
An Application of Warm Compress in Reducing Pain Level at First
Stage of Active Phase
Dwi Handayani, Ika Nur Saputri, Diah Evawanna Anuhgera, Riris Sitorus, Raisha Octavariny, and
Wilda Wahyuni Siregar
Institut Kesehatan Medistra Lubuk Pakam, Sumatera Utara, Indonesia
raisha.oct@gmail.com, wilda09wahyuni@gmail.com
Keywords: Warm Compress, Pain Scale, First Time.
Abstract: During the first stage of normal labor, the intensity of pain level by patients is increasing with different quality
of pain in each patient. Severe pain generally occurs in the active phase of the first stage of labor. Mothers
generally feel increased discomfort, sweating, nausea and vomiting. Warm compresses are expected to reduce
the scale of pain experienced by birth mothers. The population was 30 people and taken using accidental
sampling technique. The results showed that there was an influence of the use of warm compresses on the
change in pain scale when the active phase 1 where p value <0.04 (α ≤ 0.05) .The suggestion for mothers in
order to use the method of warm compresses to reduce the scale of pain when the active phase of labor.
Midwives are expected to be able to intervene in the form of warm compresses to reduce labor pain because
it has been proven to have an effect on reducing the intensity of laborpain.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the factors that influence the level of labor
pain is the experience of childbirth (Jordan, 2015).
Primigravida mothers do not have birth experience
compared to multigravida mothers. Primigravida
mothers generally feel anxious and afraid to face
childbirth (Afifah, 2015). This condition stimulates
the body to release stress hormones, namely the
catecholamine and adrenaline hormones .This
catecholamine will be released in high concentrations
during labor if the mother cannot eliminate her fear
before giving birth.
Labor pain is characterized by uterine
contractions, actual contractions have occurred in the
30th week of pregnancy called Braxton hicks
contractions due to changes in the hormones estrogen
and progesterone but are irregular, painless and
contraction strength of 5 mmHg, and the strength of
Braxton contractions. These hicks will be his strength
in labor and are regular in nature. Sometimes the
discharge of amniotic fluid that usually breaks before
the opening is complete, but can also come out before
labor. With the expected labor rupture can take place
within 24 hours (Gadysa, 20 14).
During the delivery process there is a decrease in
the head into the pelvic cavity which presses the
pudendal nerve so that is triggers the pain sensation
felt by the mother. In addition labor pain is also
caused by contractions that take place regularly with
intensity that is getting stronger and more frequent.
This condition affects the physical and psychological
nature of the mother (Manurung, 2015).
During the first stage of normal labor, the
intensity of pain felt by the patient increasingly
increases with the quality of pain that is different in
each patient. Severe pain generally occurs in the
active phase of the first stage of labor. Mothers
generally feel increased discomfort, sweating, nausea
and vomiting. The mother will also feel shaking in the
thighs and legs, pressure on the bladder and rectum,
back pain and pale around the mouth (Yanti, 2017).
As a result the uterus becomes increasingly tense
so that blood flow and oxygen into the uterine muscle
decreases because the arteries shrink and narrow
which can cause pain that is inevitable (Bobak, 2016).
One of the most tiring and severe, and most
pregnant women feel pain or pain during labor is the
active phase 1. The use of warm compresses for areas
of tension and pain are considered able to relieve
pain. Warm reduces muscle spasms caused by
ischemia which stimulates neurons that block the
Handayani, D., Saputri, I., Anuhgera, D., Sitorus, R., Octavariny, R. and Siregar, W.
An Application of Warm Compress in Reducing Pain Level at First Stage of Active Phase.
DOI: 10.5220/0009471502250231
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology (ICHIMAT 2019), pages 225-231
ISBN: 978-989-758-460-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
225

transmission of further painful stimuli causing
vasodilation and increased blood flow to the
compressed area (Walsh, 2015).
Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional
experience due to actual or potential tissue damage.
Pain is the main reason for someone to seek health
care assistance. Pain occurs with many disease
processes or simultaneously with several diagnostic
or treatment examinations. Pain is disturbing and
makes it difficult for more people than any disease
(Brunner and Suddarth, 2010).
Various attempts have been made to decrease the
labor pain, both pharmacological and non-
pharmacological. Pharmacological pain management
is more effective than non-farmacological. However,
it is more expensive and potentially has adverse
effects. Pharmacological therapy is the use of an
epidural which have the side effect namely reducing
the pressure of blood that can interfere with blood
circulation to the fetus. While
non-pharmacological methods are cheap, simple,
effective, and without adverse effects.
Non-pharmacological methods can increase
satisfaction during labor if the mother
can control her feelings and fears (Judha, 2017).
Non-pharmacological methods include
distraction techniques, biofeedback, self-hypnosis,
reducing pain perception, and cutaneous stimulation
(massage, warm baths, hot or cold compresses,
transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) (Potter,
2015). Giving hot compress/ warm on the body area
will give a signal to the hypothalamus through the
spinal cord. When heat-sensitive receptors in the
hypothalamus are stimulated, the effector system
emits a signal that initiates sweating and peripheral
vasodilation. Changes in the size of blood vessels are
regulated by the vasomotor center of the medulla
oblongata from the brain stem, under the influence of
the hypotalamic anterior portion so that vasodilation
occurs. The occurrence of vasodilation causes
discharges / loss of energy / heat through the skin to
increase (Wolf, 2013).
The heat channeled through hot compresses can
relieve pain by removing inflammatory products,
such as bradykinin, histamine, and
prostaglandins which will cause local pain. Heat also
stimulates nerve fibers that close the gate so that the
transmission of pain to the spinal cord and brain can
be inhibited (Price, 2015). The compress with Hot
Tubes can seen in the below Figure 1:
Figure 1: Compress with Hot Tubes.
Warm compresses are to provide warmth to
certain areas by using fluids or devices that cause
warmth to the parts of the body that need them. This
action besides to expedite blood circulation is also to
relieve pain, stimulate intestinal peristaltic,
discharged inflammatory sap to be smooth, and
provide calmness and pleasure to the client. Giving a
compress was done on inflammation of the joints,
muscle spasms, flatulence, and cold (Istichomah,
2014).
The warm compress method can use a variety of
methods such as towels or washcloths dipped in warm
water and placed on the body parts (towels covered
with plastic around the compress area so that heat
does not spread out), using hot bags or bladders, hot
showers, sunbathing in the sun, use a warm blanket, a
hot pillow.
The use of warm compresses for areas of
tension and pain are considered capable of relieving
pain. It greatly reduces muscle spasm caused by
ischemia which stimulates neurons that block the
transmission of further painful stimuli causing
vasodilation and increased blood flow to the
compressed area (Walsh, 2015). Mechanisms of pain
control in childbirth can seen in the below of Figure
2:
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
226
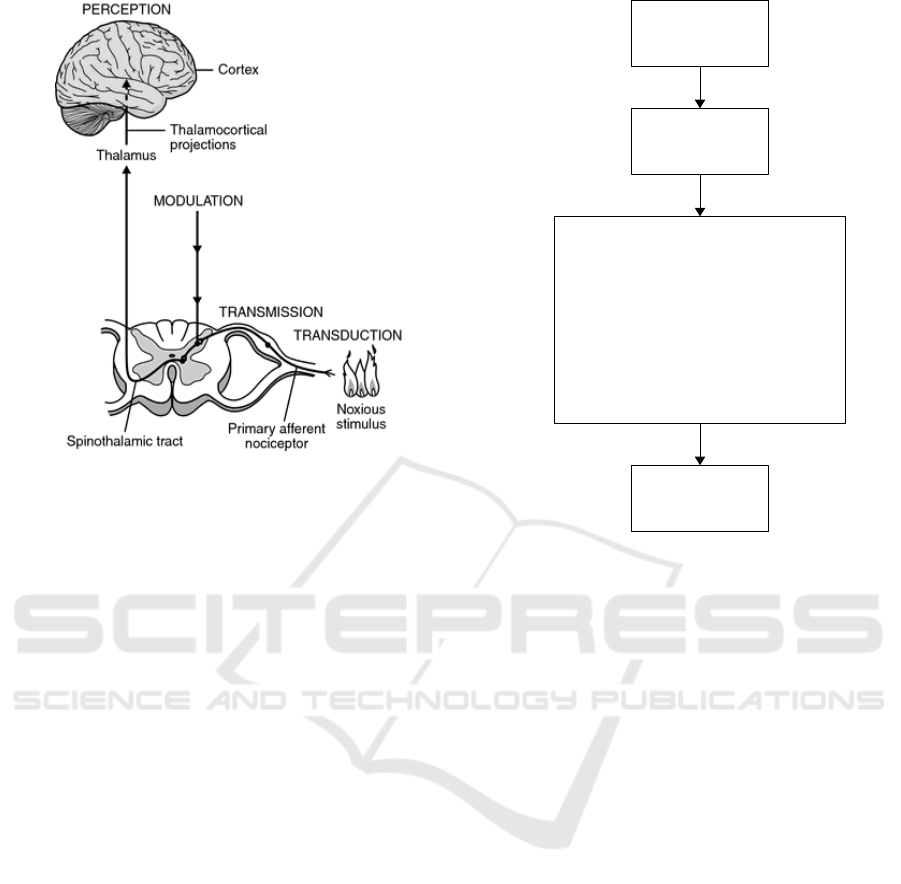
Figure 2: Mechanisms of pain control in childbirth.
Survey conducted by researchers on November
2018 at the Galang Health Center in Deli Serdang
Regency, 153 maternal mothers were obtained during
the month of August-October 2018. The average
number of maternity patients was 51 people and the
average number of women giving birth was
primiparous mothers with a total of 35 people. Based
on observations 5 mothers who will give birth can be
seen that the Galang health center does not do a warm
compress on mothers who are going to give birth to
reduce labor pain but only to relax deep breathing.
Therefore, researchers are interested in conducting a
study entitled the use of warm compresses to change
the pain scale when the Active Phase I phase. The
flow of paint management can seen in the Figure 3.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
This research was conducted by using a pre-
experimental ( One group pre and post test design )
that is a study that used a group of subjects,
measurements were carried out before and after
treatment that analyzed the effect of using a warm
compress on changes in pain scale at the active phase.
The location of the study was conducted at the Galang
Health Center, Deli Serdang Regency. Sa MPEL on
research amounted to 3 0 people. The time of the
study will be in October 2018 - April 2019.
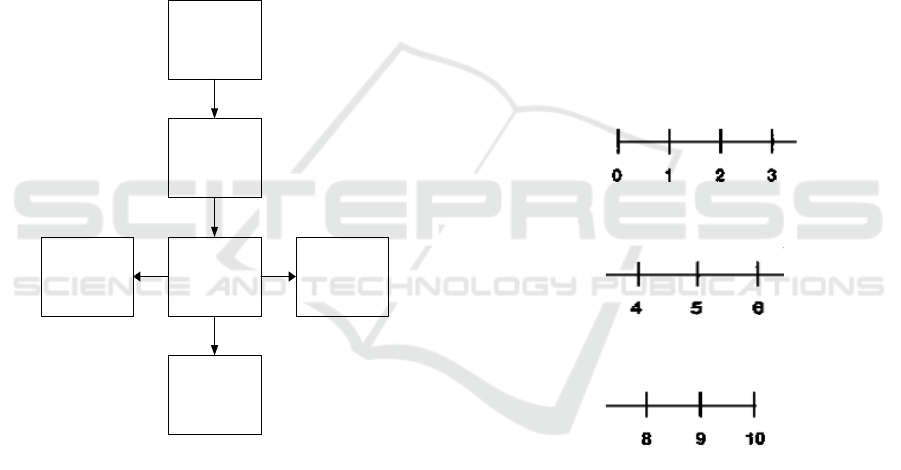
Labor Pain
Warm Compress
· Widen blood vessels
(vasodilation).
· Give additional nutrients
and oxygen to cells and get
rid of body wastes.
· Increase blood supply to
areas of the body.
· Speed healing.
· Can be soothing.
Pain scale
changes occur
Figure 3: Flow of paint management.
Sample criteria in this study were divided into two
namely inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria. The
inclusion criteria in this study are willing to be a
research respondent and sign the information concent
given, the mother is active during the first phase,
opening 4 to 9, she does not get drugs that have anti-
pain effects, mothers in normal or physiological labor
without laborinduction. The exclusion criteria in this
study are mothers who have or have wounds in the
back area, mothers in pathological deliveries, mothers
receive pharmacological therapy to reduce pain.
Data collection methods use primary data and
secondary data, where primary data is obtained from
the first source, both from individuals or individuals
such as interviews or the results of questionnaires that
are commonly used by researchers and researcher’s
observations. Secondary data is often referred to as
the method of using document material, because in
this case the researcher does not directly retrieve the
data himself but examines and utilizes the data or
documents produced by other parties. Secondary data
were obtained from the Galang Health Center
Data analysis for bivariate calculations in this
study used paired sampling test with a degree of
confidence of 95%. A variable is said to be related or
influential when the value of p ≤ α (= 0.05). This
proof is carried out to prove the hypothesis of the
effect of the use of warm compresses on the change
An Application of Warm Compress in Reducing Pain Level at First Stage of Active Phase
227
in pain scale in the active phase. The hypothesis in
this study is, there are differences in the scale of pain
before and after a warm compress is performed on the
active phase of maternity mothers in the first stage.
The flow of the research starts from gathering the
population, then looking for samples that fit the
research criteria. Next do a pain scale measurement
before a warm compress, using a vase and then do a
warm compress on the patient. After that, measure the
patient's pain scale again after the intervention. Then,
the data analysis in accordance with the data that has
been obtained.
Determination of the bourbanis pain scale score is
done by measuring the distance between the end of
the line on the painless line to the point indicated by
the patient, (Gillian A., Hawker, Mian, et al, 2011).
The research flow can seen in the Figure 4:
POPULATION
SAMPLE=30
WARM
COMPRES
PRE TEST POST TEST
DATA ANALYS
Figure 4: Research flow.
Examination of a procedure n pain with pain scale
bourbanis are as follows:
1. Explain to the patient the purpose of the
measurement
2. Explain to the patient that the patient is showing
pain based on the number listed according to the
level of pain felt by the patient.
3. Encourage patients to choose or move the
numbers on the bourbanis pain scale according to
the intention of the pain bags felt.
4. Giving hot compresses on the area of the patient's
body.
5. Advise the patient to choosing/ moving the
direction of the arrow on the pain scale bourbanis
according to the intensity of pain that feels right.
6. Record and then interpret the meaning of pain
stated by sufferers by comparing the pain scale
before and after treatment
There are several pain scales that can be used. In
general, this scale was divided into categorical scales
(no pain, mild illness, moderate pain, and severe
pain). Or use of a scale that is described as a
horizontal or vertical line whose edges are given a
value of "0" indicating no pain and "10" indicating
severe pain.
In this research, the most subjective characteristic
of pain is the severity or intensity of the pain. Clients
are often asked to describe pain as mild, moderate or
severe. However, the meaning of these terms is
different for nurses and clients. From time to time this
type of information is also difficult to ascertain.
Figure 5 explain about pain scale according to
bourbanis. The pain scale calculation according to
bourbanis was used. Where the pain scale is is divided
into five categories: no pain (value 0), mild pain
(value 1-3), moderate pain (value 4-6), controlled
severe pain (value 7-9) and severe pain uncontrolled
(value 10).
No Pain Mild Pain
Moderate Paint
Controlled
Severed Pain
Uncontrolled
Severed Pain
Figure 5: Pain Scale According to Bourbanis.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Before, warm compresses were performed for women
who experienced mild pain of 3 people (10%),
moderate pain in 15 people (50%), severe pain in 12
people (40%). From the observations made, the
respondent's pain response before giving a warm
compress ranged from 4-6. Most respondents
complained of severe pain with an average scale of 7
as shown in Table 1. Pain is influenced by various
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
228
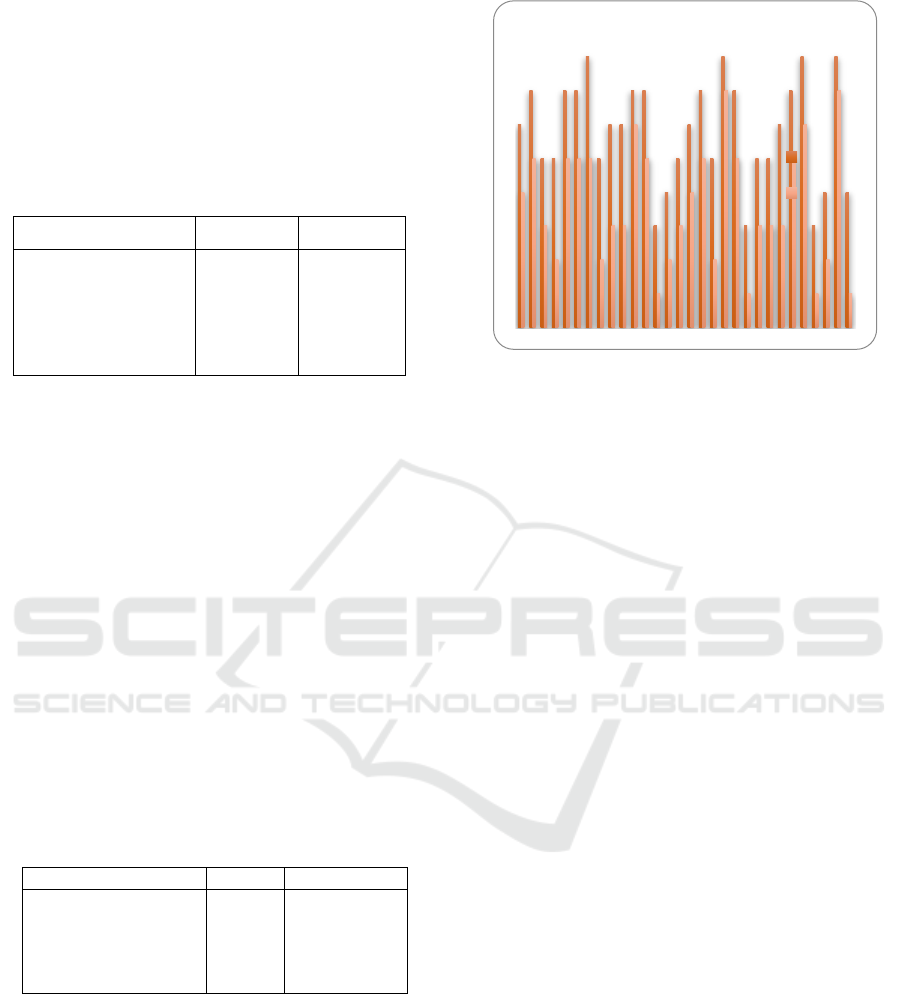
factors. These factors include age, sex, culture,
meaning of pain, location and severity of pain,
attention, anxiety, fatigue, previous experience and
family and social support. Some of these factors have
been found on the observation sheet such as age, sex,
ethnicity and administration of pain-reducing drugs.
Table 1: Distribution of Frekuensi Pain Scale before Warm
Compress.
Variable
n = 3 0
%
Mild Pain
Moderate pain
Severe pain
controlled
Uncontrolled Severe
Pain
3
15
12
0
10
50
40
0
After warm compresses were performed for
women who experienced mild pain as many as 15
people (50%), moderate pain 13 people (50%), severe
pain controlled 2 people (6.7%). The results showed
the majority of the pain scale on respondents after the
intervention was mild pain by 15 people (50%),
moderate pain by 13 people (43.3%) and the minority
of pain intensity was controlled by 2 people (6.7%)
Of the 30 respondents the mean pain scale
measurement for respondents after the intervention
was 3.633, with a standard deviation (SD) of 1.79046
. Measurement of pain is lowest 1 and highest 7. From
the estimated interval results it can be concluded that
95% CI is believed to be the average measurement
after the intervention is 2.97 to 4.3.Frequency
distribution of pain scale after warm compress can
seen in the Table 2.
Table 2: Frequency Distribution of Pain Scale after Warm
Compress.
Variable
n = 3 0
%
Mild Pain
Moderate pain
Severe pain controlled
Uncontrolled Severe
Pain
15
13
2
0
50
43.3
6.7
0
The following is a difference in pain scale data
before and after a hot compress, which can be seen
that there are significant changes before and after the
intervention can seen in the Figure 6:
Figure 6: Pain Scale Before and after Intervention.
Table 3 explain than the results of the analysis of
the average scale of pain when the active phase 1
before being given a warm compress of 5.8000 with
a standard deviation of 1.54026 and an error standard
of 0.28121 where the pain scale is known at least 3
with a maximum pain scale of 8 . The Average pain
scale when one of the active phase after given a warm
compress of 3.6333 with a standard deviation of
1.79046 and 0.32689 in which an unknown error
standard pain scale at least 1 the pain scale maximum
of 7 . Based on a mathematical calculation of the
difference in decrease in the average scale of pain
when the active phase 1 before and after the
intervention is 2.1667. By using the statistical test
Paired Samples T Test obtained p value = 0.04 (α
<0.05 ). This study found that there was an influence
of the use of warm compresses on the scale change of
pain when the active phase 1 was in primipara in
Galang Health Center, Deli Serdang Regency.
This is consistent with the theory that warm
compresses are factors that influence the reduction in
labor pain. Warm compresses can make the body feel
relaxed because of the warmth of the water which
helps blood vessels to widen so that blood flow is
smooth. The results of this study are supported by the
interview method when observing maternity pain in
maternal, this observation method uses a tool in the
form of a VAS (Visual Analouge Scale) pain level
questionnaire, a rubber bottle for compressing warm
water with a temperature of 37º-41ºC and a towel
towelpengalas to be placed on the lower back of the
mother.
Before
After
An Application of Warm Compress in Reducing Pain Level at First Stage of Active Phase
229

Table 4: Differences in pain scale stage 1 before and
after warm compresses are given.
Pain
Scale
The
mean
Elementary
school
P value
Before the
intervention
After the
intervention
5,8000
3,6333
1.54026
1.79046
0.04
A similar opinion regarding the results of this
study was demonstrated by Arsitya (2015) in her
study entitled the effect of giving warm compresses
to the reduction of labor pain in BPS
KusniSrimarwartiDlingoBantul Yogyakarta in 2015.
In the study showed a significant effect of warm
compresses on labor pain the first method used
method in this research is to use the method of
observation and interviews.
Most of the mothers in the party experienced a
sense of comfort after being given a warm compress.
Warm compresses applied to the mother's lower back
in the area where the fetal head presses on the spine
of the head will reduce pain, warmth will increase
circulation to the area so as to improve tissue pressure
caused by pressure. This warm compress has proven
to be effective in reducing labor pain and helping to
reduce pain during labor. Overall based on what we
have observed, all respondents on average said that
the labor pain they felt was reduced even though the
responses they gave differed.
The above findings are in line with the results of
Yani's (2015) Effect of Giving Warm Water
Compresses on the Feeling of Comfort in Childbirth
Process Active Phase, which shows that giving warm
water compresses that are given on the lower back of
the woman for 20 minutes in the area where the fetal
head presses the spine will reduce labor pain, the
active phase Increases circulation to the area so that
tissue tissue repair is caused by pressure. Heat can be
channeled through conduction (hot water bottles,
electric heating pads, lamps, warm dry and moist
compresses) or conversion (Ultrasonography,
diathermy).
Based on the result of researchers was concluded
that using warm compresses can decrease the pain
when one of the active phase. Warm compresses are
useful for increasing local skin temperature, blood
circulation and stimulating blood vessels, reducing
muscle spasms and increasing pain threshold,
relieving pain sensation, stimulating intestinal
peristalsis, removing inflammation of the sap and
providing calm and comfort to the mother inpartu.
Based on the researchers' assumptions, warm
compresses are very useful in reducing labor pain
because warm compresses can increase local skin
temperature, improve blood circulation, reduce
muscle spasms, eliminate pain sensations, provide
calm and comfort to the mother inpartu so that pain
can reduce labor pain.
4 CONCLUSIONS
There is an influence of the use of warm compresses
to changes the pain scale of the active phase 1 style in
Galang Health Center, Deli Serdang Regency where
the p value <0.04 (α ≤ 0.05) .
5 SUGGESTIONS
Women can use this method of warm compresses to
reduce the scale of pain when the active phase of
labor. The results of this study are expected to be
input for public health center and can improve
services in managing labor pain, by providing
knowledge about the management of labor pain with
warm compresses. Midwives are expected to be able
to intervene in the form of warm compresses to
reduce labor pain because it has been proven to have
an effect on reducing the intensity of labor pain. Next
researcher with a wider area and the respondents are
more so the results are more effective, but it is also
necessary to develop research with other factors that
influence the reduction of pain in the birth mothers of
the first stage phase active.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
To the Chancellor of the Medical Institute of the
Lubuk Pakam Medistra who has given permission to
carry out research, the Chairperson of the
MEDISTRA Foundation Lubuk Pakam who has
provided financial assistance in conducting research,
the Head of primary health care who has provided
data information to researchers and allowed
researchers to collect research data obtained from the
primary helath care.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
230

REFERENCES
AHCPR, 2015. Panduan penatalaksanaan nyeri. Jakarta.
Pusdiknakes. www.pusdiknakes.go.id.
Arifin, 2016. Pengertian kompres hangat.
Http://www.repository.usu.ac.id. Bobak,
2015.Keperawatan Maternitas. Jakarta : Penerbit EGC
Ayu, E.I. (2015). Kompres Air Hangat Pada Daerah Aksila
dan Dahi Terhadap Penurunan Suhu Tubuh pada Pasien
Demam di PKU Muhammadiyah Kutoarjo. Jurnal Ners
dan Kebidanan vol 3 No.1, 10-14. Diakses dari
www.researchgate.net pada 9 Januari 2018
Brunner, Suddarth, 2013. Keperawatan medical medah.
Jakarta: Penerbit EGC
Bare, B. G., dan Smeltzer, S. C. (2015). Buku Ajar
Keperawatan Medikal Bedah Brunner dan Suddarth.
Jakarta : EGC
Bobak, I. M., at all. (2014). Keperawatan Maternitas.
Jakarta : EGC
Brockopp, D. Y., dan Hastings, M. T. (2010). Dasar-Dasar
Riset Keperawatan. Jakarta : EGC
Depkes RI. (2010). Visi Misi Indonesia Sehat. Diambil 22
September 2010, dari http://www.depkes.go.id
Fraser, D. M., dan Cooper, M. A. (2009). Buku Ajar Bidan
Myles. Ed-14. Jakarta : EGC
Gadysa, G. (2009). Persepsi Ibu Tentang Metode Masase.
Diambil 27 September 2010, dari
http://luluvikar.wordpress.com
Jones, K., dan Henderson, C. (2005). Konsep Kebidanan.
Jakarta : EGC
Depkes RI, 2016. Profil kesehatan Indonesia 2013. Jakarta
: DepartemenKesehatanRepublik Indonesia
Dinas Kesehatan Provinsi Sumatera Utara, 2017. Profil
Kesehatan Sumatera Utara. DinasKesehatan Sumatera
Utara
Dorland, 2014. Keterampilan Dan ProsedurDasar, Jakarta
: EGC
Farrer, 2015. Perawatan maternitas. bab perawatan wanita
dalam persalinan. Jakarta: EGC
Gadysa, 2017. Nyeri persalinan. Jakarta: EGC
Hawker, Mian, Kendzerska, 2011. Measures of Adult Pain.
Arthritis Care & Research.American College of
Rheumatology.
Hidayat, 2018. Metode penelitian keperawatan dan teknik
analisa data. Jakarta : Salemba Medika
Jordan, 2016. Teori pengukuran nyeri dan nyeri persalinan.
Yogyakarta : Nuha Medika
Kartono, 2017. Apa yang anda hadapi minggu per minggu.
Http://www.infoibu.com.
Kemenkes, R.I. 2016. Rencana Strategis Kementrian
Kesehatan Tahun 2015 - 2019. Kepmenkes No.
HK.02.02/MENKES/52/2015. 7(April). 1 doi: 351.077
Ind r
Klimek, Bergmann, Biedermann, et all, 2017. Visual
analogue scales (VAS): Measuring instruments
Kinney, 2016.Nyeri persalinan. Http://www.unimus.ac.id.
Kusyati, 2015. Konsep kompres hangat.
Http://www.infomedia.co.id.
Leveno, K., J. (2009). Obstetri Williams. Ed-21. Jakarta :
EGC
Mander, R. (2003). Nyeri Persalinan. Jakarta : EGC
Meiliasari, M., dan Danuatmaja, B. (2004). Persalinan
Normal Tanpa Rasa Sakit. Jakarta : Puspa Swara
Manurung,2015. Pengaruh teknik pemberian kompres
hangat terhadap perubahan skala nyeri persalinan
pada klien primigravida
http://poltekkesjakarta1.ac.id/file/dokumen/79jurnal_S
Uryani.pdf
Mochtar, 2015. sinopsis obstetri. bab janin (passanger),
jalan lahir (passage) dan tenaga (power). Jakarta: EGC
Notoatmodjo, S. 2005. Metodologi penelitian kesehatan.
Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Notoatmodjo, Soekidjo. Promosi kesehatan dan Perilaku
Kesehatan.Rinekacipta. Jakarta. 2017
Nursalam. (2008). Konsep dan Penerapan Metodologi
Penelitian Ilmu Keperawatan. Jakarta :
SalembaMedika
Potter, 2015. Buku ajar fundamental keperawatan. Jakarta:
EGC
Prawirohardjo, S. (2005). Ilmu Kebidanan. Yogyakarta :
Yayasan Bina Pustaka Sarwono Prawirihardjo
Price, S., dan Price, L. (1997). Aromaterapi. Jakarta : EGC
Rahmadani, F. (2009). Pengaruh Pijat Punggung Terhadap
Penurunan Intensitas Nyeri Persalinan Kala I Fase
Aktif Pada Ibu Primipara. Medan : tidak dipublikasikan
Ratih, R. H. (2010). Pengaruh Metode Masase Terhadap
Pengurangan Intensitas Nyeri Pada Persalinan Kala I.
Medan : tidak dipublikasikan
Saifuddin, 2016. Ilmu kebidanan. bab fisiologi dan
mekanisme persalinan normal.Jakarta: Yayasan Bina
PustakaSarwonoPrawirohardjo
Saryono, 2017. Statistika bidang kesehatan, keperawatan,
kebidanan, kedokteran. Yogyakarta :Penerbit
Fitramaya
Sastrawinata, 2017. Dasar-Dasar Metode Penelitian
Klinis. Jakarta :SagungSeto
Simkin, 2017. Buku saku persalinan, Jakarta : EGC
Smeltzer, S.C bare B.G, 2013. Keperawatan Medikal
bedah. Jakarta : EGC
Tamsuri, 2013. Konsep dan penatalaksanaan nyeri.
Jakarta: EGC
Wahyuni, 2016. Efektifitas pemberian kompres panas
terhadap penurunan nyeri phlebitis akibat pemasangan
intravena line Di RSU Aisyiyah Dr.Sutomo, Ponorgo.
http://www.unimus.unpvj.ac.id. Di aksestanggal 02
Desember 2018
Walsh, 2016.Buku Ajar Kebidanan Komunitas.Jakarta :
EGC
Winkjosastro, 2015. Ilmu penyakit kandungan dan
keluarga berencana. Jakarta :Penerbit Yayasan Balai
Pustaka Sarwono Prawirohardjo
Young, C., Koopsen, C. (2017). Spiritualitas, Kesehatan,
danPenyembuhan.Medan : Bina MedikaPerintis
Yunita, Dian Sari. Ni Luh. Rekawaty, Eka. 2019.
International Journal of Nursing and Health Service.
Vol 2 (2).
An Application of Warm Compress in Reducing Pain Level at First Stage of Active Phase
231
