
The Physical Education Teachers’ Skill in Arranging Authentic
Assessment Rubrics
Fuaddi
1
, Tomoliyus
1
, Rifki Nanda Putra
2
1
Master Program of Sport Science, Yogyakarta State University, Indonesia
2
Graduate Program, Padang State University, Padang, Indonesia
Keywords: Teacher’s skill, assessment rubric, authentic assessment, physical education
Abstract: This research aims to identify the competency of physical education teachers in arranging the authentic
assessment instrument. This study used mixed method research with exploratory sequential design which
was a modification from the model (Creswell, 2012). The research participants were 40 physical education
teachers in in Junior High Schools at Kulonprogo Regency, Yogyakarta with the purposive sampling. The
quantitative data in this research were analyzed with the quantitative descriptive statistic using the method
by Miles & amp; Huberman (1994). From the result of data analysis, there were 70% of the teachers who
did not understand about authentic assessment, 25% of the teachers did not well understand, and 5% of the
teachers had good understanding, 90% of the teachers did not have authentic assessment rubric, 7% of the
teachers had rubric but it still did not find the demand of authentic assessment, and 3% of the teachers
already had appropriate rubric. 92,5% of the teachers was difficult to implement authentic assessment, 5%
of the teachers had few difficulties in doing so, and 2,5% of the teachers did not face the problem. Also,
95% of the teachers stated that they were unable to develop authentic assessment rubric, and 5% of the
teachers were still unable to make assessment rubric, and none of the teachers were able to arrange an
assessment rubric.
1 INTRODUCTION
The competency in arranging assessment instrument
is a part of teacher’s pedagogy competence, is one of
competences which should be mastered by every
teacher. It is because this competence is one of the
three dimensions which are related in producing
good education (Penney, Brooker, Hay & Gillespie,
2009) especially in physical education. It places the
assessment aspect as an unseparated aspect in
developing the quality of education. Moreover,
Tomoliyus, et al., (2016) state that learning will be
better if the learning materials taught in class and the
learning assessment are good and otherwise, the
learning materials and learning assessment will be
better if the learning strategy involved is good.
Even though many studies have examined the
importance of assessment aspect in the learning
process, (Lopez-Pastor et al, 2013) the popular
assessment often used in school is still the traditional
one. Moreover, that kind of assessment method is
irrelevant with the recent needs because it is partial
in assessing student’s learning achievement, but
nowadays teachers of physical education realize that
the test fails to produce information of what is
possible to be learned by children through the
physical education in school (Lopez-Pastor et al,
2013). One of the assessment methods which is
appropriately considered and comprehensive is the
authentic assessment (Callison, 1998). This kind of
assessment is appropriately implemented in
assessing student’s learning development in physical
education.
The changing in curriculum 2006 becoming
curriculum 2013 demands the change in student’s
learning achievement of physical education.
Previously, the assessment was conducted in the
middle of semester and in the end of semester.
Recently, in curriculum 2013 (Regulation of
Ministry of Education and Culture of Republic of
Indonesia No. 66 Year 2013 about the standard of
assessment), the assessment is conducted daily, in
the middle of semester, and at the end of semester.
In the previous curriculum, in assessing the results
of physical education learning in school, teachers
usually use the instrument of sport skill test which is
Fuaddi, ., Tomoliyus, . and Putra, R.
The Physical Education Teachers’ Skill in Arranging Authentic Assessment Rubrics.
DOI: 10.5220/0009785303030308
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 303-308
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
303

conducted in the middle and in the end of semester.
This thing is reinforced by the finding from
Komarudin (2016) which found that teachers of
physical education assess the learning achievement
of students 100 % by using traditional assessment
(sport skill test). In curriculum 2013, when a teacher
assesses the students, the teacher should use
authentic assessment in the daily assessment
(Permendikbud RI No. 66 Thn. 2013 Tentang
Standar Penilaian Penilaian), whereas the final
semester assessment can use skill test or authentic
assessment only. Because of the changing of
curriculum, do physical education teachers already
have competence in arranging and conducting the
authentic assessment instrument? Then, this
research aims to analyze teachers’ competence in
arranging and using authentic assessment
instrument.
One of the most important things to be
considered in increasing students’ learning
achievement is the quality of teachers (Report &
Objectives, 2003). As a professional worker, teacher
certainly should have competence to be mastered, in
the Constiution of Republic of Indonesia No. 14
Year 2005 about teachers and lecturer which is
included in the Department of National Education
(2005:16) which states that teacher’s competence is
“A set of knowledge, skill, and behaviour which
should be possessed and mastered by teachers or
lecturers in implementing their professional duty”.
Therefore, every teacher should possess each
competence which will support the learning process.
To be able to create a good learning, a teacher
should master a least four professional competences.
In the Constitution of Republic of Indonesia No.19
Year 2005 Article 28 about national education
standard, competence in the level of elementary,
early child and middle school consist of: a.
Pedagogical Competence; b. Personality
Competence; c. Professional Competence; and d.
Social Competence.
The pedagogy competence is a competence
which has a significant effect as the factor in
deciding the learning achievement of students (Ada
& Azisah, 2016). Many studied show that teacher’s
pedagogy competence has influence to the
improvement of students’ learning achievement
(Goldhaber & Brewer, 2000; Darling-Hammond,
Berry & Thoreson, 2001; Goldhaber & Anthony,
2004; Vandervoort et al., 2004; Suciu & Mata, 2011;
Ada & Azisah, 2016). For that reason, in
improving students’ learning achievement, all
related institutions should give attention to increase
teacher’s pedagogy skill.
The ability in assessing and evaluating is a part
of teacher’s pedagogy competence (Report &
Objectives, 2003), without a good assessing ability,
teacher will not able to know whether the learning
that they did is successful or not. For that, teacher
should master the assessing competence and also
evaluate the learning achievement.
Then, authentic assessment is an assessment
which is conducted by directly observing the
learning process, and the score given in the time so it
is also called as work performance assessment
(Lund, 1997; Lund, 2010; Mardapi, 2016; &
Komaruddin, 2016). According to the Regulation of
Ministry of Education and Culture No. 66 Year 2013
about the standard of Education Assessment, it is
stated that authentic learning is a whole assessment
in every competence which consists of attitude,
knowledge, and skill by using various assessment
techniques both during the process and in the result
of the learning. Conceptually, an authentic
assessment indicates the repair in the assessment
process conducted by teacher to the learning
achievement of students. Because in the authentic
assessment, teacher is demanded to do assessment
based on the three domains possessed by students,
the scores which are produced will be more
objective for all students. In implementing an
authentic assessment, rubric becomes important
thing to be used in avoiding the subjectivities of
teacher (Menedez-Verela & Gregori-Giralt, 2015).
Besides, according to Lund (2006), the authentic
assessment is crucial in the report of program, and a
good rubric is very essential for the assessment.
Shaw (2014) states that rubric is an important
assessment tool for giving students’ learning
evidences. Tomolius (2012) and Majid (2014) state
that rubric is an assessment guidance which gives
description of assignment criteria or competence
which is wanted by teachers and training in
assessing or scoring based on the students’ work
result. Rubric consists of two types: holistic and
analytic rubric (Majid, 2014). Besides, the function
of rubric in assessment will help to decrease
hesitation of teacher in giving assessment (Arends,
2012). Birrky (2012) states that rubric can help to
assess the quality of skill which is conducted or the
result to give feedback to students. Also, the rubric
can help students in understanding target for their
learning and the quality standard for certain
assignment, and also to make good assessment about
their works which can inform revision and their
performance improvement (Reddy & Andrade,
2009).
A good rubric should describe verbal description
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
304

and identify important components which are
expected from the assessment, and target the
knowledge and relevant skill which need assessment
by teachers to be demonstrated (Lund, 2006).
Besides, rubric is also well considered if it has high
validity and reliability (Kimberlin & Winterstein,
2008; Rihtiana & Tomoliyus, 2014; Tomoliyus, et
al., 2016). Valid means the size which shows the
validity or similarity of the result which is obtained
from the provided instrument, that is a tool used to
measure something (Arikunto, 2001; Kimberlin &
Winterstein, 2008; Sugiyono, 2017). Whereas,
reliable is the consistence of an instrument, that is an
instrument which can be used which should have
same results although the quantity or period given is
different (Miller, 2002; Kimberlin & Winterstein,
2008; Sugiyono, 2017).
2 METHODS
This research employed mix type research with
exploratory sequential design. Therefore, the first
procedure is to collect quantitative data by
distributing questionnaires to obtain early data from
the research subjects. After that, the next procedure
is to collect qualitative data through the interview
and also collecting the assessment instrument which
can be used by teachers as an effort in explaining the
relationship found in quantitative data, this model is
a modification of model (Creswell, 2012). The
instrument used is questionnaire and interview sheet.
Questionnaire is used to see teachers’ understanding
of authentic assessment, the implementation and also
suggestions of assessment repairment. The
qualitative instrument is interview sheet used to see
the truth of questionnaire data given by the teacher,
and also assessment instrument usually given by the
teacher.
The number of population in this research was 62
physical education teachers, and the object in this
research was physical education teachers in junior
high school at Kulon Progo Regency which
consisted of 40 teachers. Whereas, 22 other people
were not included into the criteria required by
researchers. Totally, there were 32 male teachers and
8 female teachers. The sample of the research was
purposively selected by considering the period of
teaching and status of teachers as the civil servants.
This research was conducted at the Musyawarah
Guru Mata Pelajaran (MGMP) or the discussion of
subject teachers in the level of Junior High School.
The quantitative data were analyzed by
quantitative descriptive statistic. Whereas, its
qualitative data were qualitatively analyzed by using
the method from Miles & amp; Huberman (1994)
which covers three steps, they are: data reduction,
data display, and conclusion and verification.
Qualitative descriptive was used to explain
qualitative data, which consist of respondent’s
opinion about their understanding, and the
instrument which is usually used, and also
suggestions of respondents’ assessment repairment.
3 RESULTS
Standard competency of teacher in doing assessment
should be skilful in some ways: selecting and
developing assessment method; manage, print, and
interpret the interpretation; use assessment result to
take decision and grading; communicate the
assessment; and admit the unethical assessment
practices (Mertler, Green, & Campbell, 2005). As an
effort to see teacher’s ability in arranging authentic
assessment rubric, teacher is supposed to possess
some additional understandings, they are: (1)
Teachers’ understanding towards authentic learning,
(2) Teachers’ assessment sheet/rubric, (3) the
difficulty in the implementation of authentic
assessment, (4) Steps in developing assessment
rubric. To develop and use good assessment
instrument, a teacher should previously know about
the assessment. To make it easier, see the table .1
below;
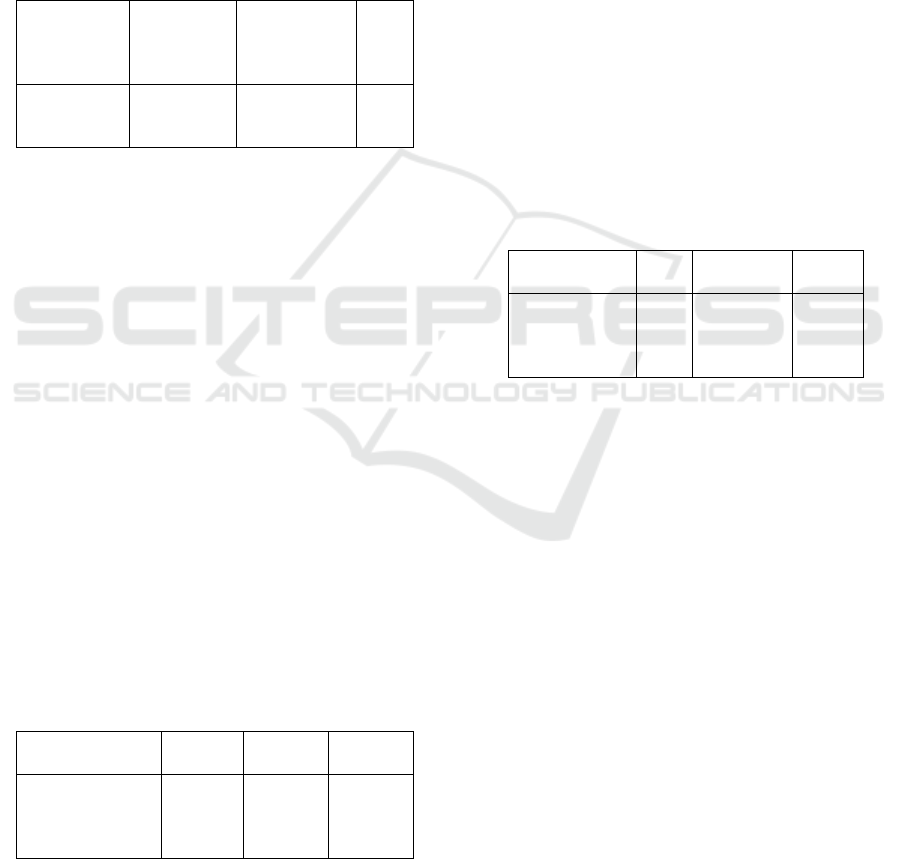
Table 1: The level of teachers’ understanding towards the
authentic assessment
Competence
Factor
Understand
Less
Understand
Not
Understand
Pemahaman
Terhadap
Penilaian
Autentik
Secara
Teoritik
5%
25%
70%
The table above shows information that 70% of
teachers does not understand authentic assessment,
25% of teachers has less understanding towards the
authentic assessment, and 5% of teachers has good
understanding about authentic assessment.
"Teacher states that he does not agree with the
type of assessment used in curriculum 2013. Since
the stipulation of curriculum 2013, teachers are only
asked to change the old assessment system with the
new assessment system which is set by
government".
The Physical Education Teachers’ Skill in Arranging Authentic Assessment Rubrics
305
The statement of teacher above shows that
government does not obviously give understandings
to teachers related to the assessment used in
curriculum 2013, government only asks teachers to
practice the assessment which already became
national provision.
After teachers understand about authentic
assessment, the assessment instrument used by
teachers after the stipulation of curriculum 2013
should be looked. The description of the research
can be seen in the table 2 below:
Table 2: The use of rubric by teachers
Competence
Factor
Have the
Aauthentic
Assessment
Rubric
Have the
Unapropriate
Authentic
Assessment
Don’t
Have
Assessment
Instrument
Used
3%
7%
90%
From the table above it can be obtained some
information that 90% of teachers state that they have
authentic assessment rubric, 7% of teachers has
rubric but it is not totally appropriate with authentic
assessment, whereas 3% of the rest states that they
already had rubric.
"Teacher stated that all this time in assessing
students' learning standards, they more frequently
used skill test, and they did not use the rubric as a
guidance in assessing students".
The statement of teacher above shows that there
are many teachers who use traditional assessment in
assessing students’ learning achievement, especially
in physical education. Because this kind of
assessment does not need rubric and many of them
already mastered the way how to conduct the test
and the measurement.
Furthermore, the factor of teachers’ competency
which should be fulfilled is whether teacher has
difficulty or not and what kind of difficulty that they
face. To see the description, see table 3 below:
Table 3: The difficulty of teachers in implementing
authentic assessment
Competence Factor
No
Difficulty
Few
Difficulties
Many
Difficulties
The Difficulties in
the Implementation
of Authentic
Learning
2,5%
5%
92,5%
From the table above, it can be obtained
information that, teachers are difficult to implement
authentic assessment in assessing students’ learning
achievement. It is seen from 92,5% of teachers faces
difficulties in implementing authentic assessment at
school, 5% of teachers has few difficulties, and 2,5%
of the rest has no problem.
"Teacher states that many factors cause
difficulties which are experienced by teachers.
Because of the lack of understanding, the lack of
training conducted by the related institution, lack of
time which is available in conducting an assessment,
and there is no clear guidance in giving score to
students ".
The statement of teacher above shows that, many
factors which complicate them in implementing
authentic assessment in learning, whether from
teacher’s individual factor or the factor from
government.
Then, one last thing that should be known is
teacher’s knowledge about the steps in developing
and using assessment instrument. The description
can be seen in the table 4 below:
Table 4: Teacher’s Knowledge about Steps in Developing
the Rubric
Competence
Factor
Able
Less Able
Unable
Steps in
Developing the
Assessment
Instrument
0%
5%
95%
From the table above, it can be obtained the
information that, 95% of teachers was unable to
develop the authentic assessment rubric, and 5% of
teachers was still unable to make assessment rubric
and 0% of teachers stated that they could develop
and arrange authentic assessment rubric by
themselves.
"Almost all teachers state that they do not have
the ability to develop and some of them say they
were still doubtful whether they could or not to
develop the assessment instruments. It is because
there is no specific training given to teachers related
to the way to develop assessment instruments which
are suitable for the purpose of learning and have the
standards of each school. "
The statement from the teacher above shows
that, the government is still not paying attention to
teacher's need for training in the development and
preparation of assessment instrument, so it makes
teachers are difficult to make assessment instrument
which are appropriate with the standards of each
school.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
306

4 DISCUSSION
Based on the analysis from all answers given by
teachers, the assessment conducted gives difficulties
for every teacher in the effort to evaluate the
learning conducted at school. The assessment in
physical education becomes a problem that
complicates teachers even for more than 40 years
ago (Lopez-Pastor et al, 2013). Physical education
teacher cannot perfectly do the assessment aspect at
school (Ali, Som & Salimin, 2018). Besides,
teachers do not have skill to make their own
assessment instrument which fulfills the
requirements as a good assessment (Aji & Winarno,
2016), it is because a few of trainings which is
conducted in how to make and use rubric (Jonsson,
2014). Assessment is a process which is difficult for
teachers especially for physical education teachers
(Lorente & Kirk, 2016). Physical education teachers
usually spend 40% until 60% of his/her time to solve
the children’s assessment problem (Birky, 2012).
Therefore, the making of assessment rubric is
important to ease teachers’ performance in
assessment (Birky, 2012). Rubrics could provide
information to teachers about criteria which are
assessed from students’ assignment and teachers will
be no longer busy in assessing (Lund, 2006).
5 CONCLUSIONS
From the data analysis conducted by the author,
assessment still remains a problem especially for
physical education teachers. Many teachers assess
students’ learning achievement without using rubric.
There are some teachers who are able to give the
good and transparent assessment by using rubric
which can be seen directly by students as a way to
give more focused assignment and also as a way to
reinforce students as the assessor of themselves.
REFERENCES
Aji, B. S., & Winarno, M. E. (2016). Pengembangan
Instrumen Penilaian Pengetahuan Mata Pelajaran
Pendidikan Jasmani Olahraga dan Kesehatan (Pjok)
Kelas VIII Semester Gasal. Jurnal Pendidikan: Teori,
Penelitian, dan Pengembangan, 1(7), 1449-1463.
Ali, S. K. S, Som, F. M & Salimin, N. 2018. Pelaksanaan
penilaian dalam mata pelajaran pendidikan jasmani di
sekolah menengah. International Journal of
Education, Psychology and Counseling, 3(13), 10-17.
Arends, R. I. 2012. Learning to teach. (9
rd
ed). New York :
Central Connecticut State University.
Arikunto, S. (2001). Prosedur penelitian suatu pendekatan
praktek. Yogyakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Birky, Beth. 2012. Rubric : A good solution for
assassmant. Journal For Physical and Sport. 25(7),
19-21.
Callison, D. (1998). Authentic Assessment Moving toward
Authentic Assessment. Originally Published School
Library Media Activities Monthly, 14(5).
Darling-Hammond, L., Berry, B., & Thoreson, A. (2001).
Does teacher certification matter? Evaluating the
evidence. Educational evaluation and policy analysis,
23(1), 57-77.
Goldhaber, D. D., & Brewer, D. J. (2000). Does teacher
certification matter? High school teacher certification
status and student achievement. Educational
evaluation and policy analysis, 22(2), 129-145.
Goldhaber, D., Perry, D., & Anthony, E. (2004). The
National Board for Professional Teaching Standards
(NBPTS) process: Who applies and what factors are
associated with NBPTS certification?. Educational
Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 26(4), 259-280.
Jonsson, A. (2014). Rubrics as a way of providing
transparency in assessment. Assessment & Evaluation
in Higher Education, 39(7), 840–852.
Kimberlin, C. L., & Winterstein, A. G. (2008). Validity
and reliability of measurement instruments used in
research. American Journal of Health-System
Pharmacy, 65(23), 2276-2284.
Komarudin. 2016. Penilaian hasil belajar pendidikan
jasmani dan olahraga. Bandung : PT Remaja Rosda
Karya.
López-Pastor, V. M., Kirk, D., Lorente-Catalán, E.,
MacPhail, A., & Macdonald, D. (2013). Alternative
assessment in physical education: a review of
international literature. Sport, Education and Society,
18(1), 57–76.
Lorente-Catalán, E., & Kirk, D. (2016). Student teachers’
understanding and application of assessment for
learning during a physical education teacher education
course. European Physical Education Review, 22(1),
65-81.
Lund, J. L. (2006). NASPE/NCATE Report Preparation
for the Accreditation Process. Journal of Physical
Education, Recreation & Dance (JOPERD), 77(3),
13–31.
Lund. J. 2014. Authentic assessment: Its development &
applications. Journal of Physical Education,
Recreation & Dance. 68(7), 25-29.
Majid. A. 2014. Penilaian autentik proses dan hasil
belajar. Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya.
Menéndez-Varela, J.-L., & Gregori-Giralt, E. (2015).
Kontribusi rubrik untuk validitas penilaian kinerja:
studi tentang konservasi-restorasi dan desain gelar
sarjana. Penilaian & Evaluasi di Pendidikan Tinggi,
41 (2), 228–244.
Mertler, C. A., & Campbell, C. (2005). Measuring
Teachers' Knowledge & Application of Classroom
Assessment Concepts: Development of the"
Assessment Literacy Inventory". Online Submission.
The Physical Education Teachers’ Skill in Arranging Authentic Assessment Rubrics
307

Mertler, C. A., Green, B., & Campbell, C. (n.d.).
Application Teachers ’ of Assessment Concepts :
Development.
Miller, D, K. (2002) Measurement by the physical
educator, why and how, (4
rd
ed). New York: Ny Mc.
Graw Hil.
Penney et all. 2009. Curriculum, pedagogy and
assessment: three message systems of schooling and
dimensions of quality physical education. Sport,
Education and Society. 14(4), 421-442.
Peraturan menteri pendidikan dan kebudayaan Republik
Indonesia Nomor 104 tahun 2014 tentang
penilaian hasil belajar oleh pendidik pada pendidikan
dasar dan pendidikan menengah.
Peraturan menteri pendidikan dan kebudayaan republik
indonesia Nomor 66 Tahun 2013 tentang standar
penilaian pendidikan.
Rihtiana. V, Tomoliyus. 2014. Development of Technical
Skills Assassment Intrument Forehand and Backhand
Drive Table Tennis at Early Age Athletes. Jurnal
Keolahragaan, 2(2), 216-227.
Shaw, G.F. 2014. Introducing rubrics to physical
education teacher candidates. Journal of Physical
Education, Recreation & Dance. 85(6), 31-37.
Slamento. 2013. Belajar dan faktor-faktor yang
mempengaruhinya. Jakarta : Rineka Cipta.
Suciu, A. I., & Mata, L. (2011). Pedagogical
competences–the key to efficient education.
International Online Journal of Educational Sciences,
3(2), 411-423.
Sugiyono. (2017). Metode penelitian pendidikan.
Pendekatan kuantitatif, kulaitatif dan r&d. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Tomolius. 2012. Cara membuat rubrik penilaian berbasis
kinerja permainan net game. Jurnal ISSA jurnal ilmu
keolahragaan. 2. 76-91.
Undang-undang Republik Indonesia Nomor 14 Tahun
2005 tentang guru dan dosen.
used in research. (2008), 65.
Vandevoort, L. G., Amrein-Beardsley, A., & Berliner, D.
C. (2004). National Board Certified Teachers andTheir
Students' Achievement. education policy analysis
archives, 12, 46.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
308
