
Traditional Game based Learning Model to Improve Elementary
School Students’ Motor Abilities
Silvia Tetra Oktavia
1
, Panggung Sutapa
1
1
Sport Science Study Program, Postgraduate Program, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Learning Model, Traditional Game, Motor Ability
Abstract: The research intended to produce a good, effective and fun traditional game-
b
ased learning model to
improve the elementary school students’ motor ability. The development of this research went through
several steps: (1) initial product development and expert validation, (2) small-scale trial and revision, (3)
large-scale trial and revision, (4) operational or effectiveness test, (5) production of the final product an
d
dissemination. The instruments used to collect the data included (1) interview recorders; (2) value scale; (3)
observation sheets of the model draft; (4) observation sheets of the model effectiveness. The data were then
analyzed in descriptive quantitative and qualitative ways. This research resulted in a traditional game-
b
ase
d
learning model consisting of five games, namely: (1) fortified, (2) cat and mouse, (3) like a snake, (4) sac
k
race, and (5) shell stilts running race, equipped by their manual or guideline forms. All those items were
packed in the form of a series of activities
1 INTRODUCTION
Learning process which requires the students’ motor
ability in elementary school has become a concern
for many people. The concern included one of the
barriers of motor learning activities in elementary
schools that is the physical education teachers’ lack
of knowledge in applying proper model for motor
learning activities. This phenomenon is caused by
limited references or reading resources available for
the teachers about how they are supposed to apply
appropriate motor learning model to support the
achievement of desired learning outcomes.
Planning on good physical activities is very
helpful for children to optimize their ability to move
especially the ability of gross motor and loco motor
motions (Aryamanesh & Sayyah, 2014). Regular
exercise is a way to encourage children to be active
and develop their motor skills, all of which can play
important roles in their life (Santrock, 2007).
A relevant research related to gross motor skills
is about the difference of children’s gross motor
skills between two types of preschools conducted by
Chow & Lobo (2013). This research focused on
educational goals that influence the types of
preschool (public vs. private) in the development of
motor skills of boys and girls aged 3 to 6.5 years. On
that research, the schools’ teachers provided several
tests which formed the basis of the students’ motor
skills. Finally, based on the analysis conducted, it
indicated that students who came from private
preschools showed better loco motor skills than
those who came from public preschools did.
The next relevant study was entitled "The Obese
Students’ Mastery of Gross Motor Skills in
Preschools and Early Elementary Schools" (Nafiseh
& Saidon, 2014). This study aimed at determining
the obese children’s need for gross motor skills in
preschools and early elementary schools and
showing the differences between the two groups.
The data analysis methods used were two-way
analysis (ANOVA) and descriptive in which
statistical criteria were significantly effective. The
results of the research conducted showed a
significant difference between the implementation of
gross motor skills for obese children in preschools
and early elementary schools. It could be concluded
that the low-fat children’s gross motor skills were
worse compared to the others with the normal fat.
Indonesia has abundant cultures including its
traditional games. Playing traditional games is the
process of doing activities which make children
delighted by using simple tools based on the
conditions or circumstances and is the result of
Oktavia, S. and Sutapa, P.
Traditional Game based Learning Model to Improve Elementary School Students’ Motor Abilities.
DOI: 10.5220/0009787704050411
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 405-411
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved
405

exploring local culture according to ideas and
lectures from the ancestors (Arlina, 2008).
Traditional games are believed to have better
impact on the development of children's potential; if
modern games prioritize individualization,
traditional games provide more opportunities for
children to socialize and collaborate in groups. This
is also reinforced by Bordova & Leong (2003) that
young children spend less time playing with their
peers and tend to spend their playing time alone,
moving on from educational toys to video and
computer games.
In the learning process, one way to make
children more interested and enthusiastic in
participating is to have variations. Variation in
learning process is a change in the process of
activities which aim at increasing students’ learning
motivation, as well as reducing boredom and
saturation (Mulyasa, 2010).
Therefore, in this research, to make motor skill
learning activities interesting and challenging for
children, some traditional games which have been
developed according to the rules and used tools were
utilized. In this case, it is believed that traditional
games involve physical activities which can improve
the players’ motor skills.
The problem faced by Physical Education
teachers in elementary schools is that children are
less enthusiastic and reluctant to do active sports
(involving gross motor skills), because of boring
learning activities. Children are more interested in
doing electronic games such as online games, play
stations, and other electronic games. Children feel
very comfortable to do those games without getting
bored for a long period of time. On the other hand,
the children themselves state that they only feel tired
and bored with what has been taught by the teachers
and do not like to do the activities of running and
jumping. Games which are carried out for a long
time (≥2 hours) without being balanced with good
physical activity will have a negative impact on
children’s physical and psychological health.
Griffiths (2010) states boys and girls who used
screen-entertainment for any duration but still
participated in sports had fewer emotional and
behavioral problems, but more pro-social behavior,
compared to those who used screen-entertainment
for 2 hours per day but did not participate in sport.
In this study, to attract and challenge children in
learning motor skills, the process needs to utilize
traditional games which have been developed
according to the rules and used tools. These
traditional games involve physical activities which
can improve the perpetrators’ motor skills. This is in
accordance with one of the objectives of Physical
Education, which is to develop individuals
organically; in the form of functional capacity,
namely strength, agility, speed, and others. Many
kinds of traditional games that can be used as tools
to play include: gobak sodor, fortified, cricket,
mouse and cat, jump rope and others. Those games
are very suitable to improve motor skills of the
children by stimulating them to move. Frequent
movement will stimulate the children’s organs to
work and to adjust to the intensity of their
movements, and this will affect his motor skills.
However, many elementary students have not
mastered the techniques and rules of traditional
games, because they prefer to play more modern
games. Therefore, children still make mistakes when
playing the traditional games.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
2.1 Development Model
This type of research was Research and
Development that was research type used to produce
certain products, and test the effectiveness of the
product (Sugiyono, 2014).
The research using the development model is a
process used to develop or validate a process used in
education and learning. The steps of the
development research model according to (Borg &
Gall, 2007) namely (1) conducting preliminary
studies and information gathering (literature review,
field observations, research frameworks), (2)
planning (research objectives, order of learning,
various forms of participation), (3) developing the
initial product (preparing learning material, planning
the initial draft of the product), (4) validating and
revising product draft based on results from expert
validation, (5) conducting initial trials (small scale
tests) and revisions (6) conducting field trials (large
scale tests) and revisions (7) carrying out operational
test/ product effectiveness test (8) producing the
final product which is a traditional game-based
learning model to improve motor skills of the
elementary school students.
2.2 Target/ Subject of Research
The small- scale trial stage was held at Gejayan
State Elementary School involving 29 third grade
students. The large- scale trial stage was conducted
at Puren State Elementary School involving 32 first
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
406

grade students and at Ngringin State Elementary
School involving 33 second grade students.
2.3 Research Instrument and Data
Collection Technique
The research instruments included: (1) interview
recorders, (2) observation sheets, (3) questionnaires
for material experts, media experts, and trial
subjects, and (4) instruments for observing model
effectiveness.
2.4 Data Analysis Technique
The collected data were analyzed by descriptive
quantitative and descriptive qualitative analysis. The
descriptive quantitative analysis was employed to
analyze the following (1) data obtained from the
value scale as a result of the assessment of material
experts on the initial draft of the model before trial
implementation on the field, (2) data of observation
result from material experts on field trials, (3) data
of observation results of material experts'
observations on the effectiveness of the model.
While descriptive qualitative analysis was conducted
on: (1) data from interviews with elementary school
teachers during preliminary studies, (2) data
deficiencies and inputs from material experts on the
game model both before the trial and after the trial
on the field.
3 RESEARCH RESULT
The learning model developed in this research was
traditional game based learning model to improve
the motor skills of elementary school students. This
traditional game based learning model was
developed based on potentials and problems,
analysis of interview results and direct observations
in the field. Observations were conducted at four
schools, including SDN Gejayan, SDN Puren, SDN
Ngringin, and SDN Sleman 4.
From the results of observations and interviews
conducted on four Physical Education teachers in
schools, the analysis of needs obtained are: (1) lack
of understanding and creativity of teachers in
developing varied and interesting traditional game-
based learning models, (2) lack of facilities and
infrastructure that can support the process of motor
learning, (3) limited time owned by the teachers to
provide a model of motor learning, (4) minimum
ability of students to perform motor movements, (5)
less interesting and less enjoyable provided leaning
models, that children still look less enthusiastic and
reluctant to do sports.
Traditional games developed were various
traditional games that have been selected and in
accordance with the characteristics of learning
materials, and the characteristics of elementary
school students, as well as the characteristics of
motor skills components, so it was hoped that this
traditional game-based learning model could attract
the interest and attention of students to do so in
order to improve their motor skills.
Based on the need analysis and observation
results, it was concluded that in implementing
Physical Education at schools, teachers needed a
game model that could train students to improve
their motor skills based on the applicable curriculum
goals. Therefore, the development of traditional
game-based learning models to improve students'
motor skills was needed in elementary schools.
The final goal of this development research was
to produce a product model of traditional game-
based learning to improve the motor skills of
elementary students. In addition, for the practicality,
this learning model was also equipped by the manual
or guideline. The purpose of making the manual was
to explain more specifically about how to use this
model, so that teachers as practitioners in the field
and readers would understand and be able to use this
model. Video games are packaged in the form of a
DVD (Digital Video Disc) as a guide for the
procedures for implementing the game, as for the
product specifications developed, namely:
Materials, 1) the development of the contents and
objectives of the game model was guided by the
Basic Competences (KD) of lower grade students,
and was adjusted to the characteristics of elementary
school students with an age range of 7 to 9 years old;
2) The traditional game in the manual contains three
parts, namely: (a) the initial activity which contains
the implementation before the learning process
begins from preparing students to warming up, (b)
the core activity contains the implementation of the
learning process of motor skills with five traditional
game activities, namely: (1) fortified; (2) cat and
mouse; (3) like a snake; (4) sack race; and (5) shell
stilts running race games. Those five traditional
game activities in this book can be used by the
teachers for five meetings with different Basic
Competences. The time used is 3x35 minutes/
meeting, and the chosen material includes practicing
physical activities for motor skills (balance, strength,
agility, coordination, and speed) through simple
games or traditional games; (c) closing activities
Traditional Game based Learning Model to Improve Elementary School Students’ Motor Abilities
407
containing cooling down activities, evaluation of the
implementation of traditional games, and reflection
on the meaning of traditional games; 3) The manual
contains the definition of traditional games, game
objectives, needed tools, game procedures, game
duration, assessment, safety standards, field
drawings and field size, and learning domain
assessments including (1) cognitive aspects related
to understanding and knowledge; (2) psychomotor
aspects related to motor skills; (3) affective aspects
related to cooperative behaviour.
Learning equipment, the tools used in the
learning process are common tools which are
affordable, easy to obtain and safe to use, which can
train to improve the motor skills of elementary
students. Those tools include: plastic balls, ribbons,
baskets, sacks, cones, shell stilts.
Development DVD, This game model uses
DVD-R pieces plus GT-ProMulti Speed 16 X. The
capacity of one DVD-R chip is 4.7 GB sp 120 min.
The game development DVD can be used on all
types of computers and laptops with a minimum
specification of the operating system Windows XP
or Mac OS, resolution 1024 x 800 pixels, Pentium
IV processor 1.66 GHz, 512 Mb of RAM, VGA on
board 32 Mb, and HDD 40. It also has a CD / DVD
drive. The development DVDs of traditional game
models to improve the motor skills of elementary
students can also be used on DVD players of all
types and brands.
The final product of the game consists of: (1)
fortified; (2) cat and mouse; (3) like a snake; (4)
sack race; and (5) shell stilts running race games,
completely presented as follows.
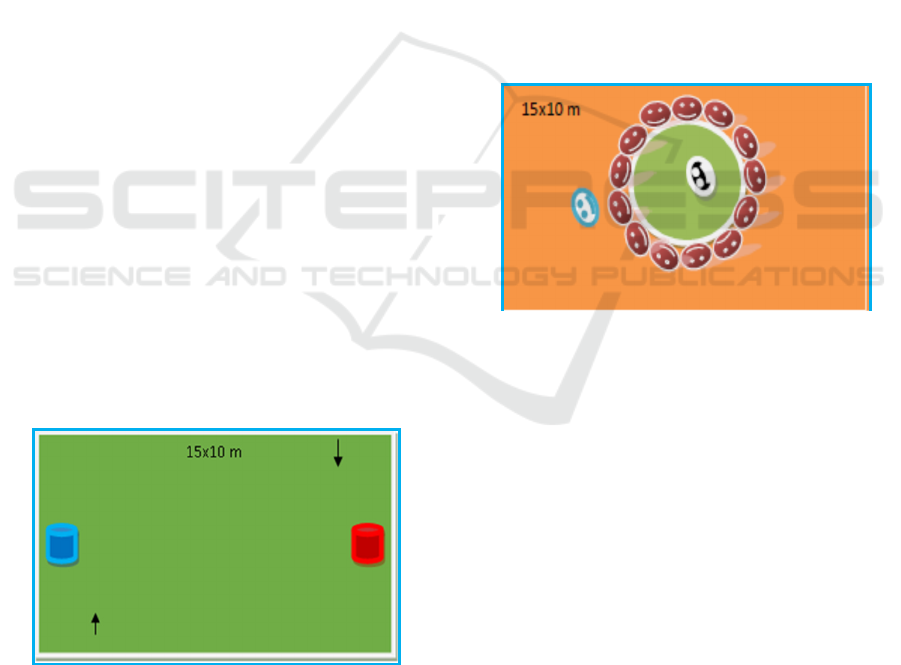
3.1 Fortified Game
Figure 1: Fortified Game
1) Before the game starts, a draw is held, the
winning team starts the game by exiting the castle to
lure opponents; 2) Each team consists of at least 5
children or more; 3) Each player functions as an
angler and also as a pursuer or hunter. He/ she will
be the chase of the opposing team if the opponent
first leaves the fort, and he/ she will be the one
pursued by the opponent when he/ she leaves the
fort. 4) Affected members will be a prisoner from
the opponent, the way to catch the opponent is
simply to throw the ball against the opponent's lower
leg.
1) Prisoners collected in captive area can be free if
their unattended members can release by
touching their body parts.
2) Fortress of a team is declared to be burned if
one of the team members can burn the
opponent's fortress by throwing the opponent's
fortress with the ball on target / entering the
basket.
3) After one of the fortress teams is burned down,
the game continued with a team that managed to
burn to function as an angler.
3.2 Cat and Mouse Game
Figure 2: Cat and Mouse Game
1) Players must consist of at least 6 children or
more.
2) Before the game is started, the lottery is
conducted to determine whom to play roles as
the cat and mouse. The one who loses the
lottery plays as the cat, and the one who wins
the lottery formed a circle, holding hands.
3) The mouse tries to avoid the cat throwing ball
by entering through a circle surrounded by other
children, while cat tries to catch the mouse by
throwing the ball into the mouse’s lower leg.
4) Children who form a circle are freed to block
the movement of cat, by squatting with the
hands cannot be separated.
5) The cat or mouse may not break the coupling
hands.
6) If the mouse is caught, the mouse alternates to
become the cat.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
408
3.3 Like a Snake Game
Figure 3: Like a Snake Game
1) Before the game begins, a lottery is held to
divide the player into 2 groups.
2) Players must consist of at least 5 children or
more for each team.
3) One of the players is selected to be the head of
the snake, then the other students become the
tail and march behind the head.
4) The game starts after the teacher blows the
whistle.
5) Group members hold on to each other's waist,
not to let the handle slip.
6) The group member who is the head of the snake
tries to throw the member of the opponent's
backmost group, by throwing the ball into the
opponent's lower leg.
7) Group members who play the role as tail must
be able to avoid throwing groups of opponents
8) If the last member of the group is hit, he/she
must leave the playing field
9) The group whose members are out is the losing
group.
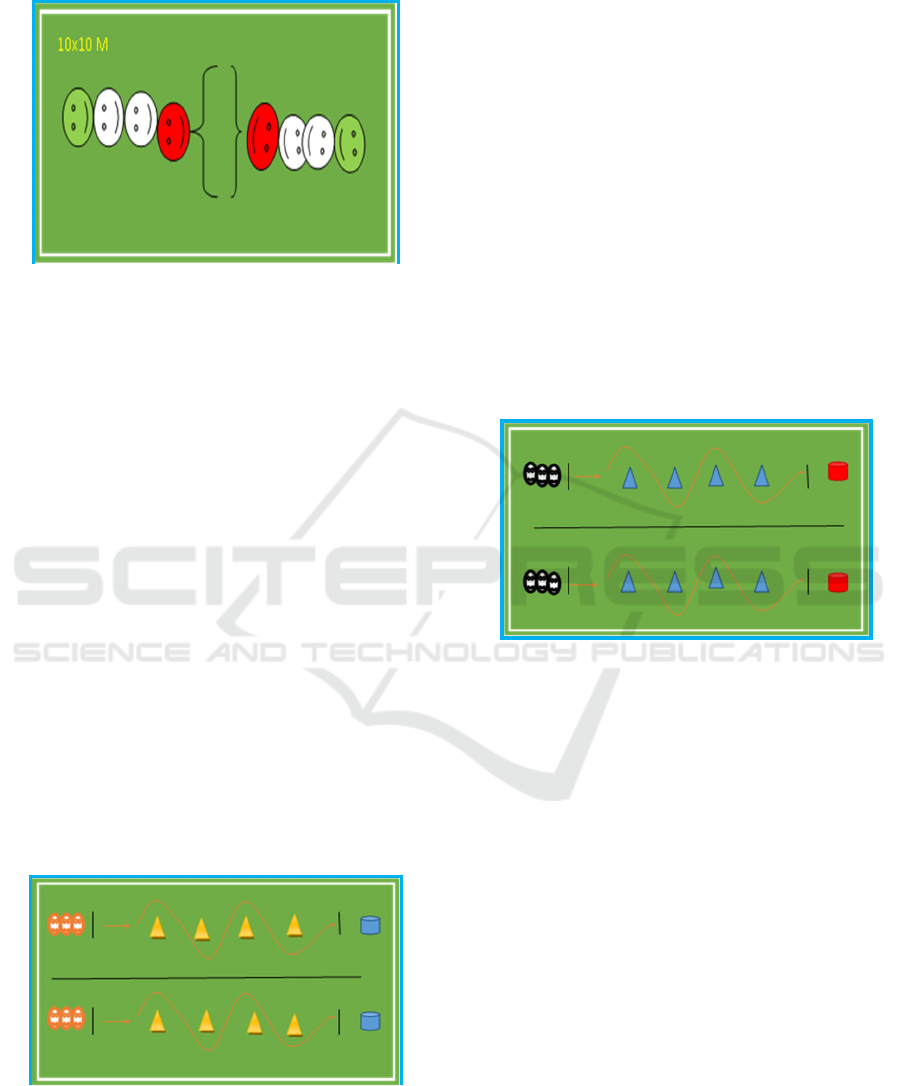
3.4 Sack Race Game
Figure 4: Sack Race Game
1) Players must consist of at least 4 children or
more.
2) Players put their legs into the sacks.
3) Players get ready to wait for the whistle/ signal
to start.
4) After hearing the whistle, the player jumps up
and down with two legs inside the sacks from
the start line to the finish line.
5) Players avoid barriers, by jumping zigzag.
6) Players can only jump up and down, not run and
walk in sacks.
7) After passing through the barriers, the player
throws the ball at the target.
8) After throwing the ball, the player returns to the
starting position, by jumping up and down, then
proceeds with the other players by high five.
3.5 Shell Stilts/ Egrang Batok
Traditional Game
Figure 5: Shell Stilts/ Egrang Batok Traditional Game
1) Players are divided into two groups.
2) Players must consist of at least 4 or more
children.
3) Players get ready on the shell with their legs
clamped on the rope, and both hands hold the
rope.
4) After hearing the whistle, the player tries to
walk from one place to another.
5) Players try to avoid barriers/ cones, by way of
zigzags.
6) Players may only walk, may not run and jump.
7) After passing the barriers/ cones, the player
throws the ball to the target.
8) After throwing the ball, the player returns to the
starting position by way of zigzags, then
continued by other players by high five.
Traditional Game based Learning Model to Improve Elementary School Students’ Motor Abilities
409

4 DISCUSSION
The ultimate goal of this development research is to
produce a traditional game based learning model to
improve elementary school students' motor skills. In
addition, for the practicality, this learning model was
also equipped by the manual or guideline. The
purpose of making the manual was to explain more
specifically about how to use this model, so that
teachers as practitioners in the field and readers
would understand and be able to use this model.
Video games are packaged in the form of a DVD
(Digital Video Disc) as a guide for the procedures
for implementing the game.
Based on the effectiveness test conducted in
Gondolayu State Elementary School and Sleman 4
Elementary School for four meetings with traditional
games consisting of: (1) fortified; (2) cat and mouse;
(3) like a snake; (4) sack race; and (5) shell stilts
running race games, the implementation of this
learning model can improve students' cognitive,
affective, and psychomotor aspects. This is indicated
by the completion of students' abilities in each
aspect after being given traditional games for four
meetings.
Capacity building occurs due to the association of
knowledge obtained by children at previous meeting
with new knowledge and association gets stronger
when repeated. This is based on the law of exercise
learning theory proposed by Thondrike (Rahyubi,
2014) that states "the principle of exercise law
shows that the main principle in learning is
repetition, the more often repeated subject matter
will the easier it will be mastered". The research
results are also supported by results of Hands &
Martin (2003) finding that physical activity learning
programs (fundamental movements) integrated with
learning in schools can significantly improve
children's cognitive, psychomotor, and affective
abilities.
Furthermore, Strong (2005) states "Physical
activity is important for all children because of the
associated benefits to physical, social and
psychological health". Physical activity is also very
beneficial for children's health physically, socially
and emotionally. This shows that doing physical
activities is very beneficial to the development of
children both cognitively, psychomotorically, and
socially and the child gets health improvement by
doing physical activities.
The statement regarding physical activity
influences the development of the positive
reinforced from the research results of Fedewa &
Ahn (2011: 9) "The present study shows that
physical activity has a significantly positive impact
on children's cognitive outcomes and academic
achievement". Physical activity has a positive effect
on improving cognitive abilities and increasing
children's academic achievement. In addition,
physical activity can also improve children's social
abilities. This is as stated by Liu, Karp, & Davis
(2010: 1) "Physical education is not only able to
help children to develop psychomotor skills, but it
can provide psychological benefits through the
development of personal and social responsiveness
and appropriate social behaviour.
The connection with the results of the study is
that the traditional game learning model for
elementary school students if done repeatedly will
cause brain nerve connections and become
permanent so that it further increases the ability to
recognize letters, concepts and numbers (cognitive
abilities), basic motor skills (motor skills) and the
formation of active lifestyles and excitement
(affective).
5 CONCLUSION
The model of this development research is in the
form of traditional game based learning model
guidebook to improve the elementary school
students’ motor skills. The game guidebook contains
five traditional game models consisting of (1)
fortified, (2) cat and mouse, (3) like a snake, (4) sack
race and (5) shell stilts running race games,.
REFERENCES
Arlina, 2008. Pengertian dan sejarah kebudayaan. Cerdas
Jaya. Tangerang
Aryamanesh, S. & Sayyah, M., 2014. Effect of Some
selected Games on the Develop-ment of Locomotor
Skills in 4-6 Year-Old Preschool Boys. International
Journal of Sport Studies. Vol., 4 (6), 648-652.
Bordova, Elena&Leong, J. Deborah., 2003. Do play and
foundational skills need to compete for the teacher’s
attention in an early childhood classroom. Journal
ERIC Digest. Volume 89, Issue, pp. 213-219.
Borg, W.R. & Gall, M.D., 2007. Educational research.
(An introduction), 7th edition. Longman. New York &
London.
Fadewa, A.L. & Ahn, S., 2011. The effects of physical
activity and physical fitness on children's achievement
and cognitive outcomes: A meta-analysis. Research
quarterly for exercise and sport. 82.3: 521-35.
Griffiths, L. J., et.al. 2010. Association between sport and
screen-entertainment with mental health problems 5-
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
410

year-old children. International Journal of Behavioral
Nutrition and Activity. (87): 512-37.
Hands, B.P. & Martin, M., 2003. Implement-ing a
fundamental movement skill program in an early
childhood setting: The children's perspectives. Health
Sciences Papers and Journal Articles. Fremantle WA:
University of Notre Dame.
Liu, M.H.C., Karp, G.G., & Davis, D., 2010. Teaching
learning-related social skills in kindergarten physical
education. Journal of physical education, recreation &
dance, 81(6), 38-44.
Mulyasa, 2010. Manajemen paud. PT Remaja Rosdakarya.
Bandung
Nafiseh & Saidon., 2014. Mastery of gross motor skills in
preschool and early elementary school obese children.
Early Child Development and Care. Volume 184,
Issue 5.
Rahyubi, 2014. Teori-teori belajar dan aplikasi
pembelajaran motorik deskripsi dan tinjauan kritis.
Nusa Media. Bandung
Santrock, J.W., 2007. Perkembangan anak, Edisi
kesebelas jilid 1, (penterjemah Mila Rahmawati dan
Ana Kuswanti). Erlangga. Jakarta.
Strong, W.B., 2005. Evidence based physical activity for
school-age youth. J. Pediatr. 146:732–737.
Sugiyono, 2014. Metode penelitian kuantitatif, kualitatif
dan r & d. Alfabeta. Bandung.
Traditional Game based Learning Model to Improve Elementary School Students’ Motor Abilities
411
