
Nurse Satisfaction in Implementing Activities based on
the N-ABC Mira System
Mira Asmirajanti
1
, Achir Yani S. Hamid
2
, Rr. Tutik Sri Hariyati
2
and Boy S. Sabarguna
3
1
Department of Nursing, Faculty of Health and Sciences, Universitas Esa Unggul, Jakarta 11510, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Indonesia, Depok, West Java 16424, Indonesia
3
Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta 10430, Indonesia
Keywords: Nurses, Nursing Activities, Nurse Satisfaction.
Abstract: Background: Caring and recording nursing care are activities of every nurse. The main problem is that
nursing activities at the hospital have not been used as a basis for awarding appreciation points. Even
though, in daily lives, nurses are constantly on the patient's side to perform nursing care. The study's
purpose was to evaluate nurse satisfaction in implementing activities based on the N-ABC Mira system.
Methods: The study was conducted at RSDK Semarang, using a quasi-experimental design, repeated
measurements before implementation; trial 1; 2 and 3. This study randomly sampled 226, 199, 161 and 92
practical nurses with a minimum work period of 1 year, also through nursing documentation on 10 most
frequent diseases in July-December 2018, taken incidentally. Data was collected and analyzed using RM
GLM, t-Test, ANOVA, Pearson's Correlation. Results: It showed significant differences between before and
after the N-ABC Mira system to nurse satisfaction with nursing activities (6,657, p=0,0001); decision
making (2,999, p=0,0001) and award points (6,585, p=0,0001), which were influenced by nurse aspects,
management, and technical support. Conclusions: The differences between before and after the
implementation of the N-ABC Mira system can increase nurse and patient satisfaction, so N-ABC Mira is
recommended at the hospital.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nurses as professional service providers in hospitals
are important health workers. The nurse has the
longest and most intense relationship with the client,
from entering the hospital to being discharged.
Nurse activities must focus on resolving issues and
meeting client needs, both independently and
collaboratively (1). Nurses must respect patients by
working continuously and systematically (2)
Nursing activities consist of assessment,
determination of nursing diagnoses, determination of
outcomes, planning, implementation and evaluation
(3) by always paying attention to client safety
according to service standards, (4) so as to provide
satisfaction to nurse (5). Nurse job satisfaction is
considered an important component so that nurses
work according to their objectives. Financial
remuneration is one of the important things that
contribute to nursing satisfaction in the form of
rewards (6).
A study of the implementation of the
remuneration system and service performance stated
that as many as 71.2% of respondents expressed
dissatisfaction and were very dissatisfied with the
implementation of the remuneration system (7).
Nurses feel the amount of remuneration is not
commensurate with their workload and performance.
Improving the remuneration points needs to be
sought to improve the job satisfaction of nurses (8)
and appreciate their performance. Calculation of
awards and professional payments can be made
based on actual workload and nursing care (9).
Calculation of reward points from nursing activities
based on documentation of nursing care can increase
nurse satisfaction (10).
Type A State Hospitals in Semarang and Jakarta
are hospitals that have provided remuneration in
Indonesia, but nursing activities have not yet
become the basis for calculating remuneration. Both
hospitals have used information management and
electronic medical records, however, documentation
of nursing activities is still carried out manually. The
228
Asmirajanti, M., Hamid, A., Hariyati, R. and Sabarguna, B.
Nurse Satisfaction in Implementing Activities based on the N-ABC Mira System.
DOI: 10.5220/0009590202280233
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health (ICOH 2019), pages 228-233
ISBN: 978-989-758-454-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

results of observations and focus group discussions
in September 2016 - January 2017 stated that
nursing activities based on nursing documentation
were not optimal. Less than 80% of nursing
activities do not meet standards. Manual
documentation requires a long filling time, thus
reducing the time of patient visits by nurses. The
incompleteness of nursing documentation results in
difficulty in finding data and calculating nurse
awards.
The information system is one solution to be able
to increase nurse activity and nurse satisfaction in
documentation (13), save time and can reduce the
risk of data loss (14) and facilitate the calculation of
financing. Funding in almost all hospitals in
Indonesia has used hospital management
information systems. A nursing management
information system based on nursing activities has
also been developed in Indonesia. Some nursing
information systems that have been used are the
Generic Open Hospital Management Information
System (SIMRS GOS) prepared by the Directorate
General of Health Business Development (Ditjen
BUK) Ministry of Health of the Republic of
Indonesia (kemkes.go.id, 2015) and the Nursing
Management Information System that has been
developed by Roro (SIMPRO) (15). One of the
hospitals (RS) in Indonesia that has utilized the
Generic Open Hospital Management Information
System (SIMRS GOS) is the RSDK.
Referring to the previous introduction, it is
necessary to reform and develop the award of nurses
based on nursing activities. One of the information
systems for financing based on nursing activities that
have been developed is the Nursing Activity Based
Costing Mira System (N-ABC Mira) which is
suitable for nurses in Indonesia and hospital needs.
The purpose of this study was to determine
differences in nurse satisfaction before and after
using the Nursing Activity Based Costing Mira
System (N-ABC Mira).
2 RESEARCH METHODS
This research uses a quantitative method, a quasi-
experimental study (pre-post without control). This
study was tested before implementation and 3 times
repeated testing after implementation, with
documentation samples following the number of
nurses. Documentation was taken incidentally from
the 10 most diseases in Surgical Medical patients.
Samples of nurses with a minimum of 1-year work
experience criteria were randomly selected before
the study was conducted. There were 226 nurses in
the sample before implementation, 199 in the first
trial, 161 nurses in the second trial, and 92 nurses in
the third trial. Data were collected in July -
December 2018 at Semarang RSDK and analyzed
using the GLM RM, t-Test, ANOVA, Pearson's
Correlation. This research has also passed the ethical
research review (ethical clearance) from the Faculty
of Nursing, University of Indonesia number 2513 /
UN2.F12. D / HKP.02.04 / 2016.
3 RESEARCH RESULT
The N-ABC Mira system is an information system
that automatically calculates award points based on
recording nursing activities. This system makes a
calculation of nurse award points easier and more
precise. Reward points will be recorded
immediately if the nurse clicks on each activity
carried out. Henderson's need theory, a theory of
technological competence as part of caring in the
Locsin nursing profession, Lewin's theory of
change, clinical pathway theory, remuneration
theory, and information systems theory are theories
that underlie the development of N-ABC Mira
system. The N-ABC Mira system is internet-based
and comes with authorization for each user. The
development of this system is tailored to the needs
of users and can be transplanted easily to
information systems that have been used by
hospitals, for example, Hospitals that already
utilize the Generic Open Hospital Management
Information System (SIMRS GOS).
Nursing activities are the activities of nurses in
providing nursing care, starting from the assessment
of each patient who comes to the inpatient room,
determines nursing diagnoses and interventions,
provides information and education, conducts
discharge planning, establishes nursing outcomes
and evaluations and fills N-ABC Mira system
applications. Nursing activities are implemented by
modifying clinical pathways into nursing pathways
that are applied to the N-ABC Mira system. Every
activity that has been carried out will be
automatically captured in the nursing records and
becomes the basis for setting the nurse's award
points.
Nurse Satisfaction in Implementing Activities based on the N-ABC Mira System
229
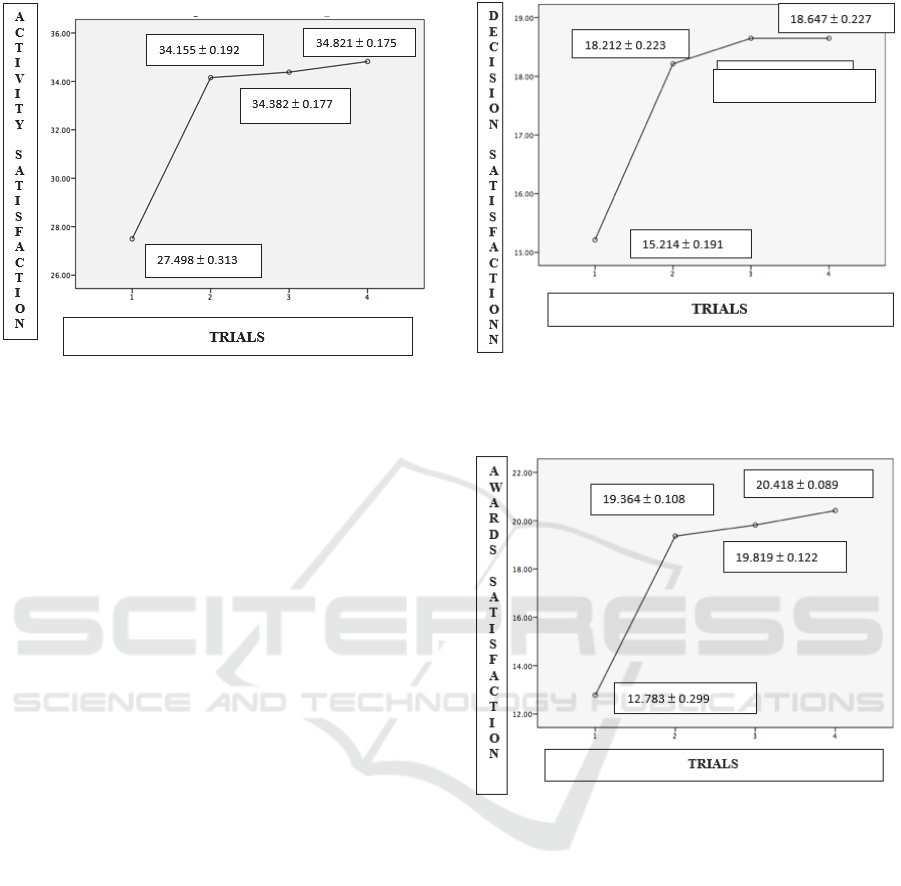
Figure 1: Differences in nurse satisfaction with nurse
activity between before, the first trial; second and third
after using the N-ABC Mira system in Semarang Hospital
in 2019.
Figure 1. shows the differences in nurse
satisfaction with nursing activities that illustrate
nurses' perceptions regarding feelings when carrying
out and recording nursing activities before and after
using the N-ABC Mira system. ANOVA (post-hoc)
test results were significant between before and the
first try after using the Mira N-ABC system at
6.65761 (p = 0.0001). In the first and second trials,
trials 2 and 3 after using the N-ABC Mira system
there was an increase but it was not significant. It
can be interpreted that before using the N-ABC Mira
system, nurses' satisfaction with the activities of
nurses is not satisfied (range of values between 20-
29) and after using the N-ABC Mira system, nurses'
satisfaction can be interpreted as satisfied (range of
values of 30-39).
Figure 2. shows the differences in nurse
satisfaction with decision making. This illustrates
nurses' perceptions regarding feelings when
determining appropriate activities in inpatient care
before and after using the N-ABC Mira system.
ANOVA (post-hoc) test results were significant
between before and the first trial, after using the N-
ABC Mira system of 2.99924 (p = 0.0001). An
increase was found but was not significant in the
first and second trials, as well as the second and
third trials after using the N-ABC Mira system. It
can be interpreted that there is nurses' dissatisfaction
with decision making before using the N-ABC Mira
system (range of values between 12-17) and there is
satisfaction after using the N-ABC Mira system
(range of values 18-23).
Figure 2: Differences in Nurse Satisfaction with Decision
Making before, first trial; second and third after using the
N-ABC Mira system in Semarang Hospital in 2019.
Figure 3: Differences in Nurse Satisfaction with Award
Points before, first trial; second and third after using the
N-ABC Mira system in Semarang Hospital in 2019.
Figure 3. shows the differences before and after
using the N-ABC Mira system regarding nurse
satisfaction with reward points, which illustrates
nurses' perceptions regarding feelings when getting
appropriate rewards. ANOVA (post-hoc) test results
were very significant (p = 0.0001) between before and
after using the N-ABC Mira system in the first trial,
with a score of 6.58554. There was no significant
increase (p = 0.098) in the first trial and after the
second trial, as well as in the second trial and after the
third trial using the N-ABC Mira system. This can be
interpreted that there is a nurse's dissatisfaction with
the award points, before using the N-ABC Mira
system, (range of values between 12-17), while nurses
were identified as satisfied after using the N-ABC
Mira system (range of values 18-23).
18.647 0.227
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
230

4 DISCUSSION
N-ABC Mira system is a system for calculating
nurse award points based on the recording of nursing
care activities that have been carried out. N-ABC
Mira system is a system that facilitates nurses in
carrying out their activities. Nurse activities at the
hospital are numerous, from the arrival of the patient
to the hospital to being discharged (16). However,
nurses still need time to adapt to changes, so, N-
ABC Mira system training needs to be given. Nurses
must understand how to use the system properly in
order to record the activities of providing nursing
care in the hospital. Training is conducted as an
effort to reduce resistance and support change (17).
Good job satisfaction will improve performance
and patient satisfaction with nursing services (18).
The results showed differences in nurse satisfaction
with nursing activities based on nursing care
documentation between before and after using the
N-ABC Mira system in the first trial, which was
27,498 (68.75%) and 34,155 (85.39%). The analysis
showed a significant difference (p = 0.0001)
between before and after implementation in the first
trial. There was no significant difference between
before and after the implementation of the N-ABC
Mira system in the first trial to the second trial, and
in the second trial to the third trial. This shows that
good planning needs to be done to make changes.
Changes in an organization must be planned
carefully. Central to change is behavior change so
that good reward and punishment must be
considered for successful change (19).
N-ABC Mira system is an information system
that in addition can store nursing care data, it can
also be used for nurses' assessments, through a
complete system, easily and quickly applied, so
nurses can visit patients more often. Computer-based
documentation makes the nurse's work simpler, so
nurses can focus on providing nursing actions (20).
Caring as a major element in nursing care, and
nurses must be able to apply it to patients (21). N-
ABC Mira system can help nurses to nurse activities
in providing nursing care, thereby increasing nurses'
satisfaction.
Nurses' satisfaction with the decision to provide
nursing care will increase if they can provide
nursing care according to the patient's needs. N-
ABC Mira system makes it easy for nurses to choose
menus and items that are in accordance with the
results of the assessment that has been done, making
it easier for nurses in making decisions to determine
appropriate nursing care. The results showed that the
most significant differences in nurse satisfaction
with decision making were between before the first
trial, using the N-ABC Mira system, amounting to
15,214 (63.38%) and after the first trial, amounting
to 18,212 (75.88%). There is no significant
difference after using the N-ABC Mira system,
namely in the first trial to the second trial, as well as
in the second trial to the third trial. These results
illustrate that making nursing care decisions by
nurses to patients requires management support.
This is consistent with the results of the study
(22) that nurses need management support. Quick
access to information enables decisions that are
appropriate to the nursing activity program and
evaluates results effectively and efficiently, thereby
increasing patient safety and reducing risks to the
patient (22). N-ABC Mira system can help nurses to
make decisions in the provision of nursing care.
N-ABC Mira system is a system of recording
every activity of nurses in the provision of nursing
care that has been done and calculation of nurse
award points. According to (6) that nurses have a
high workload and are not comparable with the
remuneration and professional awards received.
Professional remuneration and appreciation must
reflect the activities, education, and skills in
providing daily nursing care. Appropriate
appreciation will give satisfaction to the nurse. The
results of this study indicate that there is a
significant difference (p = 0.0001) in nurse
satisfaction with respect points between before and
after using the N-ABC Mira system in the first trial,
12,783 (53.25%) and 19,364 (80.68%). This is
consistent with what was stated (23) that the
calculation of the financing of nurses' activities in
providing nursing care would be more effective
based on documenting patient nursing care. N-
ABC Mira system as an information system that can
store nursing care documentation data and can be
used as a reference in calculating award points.
N-ABC Mira system was developed to facilitate
better appreciation for nurses. The results showed
there was a difference in mean nurse satisfaction
with reward points of 6.58554, which was very
significant (p = 0.0001) between before intervention
and after the N-ABC Mira system in the first trial,
but in first trial to second trial and from second trial
to third trial after using the N-ABC Mira system the
difference in mean nurse satisfaction was not
significant. Based on these results, nurses need to be
encouraged to make changes. The results of this
study are supported by satisfaction theory (24)
which focuses on satisfaction on 3 relationships,
including the relationship of motivation with
performance; a relationship of performance with
Nurse Satisfaction in Implementing Activities based on the N-ABC Mira System
231

appreciation and relationship of appreciation with
personal goals. Many workers do work because of
obligations, not because they are motivated at work.
This is because there have not been many awards
relating to nursing activities. That caused many
nurses to decide to work abroad. In accordance with
the results of research on the Policy Brief from (25)
that in Indonesia 60% of health workers are nurses.
Nursing has heavy workload, and it is not valued as
a profession and professional staff by other
professions, besides, the scope of work is unclear
due to many non-nursing assignments, also added by
exposure to work risks that are not matched by
adequate work protection and the lack of a proper
reward system to be a push factor for Indonesian
nurses to migrate and meet more global markets.
N-ABC Mira system is expected to reduce
Indonesian nurses from migrating and meet the
global market because this system can help
overcome problems in calculating nurse award
points based on nursing activities. N-ABC Mira
system needs to be properly socialized and informed
in order to get support from PPNI and HPMI
organizations and from policymakers such as BPJS
and PERSI. Nurses are the largest group of
professionals in hospital health services (26). Nurses'
activities in providing nursing care will be of good
quality if managed properly and nurses have good
motivation to carry out so that they require clear
policies related to the management of nursing care.
The use of the N-ABC Mira system in hospitals will
change the order of nursing services and require
good encouragement. According to Lewin, drivers
need to make 3 steps of change. The first step,
analyzing the situation to find out the factors
inhibiting and driving change. The second step,
conduct training and actual changes in nursing
practice. The third step is used to evaluate the
stability and effectiveness of changes that occur in
nursing practice (27). According to (28) that
motivating nurses can be done by managers by
increasing nurse knowledge through formal and
informal education and training, as well as good
career paths.
N-ABC Mira system is a system developed for
nursing activities and calculation of reward points
that requires validation of the head nurse before
being established. The head nurse must assess the
compatibility between the recording and the nursing
care that has been given to the patient. According to
(29) the supervision of the head nurse must be done
regularly and continuously. Providing optimal
nursing care to patients can increase patient
satisfaction and reduce the length of stay in the
hospital (21). The results of N-ABC Mira system
research showed that management support has a
positive direction towards nursing activities based
on nursing care documentation, nurse satisfaction
with nursing activities, decision making, and award
points. This means that the N-ABC Mira system
requires management support in its implementation
so that nursing activities can run better and faster.
5 CONCLUSIONS
N-ABC Mira system is an information system that is
used to calculate award points based on internet-
based nursing activities documentation. There is a
significant difference in nurse satisfaction with
nursing activities, decision making, and reward
points between before and after trial 1 of the N-ABC
Mira system. N-ABC Mira system is influenced by
aspects of nurses, management support and technical
support. Hospitals as an institution of service with
nurses as the most personnel can use the N-ABC
Mira system to support the calculation of reward
points for nurses' activities in providing nursing care
and hospitals that already have information systems
that can transplant N-ABC Mira system. The N-
ABC Mira system application needs to be socialized
to PPNI, HPMI, PERSI, and BPJS as a health
insurance agency to finance nurse activities in order
to get support and be implemented as a basis for
determining nurse award point policy.
REFERENCES
Asmirajanti, M. (2014). Pengaruh pelaksanaan caring
perawat terhadap kepuasan pasien di ruang rawat inap
rumah sakit umum daerah Bandung. Journal Inohim,
2(2), 140–144.
Asmirajanti, M., Hamid, A. Y. S., Hariyati, R. T. S., &
Sabarguna, B. S. (2018). Aktivitas perawat
berdasarkan dokumentasi asuhan keperawatan.
Aydin, N., & Akansel, N. (2013). Determination of
accuracy of nursing diagnoses used by nursing
students in their nursing care plans. International
Journal of Caring Sciences, 6(2).
Bakari, H., Hunjra, A. I., Shabbir, G., & Niazi, K. (2017).
How does authentic leadership influence planned
organizational change? the role of employees’
perceptions: integration of theory of planned behavior
and lewin’ s three step model. Journal of Change
Management, 0(0), 1–33. https://doi.org/10.1080/
14697017.2017.1299370
Bogossian, F., Winters-Chang, P., & Tuckett, A. (2014).
“The pure hard slog that nursing is…”: A qualitative
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
232

analysis of nursing work. Journal of Nursing
Scholarship, 46(5), 377–388. https://doi.org/10.1111/
jnu.12090
Brock, D., Abu-Rish, E., Chiu, C.-R., Hammer, D.,
Wilson, S., Vorvick, L., … Zierler, B. (2013).
Interprofessional education in team communication:
working together to improve patient safety.
Postgraduate Medical Journal, 89(1057), 642–651.
https://doi.org/10.1136/postgradmedj-2012-000952rep
Fang, Y., Li, C., & Wang, M. (2016). The development
and evaluation of a nursing information system for
caring clinical in-patient. Technology and Health
Care, 24. https://doi.org/10.3233/THC-151106
Gurung, T. B. (2018). The Principles of Interdisciplinary
research in small scale fisheries. https://doi.org/
10.1007/978-3-319-94938-3
Hamid, A. Y. S., Chandra, Y. A., Prayetni, & Masfuri.
(2018). Policy Brief: migrasi perawat dan
pendayagunaan perawat returnee berbasis brain
circulation design. In Kebijakan.
Hariyati, Hamid, A. Y., Eryando, T., & Hasibuan, Z.
(2012). Optimalisasi kinerja sistem informasi
manajemen keperawatan berbasis model simpro.
Universitas Indonesia.
Hariyati, R., Delimayanti, M.., & Widyatuti. (2011).
Developing protototype of the nursing management
information system in puskesmas and hospital, Depok
Indonesia. Business Management, 5(22), 9051–9058.
https://doi.org/10.5897/AJBM11.2356
Hertog, A. Den, & Gliesche, K. (2012). Pathway-controlled
fast-track rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty: a
randomized prospective clinical study evaluating the
recovery pattern , drug consumption , and length of stay.
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 132, 1153–1163.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-012-1528-1
Heslop, L. (2012). Status of costing hospital nursing work
within Australian casemix activity-based funding
policy. International Journal of Nursing Parctice, 2–6.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-172X.2011.01992.x
Jefferies, D., Johnson, M., Nicholls, D., & Lad, S. (2011).
A ward-based writing coach program to improve the
quality of nursing documentation. International
Journal of Medical Informatics. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.nedt.2011.08.017
Kitson, A., Marshall, A., Bassett, K., & Zeitz, K. (2012).
What are the core elements of patient-centred care? A
narrative review and synthesis of the. Journal of
Advance Nursing, (May), 3–15. https://doi.org/
10.1111/j.1365-2648.2012.06064.x
Lake, E. T., Germack, H. D., & Viscardi, M. K. (2016).
Missed nursing care is linked to patient satisfaction: A
cross-sectional study of US hospitals Missed nursing
care is linked to patient satisfaction: a cross-sectional
study of US hospitals. BMJ, (August).
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2015-003961
Lammintakanen, J., Saranto, K., & Kivinen, T. (2010).
Use of electronic information systems in nursing
management. International Journal of Medical
Informatics,
79(5), 324–331. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2010.01.015
Lee, N. J., Jang, H., & Park, S. Y. (2016). Patient safety
education and baccalaureate nursing students’ patient
safety competency: A cross-sectional study. Nursing
and Health Sciences, 18(2), 163–171. https://doi.org/
10.1111/nhs.12237
Mandagi, F. M., Umboh, J. M. L., & Rattu, J. A. M.
(2015). Analisis faktor-faktor yang berhubungan
dengan kinerja perawat dalam menerapkan asuhan
keperawatan di RSU bathesda GMIM Tomohon.
Jurnal E-Biomedik, 3(3).
Mcneil, R., Guirguis-Younger, M., B Dilley, L., Turnbull,
J., & Hwang, S. W. (2013). Learning to account for
the social determinants of health affecting homeless
persons. Medical Education, 47(5), 485–494.
https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.12132
Moon, M., & Moorhead, S. (2011). Relationship of
nursing diagnoses, nursing outcomes, and nursing
interventions for patient care in intensive care units
(University of Lowa; Vol. 3526851). Retrieved from
http://search.proquest.com/docview/1081475100?acco
untid=13042%5Cnhttp://oxfordsfx.hosted.exlibrisgrou
p.com/oxford?url_ver=Z39.88-2004&rft_val_fmt=in
fo:ofi/fmt:kev:mtx:dissertation&genre=dissertations+
&+theses&sid=ProQ:ProQuest+Dissertations+&+Thes
es+Global&
Setyaningrum, I., Hariyati, S., & Novieastari, E. (2016).
Peningkatan kelengkapan dokumentasi dan kepuasan
perawat pada pengawasan hospital acquired infections
(HAIs) berbasis komputer. Keperawatan Indonesia,
19(1), 33–40.
Soetisna, T. W., Ayuningtyas, D., & Misnamiarti. (2013).
Penerapan sistem remunerasi dan kinerja pelayanan
implementation of remuneration system and service
performance. 17–23.
Winarsih, R., Nursalam, & Dian, N. (2015). Budaya
organisasi dan quality of nursing work life terhadap
kinerja dan kepuasan kerja perawat di RSUD dr.
soetomo Surabaya. Ners, 10 No. 2.
Windyastuti, Kristina, T.., & Santoso, A. (2016).
Pelatihan preceptorship untuk meningkatkan adaptasi
perawat baru di rumah sakit.
Wirawan, E. A., Novitasari, D., & Wijayanti, F. (2013).
Hubungan antara supervisi kepala ruang dengan
pendokumentasian asuhan keperawatan di rumah sakit
umum daerah ambarawa. Jurnal Managemen
Keperawatan, 1, No. 1, 1–6. Retrieved from
https://jurnal.unimus.ac.id/index.php/JMK/article/view
File/943/995
Nurse Satisfaction in Implementing Activities based on the N-ABC Mira System
233
