
The Key Solution for Quality Improvement of Patient Safety in the
Intensive Care Unit: A Quality Assurance Study
at Budhi Asih Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia
F. E. Selanno
1*
, H. F. Rachmat
1
, H. P. A. Purwanto
1
, S. A. Diva
1
, S. Susilawati
1
and M. S. Muchtaruddin
2
1
General Practitioner, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
2
Department of Community Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
sukmasusilawati@gmail.com, muchtaruddin.mansyur@gmail.com
Keywords: Intensive Care Unit, CPPT, integrated patient development records, paramedic ambiguity, quality assurance
Abstract: The management of Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients need a high standard of service and collaborative
inter-multidisciplinary therapy. Every issue in the quality of service in the ICU is very essential. Therefore,
a comprehensive analysis is required to improve the quality of care and patient safety. This qualitative study
was conducted in November 2017 at Budhi Asih Hospital, Jakarta. Data was taken through general
observation and systematic review. We used Standard Operating Procedure, indicator, and target from the
Hospital as the basic standard for ICU service. All data were analyzed using a quality assurance method.
The decision for the main issue have been made through IxTxR method, and the ambiguity of paramedic
was chosen. The cause of the problem then identified by fishbone diagram and prioritized by IxTxR
method, and obtained that integrated patient development sheet has not filled complete enough by the
doctors. The solution was determined by (MxIxV)/C method, using printed media such as banner and
pamphlet as a reminder for the doctors, and evaluated by the qualitative method. We conclude that
Intervention by applying printed media was effective as a reminder for the doctor to fill integrated patient
sheet more complete and to help decrease paramedic ambiguity in performing medical instructions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Intensive Care Unit (ICU) is an independent part of
the hospital that be equipped with a special and
important device in order to observe, care, and treat
the patient in acute or injured condition, patient with
complication, patient with a life-threatening
condition or potentially life-threatening with the
expected reversible condition. Patients in ICU are
patients with an expected reversible condition that
need to be observed strictly and post undergo the
invasive procedure with deterioration risk
(Kemenkes RI, 2010).
In Indonesia, type C hospital or higher as a
referral service provider must have an ICU with
professional service and patient safety.
There are
several Standard Operating Procedures (SPO) and
protocols in service organizing that include various
criteria and service guideline such as facility,
medical service technique, patient disposition flow,
human resources in ICU, et cetera. SOPs and
protocols also affect patient prognostic, length of
stay, and nosocomial infection prevention.
Pertaining to that, appropriate therapy,
communication among medical staff, and complete
Integrated Patient Development Sheet have
significant roles in the ICU service.
However, these
criteria might have not well implemented in several
settings due to a few conditions, which are really
crucial to the patient's safety. Build upon that, the
aim of this study is to improve the quality of care
and patient safety in ICU. Authors realized the need
to perform further review so that service quality in
the ICU of Budhi Asih Government Hospital can be
improved, so the medical service in the ICU can
always meet a high standard and comprehensive
procedure (Kemenkes RI, 2010).
Selanno, F., Rachmat, H., Purwanto, H., Diva, S., Susilawati, S. and Muchtaruddin, M.
The Key Solution for Quality Improvement of Patient Safety in the Intensive Care Unit: A Quality Assurance Study at Budhi Asih Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0009859500870093
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease (ICTROMI 2019), pages 87-93
ISBN: 978-989-758-469-5
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
87

2 METHODS
This quality assurance is held from November 1
st
to
November 10
th
, 2017 at the ICU of Budhi Asih
Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia. Targets in this quality
assurance were paramedic, the doctor in charge, and
medical staff of the ICU. Study staff collected data
by observing the facility, and all 25 paramedics and
15 doctors who were in charge through the 3 weeks
of the study. Authors also analyzed the SOPs
(Kemenkes RI, 2010), program indicator and
achievement in the ICU (official webpage RSUD
Budhi Asih, 2019), and performed a deep interview
to find the problems that were not stated in the
SOPs. All data were then compared with national
and international standard. Problem identification
was created to list the problems. All of the problems
list formulated using a scoring system to determine
the priority issue.
The priority of problem is determined from the
calculation with several components, such as
importance (I), technical feasibility (T), and
resources availability (R) or IxTxR method
(Departemen Ilmu Kesehatan Komunitas Fakultas
Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia, 2017). Problem
with the highest score is selected to be the priority of
the problem. Importance shows how important to
solve the problem. There are several components
that affect the value of importance; Prevalence (P)
which is determined from the exact prevalence of
the problem or gap between target indicator and
achievement, Severity (S) shows how bad is the
impact if the problem is not solved immediately.
Then, Rate of increased (RI) shows how fast the
problem would increase if the problem is not solved.
Degree of unmet need (DU) shows the magnitude of
the people desire that is not fulfilled if the problem
is not solved. Social benefit (SB) shows the
magnitude of benefits to society. Public concern
(PB) shows the magnitude of public concern or
interest in the problem if the problem is solved. The
last one is Political climate (PC) that shows the
current political condition that can be a support of
problem-solving.
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
3.1 Quality Assurance
Based on the International Standard Organization
(ISO), the definition of quality assurance is “all
those planned and systematic actions necessary to
provide adequate confidence that a product and
service will satisfy given requirement for quality”.
Quality assurance is important to identify the
problem in quality services and find the available
resources with measurable implementation
(Departemen IKK FKUI, 2017).
The purpose and benefits of quality assurance are
to improve service quality and patient satisfaction
and also assisting the organization or institution of
the service provider through quality improvement.
The implementation of good quality assurance
requires the active participation of the parties service
providers. Assessment of output must be thorough,
objective and relevant. Thus, the result will give
significance to real change and perceived by the
providers. Ultimately, the evaluation of the target
implementation of the solution should also be
appraised appropriately (Departemen IKK FKUI,
2017).
The steps done in the process of making a quality
assurance are identification of the problems and list
the priority, look for the cause of the problems use
the fishbone diagram and determine the priority,
identify alternative solution and determine the
priority, conduct an intervention and evaluate
according to the target set (Departemen IKK FKUI,
2017).
3.2 Integrated Patient Development
Sheet
Integrated patient development sheet is inner sheet
completeness of a status containing all patient
development records, which may be starting at the
inpatient room, ER, or outpatient clinic. This sheet is
filled by all health personnel involved in patient
care. Record of the progress of patients data (follow
up data) can be written by S-O-A-P method, namely:
S (subjective), O (objective), A (assessment), P
(planning) which contains the current complaints,
results of physical examination, analysis of the
problems or a diagnosis of the disease, and patient
care and management plans, respectively (Karniasih,
2019)
.
In addition to this method, there are also methods
namely ADIME (Assessment, Diagnosis,
Intervention, Monitoring, and Evaluation) and the
DART method (Description, Assessment, Response,
and Treatment) (Departemen IKK FKUI, 2017).
This sheet has a very important role as a media
bridging communication between the parties
involved in patient care. It also contains important
data to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy and
record any medical history received from the patient.
ICTROMI 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease
88

Incomplete or error entry of the sheets can lead to a
fatal effect on the patient’s therapy and the patient’s
prognosis (Karniasih, 2019; Puspita, 2019).
3.3 Media Socialization
Media is defined as a tool or means of
communication. Media socialization is all parties
which are the mediator or means of socializing or
disseminating certain things. Some forms of media
socialization among others family, social
community, place of education, work environment,
and mass media (KBBI, 2019)
The use of mass media later become more
effective because of technology development. The
mass media is divided into two: print media and
electronic media. The print media includes banners,
tabloid, magazines, etc. The use of banners or
pamphlets as printed media are aimed to give
information easily that can be seen by many people
and lasting longer in the target area.
3.4 Profile of Budhi Asih Government
Hospital
Budhi Asih is a type B hospital with non-teaching
category, in accordance with the Decree of the
Minister of Health of the Republic of Indonesia
Number: 434 / Menkes / SK / IV / 2007.8 Hospital
located at Jalan Dewi Sartika, Cawang III No. 200,
Jakarta Timur, DKI Jakarta.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Problem Identification
Identification of problems for quality assurance in
the ICU of Budhi Asih Government Hospital was
through data assessment, field observations,
paramedical interviews, and discussions with field
supervisors. There was also ICU indicators in the
Budhi Asih Government Hospital.
Table 1: ICU Indicators Budhi Asih Government Hospital.
No. Indicator Target Achievements
1. Readmission of
patients within
<72 hours
<3% 0 %
2. Nosocomial events
in ICU
<10% 3%
3. Doctor in charge
visit
> 75% 100%
According to the data from field observations,
paramedical interview, and discussion with the
supervisor, there were some problems occurring in
the ICU of Budhi Asih Government Hospital: the
ambiguity of paramedics in carrying out medical
instructions, transition room of the ICU, and human
resource management of the ICU nurses.
4.1.1 The Ambiguity of Paramedics in
Carrying Out Medical Instructions
There are some factors that influence the ambiguity
of paramedics in running medical instructional:
doctor in charge does not conduct routine patient
visits, irregular schedule of doctor in care visits,
short time of patient visits, the writing of medical
instructions is too short and does not describe the
patients condition completely, did not read another
review instruction from other departments, and did
not read back to the post from doctor in charge from
other department.
4.1.2 Transition Room of the ICU
Based on the technical implementation of Intensive
Care Unit (ICU) at the hospital by the Ministry of
Health Republic Indonesia mentioned that in the
structure of ICU, it is necessary to have transition
room that is separated from the patient care room
(Kementrian Kesehatan RI, 2010). Based on field
observations, there was no effective transition room
with room restrictions and clear access in the ICU of
Budhi Asih Government Hospital.
4.1.3 Human Resource Management of the
ICU Nurses
Based on the standards for ICU in the United
Kingdom, each patient in the ICU must be treated by
one ICU nurse. It aims to monitor the patient’s
progress and implementation of medical instruction
more carefully and precisely. Based on field
observation and interview to the ICU heads, it was
found that the numbers of ICU nurses in Budhi Asih
Government Hospital were sufficient.
The Key Solution for Quality Improvement of Patient Safety in the Intensive Care Unit: A Quality Assurance Study at Budhi Asih Hospital,
Jakarta, Indonesia
89
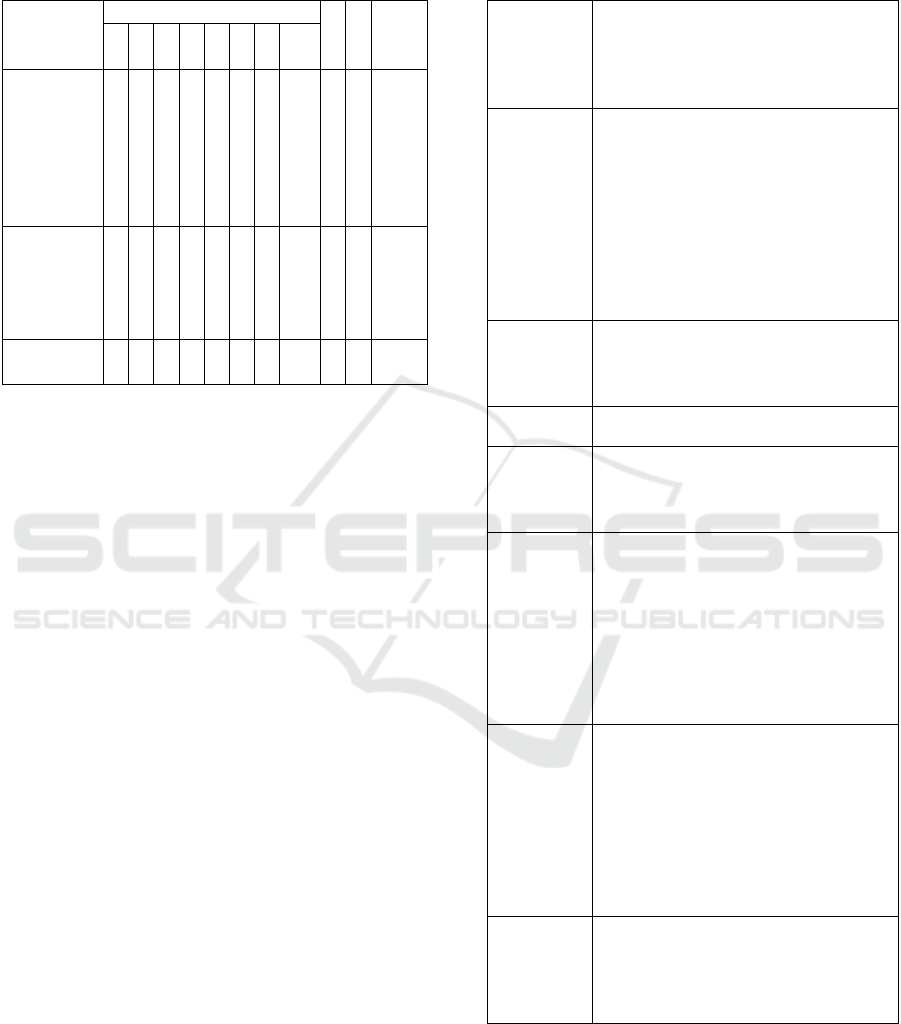
4.2 Selection the Priority of Problem
Table 2: Selection Priority of Problem.
Problem
I
T R Sum
P S
R
I
D
U
P
B
S
B
P
C
Su
m
The
ambiguity
of
paramedics
in carrying
out medical
instructions
5 5 3 5 5 23 5 5 575
Human
resource
managemen
t of ICU
nurses
5 4 3 5 4 21 3 3 189
Transition
room
3 3 3 2 2 13 3 2 78
Abbreviations and acronyms:
I = Importance
P = Prevalence
S = Severity
RI = Rate of increase
DU = Degree of unmet need
PB = Public concern
SB = Social benefit
PC = Political climate
T = Technical feasibility
R = Resources availability
4.3 Identification Cause of Problem
Table 3: Identification Cause of Problem.
Man
Limited od human resources;
Doctor in charge handle more than
one patients;
Nurses sometimes have to observe
more than one patient.
Method
Write, Read, and Confirmation
method between doctor on duty and
nurse had not gone well;
The communication mechanism
regarding medical instruction
between the doctor in charge and
the nurse had not gone well;
Doctor’s writing in integrated
patient development sheet is hard to
read
Money
Limited funds for training of ICU
nurses
Limited funds for procurement
completeness status
Material
Cardex sheets are not practical
Planning
Unpredictable time visit of a doctor
in charge
Commitment for meetings between
the doctor in charge and nurses
Organizing
Collaboration between department
There is no SOP on mandatory
meetings to discuss the case of ICU
patients
Human resources management of
ICU nurses
There is no SOP about
communication between
department
Actuating
There are no regular meetings at
least every week to discuss ICU
patients
The incomplete and unclear
integrated patient development
sheet filling by the doctor in charge
Difficult to confirm the treatment
of the patient to the doctor in
charge
Controlling
There is no routine evaluation of
filling integrated patient
development sheet
There is no evaluation of SOP from
RSUD Budhi Asih
ICTROMI 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease
90
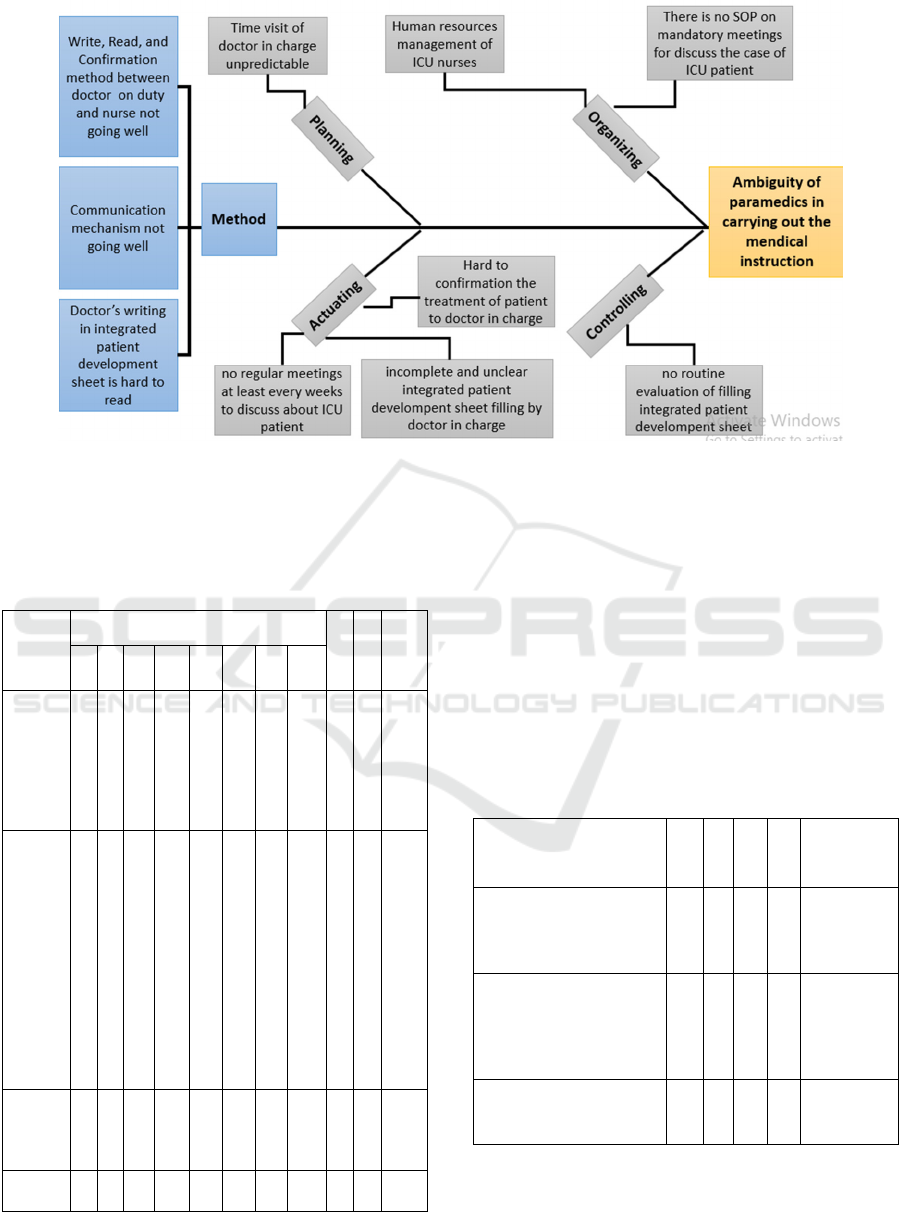
Figure 1: Chart the Cause of Problem.
4.4 Selection the Priority of the Cause
of the Problem
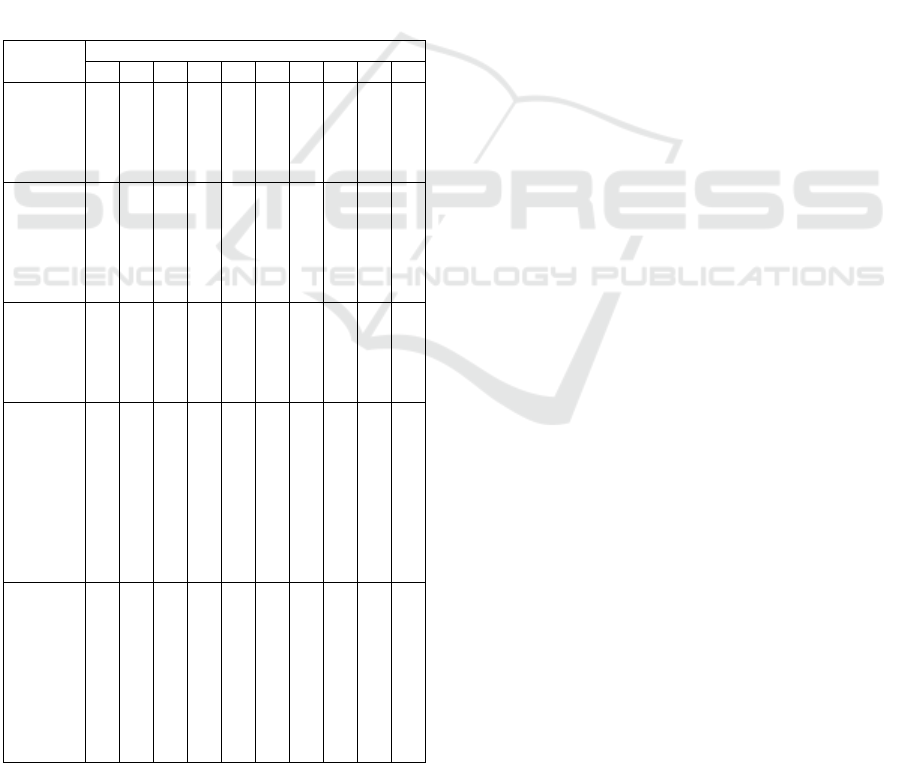
Table 4: Selection of the Priority of the Cause of Problem.
Problem
I
T R
Sum
mary
(I x T
x R)
P S RI DU PB SB PC Sum
No
weekly
meetings
to discuss
the case
of ICU
patients
5 3 4 2 2 3 19 3 2 114
The
incomple
te and
unclear
integrate
d patient
develop
ment
sheet
filling by
the
doctor in
charge
4 5 5 3 2 5 24 5 5 600
Doctor
on duty
had other
busyness
3 2 3 4 3 3 18 2 2 72
Lack of
nurses
2 2 2 1 3 3 13 1 1 13
Abbreviations and acronyms:
I = Importance
P = Prevalence
S = Severity
RI = Rate of increase
DU = Degree of unmet need
PB = Public concern
SB = Social benefit
PC = Political climate
T = Technical feasibility
R = Resources availability
4.5 Selection the Priority of Problem
Solution
Table 5: Selection of the Priority of Problem Solution.
Problem M I V C
Summary
((M x I x
V) / C)
Socialization of
integrated patient
development sheet
through formal meetings
3 4 2 3 8
Use banners or
pamphlets as a reminder
to fill an integrated
patient development
sheet
4 5 3 4 15
Integrated patient
development sheet
evaluation periodically
4 2 4 3 10,6
Abbreviations and acronyms:
M = Magnitude
I = Importance
V = Vulnerability
C = Cost
The Key Solution for Quality Improvement of Patient Safety in the Intensive Care Unit: A Quality Assurance Study at Budhi Asih Hospital,
Jakarta, Indonesia
91
The intervention was held between November 6th
and November 11th, 2017 by putting the banner and
pamphlets on the table of each bed in the ICU of
Budhi Asih. We hoped by reading the banner when
entering the ICU room and the pamphlets on the
table of each bed, the physician in charge would fill
the ‘Integrated Patients Development Sheet’ well,
clearly, and completely. These are very important to
do, as stated in the Standard Operation Procedure
(SOP) of Budhi Asih hospital regarding the
importance of effective communication, and
according to the World Health Organization (WHO)
about patient safety. Therefore, ICU in Budhi Asih
hospital was able to perform WHO standardized
patient care, especially in medication safety and
effective communication.
Table 6: Evaluation Results of Intervention Using Banner
and Pamphlet About Integrated Patient Development
Sheet at ICU Budhi Asih hospital.
Questions
Response
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Physician
in charge
read the
banner and
pamphlet
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Duration of
a physician
in charge
read the
banner and
pamphlet
< 1
min
ute
< 1
min
ute
< 1
min
ute
1-5
min
utes
< 1
min
ute
< 1
min
ute
1-5
min
utes
< 1
min
ute
< 1
min
ute
< 1
min
ute
The banner
and
pamphlet
are easy to
understand
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
The
banners
and
pamphlet
help the
paramedics
to perform
the
instructions
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
The
instructions
from a
physician
are charge
is better,
clearer and
more
complete
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
We evaluated the intervention by using
questionnaires to the paramedics (Table 6). The
responders said that all physicians read the banner
and pamphlets with duration time about less than
one minute to five minutes. All the responders
agreed that the banner and pamphlets were relatively
easy to understand, helped them perform the medical
instructions, and the instructions from the physician
were better, clearer and more complete. Some
physicians also filled the ‘Integrated Patient
Development Sheet’ by themselves, while they
previously did not. The hospital management also
agreed to multiply the banner and pamphlets so this
method could be adapted to other units.
In consideration of time available during the
study, we did not perform the quantitative evaluation
on the ‘Integrated Patient Development Sheet' before
and after the intervention. We also have some other
considerations: the amount of patient in ICU Budhi
Asih hospital is unpredictable and changed over
time. In the case of limited numbers of patients, we
also had limited time for observation. On the other
hand, not all patients fitted our inclusion criteria that
every patient should have been visited by at least
two different physicians in charge.
The quantitative evaluation of ‘Integrated Patient
Development Sheet’ was done by comparing the
completeness of the form before and after the
intervention, whether any improvement of the
‘Integrated Patient Development Sheet' percentage
that has been filled well, clearly and completely. We
also compared the ambiguity level of paramedics
before and after the intervention. Our aim was to
achieve a better quality of written instructions in the
‘Integrated Patient Development Sheet’. Less or no
ambiguity level from paramedics was also one of
our goals. With that, hopefully, Budhi Asih
Government Hospital could fulfill all of the
requirements in the SOP.
5 CONCLUSION
We found that banner and pamphlets as a reminder
to the doctors in charge to fulfill the Integrated
Patient Development Sheet are the key solution to
improve the quality of patient safety in the ICU
room of Budhi Asih Government Hospital. The
banner and pamphlets should be distributed to more
units other than the ICU. Furthermore, there should
also be a routine evaluation of ‘Integrated Patient
Development Sheet’ and ambiguity of the
paramedics in performing medical instructions
written on.
ICTROMI 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease
92

REFERENCES
Kementrian Kesehatan RI [PDF], 2010. Petunjuk teknis
penyelenggaraan Intensif Care Unit (ICU) di rumah
sakit.
Official Webpage RSUD Budhi Asih Jakarta Timur, 2018.
RSUD Budhi Asih Jakarta Timur. Available from :
http://www.rsudbudhiasih.com
Departemen Ilmu Kesehatan Komunitas Fakultas
Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia, 2017. Slide kuliah
Quality Assurance.
Karniasih, P., 2019. Penulisan SOAP. Available from:
https://www.scribd.com/doc/279351988/Penulisan-
SOAP-Keperawatan-Dra-Pipih-Karniasih-MKep-pdf
Puspita, D., 2019. Panduan Pengisian CPPT. Available
from: https://kupdf.com/download/panduan-pengisian-
cppt_59f4b2e4e2b6f5a03b299e8e_pdf
Kementrian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Republik
Indonesia, 2019, Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia.
Available from : https://kbbi.kemdikbud.go.id
The Key Solution for Quality Improvement of Patient Safety in the Intensive Care Unit: A Quality Assurance Study at Budhi Asih Hospital,
Jakarta, Indonesia
93
