
The Perceptions of Junior High School Students in Yogyakarta on
Effects of the Internet on Sport Participation Events
Mela Suhariyanti
1
, Tomoliyus
1
1
Graduate School Program, Yogyakarta State University, Jl. Colombo No.1 Yogyakarta, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Effect, Event, Internet, Perception, Sport
Abstract: The management of internet use has become a great social problem among children or adolescents
worldwide. The aim of this study is to show the contribution of internet on the sport participation events.
This is a descriptive research with qualitative and quantitative approach. The samples of the study were 59
students; 20 boys and 39 girls with ages between 12-16 years. The data were collected using two
techniques; literature review and Google form with closed questions. The instruments were from Young
(1998) about Internet Addiction Test (IAT) and Cho’s research (2010) about participation of sports. The
result showed that most of the students spent their time by not looking at sport events but for other else. This
result showed the need for consistent education of using the internet for the students or adolescents to allow
all the benefit from sports to them, like physical and mental benefit as wellbeing, and also to allow the
discounted results of future athletes as a high performance. In conclusion, if internet is well used by junior
high school students, it will provide them with the knowledge of physical sports and education. Moreover,
the physical sports teachers and coaches will get the facility to train athletes so quickly. In contrast, it will
negatively affect students if they don’t know how to manage the time allocated to use the internet
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowdays, technological progress can be felt
increasingly and makes everyone able to take
advantage of internet facilities as a fulfillment of the
needs. The main advantage of the Internet is its
ability to connect billions of computers and devices.
US Department of Health and Human Services 2008
explains that not only does the internet create
convenience in sharing and receiving information
between users, another advantage of the
modern internet is its ability for automation like (1)
Information, knowledge, and learning, (2)
connectivity, communication, and sharing, (3)
Address, mapping, and contact information, (4)
Banking, bills, and shopping, (5) Selling and making
money, (6) Collaboration, work from home, and
access to a global workforce, (7) Donations and
funding, (8) Entertainment.
Internet users in Indonesia experienced an
increase in 2018. Based on the results of an
Indonesian Poll study in collaboration with the
Association of Indonesian Internet Service Providers
(APJII), the number of internet users in Indonesia
grew by 10.12 percent. According to APJII, this
survey involved 5,900 samples with a 1.28 percent
margin of error. The result of a total population of
264 million people in Indonesia was that there are
171.17 million people or around 64.8 percent who
have been connected to the internet. This shows an
increase compared to 2017 where Indonesia's
internet penetration rate was recorded at 54.86
percent in which it is possible that there may be
opportunities for it to continue to increase every
year. On Internet usage penetration by age, the
highest position was obtained at the age of
adolescents or 13-18 years at around 75.50%.
This certainly can be concluded that the majority of
internet use is school students. This survey also
reveals that the internet use by the sample was
mostly for chatting and accessing social media. In
other words, the Indonesian samples used internet
for entertainment activities (compas.com).
Coleman, R., & Ramchandani, G, (2010) explain
that nowadays internet is used as a social media for
learning in every field like sport industry, sport
marketing, physical education, sport nutrition,
self-defense sport and other else. Many professional
sports organizations use their websites to enhance
communication with customers by providing
Suhariyanti, M. and , T.
The Perceptions of Junior High School Students in Yogyakarta on Effects of the Internet on Sport Participation Events.
DOI: 10.5220/0009796205330539
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 533-539
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
533

information about organization and products (scores,
news, ways to acquire and renew season tickets, etc.)
The effectiveness and success of these sites
depend on how consumers perceive their value and
quality provided by (X. Zhang and V. R. Prybutok,
2005). The popularity and growth of online sport
consumptions suggest a clear opportunity for sports-
related- marketers to effectively use the Internet as a
key component within an overall marketing strategy.
To effectively leverage the opportunities that the
Internet affords to an organization, organizations
must gain a clear understanding of online sport fan
behavior (Y. Hur, Y. J. Ko, and J. Valacich, 2011).
The growth of Internet usage among online sport
participants are also evidenced by traffic patterns at
popular websites.
Currenly, Internet plays a major role in the lives
of young people. Children and youngsters engage in
online activities both inside and outside the
classroom (Sefton Green, 2004). Nevertheless,
media generates profit through sports while sports
and its contents are transmitted through media.
Sports and media are developing and expanding
through this symbiotic relationship. This
interdependent phenomena and symbiotic
relationship can be referred to as sports media
(Weedon, G., Wilson, B., Yoon, L., & Lawson, S.,
2016). If a sport or game has legislation to protect it,
it will get benefit from technology. Technology
ensures fairness in sports and games. Sports are big
businesses, and there is a lot of money invested into
the design and development of sport equipment and
clothing to help athletes improve their performance
(Rothschild, P. 2011).
Even though it provides more benefit, sometimes
the negative effects occur. Some of
the disadvantages of the internet for students in
points are: students become addicted and are
dependent on internet, and may not focus on
personal works and studies. Compared with adults,
adolescents are more vulnerable to Internet
addiction, because they have high novelty-seeking
but low self-control (Spada, 2014) and are
particularly sensitive to peer influence (Somerville,
2013).
The Pew Research Center in 2014 found that
53% of internet users admitted that it is very difficult
if they do not to use their internet and smartphones.
They consider smartphones and the internet to be
very important in everyday life (Caumont, 2014).
About 1 of 8 Americans shows signs of internet
addiction and 82% of respondents who took the
survey reported that the time they spent online was
more than 5 hours per day, increasing internet
addiction.
Internet addiction is referred to as pathological
internet because this lifestyle is very dependent on
normal life which is always dependent on the
internet for the users (Ozturk & Ozmen, 2011).
Internet addiction can be broadly conceptualized as
an inability to control one's use of the Internet which
leads to negative consequences in daily life (Spada,
2014). Internet addiction also means more important
on mental problems to many people around the
world. Wang et al., (2013) hopes that the formation
of internet addiction can be interpreted by internet
users who have low self-control. Internet addiction
also causes a person to become unfocused on his
work even on the study that he is currently
undergoing. Another negative impact is social
isolation due to heavy use of internet. Obesity and
depression may also occur through spending more
time on computer.
In the case of internet addiction, according to
research by (Liang, L., Zhou, D., Yuan, C., Shao, A.,
& Bian, Y. (2016) for 1,715 adolescents in grades
6-8 in China, internet addiction was caused by
depression. Internet addiction shown between
women and men are different; men use the internet
only more for entertainment and use it less on the
internet to find information compared to women.
Although men and women tend to have the same
activities in using the Internet, men prefer to go
online with friends compared to women.
For children, we can suggest many benefits from
watching sport events through internet because there
are many types of learning and teaching in
education. One of them is visual methods, imagery
which can help children to improve skills, motoric,
and their competences. Gilchrist, P., & Wheaton, B.
(2017) in his study found that sport helps children to
developmental and physical toughness. Sports shape
their bodies and make them strong and active.
Children should actively participate in sports to
avoid being tired and lethargy. This is because sports
improve their blood circulation and their physical
well-being (Wankel, L. M., & Berger, B. G. 1990).
Regarding the benefits of exercise according to
(Hassmen, Koivula, & Uutela, 2000; Salmon, 2001;
Scully, Kremer, Meade, Graham, & Dudgeon, 1998;
Warburton, Nicol, & Bredin, 2006), sports activities
have many positive effects to the body and to
psychology such as reducing stress, depression, and
anxiety because exercising can produce endorphin
hormones that make a person happier during and
after carrying out sports, and can reduce activities
that are less nature such as playing games.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
534

Much research already showed the benefits of
using the internet, and the relationship between the
internet and sport participation for everybody.
However, how children in Yogyakarta uses internet
is still unknown. There is a need for investigation to
know if the use of the internet allows the
development of sports in all branches, and to know
the effects of internet on the result of children in the
class. This study is concentred on Yogyakarta junior
high school children. This section is made up of
different parts. First, we reviewed some of the most
important studies that have been carried out on
sports and the internet. Subsequently, we would go
on to comment on the most representative concepts
related to the study, among which we find attitudes,
and perceptions of students. In addition to the
attitudes aspect, a section would be devoted to
analyze the effects of internet on development of
sports that have taken place in this research topic,
specifically on the development of scales to measure
the construct of attitudes towards the internet.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This study is a descriptive research with
mixed-method approach; qualitative and quantitative
approach. The samples were junior high school
students in Yogyakarta, ages 12-16 years, who are
still using internet as a source of information. The
whole samples were 59 students by quota sampling.
The data were collected using two techniques;
literature review and internet Google form with
closed questions.
The Questionnaires have 6 subscales, adopted
from Young (1998) about Internet Addiction Test
(IAT) and Cho’s research (2010) about participation
of sports. After getting the data, we analyzed the
data by SPSS 24 to know the prevalence and
frequency of the feeling and the using of the internet
in the field of sport participation.
The questions related to sports participation were
adopted from research by Cho, Kwon, and Jeon's
(2010) including frequency, intensity, and duration.
The Frequency question is "During the week, how
often do you participate in sports or physical
exercises in your free time?". The frequency of
sports participation is categorized into almost none,
1-2 days /week, 3 days /week, 4-5 days /week, and
6-7 days /week. The intensity of sports participation
is the question of "How is your level of exercise
seen from your breathing during your exercise". The
answers are categorized into several types including
using very light breathing (such as breathing
normally, can still laugh and chat with people
around), mild breathing (controlled with breathing
that starts fast), moderate breathing (slightly
panting), heavy (panting and still able to talk a
little), and breathing very heavy (very heavy (unable
to chat, very focused). The response to the above
questions consists of A 5 point Likert type format
which is used with values ranging from 1 (very light
breathing) to 5 (very severe breathing). The duration
of exercise participation is categorized to be less
than or equal to 10 minutes, 20 minutes, 30 minutes,
40 minutes, and more than 50 minutes. The 5-point
Likert type response format is used with values
ranging from 1 (almost 10 minutes) to 5 (more than
50 minutes). Average frequency, intensity, and
duration values are used for analysis. Higher scores
reflect higher levels of physical exercise and sports
participation.
3 RESULT
In this part, we would have to make up the results
from the research and a kind of discussion. Counting
was done by gathering the identical answers. The
results obtained were calculated as a percentage of
the totals from the questionnaires. Pie was used for
interpretation of results. The following are the
results from all the respondents.
3.1 What Do You Do When You Open
Your Internet?
Figure 1: Things that are often opened when playing the
internet
The result of this question showed that junior high
school students used internet for other activities like
watching movies which is not related to sport events
or participation. Only 18 students or 6% of the
population surveyed were watching game like sport
events. 81,4% of the samples surveyed used internet
for chatting, social media, and watching YouTube.
So, there is a lack of correlation between the use of
the internet and sport participation.
The Perceptions of Junior High School Students in Yogyakarta on Effects of the Internet on Sport Participation Events
535
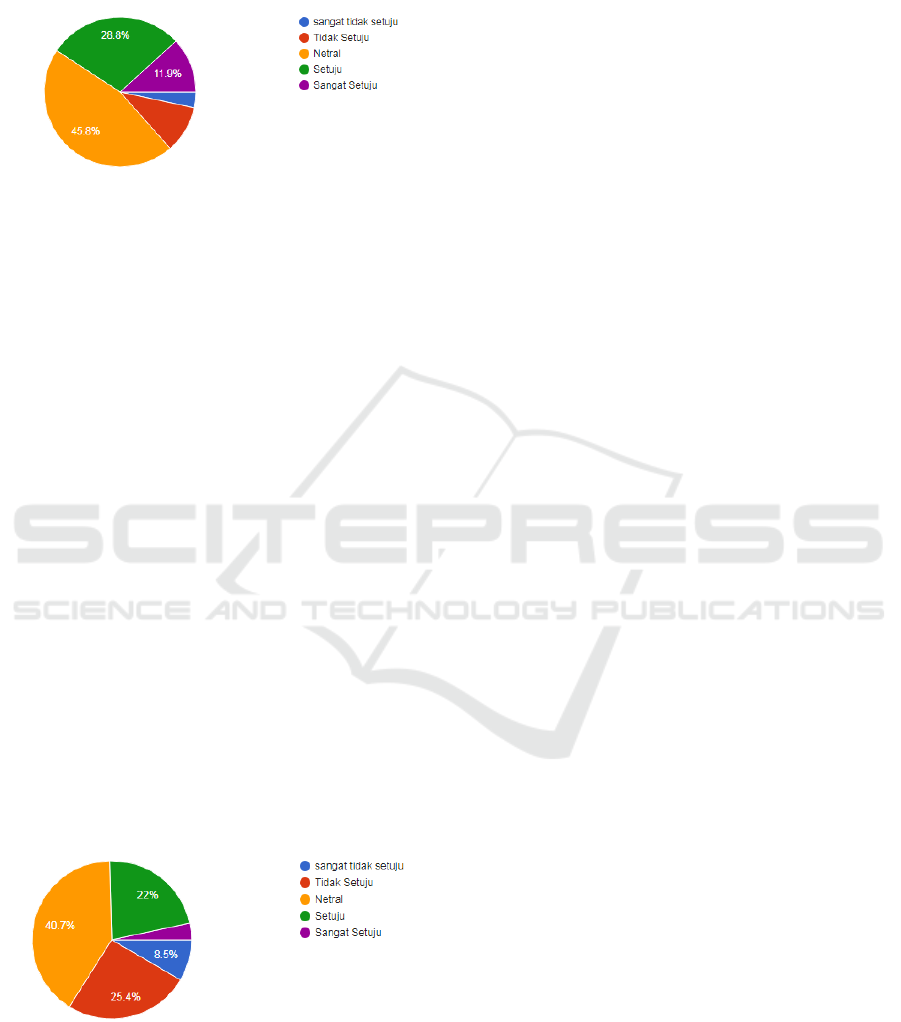
3.2 Are You Able to Manage Your
Time Allocated to Use Internet?
Figure 2: Allocating time towards using the internet
The surveyed showed that only 40,7% were able to
manage the time, but 59,3% were not able to take
care of the time, in other words, it means that they
spent a lot of time doing activities online with the
internet instead of watching sport events. The effects
of the loosing of most time influenced the
decrementing of performance in sports and in results
of study in other courses. These are reasons why
parents and high school teachers have to educate
students of high school on how to get profit from the
internet of watching sport events.
Playing sports helps reduce body fat or controls
your body weight. Sports allow you gain the
satisfaction of developing your fitness and skills.
Sports can help you fight depression and anxiety.
Playing sports helps strengthen bones. Not only that,
exercises also provide another good benefit which is
to make our brain more intelligent. By actively
participating in sports, our body becomes fitter so
we are more focused on receiving and processing
information.
3.3 Correlation between Results in
Class and Time Used on the
Internet
Figure 3. correlation between results in class and time
used on the internet
The result showed that 66,1% of students were
having a lack of good results in the class. This result
explains from the most time spent on the internet.
This result should help teachers and students’
parents to emphasis on the students’ education in
order to allow incrementing of performance in every
course.
4 DISCUSSION
The research showed the perception of junior high
school students on using the internet. It was found a
great lack of using internet on sport participation
where more than 66% of them used the internet for
chatting, watching YouTube, and accessing social
media. The use of the internet shows that most
students only used the internet as entertainment, not
for learning activities. Students were very familiar
with the entertainment features in their devices and
it happened every day. The reserch done by
Kominfo (2015) confirmed that the use of the
internet in Indonesia is dominant in news and
entertainment searches. In educational content, it
was only a very small amount, which is 5 percent of
the total. It was also illustrated that the programs
most favored by dominant viewers are entertainment
and information (Kusuma dan Hardiyanto, 2015).
That was very worrying considering that children
and adolescents still have a very unstable emotional
condition, and they have not been able to sort out the
good information from the thousands of information
they get through their devices. So, prevention not to
use the internet in digital age for teenagers now this
is considered very difficult.
They also tend to be easily influenced by the
social environment without first considering the
positive or negative effects received when doing
internet activities (Ekasari & Dharmawan, 2012). In
fact, Longstreet, Brooks, and Gonzalez (2019)
revealed that there is a significant relationship
between someone who is addicted to the internet
with negative emotions. Individuals with internet
addiction were 2–3 times more likely to suffer from
depression or anxiety than those without internet
addiction (Ho et al., 2014). This problem is also
caused because young students have not been able to
sort out useful internet activities.
The result of the time allocation of the internet
use by junior high school students in Yogyakarta
was that more than 50 percent of the survey results
revealed poor time management in internet use. This
resulted in sleeping late at night, poor control of
time to play the internet, and often delaying work
school just to play the internet.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
536

The positive influence offered by the internet is
not proportional to the negative impacts of the use of
the internet itself if it is not well managed. This
incident is a problem that occurs in Yogyakarta
adolescents students even though these students will
be the spearhead of the nation. In fact, they are
complacent when getting internet facilitation that is
presented to facilitate all their activities without
creating new creativity in the world of education that
is being lived. Of course, if it is associated with
educational institutions, internet addiction is the
responsibility of all elements in the schools,
especially to teachers.
The teacher also has a share in spreading internet
addiction. Davis (2001) mentions that this event is
referred to as a cognitive model of internet
addiction. Social approval or social isolation will
cause internet addiction in students. In schools, this
relationship is the responsibility of the teachers
because it is related to its relationship with the
formation of students for internet addiction.
According to Bronfenbrenner (1977), the ecological
system model and social systems (eg, parents and
teachers) can interact each other. At schools,
choosing professors is an important source of social
teachers for teens. Students who lack social supports
from teachers are more likely to be vulnerable to
Internet addiction (Casas, Del Rey, & OrtegaRuiz,
2013). Besides, quality in the relationship between
students and teachers is a key factor that drives or
damages school students (Wang, 2009). If students
appreciate that their teachers support and care for
them, they will have better academics and more
problems (Wang, 2009), for example, they develop
internet addiction (Casas et al., 2013). Thus,
teachers’ supports can play a protective role in
adolescents development. Besides, perceptions of
social supports from teachers have been indicated
for the protection of adverse effects from negative
environmental conditions or stress among
adolescents (Wang & Dishion, 2012).
Rodrigues, D., Padez, C., & Machado-Rodrigues,
A. M. (2017) showed that the parenting of physical
sports teachers and student parents are involved to
increase the behavior of students in their education.
Parental participation in organized and unorganized
physical activity (PA) must be associated with
students’s participation in extracurricular sports,
then we should expect the discounted performance.
This is in line with Fahriantini (2016) who
reinforces the importance of the role of parents to
engage children in critical thinking, invite children
to have simple discussions regarding cases arising
from crimes committed in cyberspace. Parents can
also control the use of the internet but it does not
have to be in a strict way, but by controlling or
supervising persuasively while still respecting the
privacy of children. In this case, the result of a
research done by Faisal (2016) outlines that
educating children in the digital age can be done by
applying non-authoritarian parenting because
children are not happy forced but rather persuaded
and tended to be left alone, but they must also
remain supervised by parents. Besides, parents must
also be able to understand the variety of applications
that educate children and guide children to play it
well and oversee the use of the media information,
but not to deviate from the values of Islamic
education.
The results presented above showed that students
already had mental disability because it is so hard
for them to tie out from the internet. As
consequences, we cannot hope for students’s good
result or high performance in sports if they still use
the internet for other useless things instead of sport
participation. It was found the decrement of results
in the classes because of a high amount of time spent
on the internet. Mental disability, if not corrected
immediately, will add to the bad impacts. The results
of the study by Park et al., (2016) revealed that to
minimize internet addiction, good sports activities
are needed, not only to improve physical fitness but
also to increase psychological health. The more
someone participates in active sports’ activities, the
more the internet addiction would be lost. Joker's
research also revealed that the benefits of sports
participation can have a positive impact by showing
that the level of self-control over internet use is far
better compared to people who are not involved in
physical activities or sports, namely by conducting a
research on 622 teenagers consisting of 428 elite
athletes, 140 regional athletes, and 54 non-athletes.
The research done by Siebert, E. A., Hamm, J.,
& Yun, J. (2016) showed that one hundred and
forty-eight parents of children with disabilities of
having self-control were surveyed. The results of
multiple regression revealed that parents perceived
competences of their children’s physical ability and
parental supports were the key factors of promoting
physical activity behavior of children with
disabilities. Evans, D. M., & CT Smith, A. (2004), in
his study, showed that if internet is well used, it will
provide more benefit. Australian population was
surveyed about the time used on internet. 66.67%
of them were interested with internet. However,
clubs demonstrated a significantly more optimistic
view of website profitability, with 96% of
respondents believed sites offering sports content
The Perceptions of Junior High School Students in Yogyakarta on Effects of the Internet on Sport Participation Events
537

were capable of turning a profit on the internet at the
time. According to the results from the present
study, we should conclude that junior high school
students in Yogyakarta badly used the internet, so
physical sports teachers and parents are invited to
re-educate and to show the students how to use
correctly the internet to allow the performance in
physical sports. So, results in other courses will be
influenced by wise use of the internet.
5 CONCLUSION
The study n this paper showed significant lack of
using internet on sport participation for the
Yogyakarta junior high school students. This study
provides knowledge to experts in charge of using
internet. With the results obtained, we give
information to these physical sports teachers and
students’ parents to understand better the process
and the behavior of children in using internet and
how they should work with the important variables
to obtain better results and to be more successful for
in the sport events.
So, these findings supported the need to
strengthen the capacity of school teachers and
parents in early identification, detection, and
management of behavioral addictions among
students. School teachers and parents are well
placed to leverage their positions to deliver the
screening, early intervention, and preventive
interventions for behavioral addiction involving the
use of the internet to school children. Teachers or
parents should equip themselves with training or
adding insight on handling internet addiction to deal
with or prevent a student from being addicted to the
internet.
As a limitation of the study, we find the
impossibility of generalization. On the one hand, it
is due to the samples which only corresponded to the
Yogyakarta students. On the other hand, it is
because of the context; the scope of study on sports
participation and the internet use. This type of study
allows us to begin to create a theoretical basis in the
field and add knowledge about the subject. In future
studies of the same line, we must analyze the
variables in other types of events and other types of
services, and have other types of samples to be able
to offer more generalizable conclusions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We warmly thank the participants in our research
who have given written consent. Our deeply feelings
of gratitude are addressed to junior high school
students of Yogyakarta for the information provided.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We declare that there is no conflict of interest to do
this research.
REFERENCES
Coleman, R., & Ramchandani, G., 2010. The hidden
benefits of non-elite mass participation sports events:
an economic perspective. International Journal of
Sports Marketing and Sponsorship, 12(1), 19–31.
doi:10.1108/ijsms-12-01-2010-b004
Casas, J. A., Del Rey, R., & Ortega-Ruiz, R., 2013.
Bullying and cyberbullying: Convergent and divergent
predictor variables. Computers in Human Behavior,
29,580–587.
Caumont, A., 2014. Americans increasingly view the
internet, cellphones as essential. Retrieved from
http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2014/02/27/
ameri cans –increasingly -view-the- internet-
cellphones-as essentia l/
Davis, R. A., 2001. A cognitive-behavioral model of
pathological Internet use. Computers in Human
Behavior, 17, 187–195.
Evans, D. M., & CT Smith, A., 2004. Internet sports
marketing and competitive advantage for
professional sports clubs: bridging the gap between
theory and practice. International Journal of Sports
Marketing and Sponsorship, 6(2), 9–21.
doi:10.1108/ijsms-06-02-2004-b004
Ekasari, P., & Dharmawan, A. H., 2012. Dampak
sosial-ekonomi masuknya pengaruh internet dalam
kehidupan remaja di pedesaan. Departemen Sains
Komunikasi dan Pengembangan Masyarakat, Fakultas
Ekologi Manusia, IPB.
Fahriantini E., 2016. Peranan Orangtua dalam
Pengawasan Anak pada Penggunaan Blackberry
Messenger di Al Azhar Syifa Budi Samarinda.
eJournal Ilmu Komunikasi, 2016: 4(4): 44-55.
Faisal, N., 2016. Pola Asuh Orang Tua dalam Mendidik
Anak di Era Digital. Jurnal An-Nisa, IX(2) : 121- 137.
[Internet]dapat diunduh di http://e-jurnal.
stainwatampone.ac.id/index.php/an-nisa/article/
viewFile/191/184
Gilchrist, P., & Wheaton, B., 2017. The social benefits of
informal and lifestyle sports: a research agenda.
International Journal of Sport Policy and Politics,
9(1), 1–10.doi:10.1080/19406940.2017.1293132
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
538

Ho, R.C., et al., 2014. The association between internet
addiction and psychiatric comorbidity: a
meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 14, 183.
Kusuma N, Hadiyanto., 2015. Perilaku Menonton dan
Kepuasan Petani terhadap Program Merajut Asa di
Televisi TV Trans7. Bogor (ID): Jurnal Penyuluhan,
11(1) : 60 – 68.
Kominfo, 2014. Riset Kominfo dan UNICEF Mengenai
Perilaku Anak dan Remaja dalam Menggunakan
Internet Siaran Pers No.17/PIH/ Kominfo/2/2014.
[Internet] dapat dinduh dihttps://
kominfo.go.id/index.php/content/ detail/3834/S
iaran+Pers +No.+17-PIH –KOMINFO
-2014+tentang+Riset+Kominfo+dan+UNICEF+Meng
enai+Perilaku+Anak+dan+Remaja+\Dalam+Mengg
unakan+Internet+/0/siaran_pers
Longstreet, P., Brooks, S. and Gonzalez, E. S. 2019.
Internet addiction: When the positive emotions are not
so positive, Technology in Society. Elsevier Ltd. doi:
10.1016/j.techsoc.2018.12.004
Ozturk, E., & Ozmen, S. K., 2011. An investigation of the
problematic internet use of teacher candidates based
on personality types, shyness and demographic
factors. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice,
11(4), 1799–1808.
Park, J. et al., 2016 Kasetsart Journal of Social Sciences
Effect of sports participation on Internet addiction
mediated by self-control : A case of Korean
adolescents’, pp.6–11. doi:
10.1016/j.kjss.2016.08.003.
Rothschild, P., 2011. Social media use in sports and
entertainment venues. International Journal of
Event and Festival Management, Vol. 2 No. 2, pp.
139-150. https://doi.org/10.1108/17582951111136568
Rodrigues, D., Padez, C., & Machado-Rodrigues, A. M.,
2017. Active parents, active children: The
importance of parental organized physical activity in
children’s extracurricular sport participation. Journal
of Child Health Care, 22(1), 159–170.
doi:10.1177/1367493517741686
Sefton-Green, Julian., 2004. Literature Review in Informal
Learning with Technology Outside School.
Future Lab Series 7 (2004). Future Lab Archive. 5
Apr. 2010. <http://www.futurelab.org.uk/
resources/publications-reports-articles/literature-revie
ws/Literature-Review379>
S. McClung, R. Hardin and M. J. Mondello., 2004.
Marketing on the web: Collegiate athletic sites, in
Sharing Best Practices in Sport Marketing: The Sport
Marketing Association’s Inaugural Book of Papers (B.
G. Pitts, Ed.). Morgantown, Virginia: Fitness
Information Technology (FiT), pp. 35-43
Siebert, E. A., Hamm, J., & Yun, J., 2016. Parental
Influence on Physical Activity of Children with
Disabilities. International Journal of Disability,
Development and Education,64(4), 378–390. doi:
10.1080/1034912x.2016.1245412
US Department of Health and Human Services: Physical
Activity Guidelines for Americans. 2008,
Available
from:http://www.health.gov/paguidelines/guidelines/
Weedon, G., Wilson, B., Yoon, L., & Lawson, S..
2016. Where’s all the “good” sports journalism?
Sports media research, the sociology of sport, and the
question of quality sports reporting. International
Review for the Sociology of Sport, 53(6), 639–667.
doi:10.1177/1012690216679835
Wankel, L. M., & Berger, B. G., 1990. The Psychological
and Social Benefits of Sport and Physical Activity.
Journal of Leisure Research, 22(2), 167–182.
doi:10.1080/00222216.1990.11969823
Wang, M. T., 2009. School climate support for behavioral
and psychological adjustment:
Testing the mediating effect of social competence.
School Psychology Quarterly, 24, 240–251.
Wang, M. T., & Dishion, T. J., 2012. The trajectories of
adolescents' perceptions of school climate, deviant
peer affiliation, and behavioral problems during the
middle school years. Journal of Research on
Adolescents, 22, 40–53.
Wang, L. et al., 2013. Internet addiction of adolescents in
China : Prevalence , predictors , and association with
well-being, Addiction Research and Theory,
21(February), pp. 62–69. doi: 10.3109/16066
359.2012.690053.
X. Zhang and V. R. Prybutok., 2005. Consumer
perspective of e-service quality, IEEE Transactions on
Engineering Management, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 461-477.
Hur, Y., Ko, Y.J., Valacich, J., 2011. A structural model
of the relationships between sport website quality,
esatisfaction, and e-loyalty, Journal of Sport
Management, vol. 25, no. 5, pp. 458-473
https://tekno.kompas.com/read/2019/05/16/03260037/apjii
-jumlah-pengguna-internet-di-indonesia-tembus-171-j
uta-jiwa
The Perceptions of Junior High School Students in Yogyakarta on Effects of the Internet on Sport Participation Events
539
