
Learning Outcomes of Forehand Serve Skill using STAD
Learning Model
Giofandi Samin
1
1
Sport Science, Graduate Program of Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Forehand Serve, Student Team Achievement Divisions
Abstract: This quantitative research was conducted in SMPN 8 Gorontalo. It aims to determine how influential the
model of cooperative learning toincrease learning outcomes of forehand serve skills in the table tennis on
male students of VIII-5 at SMPN 8 Gorontalo. The study was conducted in18 meetings. The research’s
object was 17 students of Class VIII-5. Based on the pre-test results, it showeds that the highest scores and
the lowest score was 16 and 8 respectively. After conducting the analysis, it was obtained that Mean was
207, a standard deviation was 2.12 and variance was 4,529. The post-test results showed that the highest
score was23 and the lowest score was 16. After conducting the analysis, Mean was 324, a standard
deviation was 2:01 and variance was 4,058. The results of the pre-test and post-test showed the price tcount
18:59. Meanwhile the price obtained from the distribution list ttable was 1,746. It is clear that tcount prices
has been greater than ttable. It can be concluded that cooperative learning model type (STAD) has a very
significant influence on forehand serve skills for the male students of Class VIII-5 at SMPN 8 Gorontalo.
1 INTRODUCTION
Physical education is important and it implies that it
is not merely an ornament in a school program as a
way to keep the students busy (Sutrisno & Khafadi,
2010). Physical education is a significant part of
education itself. Through a guided physical
education class, students will develop skills in which
the activities can occupy their free time, lead them to
involve in healthy activities to promote healthy
lifestyle, develop their social skills and improve
their physical and mental health. In the physical
education, there will be problems arising in the
teaching and learning process (Riduwan, 2013).
Those factors include (1) students’ learning
motivation, (2) students’ skills, (3) teacher’s skills
and (4) learning facilities. These four factors are
dominant in determining the success of the learning
process and also the effort in fulfilling the learning
goals (Ruud, Den Hartigh, Christophe, 2018).
The weaknesses in teaching physical education
coonstitute the teaching and learning process. The
fact shows that teachers sometimes do not realize
physical education can give the students chances to
learn some valuable things. Therefore, many think
that teaching physical education can be merely
performed by asking students to go to the field,
providing balls for the students and letting them play
on their own and then the teacher’s job is only
watching them from afar as though physical
education is less important than other lessons.
The described situation from the previous
discussion can happen in any school in any part of
Indonesia including SMP Negeri 8 Gorontalo. So
far, the teaching and learning process of physical
education class has always evolved. The changes
can be seen from the achievements earned by the
school, the improved facilities and the number of
physical education teachers. However, despite many
facilities and teachers, it did not improve the
school’s achievements and had no significant impact
to the students’ skills learning results in physical
education lesson, especially in table tennis.
Table tennis game at first is only considered as
an activity to do in a leisure time, as an
entertainment or merely as recreation. Most
Indonesian people know the game as “ping-pong”
which was taken from the sound made by the ball
when it hits the table or the soft paddle. Later on the
name was changed into “table tennis” (Dini, 2013).
This game requires some basic techniques such as
the technique of holding the paddle, serve and many
other techniques.
430
Samin, G.
Learning Outcomes of Forehand Serve Skill using STAD Learning Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0009788104300434
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 430-434
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

In table tennis, most rallies are short and points
can be scored in a relatively brief period of time.
This makes it a particularly exciting sports to play
and to watch, because one of the players can
suddenly get the momentum and turn the match
(Ruud, Den Hartigh, Christophe, 2018).
This game is done on the table with a specific
standardized size. The players need to cross the ball
over the net and land it in the opponent’s area
(Wisahati, Santoso, 2010). This game also has a
game set that each set contains 11 points with rally
point system in which the first player reaching 11
points will be claimed as a winner (Kusumawati,
2015). If both players have the same point of 10 –
10, then the players need to continue the play until
there will be 2 point difference and the serve is done
alternately. This is called deuce. Table tennis game
is started by a serve and each player makes a serve
two times in a row.
Serve is the first strike in table tennis game
(Hanif, Syam, 2015). The first strike in table tennis
game is known as forehand hit or backhand hit.
Forehand strike is a strike in which the player hits
the ball; the back of the hand which holds the paddle
faces back (Sarjiyanto & Surjawadi, 2010). The
steps in doing forehand serve involve a) standing in
a posture as if taking a step, b) putting the ball in
hand, c) holding the paddle in the handshake grip
position or penhold grip, d) throwing the ball in the
air, e) hitting the ball with the forehand strike. The
steps in doing basic technique of forehand service
include preparation stage, movement stage, and final
movement stage (Simpson, 2014). Preparation stage
consists of standing in a posture as if taking a step
while facing slightly sideways from the table,
leaning the body slightly forward, placing the ball
inside the left palm and place it in front of the chest,
then focusing on the direction of the movement.
Movement stage includes pulling the paddle back,
throwing the ball in the air, and when the ball is
falling, hitting it with the paddle by swinging the
paddle towards the ball until the top of the ball.
Lastly, final movement stage includes moving the
hand to follow the ball’s movement and focusing on
the direction of the ball movement.
Furthermore, table tennis is also one of the
lessons taught in SMP Negeri 8 Gorontalo
specifically in Grade VIII. Physical education,
particularly table tennis lesson has not have the
proper coaching and the suitable teaching and
learning process, including issues of the teaching
and learning process itself, irregular schedules, lack
of school’s facilities and lack of motivation or
seriousness in providing the proper teaching process
in learning forehand serve in table tennis.
Learning effectively requires effective self-
regulation throughout the learning process. Not only
do students have to plan and execute the process for
learning, but they also need to remain on task and
resist.
The learning process is derived from
educational psychology theory and learning theory
which was designed based on analysis of the
curriculum and its implication to the operational
level (Dweck, Cohen & Siegler, 2016). The learning
technique has wider meaning than the strategy,
method or learning procedure.
It has four specific
characteristics which are not possessed by other
learning methods or strategies (Oemar, 2013). They
are rational and logical theory arranged by
educators, the target of the learning process, the
steps of the learning process needed to optimize the
learning process, 4) the learning environment needed
by the students to accomplish the target learning.
To boost the students’ motivation in engaging in
the teaching and learning process, it needs a serious
effort and a scientifically organized coaching
programme. It could be achieved by using the proper
learning technique that is easy to be understood and
will improve students’ learning skill in doing
forehand serve in table tennis game for junior high
school students in grade VIII. The results of the
learning process can be measured from how much of
the learning target is achieved while also measuring
the process of learning (Sutarmin, 2010). Bloom
categorized learning outcomes into three domains
which are: (1) cognitive (knowledge), (2) affective
(attitude), (3) psychomotor (skills) (Mashar &
Dwinarhayu. 2010). With these arising problems, it
needs to find the effective learning technique in
order to give a significant impact in learning
outcomes of the junior high school students
(Husdarta & Yudha, 2014).
The learning technique applied in SMPN 8
Gorontalo Grade 8 which is considered optimum and
suitable for improving the forehand serve skill is
cooperative method using STAD. From the five
models of cooperative learning which are being
examined, STAD is the most consistent method in
giving the positive impact (89%) (Said, 2012). The
STAD cooperative learning process is a learning
approach focusing on small groups of students to
work together in maximizing the learning condition
in order to achieve the goals (Husdarta & Yudha,
2014). This learning technique aims to expand the
students’ social, cognitive and affective skills. This
method was developed by Salvin and involves
having “competition” among the groups. Students
Learning Outcomes of Forehand Serve Skill using STAD Learning Model
431
are grouped by many ways such as skills, gender,
race and ethnics. Therefore, The STAD cooperative
learning technique is expected to be able to solve the
problems by conducting experimental study in order
to give a significant impact to the outcomes of
learning forehand service in table tennis game.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
This research is a Pre Experimental research. The
experiment design used one group pre-test and
posttest design. This research is categorized as pre-
experimental research because in the design there
was still outside variable that contributes in affecting
the making of the dependent variable caused by the
lack of controlled variables. For the specific design
of this experiment, the researcher used one-group
pretest-posttest design.
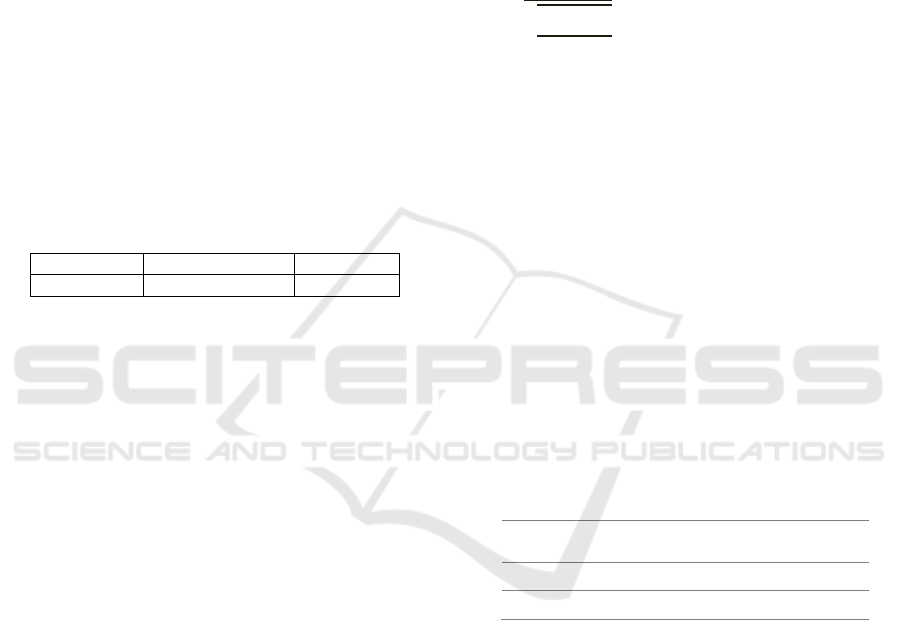
Table 1: Pre-experimental design
Pre-test Treatment Post-test
O
I
X O
2
The population in this research consists of 889
students of SMP Negeri 8 Gorontalo. There are 418
male students and 471 female students. In this case,
the population is all students of SMP Negeri 8
Gorontalo, while the target population is the male
students of grade 8 who have got different
characteristics that needed to be examined. Male
students are different from the female students in
learning physical education lesson. The sample in
this research was taken using purposive sampling.
This sampling technique is also known as
judgmental sampling which is used by determining
particular criteria for the samples (Sarjono &
Sumarja, 2010). There were nine classes in grade 8
and of those classes, there were 114 male students in
total. Based on those characteristics, the sample for
this research comprises 17 students of Class VIII-5
and later would be given STAD learning model.
The instrument used in this research is skill test
for forehand serve. Some of the tests conducted in
this research are: (1) pre-test which was conducted
by giving skill test of forehand serve to the students;
this pre-test gave each of student 5 chances of doing
forehand serve to get the prior data before the
treatment; (2) the treatment in which the researcher
would apply STAD learning model to the students
within 16 meetings for the students to master and
understand correctly the forehand serve which
follow the right steps; and then (3) post-test which
was conducted by using the same test as the pre-test.
These tests would determine how far the impact for
the outcomes in learning forehand serve is after the
treatment was applied.
To answer the research questions in this study,
the researcher used a data analysis technique which
aimed to categorize the variables and respondents by
testing the research hypothesis using t-test. The
formula used is presented as follows:
𝒕
𝑴𝒅
∑
𝑿
𝟐
𝒅
𝑵𝑵 𝟏
(1)
Notes: (Md) means the range between pre-test score
and post-test score. (Xd) Deviation for each subject
d-Md. (∑X2 d) the square sum of Deviation. (n)
Subject of the samples.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The result for this pre-experimental research is the
improved forehand serve skill learning in table
tennis using STAD learning model. This research
was conducted from August 8 to September 16,
2016 and consisted of 18 meetings. The data
analysis from both pre-test and post-test pertaining
to the students’ skill of forehand serve are explained
in table 1 as follows:
Table 2: The description of the learning outcome data
Description Mean Min Max Std.
Deviation
Pre test 12.17 8 16 2,12
Post test 19.05 16 23 2,01
From Table 1, it can be seen that the students’’
learning results consist of 17 samples. Therefore,
Mean of the pre-test is 12,17; the lowest score is 8,
and the highest score is 16 with standard deviation
of 2,12. Meanwhile, the research data show that
Mean of the post-test is 19,05; the lowest score is
16, the highest score is 23 with standard deviation of
2,01. It can be concluded that there was an impact of
STAD learning model for the students’ forehand
serve skill. The comparison from the pre-test and
post-test are described in Table 3 as follows.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
432

Table 3: The average of learning outcomes for forehand
serce skill
Data Average of Learning
Outcomes
Pre-Test 12,17
Post-Test 19,05
Based on the results of the pre-test and post-test
in Table 3, it can be found that Mean of the learning
results of forehand serve skill using STAD learning
model is 12.17 for the pre-test and 19.05 for the
post-test.
Before conducting the analysis of the hypothesis
test, the test of the precondition hypothesis was
conducted. It was carried out by normality test in
which it was done to determine whether or not the
data in the research was normal. Normality test was
performed using Chi-square formula. Based on the
analysis, the results can be seen in Table 4 as
follows.
Table 4: Results of normality test
Indicator Significant Description
Pre-Test
0,0961 0,206
Normal
Post-Test
0,0485
0,206
Normal
Based on the measurement, it was found that
𝐿
(pre-test) = 0,0961 and 𝐿
(post-test) =
0,0485; moreover 𝐿
for α 0,05; n = 17 is 0,206.
Therefore, 𝐿
for pre-test = 14,9489 and posttest
= 8,6490 is smaller than 𝐿
= 0,206 , so the
distribution of 17 male students can be considered
normal.
Homogeneity test was carried out to determine
whether or not some data population variables were
homogeneous. Homogeneity test was performed
using F-test. The results of the test can be seen in
Table 5.
Table 5: Results of homogeneity test
Significant Description
1,11 2,33
Homogeneity
From the F-test in Table 5 above, it was
concluded that 𝐹
is 1,11 and 𝐹
for α 0,05
dk denominator is n-1 (17 – 1 = 16) and dk
numerator is n-1 (17 - 1= 16). It was found that the
score is 2,33, so 𝐹
≤ 𝐹
(𝐹
= 1,11
𝐹
= 2,33). Based on the test criteria stating
that if 𝐹
≤ 𝐹
, 𝐻
is accepted and 𝐻
. is
refused Therefore, it can be concluded that the data
presented above come from a homogeneous
population.
The impact test in this research was conducted to
determine the effect of STAD learning model to the
VIII-5 male students’ forehand serve skill.. The
impact test in this research was performed using T-
test. Based on the data analysis, the results can be
seen in Table 6 as follows.
Table 6: Results of T-test
Descri
p
tion Mean T
count
d.
k
T
table
Si
g
nifc
Pretest 12,17
18,59 17 1,740 0,05
Posttest 19,05
From the results shown in Table65, it was found
that 𝑡
= 18,59 and 𝑡
for α = 0,05; dk = n-1
(17 – 1 = 16) found 1,746, therefore 𝑡
is bigger
than 𝑡
(𝑡
= 18,59 > 𝑡
= 1,740). Based
on the test criteria, it refuses 𝐻
if 𝑡
> 𝑡
and
accepts 𝐻
. Therefore, it can be concluded that there
is an impact of using STAD to the learning
outcomes of forehand serve skill.among the male
students of VIII-5 at SMP Negeri 8 Gorontalo.
4 CONCLUSION
As the data analysis and its discussion have been
explained in the previous chapter, it can be
concluded that there is an impact of using STAD
learning model towards the learning outcomes of
forehand serve skill of male students of VIII-5 at
SMP Negeri 8 Gorontalo. STAD learning model can
give a contribution to the learning outcomes of
forehand service skill. These results were affected
by the results coming from the experiment. It can be
said that STAD learning model can give a positive
influence towards the learning outcomes of forehand
service skill in table tennis game for male students
of VIII-5 at SMP Negeri 8 Gorontalo.
REFERENCES
Dini. R, 2013. Perencanaan pembelajaran dalam
pendidikan jasmani dan kesehatan. Alfabeta. Bandung.
Dweck, C.S., Cohen, G.L., & Siegler, L.X., 2016. Journal
of educational psychology. 2016. Vol. 108. No 3. 259-
299
Hanif. A. S & Syam. A. 2015. Buku sepak Takraw Pantai.
PT rajagrafindo Persada. Jakarta.
Learning Outcomes of Forehand Serve Skill using STAD Learning Model
433

Husdarta dan Yudha. S. M., 2014. Belajar dan
pembelajaran pendidikan jasmani dan kesehatan. Cv
Alfabeta. Bandung.
Kusumawati. M., 2015. Penelitian pendidikan penjasorkes.
Cv Alfabeta. Bandung.
Mashar. M. A., & Dwinarhayu., 2010. Pendidikan jasmani
olahraga dan kesehatan. Swadaya Murni. Jakarta
Pusat.
Oemar. H. 2013. Proses belajar mengajar. PT Bumi
Aksara. Jakarta.
Riduwan, 2013. Skala pengukuran variabel-variabel
penelitian. Alfabeta. Bandung.
Ruud J. R,. Den Hartigh,. & Christophe Gernigon., 2018.
Journal Of Sports Sciences, Vol. 36, No. 23, 2732–
2737
Said. H., 2012. Peran interval sprint, akselerasi sprint,
hollow sprint terhadap peningkatan kecepatan siswa
sekolah sepak bola Gorontalo. Jurnal INOVASI.
Volume 9, No.1.
Sarjiyanto. D., & Surjawadi., 2010. Pendidikan jasmani
olahraga dan kesehatan. PT Intan Pariwara. Jakarta
Pusat.
Sarjono., & Sumarja., 2010. Pendidikan olahraga dan
kesehatan. CV Aneka Ilmu. Jakarta.
Simpson. P. 2014., Tenis meja. Pioner Jaya. Bandung.
Sutarmin. 2010., Terampil berolahraga tenis meja. Era
Intermedia. Solo.
Sutrisno. B., & Khafadi. M. B., 2010. Pendidikan jasmani
olahraga dan kesehatan. CV Putra Nugraha. Jakarta.
Wisahati. A. S., & Santoso. T., 2010. Pendidikan jasmani,
olahraga, dan kesehatan. CV Setaji. Jakarta Pus
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
434
