Analisis multivariat terapan edisi ke-
dua. Yogyakarta: UPP STIM YKPN.
Wu, L.-W. (2011). Beyond satisfaction. Managing Service
Quality: An International Journal.
Yilmaz, V., Ari, E., and G
¨
urb
¨
uz, H. (2018). Investigating
the relationship between service quality dimensions,
customer satisfaction and loyalty in turkish banking
sector. International Journal of Bank Marketing.
Zahiruddin, I. (2015). Probank: Membangun perbankan
profesional. PBN (Perbanas), Ed., ed.
Zainal, V. R., Djaelani, F., Basalamah, S., Yusran, H. L., and
Veithzal, P. (2017). Islamiz marketing management,
mengembangkan bisnis dengan hijrah ke pemasaran
islam mengikuti praktik rasulullah. Jakarta: PT Bumi
Aksara.
Digital Banking, Customer Experience, and Islamic Bank Financial Performance in Indonesia
255
